The economic activities of all categories of organizations, even small ones, involve the daily creation of documents. In medium and large companies, the daily document flow amounts to tens or hundreds of official letters, orders, primary documents, and reports. In this connection, questions arise regarding the correct storage of documents. From this article you will learn the storage periods for accounting and personnel documents, the rules for compiling a list of cases, and responsibility for violating the storage procedure.
Who is responsible for determining the retention periods for documents?
Federal Law No. 125 states that individual entrepreneurs and organizations are required to ensure proper storage of archival documents, including documents on personnel. The deadlines are established by the norms of federal laws and other legal acts of the Russian Federation.
This list includes the following categories of documents:
- standard management archival documents that are generated in the process of activities of state bodies, local governments and companies, indicating storage periods - in accordance with the order of the Federal Archive No. 236;
- standard archival documents that are generated in the scientific, technical and production activities of the company, indicating storage periods - in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Culture No. 1182.
Storage periods are also established in other legislative acts. The Tax Code specifies the minimum storage period for tax documents, and the Accounting Law specifies the minimum storage period for accounting documents. Joint-stock companies are also subject to the Regulations on the procedure and periods for storing documents of joint-stock companies, approved by Resolution No. 03-33/ps of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market.
Note. According to Federal Law No. 125, documents must be included in the archival fund, regardless of the type of media and the method of their creation. Therefore, the organization must ensure the safety of all types of documents - in electronic form and on paper. Moreover, the shelf life of documents, in most cases, does not depend on the media used. Documents in electronic form with legal significance can be stored without printing.
The procedure for storing documents at the enterprise
Registers and primary documentation can be stored in both paper and electronic formats. The storage procedure is determined by the Regulations approved by Letter of the Ministry of Finance 105 dated July 29, 1983. First of all, the storage space must meet certain requirements:
- Be inaccessible to a wide range of people;
- Have suitable parameters for the state of the ambient air;
- Have a high degree of safety and fire resistance.
The storage room must be specially prepared. The ideal option would be a fireproof metal safe or cabinet with a secure lock.
A responsible person must be appointed who is charged with ensuring the safety and security of the entrusted archival documentation throughout the entire storage period. After the established deadlines, documents may be destroyed.
At the same time, a commission is assembled to evaluate the documentation regarding the expiration of their storage periods. Papers to be destroyed are transferred under a transfer deed to a specialized company engaged in processing these raw materials. The destruction of documents with an expired storage period is subject to mandatory documentation.
Storage periods for accounting documents
As stated above, storage periods are established by Federal Law No. 402. For most types of accounting documents it is 5 years. There are several nuances related to the procedure for calculating this period.
According to Law No. 402, for primary documents, accounting registers, and audit reports, the countdown of the five-year period begins from the date of the corresponding reporting year. With regard to the company's accounting policies and other documentation related to the organization and maintenance of accounting, as well as facilities that ensure the reproduction of documents in electronic form and verification of the authenticity of an electronic signature, 5 years are counted from the year in which the documents were last used for reporting .
Cash books, checkbook counterfoils, time sheets, orders, transfer requests, acts of acceptance, delivery, write-off of property, receipts, advance reports and other supporting documents that have been verified must be stored for at least five years. If disagreements arise, the period may be extended until a decision is made on the case if it is made outside the specified period.
The storage period for such documents as certificates, acts, protocols, statements, conclusions on the determination of depreciation, revaluation, write-off of assets and fixed assets is counted from the moment of disposal of assets.
Waybills are stored for 5 years, but the period can be increased to 50 years in the absence of other documents confirming harmful and dangerous working conditions.
Note. The storage period is equivalent to 50 years, applies exclusively to documents created after January 1, 2003. Previously, this period was 75 years.
Results
The storage periods for documents in the organization's archive must be strictly observed. They are defined by regulatory documents and cannot be shortened. The periods during which the company does not have the right to get rid of documents vary - from a year (for example, for a vacation schedule) to 75 years (for personal files of employees). In some cases, documents must be kept for the entire existence of the company.
You shouldn’t completely forget to sort company papers by shelf life - you can drown in a paper flood.
An expert commission, whose work should be organized on an ongoing basis, will help you get rid of documents in a timely manner. And the company’s archive will be constantly ready for new paper invasions. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Retention periods for personnel documents
Federal Law No. 125 states that documents on personnel that were completed in office work after January 1, 2003 are subject to storage for a period of 50 years. The law applies to employment contracts, additional agreements, including termination agreements, personal files and employee cards.
Similar storage requirements apply to the following categories of documents:
- orders and instructions for personnel - on admission, relocation, transfer, part-time work, remuneration, dismissal, advanced training, awards, changing data in the questionnaire, parental leave, leave without pay;
- memos;
- certificates;
- statements;
- diplomas, work books, certificates, certificates, certificates not claimed by employees upon dismissal.
Note. Civil contracts with individuals and acts related to them must also be kept for 50 years.
But there are exceptions to this rule. Documents related to disciplinary action may be destroyed after 3 years. This rule is specified in List No. 236. A similar storage period is provided for vacation schedules, as well as consent to the processing of personal data. But in the latter case, the three-year period is counted after the expiration of the consent or its withdrawal. This condition does not apply to basic documents for the processing of personal data, including instructions or regulations. They are subject to permanent storage.
Also, on an ongoing basis, you need to store the following personnel documents on your main activities, such as instructions and orders:
- on approval of the structure of the organization;
- on the creation of divisions;
- about taking office;
- on assigning the duties of the chief accountant to the manager;
- on early resignation;
- on approval and enforcement of local regulations;
- on the appointment of responsible persons.
The five-year storage period also applies to documents on administrative and economic issues (orders, instructions), and time sheets. The period can be increased 10 times if working conditions are considered dangerous or harmful. The same period is allocated for storing orders for granting leave - annual and educational, and orders for sending on business trips for workers whose activities are not related to harmful and dangerous working conditions. Orders on business trips for workers in “harmful” conditions must be kept for 50 years.
Copies of applications, reports, lists of employees, extracts from protocols, correspondence, conclusions and other documents on the issuance of financial assistance, payment of benefits, and payment of sick leave must be stored for five years. A year longer (six years) should be stored:
- pay slips and documents for them;
- payslips for the issuance of wages, fees, benefits and financial assistance.
Note. Pay slips and pay slips are subject to storage for six years if the organization maintains personal accounts for employees. Otherwise, according to Article 295 of List No. 236, these documents are subject to the right of storage for 50 years.
Retention periods for tax documents
Tax and accounting information, as well as other documents necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes, including documents confirming:
- receiving income;
- making expenses;
- tax withholding.
These norms are specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - in subparagraph 8 of paragraph 1 of Article 23 and subparagraph 5 of paragraph 3 of Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The period is counted from the end of the tax period in which the document was last used for the following purposes:
- for reporting;
- for calculating and paying taxes;
- to confirm income received and expenses incurred.
The exception applies to documents confirming losses incurred. They must be kept for the entire period of reduction of the tax base of the current tax period by the amounts of previously received losses.
Books of purchases and sales, including additional sheets to them, must be kept for four years. In this case, the countdown is carried out from the moment of the last entry in the book. Invoices must be kept for five years.
There is a five-year retention period for tax returns and tax payments. There is an exception to this rule - declarations of individual entrepreneurs for the period up to 2002; they must be stored for 75 years. The calculation of insurance premiums is prohibited from being destroyed for 50 years from the date of preparation.
Documents for calculating and paying insurance premiums must be kept for 6 years. These include cards for individual accounting of the amounts of accrued payments and other remunerations, as well as the amounts of accrued insurance premiums.
Note. Individual accounting cards must be stored for 50 years in the absence of payroll records or personal accounts. There is no direct explanation regarding the timing of the storage period for documents used to calculate insurance premiums. In this case, we can apply an analogy with tax documents, in other words, the countdown begins after the end of the billing period in which the document was last used for the purpose of calculating and paying contributions, as well as reporting.
Correspondence with fiscal services must be stored for five years, including acts, notifications, demands, decisions, objections, resolutions, statements, complaints. The period may be doubled if the complaint was filed based on the results of an inspection - desk or field. All documents in electronic form with an electronic signature, as well as certificates of UKEP verification keys, which are endorsed by technological documents and complaints, must be stored for five years. These deadlines are calculated from the moment the document is received/sent.
As a reference, contracts for the purchase of goods, works and services to meet state and municipal needs are subject to storage for five years after termination of obligations.
When should an invoice's shelf life be extended?
The previously agreed mandatory 5-year storage period for invoices may be extended. This is due to the fact that from 01/01/2015 companies can transfer tax deductions. The right to transfer VAT deductions within a 3-year period from the date of registration of goods (works, services) is enshrined in clause 2 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Taking into account the date of receipt of goods from the example considered, if the company postpones the deduction for exactly 3 years, it must be declared in the declaration for the 3rd quarter of 2024. The 5-year shelf life will need to be counted from 10/01/2024, i.e. in this case it will actually be 8 years.
When considering the extended shelf life of invoices when transferring deductions, it is necessary to remember that it cannot be transferred to a deduction when returning the advance to the buyer for 3 years. The deduction can be made only in the tax period in which the conditions provided for in the articles of Art. 171, 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 21, 2015 No. 03-07-11/41908).
The procedure for switching to a new nomenclature
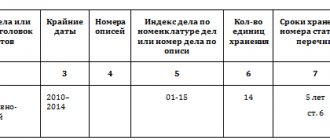
The nomenclature of cases will be needed to organize the current paperwork process and the subsequent transfer of documents for storage. The systematized list of case headings, which are drawn up in office work during the year, indicates the periods of their storage. This list will be required for the correct preparation of documents, organization of their recording/safety, as well as quick search.
The nomenclature should reflect all areas of work and functions of an individual entrepreneur or organization. Otherwise, documents that are not included in the nomenclature will appear in office work. And this can lead to violation of the storage order and loss of documents.
The order of the Ministry of Culture approved the form of the nomenclature of cases. The transition to a new nomenclature can be carried out taking into account the following nuances:
- it is necessary to enter the numbering of structural units;
- numbers will be required to create an index of cases, due to the inclusion of the serial number of cases, as well as the number of the structural unit.
As a reference. It is allowed to introduce complex indices, which consist of a group of numbers separated by a hyphen in a multi-level internal structure of the organization. These may be separate numbers assigned to departments, divisions within a department, and work groups within a department. At the second stage of the transition to the new nomenclature, rules for the formation of case headings should be developed. The title must reflect the main content and composition of the case documentation. The use of such names as “correspondence” or “documents” is prohibited. There must be specificity:
- “correspondence with the Federal Tax Service”;
- "employment documents"
Note. It is also prohibited to use specific wording in the title - “General correspondence”, “Miscellaneous”, “Incoming documents”.
At the third stage, all cases are redistributed according to storage periods, as well as the introduction of an office management procedure, according to which documents are formed by case, according to the storage period. Difficulties may arise with the exact distribution of storage periods; in this case, a binary system is used:
- all documents relate to permanent or temporary storage;
- The division of affairs into specific periods is carried out at the next stage by the employees responsible for conducting business in the company.
Helpful information. Standard R 7.0.8-2013 “SIBID. Record keeping and archiving. Terms and Definitions” establishes the rules for including electronic documents in the nomenclature. According to GOST, an electronic file is an electronic document or a set of documents, which are formed in accordance with the nomenclature of files. Electronic files are included in the nomenclature common to paper files. The addition of electronic documents to the general nomenclature is subject to the rules that apply to paper documentation.
How exactly to store documents
There are two types of storage - current and archival.
Current storage rules apply to documents that are still in use or have a storage period of less than 10 years. They are simply kept in the company: on shelves, in safes, folders - no one will blame you that the documents are not arranged in chronological order, the main thing is that they are intact.
Archival storage rules apply to documents with a long shelf life. After 10 years of storage, you take the papers off the shelf and prepare them for transfer to the archives. To do this, fold it in chronological order, number the pages, and stitch it. Create an inventory: list the documents in a binder, each with its own number, title and number of pages. The final touch is a certification sheet, which states the number of sheets in the binder and the physical condition. After that you transfer it to the archive.
The archive can be organized on the company’s premises or paid for storage by a special organization. You cannot keep documents on a balcony or in a damp basement - there are requirements for the archive. For example, a fire extinguishing system, temperature 17-19 degrees, relative humidity not higher than 50% and an alarm system. Access to documents should only be available to a limited number of persons, so that trade secrets or personal data are not disclosed.
Penalties for violating the procedure for storing documentation
One of the most common situations is a refusal to provide a document at the request of the fiscal service. The request can be sent as part of an inspection, a “counter” inspection, or without scheduling an inspection. In all of the above cases, refusal for failure to submit or late submission will result in a fine of 200 rubles.
Note. Special services, such as 1C:EDO, will help facilitate and speed up the process of sending documents to the fiscal service. It makes it possible to send tens of thousands of electronic documents simultaneously. Through the web service you can also transfer any electronic documents, including invoices, TORG-12 invoices and other documents that are created according to approved formats. This list also includes scanned copies of documents on paper:
- contracts;
- acts;
- bills.
The absence of primary documents or invoices may result in tax liability for violation of accounting rules. The size of the sanctions depends on the consequences:
- if the violation did not lead to an understatement of the tax base, the fine will be from 10 to 30 thousand rubles;
- if the lack of documents leads to an underestimation of the tax base, the fine will be equal to 20% of the amount of unpaid tax, the minimum amount is 40 thousand rubles.
The organization and its employees may be brought to administrative liability in case of non-compliance with the storage periods for documents. According to Article 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, the following fines are established for violating the rules for storing, compiling or using archival documents:
- for officials – from 3 to 5 thousand rubles;
- from 5 to 10 thousand rubles for legal entities.
A more severe penalty is provided for failure to fulfill obligations to store documents by a joint-stock company or limited liability company within the periods provided for by current legislation:
- from 2.5 to 5 thousand rubles for officials;
- from 200 to 300 thousand rubles for an organization.
Failure to comply with the storage deadlines for reporting and accounting documents on currency transactions will result in a fine of 4 to 5 thousand rubles for officials. Organizations are assessed sanctions in the amount of 40-50 thousand rubles. For violation of the terms of storage of accounting documents for foreign trade transactions with goods, works, services, information, results of intellectual property for the purposes of export control, the following penalties are provided:
- 1-2 thousand rubles for officials;
- 10-20 thousand rubles for legal entities.
Date table with changes in 2022
The storage periods for documents compiled before February 18, 2022 are determined by Order of the Ministry of Culture No. 558 of August 25. Documents drawn up after this date are subject to the requirements of List No. 236.
The table shows the most important documents for accountants with changed retention periods.
| Document | New term | Old term |
| Agreement of gift (donation) of property | until the liquidation of the organization | constantly |
| Leasing agreement | five years after the expiration of the contract or redemption of the property | constantly |
| Real estate pledge documents | ten years | constantly |
| Real estate exchange agreement | until the liquidation of the organization | five years |
| Agency agreement | fifteen or ten years depending on the type of property | five years |
| Credit or loan agreement with the condition of pledging property | ten years | five years |
| Transaction passports | Fifteen years | constantly |
| Documents on receivables and payables | five years subject to debt repayment | five years |
| Invoices | five years | four years |
| Documents confirming receipt of salary (if there are personal accounts) | six years | five years |
| Register of information on the income of individuals | Five years | Seventy five years |
| Certificate of fulfillment of the obligation to pay taxes, fees, contributions, penalties and fines | five years | no deadline set |
| Certificate on the status of settlements with the budget | five years | no deadline set |
| Calculation of insurance premiums | fifty years | no deadline set |
| Documents on revaluation of fixed assets and depreciation | five years after disposal of fixed assets or intangible assets | constantly |
| Documents on write-off of fixed assets and intangible assets | five years after disposal of fixed assets or intangible assets | constantly |
| Acts of acceptance and transfer of real estate to the new copyright holder | five years after disposal of property | constantly |
| Book of accounting of income and expenses under a simplified taxation system | five years | constantly |
At the end of the article, I would like to note once again that most of the documents compiled in the course of the economic activities of an organization or individual entrepreneur must be stored for several years.
But it is important to take into account that not only the safety and immutability of documentation must be ensured, but also the ability to quickly search it in the archive. Since the tax office can make a request for a document at any time. And the period for preparing a response established by current legislation is only ten working days. And it is impossible to ensure timely preparation of data without proper organization of the nomenclature of files - all documentation is immediately distributed by type and storage period. This approach will avoid not only the accrual of penalties, but also unnecessary labor costs.
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter