Organizations daily face situations where it is not possible to reflect property on balance sheet accounts. In accounting, off-balance sheet accounts are used to reflect transactions with valuables that are not objects of balance sheet accounting. It should be noted that information for off-balance sheet accounting, in the same way as for balance sheet accounting, is reflected in the reporting (certificate of off-balance sheet accounts f. 050730, f. 0503130 and f. 050830), and therefore it is necessary to maintain the correctness of the entered data so as not to distort reporting.
How off-balance sheet accounts work
Instruction 157n provides for thirty-one off-balance sheet accounts.
We remind you that the accounting entity has the right to use additional off-balance sheet accounts. To use additional accounts, they must be included in the working chart of accounts and approved when developing the Accounting Policy. The movement in off-balance sheet accounts is reflected as follows: the debit account takes into account the increase in the values of the account, and the credit account for the decrease, since all accounts are active. Recording on accounts, unlike balance sheet accounts, is simple; a corresponding account is not needed to generate postings.
The main business situations in which an institution, in accordance with current legislation, needs to make entries on off-balance sheet accounts.
What are off-balance sheet accounts intended for and how are they used?
The chart of accounts (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), in addition to the main balance sheet accounts, provides additional ones that carry information about the company’s temporarily owned assets, as well as about contingent rights and obligations.
Such accounts do not appear on the balance sheet and are therefore called off-balance sheet accounts. For the algorithm for compiling a balance sheet, see the material “Procedure for compiling a balance sheet (example)”.
These accounts differ from the standard ones by a three-digit code designation and registration of records using a simple system. That is, when compiling transactions, the double entry method is not used here, and business information is displayed either only by debit of the account or by credit.
Lease of non-financial assets
Before the entry into force of the amendment to Instruction 157n dated March 31, 2018, accounting for both rented property and property received for free use was kept on account 01 “Property received for use.”
In the latest edition of Instruction 157n, the purpose of account 01 is interpreted differently: “The account is intended to account for property received by an institution for use that is not leased.” These changes are associated with the introduction of account 111.40 “Rights to use non-financial assets”, which currently accounts for the rights to use non-financial assets in accordance with the terms of lease agreements. It is important to take into account the differences in accounting on accounts 01 and 111.40:
1. Account 01 accounted for each individual object of non-financial assets with inventory numbers assigned by the balance sheet holder and indicated in the transfer and acceptance certificate. In this case, the accounting object was assessed at its value indicated by the balance sheet holder. In the absence of a valuation of objects, it is allowed to take into account the conditional valuation - 1 object = 1 ruble.
2. Account 111.40 takes into account the cost of rent, and not the cost of the object itself. To reflect changes in legislation on lease transactions made during the inter-settlement period, the following actions should be taken:
- accept for accounting into account 111.40 in correspondence with 401.30 the sum expression of the cost of rent for property received for rent (the operation is documented in an accounting certificate);
- write off the balance from account 01 in relation to the leased property.
It is important to note that according to the new rules, if a lease agreement is concluded in relation to individual objects of non-financial assets, then there is no need to reflect them on account 01.
However, if a property complex, including various equipment, is leased, the lease agreement will indicate the total amount of the agreement without a breakdown by object. In this case, to ensure the safety of property and conduct an inventory, it is recommended that individual items of non-financial assets are still accounted for in account 01. To be reflected in the program “1C: Public Institution Accounting 8” ed. 2.0, property received for rent provides for the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts” with a specialized type of operation “Receipt to account 01.02”.
The document must indicate:
- information about the MOL responsible for the non-financial asset;
- information about the lessor and the lease agreement;
- information about the fixed asset itself.
Features for budgetary institutions
The use of off-balance sheets in the accounting of a budgetary institution is regulated by Instruction 157n (section 7). This section provides a list of assets that should not be included in balance sheet accounts. According to current legislation, institutions have the right to adjust this list and, if necessary, include other inventory items in it.
In accordance with paragraph 373 of Instruction 157n as amended on March 31, 2018, accounting is carried out on off-balance sheet accounts of budgetary institutions:
- valuables located in the organization without the right of operational management (rent, free use, etc.);
- valuables that are taken into account outside balance sheet accounts (fixed assets in the amount of up to 10,000 rubles, strict reporting forms, prizes, vouchers, etc.);
- obligations awaiting fulfillment.
Do you know how many off-balance sheet accounts have existed since 2015? Currently, 31 accounts are used in budget accounting!
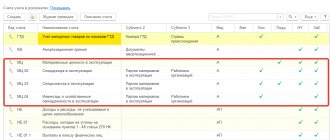
You can familiarize yourself with all the accounts that are used when maintaining records in a budgetary institution in the table.
| No. ZSCh | Name |
| 01 | "Property received for use" |
| 02 | “Material assets accepted for storage” |
| 03 | "Strict reporting forms" |
| 04 | "Debt of insolvent debtors" |
| 05 | “Material assets paid for through centralized supply” |
| 06 | “Debt of pupils and students for unreturned material assets” |
| 07 | “Awards, prizes, cups and valuable gifts, souvenirs” |
| 08 | "Vouchers unpaid" |
| 09 | "Spare parts for vehicles" |
| 10 | “Ensuring the fulfillment of obligations” |
| 11 | "State municipal guarantees" |
| 12 | “Special equipment for carrying out research work under contracts by customers” |
| 13 | "Experimental Devices" |
| 14 | "Settlement documents awaiting execution" |
| 15 | “Settlement documents not paid on time due to lack of funds in the account of a state (municipal) institution” |
| 16 | “Overpayments of pensions and benefits due to incorrect application of legislation on pensions and benefits, accounting errors” |
| 17 | "Cash receipts" |
| 18 | "Cash Outflows" |
| 19 | “Unexplained budget revenues from previous years” |
| 20 | "Debt unclaimed by creditors" |
| 21 | “OS worth up to 10,000 rubles inclusive in operation” |
| 22 | “Material assets received through centralized supply” |
| 23 | "Periodicals for use" |
| 24 | “Property transferred into trust management” |
| 25 | “Property transferred for paid use (rent)” |
| 26 | “Property transferred for free use” |
| 27 | “Material assets issued for personal use to employees (employees)” |
| 30 | “Calculations for the fulfillment of monetary obligations through third parties” |
| 31 | "Shares at par value" |
| 40 | "Assets in management companies" |
| 42 | “Budget investments implemented by organizations” |
Here are the ones that are most often used in work:
- Property accounting is carried out using 01, 02, 05, 06, 07, 09, 12, 13, 21, 22, 24, 25, 26, 27 off-balance sheet accounts.
- Strict reporting forms, prizes, vouchers and periodicals are reflected in accounts 03, 08, 23.
- Accounting for cash and settlement documents is carried out on accounts 14-19, 30.
- Accounts receivable and payable are posted to off-balance sheet accounts 04 and 20, respectively, guarantees are posted to 10 and 11.
- Financial investments are recorded in 31, 40, 42 off-balance sheet accounts.
Obtaining non-exclusive rights to use software products
Let's consider the reflection of non-exclusive rights of use to the results of intellectual activity in the accounting of an institution.
In accordance with paragraph 66 of Instruction 157n, intangible assets received for use by an institution (licensee) are subject to accounting on off-balance sheet account 01 “Property received for use” at a cost determined based on the amount of remuneration established in the agreement. For accounting in the program “1C: Public Institution Accounting 8”, ed. 2.0. non-exclusive rights to use software products are provided for in the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets (except buildings and structures) (OS-1) (Order 173-)” with the type of operation “Receipt to account 101 (102, 103), 01, 02”.
Document form “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets (except buildings and structures) (OS-1) (Order 173-n)”
The document must contain information about the organization of the sender and recipient, data about the object, accounting account and inventory number, as well as storage location.
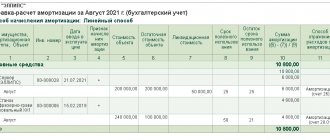
On the Depreciation tab, you must specify the amount of depreciation transferred, the depreciation parameters, and the cost account used by the institution. As a result of the document, the institution receives an increase in turnover in the debit of account 01.31 “Other movable property in use under agreements for gratuitous use” indicating the amount of the non-exclusive right to use the software product.
Analytical accounting in the context of KBK on off-balance sheet account 04
Off-balance sheet account 04 “Doubtful debts” is intended to account for doubtful debts of insolvent debtors during the period of possible resumption of the debt collection procedure.
From 01/01/2021, new analytics are provided for off-balance sheet account 04 in the context of budget income classification codes (KDB) (clause 339 of Instruction No. 157n).
When funds are received to repay the debt accounted for on account 04, the amounts are written off from off-balance sheet accounting and taken into account in the corresponding balance sheet accounts for accounting for settlements on receipts.
From this we can conclude that analytical accounting on off-balance sheet account 04 is carried out according to the same profitable BCCs for which the receivables for income were listed on the balance sheet.
However, off-balance sheet account 04 can take into account not only receivables for income, but also for expenses.
In our opinion, despite the fact that Instruction No. 157n does not provide for analytics on expense BCC, it is advisable to record accounts receivable for expenses in a similar way, i.e. according to the same codes by which the debt was recorded on the balance sheet before it was written off (codes for the classification of budget expenditures (KRB)).
This approach will allow, if necessary, to restore the debt on the balance sheet.
Please note that this rule applies only to accounts receivable for current year expenses.
Accounts receivable for expenses of previous years, in turn, are accounted for separately:
- in the accounting of government institutions - on account 1 209 36 000 according to the corresponding code from group 1 1300 130 “Other income from compensation of state expenses”;
- in the accounting of budgetary/autonomous institutions - according to account X 209 34 000 under article 510 “Receipt of cash and cash equivalents” of the analytical group of the type of sources of financing budget deficits.
Therefore, we believe that accounts receivable for expenses from previous years in off-balance sheet account 04 should be reflected using the above codes.
The concept of an off-balance sheet account
Off-balance sheet accounting includes a group of accounts and subgroups that summarize information on transactions and relate to the movement of inventory items of an enterprise. Postings with their participation are not constantly present in the company’s accounting and quarterly reporting, but are an important element in the preparation of reporting. Balance sheet accounting cannot be carried out correctly without off-balance sheet accounting, because such transactions are not reflected on the balance sheet. Despite this, after the processing process is completed, the balances appear as a final figure and are not taken into account in the balance sheets.
Application
These subaccounts have only an indirect impact on the final result of reporting on the main indicators and are not displayed in reporting or during inventory. Despite this, their structure is standard. There are debits and credits, and accounting occurs according to a standard simple scheme. They allow you to enter information about the receipt of goods and materials, which will be written off in the near future, but must be reflected in fact. These positions are not the property of the enterprise, and therefore are not taken into account in the balance sheet.
Important! Off-balance sheet accounts are a generalizing entry and they are created for analytical purposes, because even temporary positions require accounting.
Postings
Accounting does not use double entry for off-balance sheet accounts, which is clearly visible in the postings. In simple words, the balance reports the availability and type of funds, debit is the receipt, and credit is the expense or write-off. Postings provide accounting guarantee, and thanks to them, some items do not have to be shown in the financial statements. Example:
| Debit | Credit | Operation description | Total amount/RUB | Supporting documentation |
| 9 | Uncovered debt to the organization | 564000 | Standard contract | |
| 76 | 51 | Written off financial institution fees | 1340 | Standard contract |
| 8 | 60 | Receipt of new equipment from the supplier for installation work | 47868 | Equipment invoice |
| 8 | 76 | Adding commissions to the cost of equipment | 1340 | Standard contract |
| 19 | 60 | VAT | 73432 | Packing list |
| 1 | 8 | Equipment testing and commissioning | 446378 | A report drawn up by those responsible for commissioning |
| 68 | 19 | Acceptance of input VAT for deduction | 73432 | Invoice |
| 60 | 76 | Transfer of funds to an organization for outstanding debt | 564000 | Online payment |
| 76 | 51 | Repayment of debt to a financial institution | 564000 | Online payment |
| 9 | Complete debt write-off | 564000 | Debt cancellation act |
On a note! Calculation at the end of the month occurs according to the following formula: Final balance = beginning of the month + debit turnover - credit turnover.
Off-balance sheet accounts are not the main ones in accounting, but no less important because they take into account the movement of temporary assets of the enterprise. Their presence in accounting is temporary; they are not displayed in financial statements, but with their help it is easy to monitor the correctness of business transactions. The final balance must always be a debit balance. If it comes out with a minus in the program, it means that a system error occurred or the accountant entered inaccurate data.
Purpose of use
The balance sheet of any enterprise should display receipts and write-offs of all positions, but it is not always convenient for some transactions to be placed on the organization’s balance sheet, because they will interfere with the generation of reporting. These accounts are also called budget or asset accounts because they are used to account for the following items:
- Receipt or disposal of property.
- Issue or termination of security.
- Movement of material assets, including property objects: real estate, transport, land plots that do not belong to the enterprise, but are received for safekeeping.
- The movement of material assets that belong to the organization, but the cost of which has already been written off as expenses.
- Off-balance sheet accounts may collect information that may later be needed to explain certain accounting entries and will be included in the income statement.
Varieties
Using these accounts, documentation is later generated for registering a new entity or debiting funds. Despite the fact that it is not reflected in the balance sheet, correct accounting is impossible without off-balance sheet accounts. With their help, the creditworthiness, reliability and stability of the organization in the financial market are also assessed.
Not only business transactions are monitored, but also the fulfillment of obligations, write-off of debts and fulfillment of guarantee obligations. Despite the fact that accounting is kept for funds that are not owned, company employees bear full responsibility for them. Property held in subaccounts should not affect the balance sheets in any way.
On a note! The main tasks are the collection of information, as well as functions that will allow you to control the process of using values that are not the property of the company, but require accounting.
Off-balance sheet accounting accounts in budgetary institutions: concept and scope of application
Off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary institutions in 2022 can be classified into several categories based on their purpose.
Most of the off-balance sheet accounts are used by institutions in the budget system in a similar way to how they are used in private organizations. That is, an off-balance sheet account is used to register in an organization a certain object that cannot be clearly attributed to assets or liabilities “within the balance sheet.” For example, this may be because the object:
- is not the property (or a counter-obligation to the counterparty when ownership rights arise) of the organization or is not under the operational management of the institution;
- is not regularly used in business activities (as an option, it is transferred for use to another person and most of the time it is used by him);
- came into use of the organization temporarily;
- has a very low cost in comparison with the typical cost of accounting objects of the same name, which are usually placed on the balance sheet as assets or liabilities.
Examples of accounts for accounting of such objects in a budgetary institution:
- 02, which takes into account material assets in storage;
- 24, which accounts for property transferred to trust management;
- 07, which takes into account awards, cups, including challenge ones.
There are off-balance sheet accounts that perform an auxiliary function relative to the balance sheet accounts of the institution. Such auxiliary accounts include 17 and 18, which are opened for active accounts 020100000 (“Cash”), 021003000 (“Settlements with the financial authority”), 030406000 (“Settlements with other creditors”).
A complete list of criteria for placing certain objects on off-balance sheet accounts of a budgetary institution is defined in clause 332 of the Instruction by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n. In 2021, there are more than 40 different off-balance sheet accounts introduced by this order. The institution has the right to add its own accounts and subaccounts to them.
The provisions of Order No. 157n regarding the establishment of the list and procedure for using off-balance sheet accounts can be applied by all institutions of the budget system - budgetary, state-owned, autonomous. Given the provisions of special instructions on budgetary accounting in each type of institution, differences in the use of off-balance sheet accounts can be significant.