March 25, 2022 President of Russia V.V. As part of his address to citizens, Putin proposed a number of tax measures.
Thus, the previously existing personal income tax tax breaks on interest income on deposits (account balances) in Russian banks and some income on debt financial instruments are cancelled.
The law has already been signed (Federal Law dated April 1, 2020 No. 102-FZ). To pay the new tax, the mechanism for paying personal income tax will be expanded based on notifications received by the taxpayer, and tax authorities will be involved in calculating the tax. Let's try to understand the details.
Why did they decide to increase personal income tax?
Discussions about introducing a progressive personal income tax rate have been going on for a long time. In light of the coronavirus shocks, these conversations have become more active. At the same time, the issue of abolishing personal income tax for low-income citizens was discussed.
As a result, legislators did not radically change the system for calculating personal income tax, but only increased the current tax rate by two percentage points with a significant caveat - not all income received by citizens will be subject to an increased rate, but only that exceeding the legally established limit.
We will not speculate about why this particular option for adjusting the personal income tax rate was chosen. Let us dwell on the fact that, according to government forecasts, this measure will allow the budget to receive an annual increase of 60 billion rubles. Will this money be used for specific purposes? treatment of children with rare serious diseases, purchase of expensive medicines, rehabilitation means, as well as high-tech operations.
Has the personal income tax rate changed in 2019 in Russia?
It should be noted that from January 1, 2022, various amendments were made to the income tax rules. However, legislators do not plan to adjust income tax rates this year. This means it will remain unchanged.
EXAMPLE The personal income tax rate on dividends in 2022 for non-residents is 15%. How much tax should Skvortsov, who is a citizen of the Russian Federation and received 38,200 rubles in August, pay? such income from?
Solution:
- The amount of tax that must be paid to the treasury will be:
38,200 x 15% = 5,730 rubles.
- Skvortsov will receive:
38,200 – 5730 = 32,470 rubles
Will individual entrepreneurs be subject to the tax on the rich?
The President said nothing about the application of the 15% personal income tax rate to the income of individual entrepreneurs.
Most likely, the new procedure for calculating personal income tax will affect individual entrepreneurs on OSNO, which, according to the current rules, pay 13% personal income tax on income received. Earning more than 5 million rubles. per year, entrepreneurs with such a taxation system will have to pay an increased amount of personal income tax to the treasury.
In order to save money, such businessmen may decide to change the traditional taxation system to one of the special regimes (STS or PSN).
Professional income tax (PIT) for self-employed people
As we said above, NAP payers can be individuals and individual entrepreneurs who do not have employees.
Law No. 422-FZ does not contain a specific list of activities that NAP payers can engage in. It contains only a list of persons who cannot apply this special regime. In particular, persons: • applying other special tax regimes, that is, individual entrepreneurs cannot combine self-employment with the “simplified tax system”, patent and the general taxation system; • selling excisable goods and products subject to mandatory labeling (medicines, tobacco products, cars, fuels and lubricants, and so on); • working in the interests of another person on the basis of commission agreements (with the exception of the provision of services for the delivery of goods subject to the use of the seller’s cash register); • reselling goods and property rights on a professional basis; • extracting and selling minerals;
The following income is not subject to the payment of NAP (Part 2, Article 6 of Law No. 422-FZ): • received within the framework of labor relations; • from the sale of real estate, transport; • from the transfer of property rights to real estate, for example, from the rental of non-residential premises (in particular, apartments - letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 7, 2020 No. 03-11-11/106478). An exception is income from rental (hiring) of residential premises; • state and municipal employees, including those undergoing military service. An exception is income from leasing (renting) residential premises (letter of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated April 19, 2021 No. 28-6/10/B-4623, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2020 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] ); • from the sale of property that was used for personal needs; • from the sale of shares in the authorized (share) capital of companies, shares in mutual funds of cooperatives and mutual funds, from securities and derivative financial instruments; • from conducting activities under simple partnership agreements (joint activity agreements) or property trust management agreements; • under civil contracts, if the customer is a current employer or a former employer who was less than two years ago; • from the assignment (assignment) of rights of claim; • received in kind; • from arbitration management, advocacy and valuation activities, from the activities of a mediator, a notary engaged in private practice.
On income that is not recognized as income from the sale of goods, works, services, NPT is not paid. For example, this includes such type of income as income from bank deposits (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 17, 2021 No. 03-11-11/10928).
Thus, the NAP payer can be a citizen or individual entrepreneur who independently performs work, provides services, or sells goods they have manufactured. The types of activities of the self-employed include: • provision of legal or accounting services; • organization of holidays; • provision of services for the transportation of goods and passengers; • renting apartments daily or for a longer period; • provision of photo and video shooting services; • production of goods; • provision of cosmetic services and so on.
What income will be subject to personal income tax at a rate of 15 percent?
Until a law with amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation appears, it is premature to talk about what list of income will fall under the new tax scale. Let us remind you that the following personal income tax rates are currently in effect depending on the type of income received:
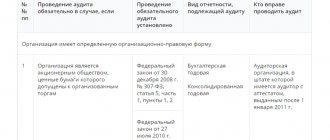
| Type of income | Personal income tax rate | Normative reference |
| Wages and other income of residents, except those taxed at a rate of 35% | 13% | clause 1 art. 224, paragraph 2 of Art. 214 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Wages of non-resident foreigners with a patent, citizens of the EAEU, highly qualified specialists, refugees and those who have received temporary asylum in the Russian Federation | 13% | clause 3 art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance dated February 27, 2019 No. 03-04-06/12764, dated January 24, 2018 No. 03-04-05/3543 |
| Dividends from non-residents | 15% | clause 3 art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Other income of non-residents | 30% | clause 3 art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| Winnings, prizes and material benefits of residents | 35% | clause 2 art. 224 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
The table shows only the main personal income tax rates. In addition to them, others also work. For example, income in the form of interest on mortgage-backed bonds is taxed at a rate of 9% (clause 5 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It is not yet clear whether the increased personal income tax rate of 15% will be applied to income received by citizens from the sale of expensive property. Now such income is taxed at a rate of 13% if the period of ownership is less than the legally established limit (clause 17.1 of Article 217, clause 2 of Article 217.1, subclause 2 of clause 1 of Article 228, clause 1 and clause 4 of Art. 229 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And how will deductions be applied? According to the current rules, they reduce only that income that is subject to personal income tax of 13%. We will wait for official clarification on this issue.
Innovations for non-residents
As is known, a tax resident of the Russian Federation is recognized as a person who was actually in Russia for at least 183 calendar days over the next 12 consecutive months (Clause 2 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, in 2022, to obtain resident status, it was enough to stay in Russia for at least 90 calendar days (Federal Law No. 265-FZ dated July 31, 2020; there is no information yet about the extension of this rule to 2022). Individuals who do not meet the specified requirement for time of stay in the Russian Federation are considered tax non-residents.
Rate 30%
The personal income tax rate for non-residents will generally not change and will be 30% (clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
But there is also an innovation. Starting from 2022, it is necessary to determine separate tax bases in relation to the following income of non-residents (new clause 2.2 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- For winnings received by participants in gambling and lotteries.
- On transactions with securities and derivative financial instruments.
- For repo transactions, the object of which is securities.
- For securities lending transactions.
- Based on the income of the participants of the investment partnership.
- By income: from the sale of real estate and (or) shares in it; in the form of real estate received as a gift.
- For all other types of income (including wages) subject to the personal income tax rate of 30%.
Personal income tax should be transferred in one payment for all non-resident employees of an organization (separate division) or individual entrepreneur.
Generate personal income tax payment slips with current details
Rate 13% (or 15%)
A reduced rate of 13% is now applied to some non-resident income. We are talking about the salaries of foreigners working on the basis of a patent, refugees, highly qualified specialists, etc. (Clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For income received in 2022 and beyond, the rule will apply.
If the cumulative total of such income from the beginning of the year is 5 million rubles. or less - the rate is 13%.
If the cumulative total from the beginning of the year is more than 5 million rubles. — the bet consists of two parts. The first part is 650 thousand rubles. The second part is 15% of the amount exceeding 5 million rubles.
The order of transfer will be as follows.
In a situation where not a single non-resident employee of a company (separate division) or individual entrepreneur has had the indicated income exceed 5 million rubles since the beginning of the year, the tax should be transferred in one payment.
If the income of at least one non-resident employee has exceeded 5 million rubles since the beginning of the year, the tax should be transferred in two installments. The first includes personal income tax related to bases of 5 million or less. The second is personal income tax related to bases over 5 million.
Example of calculating personal income tax 15%
While the new procedure has not been prescribed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, we can only guess how the tax on the rich will be calculated from 2021.
Let us give an example of calculating personal income tax according to the new rules, based on the fact that only those incomes that are taxed at a rate of 13% in 2020 will be taxed at a rate of 15% (salaries of the majority of resident citizens, income of residents under construction contracts, etc.).
Example
The monthly salary of the head of one of the divisions of an oil and gas company is 337,000 rubles. In June, he was paid a bonus based on the results of work for the previous year in the amount of 2,000,000 rubles. Let us agree that this person does not have the right to deductions for personal income tax.
See the table for the distribution of income received. For clarity, the calculation of personal income tax is presented according to the old and new rules:
After the introduction of new rules for calculating personal income tax, the taxpayer from the example considered will pay a larger amount of income tax to the budget. The difference will be 20,880 rubles. (806,600 ? 785,720).
Tax Features
Personal income tax is a contribution required to be paid when receiving money from almost any source. Absolutely all people are required to do it. And for officially employed persons, deductions are made by their enterprise. Also see “Who pays personal income tax”.
To determine the amount of personal income tax for deduction to the budget, you need to use a simple formula:
PN = S x N
PN – income tax; S – the amount on the basis of which the calculation is made; N – interest [personal income tax rate].
EXAMPLE PJSC Antey awarded employee Govorov a salary of 35,800 rubles, as well as a bonus of 11,000 rubles. For him [personal income tax rate is 13]%. How much percentage of personal income tax salary should be transferred to the budget?
Solution: (35,800+11,000) × 13%=6084 rub. – the amount of income tax.
As a result, Govorov will receive in his hands: 46,800 – 6,084 = 40,716 rubles.
Also see “We calculate personal income tax from the amount in hand.”
It is important to remember that persons who received:
- state benefits for unemployment, pregnancy and childbirth;
- pensions and social benefits;
- scholarships;
- funds from inheritance;
- maternal capital.
The full list can be found in Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Also see “Is it necessary to tax maternity benefits with personal income tax?”
Let's sum it up
- At the proposal of the President of the Russian Federation, a progressive personal income tax rate of 15% will be applied from 2022 to citizens’ incomes exceeding RUB 5,000,000.
- The tax on the rich will affect those citizens who have a high income, as well as entrepreneurs using OSNO if their annual income is above 5 million rubles. Most citizens, given the average salary in the country, will not be affected by this innovation.
- Additional funds received into the budget from the introduction of an increased personal income tax rate are planned to be used for specific purposes - the treatment of children with rare serious diseases.
Hello Guest! Offer from "Clerk"
Online professional retraining “Accountant on the simplified tax system” with a diploma for 250 academic hours . Learn everything new to avoid mistakes. Online training for 2 months, the stream starts on March 1.
Sign up
How is tax calculated?
The tax is calculated as follows: there is non-taxable interest income tied to the key rate of the Central Bank, and on the remaining interest received you must pay 13% personal income tax. It is from interest , not from the deposit amount.
When the law was adopted, it was assumed that on average taxes would be paid on deposits amounting to close to 1 million rubles, but the bar was lowered.
So, as of January 1, 2022, the key rate was 4.25%, and interest of 42,500 rubles was not taxed. If we put in 1 million rubles. at 5%, you would receive interest of 50,000 rubles. 42,500 is the non-taxable minimum, that is, with 7,500 you would have to pay 13% personal income tax - that’s 975 rubles of tax.
As of January 1, 2022, the key rate of the Central Bank was already 8.5%. Non-taxable interest - 85,000 rubles. Let's say we liked the deposit at 20%. We put 1 million rubles for a year, and the resulting interest income is 200,000 rubles. It turns out that we pay 13% tax on 115,000 (200,000 minus 85,000), which is 14,950 rubles. And don’t forget that our inflation is also high now, which contributes to the depreciation of savings.
You don’t have to calculate anything yourself; the Internet is full of calculators, for example, on the Assistant website. There are plenty of such calculators and in general they are similar: you can enter your amount and rate there and calculate the tax.
In addition to the fact that it has become larger, it now turns out that smaller amounts are subject to personal income tax. These amounts are moving further from a million to the lower side.
Let's look again at the conditional contribution at 20%. Already a deposit of 500,000 is subject to tax - you will have to pay 1,950 rubles, for a deposit of 450,000 - 650 rubles. That is, this is already more than 2 times less than 1 million rubles, which legislators were targeting as a large contribution.