Student agreement
If your business has a large rotation of personnel, for example, you constantly change managers, programmers, salespeople, etc., then it makes sense for you to consider drawing up apprenticeship agreements with new employees. This optimization option will allow three months while the employee is undergoing training and internship without having to charge insurance premiums on his income. In this case, the employee himself essentially loses nothing.
If desired, an apprenticeship agreement is suitable in any area of business, because a young employee, one way or another, needs to become familiar with the new place of work and the peculiarities of the activities of your enterprise.
During training in the basics of the profession, the student receives a scholarship, which should not be lower than the minimum wage (Article 204 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). The practical part (practice), which is also free of fees, can be paid at piece rates, that is, for the actual result.
- Officials of the Ministry of Finance confirmed that payments under the student agreement are not subject to insurance premiums (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-15-06/45624 dated June 21, 2022).
- A scholarship under a student agreement is not exempt from personal income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/99393 dated November 13, 2020).
To reduce tax risks, it is important that the fact of training is documented, and controllers do not have the opportunity to reclassify the apprenticeship contract into an employment contract. To this end:
- Create a study plan.
- Specify the criteria for assessing completion of training.
- Set the plan and criteria in a training statement that the principal will sign.
- Indicate in the contract the qualifications that the student will acquire after training.
Advantages of the method: Savings on insurance premiums of 15-30% of the employee’s remuneration during the first three months of work. Ease of dismissal of a newcomer who fails the test without compensation payments. Tax authorities do not object to the fact that a scholarship under a student agreement is not subject to insurance contributions.
Disadvantages of this method: The lawyer must draw up documents in a high-quality manner, taking into account the specifics of the student agreement. Otherwise, there may be risks of reclassification of the student contract into an employment contract, which will entail additional charges and sanctions.
Judicial practice in similar disputes is in favor of taxpayers (Supreme Court ruling No. 310-ES19-8828 in case No. A62-1497/2018 dated June 24, 2019).
For reference! Simplified workers with the “income minus expenses” object will not be able to take into account payments under the student agreement when calculating the single tax. However, the economic benefit from contributions is greater than the overpayment of the simplified tax system.
From March 2. Personal income tax on wages has been abolished for all individuals
Miscellaneous 03/02/2022 | 10
All individuals working in Russia are required to pay personal income tax at a rate of 13% of salary, or 15% if the total gross income during the year was more than 5 million rubles. Paying taxes is the duty of all citizens of the Russian Federation, and it is spelled out in the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the main legislative document of the state. However, starting from March 2, 2022, it was decided to abolish the personal income tax for all individuals employed in certain areas of activity. We are talking about a special decree that came into force from the day of its publication, or, to be more precise, from today. It introduces many benefits that were proposed by the Ministry of Digital Development of the Russian Federation specifically in order to prevent the outflow of specialists from Russia.
In connection with the events of recent days, more and more people living in Russia are thinking about emigrating from the country. The number of search queries on this topic has increased more than fivefold in recent years, and it continues to increase, as evidenced by data from various types of search engines. That is why the Russian authorities quickly developed a set of measures that will keep specialists in the country, preventing them from moving to any other states. All IT companies and their employees working in them can count on a number of benefits and tax breaks that will allow them to earn more, live better, and pay less taxes. In addition, they were protected from excessive control by inspection authorities.
According to the support measures, all IT companies are exempt from paying income taxes and interest from various types of regulatory authorities for three years. Also, all of them can take out preferential loans at a rate of no more than 3% for the development of new projects and services. Employees working in such companies can take out a preferential mortgage at 5% per annum and, while working in the companies, receive a deferment from conscription for military service, which will be valid until they are employed or until the conscription age is exceeded ( 27 years). In addition, the grant program for domestic software developers has been expanded, so now it will become easier and simpler to receive money from the state, because their number will increase.
In addition to all this, Russian companies will receive money from the state to improve the living conditions of employees and increase their wages. But what is much more important in this very decree is that the 13% personal income tax was abolished for all individuals who are officially employed in IT companies in the country. It's been canceled for three whole years, so you won't have to pay it for 36 months. The new decree was signed by the Prime Minister of the Russian Federation, and it has already entered into force. Thus, soon the lives of tens of thousands of people employed in areas related to information technology will change for the better, because they will be able to start earning money and not legally pay taxes on them.
Earlier it was reported that the Russian national Sberbank introduced a personal income tax tax for transfers from card to card.
Join us on Google News , Twitter , Facebook , Instagram , VKontakte , YouTube and RSS to follow the news and quickly receive interesting materials.
AKKet.com Telegram channel
Receive notifications about new materials directly in the messenger - on iOS, Windows, Android and Linux.
Taxes Personal Income TaxRussiaFinance
Compensation payments and financial assistance
With the help of compensation payments, part of your salary can be legally exempted from insurance premiums. For example, this applies to reimbursing employees for interest on their mortgage. Insurance premiums are not paid on these amounts, personal income tax is not charged on amounts not exceeding the limit of 3% of the payroll.
Some compensations are completely exempt from insurance premiums and personal income tax. This includes any of the following payments:
- travel expenses to and from your destination,
- airport service fees, commission fees,
- expenses for travel to the airport or train station at places of departure, destination or transfers,
- baggage costs (related to work trips),
- living expenses,
- expenses for payment of communication services and others.
As for financial assistance, it should be remembered that insurance premiums are not charged for payments to employees in connection with marriages, funerals of close relatives, as well as for treatment of employees and their family members (this is indicated by the resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District No. F05-26116/ 2019 dated February 20, 2020).
Advantages of the method: There are quite a few options for compensation provided to employees under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; if desired, each company will be able to replace part of the employee’s salary with the corresponding payment. At the same time, they will be exempt from personal income tax and insurance premiums in whole or in part.
Disadvantages of this method: Optimization has a temporary effect and cannot be done regularly. For companies with a large staff, the amount of savings may be insignificant in monetary terms. This method of reducing insurance premiums requires additional documentation. Not all compensation payments and financial assistance can be taken into account when calculating the simplified tax system or income tax.
What the law says
Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that such types of income of individuals as state benefits, with the exception of temporary disability benefits (including benefits for caring for a sick child), as well as other payments and compensations, are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation). paid in accordance with current legislation.
At the same time, the article directly stated that benefits that are not subject to taxation include unemployment benefits and maternity benefits. Reference:
This article does not discuss payments of a compensatory nature; the rules regarding the taxation of benefits that are in one way or another related to payments of funds for children were analyzed.
Fiscal authorities specialists have until now believed that the said Article 217 provides an exhaustive list of both taxable and non-taxable benefits.
Let's list them:
Not subject to personal income tax:
- maternity benefits.
The following are not exempt from taxation:
- benefits for caring for a sick child.
Thus, child benefits, which are paid to mothers when the child reaches the age of 1.5 or 3 years, are not indicated in any way in the article of the code. Therefore, according to financiers and tax specialists, a tax of 13 percent should be withheld from monthly child care benefits and monthly child benefits, as not specified in paragraph 1 of Article 217 of the Code (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 4, 2009 No. 03-04-07-01 /190, Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated June 18, 2009 No. ШС-17-3/121).
Officials believed that exemption from taxation of any other types of payments not expressly specified in Article 217 of the Code and, in particular, in its paragraph 1, is possible only by adding to the list of income exempt from taxation. Which is ultimately what we are seeing now. But first, let us remind you what other child benefits exist.
Splitting wages into salary and bonus as a way to reduce taxes
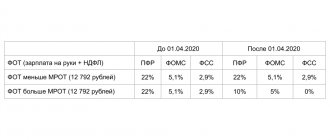
This optimization option appeared last year due to the pandemic and the introduction of preferential insurance premium rates for small and medium-sized enterprises (Article 3 of Federal Law No. 473-FZ of December 29, 2022).
Companies on the simplified tax system, included in the register of small and medium-sized businesses, consider contributions at a preferential rate of 15% from salaries above the federal minimum wage (Article 3 of Federal Law No. 473-FZ of December 29, 2022).
To use this optimization method, you need to divide your salary into a salary equal to the minimum wage and a quarterly bonus. For premiums above the minimum wage, pay contributions at a rate of 15%, not 30%.
In order to reduce claims from controllers, the reduction in staff salaries will have to be justified, and the payment of bonuses will have to be fixed in the bonus regulations, otherwise Federal Tax Service employees will be able to see in the employer’s actions a deliberate evasion of paying taxes.
Advantages of the method: Reduced insurance premium rates for the period of benefits for small and medium-sized enterprises. An additional lever appears that influences staff motivation, because the employer has the right, but not the obligation, to pay a bonus to its employees.
Disadvantages of this method: It is necessary to obtain the employee’s consent to change the terms of the employment contract; not everyone can agree to this. If the company is excluded from the SME register, the savings will stop working.
Attention! During implementation, an additional burden arises on the work of the accounting department. If the feed-in tariff is cancelled, the scheme will also lose its effectiveness.
State child care
The main legal act concerning state benefits for citizens with children is Federal Law No. 81-FZ of May 19, 1995.
Article 3 of this law contains a complete list of types of state benefits for children:
- maternity benefits;
- a one-time benefit for women registered in medical institutions in the early stages of pregnancy;
- lump sum benefit for the birth of a child;
- monthly child care allowance;
- monthly child benefit;
- a one-time benefit when placing a child in a family;
- a one-time allowance to the pregnant wife of a military serviceman undergoing military service;
- monthly allowance for the child of a military serviceman undergoing military service.
Payment of state benefits to citizens with children is made at the expense of budgets at various levels. First of all, from the funds of the Social Insurance Fund of Russia. Therefore, payments such as maternity benefits, monthly child care benefits to persons subject to compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity, made by the employer, will be compensated to him from the funds of the territorial branch of the Social Insurance Fund.
Most of the state benefits for children are paid to women entirely from the funds of the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation. But at the same time, the employer must assign these benefits, and therefore calculate them and give money to his employees. The assignment and payment of temporary disability benefits, maternity benefits, and monthly child care benefits are carried out by the insurer at the place of work (service, other activity) of the insured person (Part 1, Article 13 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ) .
Now let’s compare the list of benefits for children and the list enshrined in Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The code calls only one benefit a non-taxable benefit for children - for pregnancy and childbirth. The law provides for eight types of child benefits.
But as you can see, literal adherence to the norms of tax legislation did not allow employers to treat various child benefits equally, forcing them to charge thirteen percent on such benefits as the monthly child care allowance (when providing a mother with maternity leave until the child reaches the age of one and a half years) and monthly child benefit (in this case, the benefit is paid until the child reaches the age of three).
The monthly child care benefit amounts to at least forty percent of the insured person’s earnings, as stated in Article 11.2 of Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006. While the monthly child benefit is paid on the basis of other regulations. Currently, Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated May 30, 1994 No. 1110 “On the amount of compensation payments to certain categories of citizens” establishes monthly compensation payments in the amount of 50 rubles. for the period of parental leave until the child reaches the age of three years.
Transfer of employees to 0.5 rates
If an employee’s wages are halved, then payroll taxes are reduced in proportion to the reduction in salary.
A transfer to part-time work can be justified by the financial crisis and the deterioration of the financial situation of the enterprise. As a result, there is no need for the employee to be at work full time.
Attention! An employee is allowed to transfer to 0.5 rates based on his written application, after which an additional agreement is drawn up to his employment contract indicating a new work schedule.
An employer will be able to unilaterally introduce a part-time regime only under the following conditions operating simultaneously:
- to prevent mass layoffs of workers (in the manner prescribed by part five of Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- when organizational or technological working conditions change.
Advantages of the method: Obvious savings in personal income tax and insurance premiums by reducing the base for calculating salary taxes. If an employee refuses to be transferred to a new work schedule, it will be possible to dismiss him (under clause 7 of part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Disadvantages of this method: Employees may not like this optimization method, because it will negatively affect their future pensions and other social benefits. Labor disputes cannot be ruled out.
If the transfer to part-time work is fictitious, then this is fraught with fines, penalties and arrears for the employer. Naturally, when labor disputes arise, this fact will “pop up” first.
In this case, some entrepreneurs use a trick: they index wages with a reduction in working hours. That is, they share part of the benefits with employees. For example, if previously an employee received 25,000 rubles for 8 hours of working time, now he officially must work 4 hours and will receive 15,000 rubles. It is clear that the range of responsibilities does not decrease: the employee must complete his work, just in a shorter period of time.
Optimization of taxes by transferring to piecework wages
In some professions, earnings in the form of a salary are initially unprofitable for the employer, especially for blue-collar professions where the result of labor is achieved automatically. The employee receives the same amount regardless of the work performed during his time at work, and not for the result of his activities.
Moreover, piecework payment can be used in settlements with office workers, for example, with sales managers, consultants, lawyers, etc.
To transfer employees to a piece-rate wage system, changes will have to be made to local regulations. If the employee agrees to the new conditions, it is necessary to sign an additional agreement to the employment contract with him.
Advantages of the method: The employee’s income will depend on the amount of work performed, insurance premiums and personal income tax will decrease in proportion to the decrease in wages. If the employee does not agree to the new working conditions, there will be a reason for his dismissal (clause 7 of part 1 of Article 77 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Disadvantages of this method: Optimization does not work in all companies, since it is not always possible to transfer an employee to piecework wages. Implementation may cause severe dissatisfaction on the part of staff.
Attention! If there are no objective reasons for transferring to a new work schedule, then in the event of labor disputes the court will side with the employees.
And after a court decision in favor of the employees, tax inspectors may have questions. Therefore, it is not a fact that saving on the payment of the insurance portion of taxes will be profitable. But where piecework wages can be justified, employers begin to save.
Borrowing money from employees or founders
An alternative to a bank loan can be a loan issued by the founder or employees of the enterprise. Interest income from a loan is subject to personal income tax only, since the payment is not related to employment relationships, and insurance premiums will not have to be charged.
Personal income tax on interest under a loan agreement is calculated at the standard rate of 13% (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-04-09/63244 dated October 28, 2016, No. 03-04-05/25264 dated April 29, 2016).
Advantages of this method: If the founder or employee has free money that he can borrow from the company, then this option for optimizing tax risks does not bear any tax risks. Employees will even have the opportunity to earn additional income if the loan rate is higher than the deposit rate in a commercial bank.
Disadvantages of this method: Not all founders, much less company employees, have money that they could lend to the company, especially in a crisis. Claims from controllers can arise only if the loan agreement is interest-free and for a long period of time, for example, 5 years or more.
How to calculate income tax
The calculation formula is based on several concepts. Tax base and tax rate. The tax base is precisely income in the form of wages, from which funds will be collected into the budget. And the tax rate, as we have already discussed, is determined individually based on the type of payer. The standard rate for an employee is 13 percent.
The formula itself looks like this:
Personal income tax = Tax base * Tax rate / 100
This is the simplest option. But don’t forget that there are also tax deductions, which we talked about just above. For a more clear result, let's look at an example.
Paying the cost of medical examinations directly to the clinic
If the employee pays for medical examinations on his own, then there will be no savings on fees, so enter into an agreement with the medical institution directly. Then you will not have to pay contributions for expenses incurred related to medical examinations.
In addition, you can sign a contract for voluntary health insurance, under which mandatory medical examinations of personnel are carried out at the company’s expense. Savings also arise here, and the amounts spent are taken into account when calculating profits (letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-11-06/2/25906 dated May 5, 2016).
The advantage of this method: Complete legality, no risks. Officials unanimously confirm that contributions in this case are not calculated (letter from the Ministry of Finance No. 03-15-06/45499 dated June 21, 2022, Federal Tax Service No. BS-4-11 / [email protected] dated January 27, 2022).
Disadvantages of this method: Not all organizations require employees to undergo medical examinations; as a result, the amount of tax savings may be minimal or even zero.
Registration of employees as individual entrepreneurs
Also a rather old optimization method. If you cooperate with an individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system with the object “income,” then the company does not pay any taxes for the entrepreneur, and he is obliged to transfer 1-6% of the single tax on services provided to the budget.
Advantages of the method: Complete savings on insurance premiums and personal income tax; individual entrepreneur services can be recognized as part of tax costs, which leads to additional tax optimization. The performer does not receive any social guarantees or payments from the company.
Disadvantages of this method: Now both banks and the Federal Tax Service are paying close attention to transactions between organizations and individual entrepreneurs, especially for single entrepreneurs. In addition, such operations may come to the attention of Rosfinmonitoring, because this method is often used to withdraw “cash” in “gray” tax schemes.
When concluding an agreement with an individual entrepreneur, in most cases, judges side with the controllers and recognize the transactions as fictitious. If Federal Tax Service employees prove that the company covered up labor relations in contracts with individual entrepreneurs, then it faces sanctions and additional charges.
Attention! If an employee quit recently, almost immediately registered as an individual entrepreneur, and you began to cooperate with him, this is a clear sign of tax evasion. Especially if the work is old. The inspectors will quickly prove this, and the court will side with them.