The fact that the Federal Tax Service is working on the concept of a new tax regime for small businesses became known back in the summer. Then the department’s press service announced plans to introduce a regime that would save businesses from keeping records and submitting declarations. It was also said that the new special regime may provide for the abolition of insurance premiums, and the calculation of taxes will be handled directly by the Federal Tax Service.
Bills No. 20281-8 (on conducting an experiment) submitted to the State Duma, as well as Bill No. 20492-8 (on amending the Tax Code), make it possible to understand for what purpose, for whom and under what conditions the new special regime will apply.
The purpose of introducing AUSN
The explanatory note clarifies that the bill was developed as part of the implementation of Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated September 7, 2018 No. 204, as well as clause 5 of the List of Orders of the President of the Russian Federation dated June 26, 2021 No. Pr-1096. The innovations are aimed at improving the conditions for doing business, including simplifying tax reporting for entrepreneurs using cash register equipment (CCT).
It is expected that the adoption of the law will allow ATS payers to reduce non-production costs.
Just like the professional activity tax (NPT), the ATS will initially operate on an experimental basis in several regions:
- in Moscow,
- in the Moscow region;
- in the Kaluga region;
- in the Republic of Tatarstan.
The duration of the experiment is from July 1, 2022 to December 31, 2027.
Both organizations and individual entrepreneurs will be able to apply the AUST, but they must be registered with the tax authorities of the subjects participating in the experiment.
Newly created organizations and individual entrepreneurs must notify of the choice of AUST through the taxpayer’s personal account no later than 30 calendar days from the date of registration with the tax authority.
Already existing businesses will be able to switch to the special regime through the taxpayer’s personal account by notifying the tax authority no later than December 31.
Advantages of the new tax regime of the AUST
Exemption from submitting reports. Those who will apply the AUST will be exempt from filing a tax return, calculating accrued and paid insurance premiums, 4-FSS, SZV-STAZH and SZV-M (but there are exceptions specified in clause 3 of article 2 of bill No. 20492-8 ).
Insurance premium rates are 0%. Contributions for pension, health insurance, as well as contributions in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity will be zero. At the same time, a fixed amount of contributions for injuries has been established in the amount of 2,040 rubles. in year.
Tax calculations are carried out by the Federal Tax Service itself. Information about the taxpayer’s income and expenses is received by the tax office from the cash register and the authorized bank, as well as through the taxpayer’s personal account (if the money is received not through the cash register or through a bank account).
How to choose a tax regime: study the restrictions and calculate the tax burden
Exemption from payment of a number of taxes. In Art. 2 of bill No. 20281-8 states that organizations and individual entrepreneurs on the AUST are not exempt from performing the duties of tax agents. At the same time, they are exempt from paying taxes, but with certain exceptions:
- corporate income tax (with the exception of tax paid on income for which the tax rates provided for in clauses 16, 3 and 4 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are applied);
- tax on property of organizations (with the exception of the tax paid in respect of real estate objects, the tax base for which is determined as their cadastral value);
- Personal income tax (in relation to income received from business activities, with the exception of tax paid on income in the form of dividends, as well as on income taxed at the tax rates provided for in paragraphs 2 and 5 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- property tax for individuals (in relation to property used for business activities, with the exception of objects of taxation with property tax for individuals included in the list in accordance with clause 7 of article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, taking into account the features provided for in paragraph 2 of clause 10 of art. 378.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- VAT (exception - VAT when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation and other territories under its jurisdiction and VAT paid in accordance with Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- corporate income tax (with the exception of tax paid on income for which the tax rates provided for in clauses 16, 3 and 4 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are applied).
What are the features of determining income under Art. 346 15 Tax Code of the Russian Federation?
When simplifying any of the selected taxable objects, it is extremely important to calculate income. Indeed, with such an object of taxation as the income part of the activity, the amount payable to the budget is determined as the total amount of all those listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation of revenues, multiplied by the tax rate. When the object “income minus expenses” is selected, it is also important to correctly calculate income, because their value is involved in calculating the taxable base.
So, income from sales and non-operating income are taken into account - their full list is presented in Art. 248 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
An important question remains what income is not taken into account when determining the tax base.
There are only 3 groups of them - they are presented in clause 1.1 of Art. 346.15 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Particular attention should be paid to those listed in the first subparagraph - their exhaustive list is contained in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Read more about these earnings here.
Let's look at several practical examples that taxpayers using the simplified tax system may encounter when determining the amount of their income for tax purposes. Here are some of the commonly encountered situations:
Example 1
The non-profit educational organization Lastochka LLC provides paid educational services. Over the past year, income from the provision of such services amounted to 7 million rubles. In addition, the organization fulfilled the conditions specified by the grantor - an individual to receive a grant for the development of a training program for children with disabilities and received a grant in the amount of 5 million rubles.
The company is on a simplified “income” tax system. What amount will the tax be taken from?
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the taxable base, all income received by Lastochka LLC should be calculated. At the same time, paragraph 346.15 of the Code clearly states what income is taken into account when calculating tax.
So, income from the provision of educational services in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (this is income from sales, which are listed in subparagraph 1 of clause 1 of Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), should be included in its entirety (7 million rubles) as objects of taxation under simplification.
As for the funds in the amount of 5 million rubles received for the development of a training program for children with disabilities, they cannot but be taken into account as part of the income that should be taken into account when calculating the tax base when calculating the single tax if certain conditions are met (clause 1.1 of Art. 346.15, clause 14 of article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Conditions that allow the received grant not to be taken into account in income and provided for in paragraph 14 of Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the following:
- the grant must be received from persons who have the right to present it (individuals, non-profit organizations, foreign and international organizations and associations listed in the list approved by the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 28, 2008 No. 485);
- The purposes of the grant are the implementation of specific programs in the field of education, art, culture, science, physical culture and sports (except for professional sports), health protection, environmental protection, protection of human and civil rights and freedoms provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, social services low-income and socially vulnerable categories of citizens;
- the grantor has determined the conditions for receiving a grant, the procedure and deadlines for reporting on it;
- The grant recipient must arrange for separate accounting of income and expenses.
If the organization receiving the grant has complied with all of the above conditions, it may not take it into account as part of the income subject to the single tax.
ConsultantPlus experts spoke in detail about the nuances of accounting for income by a simplified tax payer. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Example 2
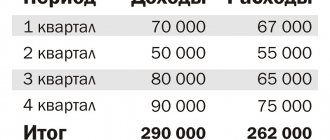
Sudnuda LLC owns 2 cruise ships, the registration of which was carried out in accordance with all the rules (the ships are registered in the International Register of Russia). During the last reporting period, the company's income from passenger transportation amounted to 10,000,000 rubles. The ships carried out cruise tours from St. Petersburg to the port cities of Finland (Hanko, Turku, Helsinki). In addition, the company provided meals for passengers on board and provided catering services. The income from this type of activity amounted to 1,000,000 rubles. during the reporting period. What amount must be taxed on if the company is on the simplified “income” tax system?
In accordance with sub. 1 clause 1.1 art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating the taxable object “income”, the income listed in Art. 251. Passenger transportation services (clause 33 of Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) cannot be classified as an object of taxation. But income received from the provision of services, in accordance with Art. 248 are taken into account when calculating the tax (clause 1 of Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This means that when calculating the simplified tax, only income in the amount of 1,000,000 rubles, which is received from the provision of catering and catering services, should be taken into account.
Example 3
Alpha LLC rents out premises it owns for RUB 50,000. per month. In addition to the rent, the company receives compensation for utility bills from the tenant. What amount should be recognized as income for taxation: only rent or including utilities, find out here .
For more information about calculating the simplified tax with the object of taxation “income”, read the article “The procedure for calculating tax under the simplified tax system “income” in 2019-2020 (6%)”
Conditions for applying AUSN
The new tax regime cannot be combined with other tax regimes.
Additional restrictions also apply:
- By field of activity: in paragraph 5 of Art. 3 of bill No. 20281-8 indicates the types of activities where the use of AUSN is unacceptable.
- Based on annual turnover: no more than 60 million rubles.
- By number of personnel: no more than 5 full-time employees.
- By volume of fixed assets: in the amount of no more than 150 million rubles.
- According to the business structure: there should be no branches or separate divisions.
Objects of taxation
The taxpayer can choose one of two objects of taxation - “income” (tax rate - 8%) and “income reduced by expenses” (tax rate - 20%, minimum tax - 3%). At the same time, he has the right to change the object annually; it is enough to notify the tax authority before December 31.
Recognition of income and expenses is carried out taking into account receipts from cash registers and non-cash payments.
Revenue recognition
The date of receipt of income is:
- date of receipt of funds (including prepayment amounts) to bank accounts or cash desks, receipt of other property (work, services);
- obtaining property rights;
- repayment of debt (payment) in another way.
Recognition of expenses
Expenses are recognized as expenses after their actual payment, including prepayment amounts.
Expenses are taken into account as expenses provided that they are made in non-cash form.
In the case of making a payment in cash to account for expenses, the specified calculation using cash register is recorded as part of the expenses.
Chapter 26_2 USN
Section 346.25. Tax Code of the Russian Federation Features of calculating the tax base when transitioning to a simplified taxation system from other taxation regimes and when transitioning from a simplified taxation system to other taxation regimes 1. Organizations that, before the transition to a simplified taxation system when calculating corporate income tax, used the accrual method, upon transition the following rules apply to the simplified taxation system: 1) on the date of transition to the simplified taxation system, the tax base includes amounts of funds received before the transition to the simplified taxation system in payment for contracts, the execution of which the taxpayer carries out after the transition to the simplified taxation system; 3) funds received after the transition to a simplified taxation system are not included in the tax base if, according to the rules of tax accounting on an accrual basis, these amounts were included in income when calculating the tax base for corporate income tax; 4) expenses incurred by an organization after the transition to a simplified taxation system are recognized as expenses deducted from the tax base on the date of their implementation, if payment for such expenses was made before the transition to a simplified taxation system, or on the date of payment, if payment was made after the transition organizations to a simplified taxation system; 5) funds paid after the transition to a simplified taxation system to pay for the organization’s expenses are not deducted from the tax base if, before the transition to a simplified taxation system, such expenses were taken into account when calculating the tax base for corporate income tax in accordance with Chapter 25 of this Code. 2. Organizations that applied the simplified taxation system, when switching to calculating the tax base for corporate income tax using the accrual method, comply with the following rules: 1) income is recognized as income in the amount of proceeds from the sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) during the period of application of the simplified taxation system, payment (partial payment) of which was not made before the date of transition to calculating the tax base for income tax on the accrual basis; 2) expenses for the acquisition during the period of application of the simplified tax system of goods (work, services, property rights) that were not paid (partially paid) by the taxpayer before the date of transition to calculating the tax base for income tax on the accrual basis are recognized as expenses, if otherwise not provided for by Chapter 25 of this Code. The income and expenses specified in subparagraphs 1 and 2 of this paragraph are recognized as income (expenses) of the month of transition to calculating the tax base for corporate income tax using the accrual method. 2.1. When an organization transitions to a simplified taxation system with the object of taxation in the form of income reduced by the amount of expenses, tax accounting as of the date of such transition reflects the residual value of acquired (constructed, manufactured) fixed assets and acquired (created by the organization itself) intangible assets that are paid before transition to a simplified taxation system, in the form of the difference between the purchase price (construction, manufacturing, creation by the organization itself) and the amount of accrued depreciation in accordance with the requirements of Chapter 25 of this Code. When a taxpayer transfers from an object of taxation in the form of income to an object of taxation in the form of income reduced by the amount of expenses, on the date of such transition the residual value of fixed assets acquired during the period of application of the simplified taxation system with the object of taxation in the form of income is not determined. When transitioning to a simplified taxation system with the object of taxation in the form of income reduced by the amount of expenses, an organization applying the taxation system for agricultural producers (unified agricultural tax) in accordance with Chapter 26.1 of this Code, the tax accounting as of the date of this transition reflects the residual value of the acquired (constructed, manufactured) fixed assets and acquired (created by the organization itself) intangible assets, determined based on their residual value on the date of transition to the payment of the unified agricultural tax, reduced by the amount of expenses determined in the manner prescribed by subparagraph 2 of paragraph 4 of Article 346.5 of this Code , during the period of application of Chapter 26.1 of this Code. When transitioning to a simplified taxation system with the object of taxation in the form of income reduced by the amount of expenses, an organization applying a taxation system in the form of a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities in accordance with Chapter 26.3 of this Code is reflected in tax accounting as of the date of the specified transition the residual value of acquired (constructed, manufactured) fixed assets and acquired (created by the organization itself) intangible assets before the transition to a simplified taxation system in the form of the difference between the price of acquisition (construction, manufacturing, creation by the organization itself) of fixed assets and intangible assets and the amount of depreciation accrued in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on accounting, for the period of application of the taxation system in the form of a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities. 2.2. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs who, before the transition to a simplified taxation system with the object of taxation in the form of income reduced by the amount of expenses, applied a taxation system in the form of a single tax on imputed income for certain types of activities or a patent taxation system, when determining the tax base for the tax, paid in connection with the application of the simplified taxation system, has the right to take into account expenses incurred before the transition to the simplified taxation system to pay the cost of goods acquired for further sale, which are taken into account as the said goods are sold in accordance with subparagraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 346.17 of this Code. Expenses directly related to the sale of these goods, including costs of storage, maintenance and transportation, when applying the simplified taxation system, are taken into account in the reporting (tax) period in which their actual payment was made after the transition to the simplified taxation system. 3. If an organization switches from a simplified taxation system (regardless of the object of taxation) to a general taxation regime and has fixed assets and intangible assets, acquisition costs (construction, manufacturing, creation by the organization itself, completion, additional equipment, reconstruction, modernization and technical re-equipment) of which, carried out during the period of application of the general taxation regime before the transition to the simplified taxation system, were not fully transferred to expenses for the period of application of the simplified taxation system in the manner prescribed by paragraph 3 of Article 346.16 of this Code, on the date of transition to the payment of corporate income tax in tax accounting, the residual value of fixed assets and intangible assets is determined by reducing the residual value of these fixed assets and intangible assets, determined on the date of transition to the simplified taxation system, by the amount of expenses determined for the period of application of the simplified taxation system in the manner provided for in paragraph 3 of Article 346.16 of this Code. 4. Individual entrepreneurs, when transitioning from other taxation regimes to a simplified taxation system and from a simplified taxation system to other taxation regimes, apply the rules provided for in paragraphs 2.1 and 3 of this article. 5. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs that previously applied the general taxation regime, when transitioning to a simplified taxation system, comply with the following rule: amounts of value added tax calculated and paid by the taxpayer of value added tax on amounts of payment, partial payment received before the transition to the simplified system taxation on account of upcoming supplies of goods, performance of work, provision of services or transfer of property rights carried out during the period after the transition to a simplified taxation system are subject to deduction in the last tax period preceding the month of the transition of the value added tax taxpayer to the simplified taxation system, if documents are available , indicating the refund of tax amounts to buyers in connection with the taxpayer’s transition to a simplified taxation system. 6. Organizations and individual entrepreneurs who applied the simplified taxation system, when switching to the general taxation regime, comply with the following rule: the amount of value added tax presented to the taxpayer applying the simplified taxation system when he purchased goods (works, services, property rights) that were not classified as expenses deducted from the tax base when applying the simplified taxation system, are accepted for deduction upon transition to the general taxation regime in the manner prescribed by Chapter 21 of this Code for taxpayers of value added tax
The role of the bank and the tax office
Individual entrepreneurs and organizations using the AUST are required to authorize the credit organization that carries out information exchange with tax authorities to transfer information about transactions on accounts opened under a bank account agreement. This can be done through the taxpayer’s personal account or through a credit institution.
The list of authorized credit organizations is approved by the federal executive body, which is responsible for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees. Such a list will be published on its official website.
It is assumed that wages of employees will be paid through an authorized credit institution. She is entrusted with the responsibility for calculating and withholding personal income tax.
The inspectorate will notify you of tax payment through the taxpayer’s personal account no later than the 15th day of the month following the tax period. The data for calculating tax must be provided to her by the bank (for non-cash payments) and the AUST payer (for payments via cash register). The deadline for providing data is until the 5th day of the month following the reporting month.
How will payers of AUSN be checked?
On-site inspections are not provided in principle. A desk tax audit is carried out within three months. And it has features:
- carried out for 12 tax periods of the expired calendar year or for tax periods falling within the period from the beginning of application in the expired calendar year by a newly created organization, a newly registered individual entrepreneur of the special regime and until the end of the expired calendar year - from February 1 of the next calendar year;
- when changing the tax regime, the audit is carried out for the expired tax periods of the current year from the day following the end of the tax period in which the taxpayer lost the right to apply the special regime;
- in case of reorganization, liquidation of an organization, termination of activities as an individual entrepreneur, the audit is carried out for the expired tax periods of the current year from the day following the day the tax authority receives the corresponding application. The taxpayer is not subject to liquidation or deregistration as an individual entrepreneur before the end of the desk audit.
How to switch to "simplified"
Entrepreneurs, already during the procedure for registering an enterprise, are required to decide on the taxation regime under which they plan to operate. You can submit a notification for the Simplified Taxation System either together with the rest of the package for state registration, or submit it later - within 30 days after submitting the main documents to the tax office.
If this does not happen, then the enterprise is automatically included in the general taxation system.
Sometimes it happens that in the process of work, businessmen understand that the simplified tax system is preferable to the operating tax system, and the question arises: is it possible to change the tax payment regime and how to do this? Yes, you can switch to the “simplified” system at any time during the operation of the enterprise. Due to its simplicity, this procedure should not cause any difficulties. To do this, the management of the enterprise must submit a notification to the tax authorities about the transition to the simplified tax system by the beginning of the next calendar year, but this must be done no later than December 31 of the current year. A standard sample notification can be easily found on the website of the Federal Tax Service.
Also read the full version of the material “how to switch to the simplified tax system.”