What could be the reason
There must always be a basis for the formation of an act, because In some way it is necessary to argue that inventories are being written off.
If, for example, these are building materials that are used for routine repairs, to confirm the write-off act, an order must be issued on behalf of the chief director to carry out repair and finishing work in any premises.
If the act is issued after an inventory has been carried out, then the basis for the paper should be its results, or rather, the documents that were obtained as a result of the inventory. The following may also be grounds:
- demand-invoice;
- limit-fence card;
- invoice for release to the side;
- statement of issue of supplies, etc.
For what reasons are inventory items written off?
The act is a document for writing off inventory items from the balance sheet for a number of circumstances.
Reasons why goods cannot be sold in the future:
- damage to goods;
- failure;
- breaking;
- deprivation of properties;
- expiration of storage time.
During storage, goods lose their consumer properties and become unusable due to breakage. The act is drawn up due to the lack of possibility of their further use.
The form for the act of writing off goods is drawn up according to the TORG-16 form. This form of the form was ratified by Resolution No. 132 of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation of December 25, 1998 and is used when defects or defects are detected in materials.
In this document you need to write down the entire list of information with the characteristics of the products:
- Name;
- vendor code;
- price;
- quantity;
- weight;
- unit of measurement;
- the reason for writing off this product.
As for the regulated document form for the seizure of inventory items for other reasons, it simply does not exist. Such an act may be free-form.
However, to prove the expenses incurred by employees, drawing up a document for the withdrawal of commodity valuables is mandatory, regardless of which invoice was issued for the release of material from the warehouse.
The document provided for by the accounting policy of the enterprise will confirm the fact of use of materials for organizational purposes.
Components
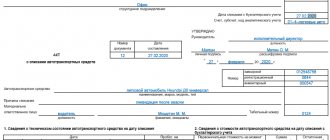
The act of writing off inventories has two pages in the form. The first must contain the signature of the head of the institution. The second is the “autographs” of all members of the commission convened regarding the writing off of materials. A table that starts on the first sheet and ends on the second can be longer. Also on the first page, in the upper right corner, there is a separate space for the director’s signature with the date of signing. Directly below it is a miniature table containing the codes. In the document form available for download on this page, the form code for OKUD is immediately marked - 0504230. When filling out, all that remains is to enter the date of write-off of inventories, the code for OKPO and KPP.
No matter how many pages there are in a specific act on the write-off of inventories, it must contain a header, a main tabular part and a conclusion.
At the top of the act it is always written:
- Document number and date of its adoption.
- Name of the institution.
- His Taxpayer Identification Number.
- Name of the structural unit (if any).
- Financially responsible person (position, full name).
- Position, surname and initials of the chairman and members of the commission in whose presence the document was completed.
- Link to the number and date of the order (or instruction) on convening the commission by the head of the institution.
After a long introductory part there is a table, which should contain specific and reliable information about:
- The name of the material that is subject to write-off (was consumed) with its code.
- Units of measurement of the material mentioned.
- Consumption standards.
- How much was actually spent: quantity, price and amount (only in numbers).
- Reasons for write-off.
The last two columns are devoted to accounting entries: debit and credit. They are filled out only after the act is received by the accounting department.
Important! Data about different materials should be in different rows of the table.
A separately prescribed nuance is the total write-off amount. It is written out in a separate fragment of the table. In addition, it is written immediately after it in numbers and in words. It is the basis for further accounting operations.
At the end, five lines are left to formulate the commission’s conclusion. The chairman and members of the commission put their signatures confirming that a check at the warehouse was carried out and revealed the actual consumption of the specified materials in the specified quantity.
The form also contains a note from the accounting department stating that the act was reflected in the transaction journal for a specific date. The fact of the act must be evidenced by the seal and signature of the chief accountant with a transcript.
Rules for writing off inventory items
Inventory assets mean the following property of the organization:
- raw materials - items, things that are used in production for the manufacture of any product;
- work in progress - goods, products, the production of which has not been completed, which have not received consumer properties in accordance with their purpose, that is, those that are in the production stage;
- finished products - goods that can be sold without additional costs, having gone through all stages of production established in the relevant regulatory documents: regulations, technical instructions;
- inventories - unused property of an organization transferred for storage to warehouses.
Both the person responsible for the safety of valuables and keeping records of them, as well as the chief accountant or the head of the enterprise, can propose recycling. In order to carry out write-offs, a special commission is created in the organization, which can act on both a temporary and permanent basis. The composition of such a commission must include persons who are financially responsible for specific assets of the company, specialists in specific equipment, and the chief accountant. The powers of the commission include, inter alia, drawing up a write-off act, a sample of which is presented below.
Where is the act of writing off goods used?
In companies engaged in trading, facts of product spoilage or other cases of loss of quality of inventory items are periodically discovered. If such goods can no longer be sold in the future, they are deregistered and disposed of. To document the fact of writing off unusable inventory items, the TORG-16 form is used, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 No. 132. Although since 2013, a similar form can be developed independently.
Write-off of damaged goods can only be carried out if the act is drawn up in the presence of members of a commission approved by a special order of the head of the company. All members of the commission establish the fact that goods have lost quality and consumer characteristics and record this in TORG-16. If necessary, representatives of other authorities (sanitary authorities, consumer supervision, etc.) are involved.
The form is also used when writing off expired products, for example, medicines in pharmacies. Find out what documents to fill out when writing off expired medications in ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system yet, get a trial online access for free.
List of actions that will need to be performed after issuing a write-off act
To actually recognize the withdrawal of inventories, upon completion of the act, the accountant must formalize accounting for production.
Receipt of materials to the enterprise has the following classification:
- From suppliers for a fee.
- From our own production (production of material in-house).
- From the founders.
- When dismantling equipment.
- For barter transactions.
- Free receipt.
Based on the information specified in the seizure act and the balance sheet, the following entries are made:
- posting D94 K10 – reflects the accounting value of inventories that are subject to withdrawal;
- posting D20 K94 - shows the monetary value of deterioration or shortage of inventories (within the limits of reasonable natural loss);
- posting D20/2 K73 - shows the amount of compensation for the shortage to the guilty party (in the case when the number of units of written-off inventory exceeds the natural loss limit);
- posting D99 K10 - reflects the destruction of supplies as a result of a natural disaster;
- posting D99 K68 – restores VAT (value added tax) that was paid earlier;
- entries D91/2 K10 and D91/2 K68 – write-off of inventories under a free use agreement.
Moreover, before the accountant completes the posting indicated in the last paragraph, you need to draw up a large number of documents.
Namely:
- application for the release of materials;
- contract;
- waybill.
What happens if you don’t draw up an act
As mentioned earlier, if the valuables that are subject to withdrawal are written off from the warehouse based on the expired depreciation period or due to obsolescence, the TORG-16 form does not need to be used. In this situation, the act is drawn up in any form, indicating the serial number of the goods and the date of execution of the document.
The name of the legal entity, the full name of the director and the name of the department from which these values are written off are also required.
Listed below in order:
- name of all write-off units;
- their serial numbers;
- quantity;
- cost per unit of production;
- reason for write-off.
The last line will be the accounting value of warehouse inventory and the final figure that is subject to withdrawal. The act must be endorsed by all members of the commission, signed by the director of the organization and secured with the official seal of the enterprise.
However, in many organizations the timing of this activity may be delayed. Therefore, in exceptional situations, the manager may decide that there is no need to draw up such a document at all. Then it is recommended to take as an example systematic instructions on accounting for inventories (MPI) and on the preparation of initial documentation for the issuance of inventory and materials to various branches and departments of the organization.
To do this, the fact of transfer within the enterprise structure is recorded in the limit card of form M-8 or using the invoice forms F-11 and F-15.
To summarize, it should be noted that correct, timely written-off acts on valuable inventories significantly facilitate the dialogue between the organization’s management and tax service employees. It is, of course, better to prevent the consequences of audits, because representatives of the tax authorities are quite scrupulous in considering actions that are related to the company’s expenses.
Audit of inventories in 1C: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0
Published 11/09/2021 08:59 Author: Administrator Inventories are a common type of asset in many enterprises. A significant share of the property of organizations is industrial inventories. They are needed not only for expanding activities, but also for a stable existence. It would seem that the area of accounting for materials is not the most difficult, however, even here auditors find a bunch of errors and shortcomings! In this article we will talk about the most common ones.
Accounting for inventories is regulated by the following regulatory documents: Federal Law “On Accounting”, FSBU 5/2019 “Inventories”; Regulations on accounting and financial reporting; Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as other regulatory documents.
An audit of inventories is carried out with the aim of formulating an independent opinion on the completeness and reliability of the reflection of data on inventories in the financial statements.
Conducting an inventory audit is labor-intensive due to, as a rule, a large range of items and significant document flow for the movement of this group of assets. In addition, there is a wide variety of types of materials, methods of their receipt and use, due to which the procedure for checking them will also vary.
In addition, the specifics of the activities of a particular enterprise are largely reflected in the accounting process, therefore, universal procedures that can be used for any type of inspection are very general and must necessarily be supplemented with procedures specific to inspections of this type of enterprise.
That is why, first of all, during the preparation of the audit, information is obtained which specific inventories are used in the organization, where and for how long they are stored, what role they play in the production process, etc.
An inventory audit involves checking whether actual indicators correspond to accounting information and takes place in several stages. The inspection is carried out on the basis of the enterprise’s documentation.
When checking, the following audit procedures are performed in relation to:
— the correctness of classifying received material assets into the category of inventories;
— accurate and timely documentation of operations for the movement of goods;
— quantitative accounting, procedures for recalculating the quantity (if necessary) of material assets upon receipt of inventories and in the process of their use in activities;
— checking the accuracy of the quantitative and cost assessment of incoming (created) and retired inventories;
— evaluation of finished products;
— assessment of goods upon receipt and write-off;
— the correctness and timeliness of recording transactions for the receipt of inventories during their acquisition (manufacturing), internal movement and disposal;
— facts of short-delivery of inventories, claims regarding short-delivery or delivery of low-quality material assets;
— checking the accounting of uninvoiced supplies of inventories;
— operations for writing off materials for production and other disposal;
— determination of surpluses and shortages during the inventory, control over their correct reflection.
Checking the correctness of inventory accounting is, as a rule, selective. The sample size is determined based on the audit risk assessment carried out at the audit planning stage.
When conducting an audit of inventory accounting operations, various methods are used: analytical procedures, recalculation, inventory, oral questioning, document verification, etc.
The most common errors detected during testing:
1. There are no agreements on liability with employees who are involved in transactions with tangible assets; purchase and sale agreements for inventories with suppliers and buyers;
2. Property worth more than 40,000 rubles. (until 2022, later - the cost limit is established in the accounting policy) and according to the criteria, corresponding to fixed assets, is taken into account as part of inventory assets.
Organizations may deem insignificant the cost of low-value fixed assets and inventories , such as computers, office equipment, furniture, and workwear. For them, in the program 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8, edition 3.0, you should set the Item Type - Low-value equipment and inventories , for correct reflection in accounting.
3. There are no properly executed primary documents for the receipt of materials.
• When posting materials, the following documents are not drawn up:
— receipt order (form No. M-4) — if the quality and quantity of materials correspond to the supplier’s documents;
— certificate of acceptance of materials (form No. M-7) — if discrepancies are identified.
• A common situation is when primary documents (waybills, delivery notes) are not completed, or not all required details are filled in.
• The date of reflection in the accounting records of the receipt of material assets does not correspond to the date of their actual receipt.
• There are cases where organizations applying the general taxation system include value added tax in the cost of purchased materials.
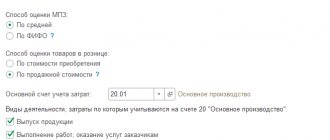
4. The method for valuing materials upon disposal, enshrined in the accounting policy for accounting purposes, has not been established or is not applied in practice.
• For example, in the accounting policy when materials are released into production and otherwise disposed of, they are assessed at average cost. In fact, the FIFO method was used;
• The method for writing off inventories has not been established. The chosen method is fixed in the accounting policy of the organization.
To see which method is installed in the software product 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8, edition 3.0, go to the “ Main ” section and select the “ Accounting Policy ” item.
5. The procedure for forming the cost of inventories has been violated.
For example, the accounting policy for accounting purposes establishes a method for reflecting costs for the purchase of materials, including transportation and procurement costs (TPC) on account 10 “Materials”.
During the audit, cases of non-compliance with the requirements of the accounting policy and the reflection of material and equipment in the cost of relevant materials were identified.
6. No reserves are created for depreciation of materials in accounting
The accounting policy for accounting purposes does not contain information about provisions for impairment of value. The organization did not use account 14 “Reserves for reduction in the value of material assets”; no valuation reserves were created.
At the same time, the norms of current legislation provide for the mandatory creation of a reserve to reduce the value of inventories if signs of depreciation of materials are identified at the reporting date.
It is necessary to develop and consolidate in the accounting policy the cases of creating a reserve and the procedure for calculating the current market value of inventories. Ignoring legal requirements may lead to unreliable financial statements.
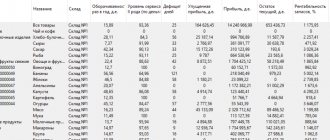
The mechanism for reflecting the decrease in the cost of material assets has been implemented so far only in the 1C: Accounting 3.0 KORP configuration, while in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8, edition 3.0 you can generate a report “Remaining goods by shelf life” , to do this, go to the “Warehouse” section and select “ Remaining goods by shelf life."
7. Any materials were not capitalized, in particular scrap metal upon disposal of fixed assets due to physical wear and tear.
Material assets remaining from the write-off of fixed assets are accounted for at the current market value on the date of write-off of fixed assets.
8. The procedure for accounting for fuels and lubricants is violated
• Waybills are not maintained, or individual waybills do not contain mandatory details, in particular a note on a pre-trip medical examination, speedometer data, and the reverse side is not filled with information about the specific destination, which does not allow one to judge whether the car is used by employees of the organization on official business. purposes.
• Analytical accounting for fuel storage locations (car tank or drivers) is not organized.
9. Account 10 “Materials” contains values only in value terms without quantity.
10. The procedure for recording the write-off of materials in accounting has been violated:
• cases of reflection in production costs (accounts 25, 26) of the cost of inventories written off due to their unsuitability for further use and without supporting documents;
• when writing off materials, only invoice requests or write-off acts are drawn up, which do not reflect information about the reason for the write-off, and there are no signatures of commission members;
• when carrying out repair work, information about the name of the object being repaired is not reflected, there is no data on the list, volume and necessity of the work performed (the reason for the repair being performed).
In 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8, edition 3.0, the ability to generate a write-off act has been implemented. You need to go to the “Warehouse” and select “Requirements-invoices” .
In the created document, you must indicate the purpose of the expense and select a commission.
Write down the finished document and print it “Act for write-off of materials”.
• Discrepancies in data on the amount of materials consumed during various construction and installation works, reflected in the acts of acceptance of work performed (form KS-2) with data from reports of materially responsible persons and accounting registers.
11. The procedure for carrying out inventory of inventories was violated
• Inventory is not carried out before preparing annual reports or when changing materially responsible persons;
• the results of the inventory of goods and materials were not properly documented;
• lack of an approved commission for inventory of inventories.
12. The procedure for recording transactions for the sale of materials has been violated
• When selling inventory items, the write-off of their actual cost is reflected by the Company in account 90 “Sales”. It was necessary to reflect the sale of inventory items using account 91 “Other income and expenses.”
• In accounting, revenue from the sale of materials is recognized as other income, VAT is calculated. However, the actual cost of materials is not reflected in other expenses. In the 1C: Enterprise Accounting program, “manual” adjustments were made.
Errors in inventory accounting occur quite often. If there are many of them, this can seriously affect the activities of the enterprise and the reliability of the financial statements.
Conducting an inventory audit will allow organizations to regularly take measures to eliminate any omissions. Compliance with legal requirements will allow the enterprise to timely identify mistakes made, both in organizing inventory accounting and in organizing the efficiency of production processes.
Author of the article: Evgenia Tarasova
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
Comments
0 LYUDMILA 11/10/2021 19:30 THANK YOU
Quote
Update list of comments
JComments