What is the tax regime
Businesses pay taxes according to certain rules and formulas. Simply put, the tax regime (or taxation system) is the set of formulas by which taxes will have to be calculated and transferred to the budget. There are several such systems in Russia, they differ in the number of taxes and their size, and in the number of reports that will have to be submitted. Each system has its own tolerances and criteria: if a business fits these tolerances, it has the right to use the system; if it “doesn’t fit in,” then it doesn’t.
- OSNO - general taxation system - the basic system on which all new companies and individual entrepreneurs find themselves “by default”, unless they choose a different regime and write a notification about it to the tax office. Therefore, OSNO is called the main system, or “classic”, and the remaining tax regimes are called special, or special regimes.
- The simplified tax system is a simplified taxation system, simplified.
- PSN - patent taxation system, patent.
- Unified agricultural tax - unified agricultural tax - for farmers and peasant farms.
- NPI - professional income tax - for the self-employed.
Single tax under the simplified tax system: what replaces it, what exceptions there are
For organizations, a simplified tax replaces the payment of taxes such as (clause 2 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Income tax. An exception is income tax paid:
- taxpayers - controlling persons for income in the form of profit of foreign companies controlled by them (clause 1.6 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- on income in the form of dividends (clause 3 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- on transactions with certain types of debt obligations (clause 4 of article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Details are in the article Income tax under the simplified tax system (nuances) .
- Organizational property tax. The exception here is the real estate tax, the tax base for which is determined by the cadastral value, which simplifiers pay on an equal basis with everyone else
Read the article “List of property taxed at cadastral value.”
- VAT. This tax is only payable:
- when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation (Article 151 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for operations in accordance with a simple partnership agreement (joint activity agreement), investment partnership, trust management of property or in connection with a concession agreement (Article 174.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
See the publication of VAT under the simplified tax system: in what cases to pay and how to take into account the tax .
If a single tax under a simplified taxation system is paid by an individual entrepreneur, then he is exempt from the following taxes (clause 3 of Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Personal income tax - in relation to income received from business activities. Exception - personal income tax:
- from dividends,
- income taxed at tax rates of 35% (clause 2 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and 9% (clause 5 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Property tax for individuals - in relation to property used for business activities. As for organizations, an exception is made here for the tax on “cadastral” objects included in the corresponding list.
- VAT - the restrictions here are the same as for organizations.
What influences the choice of tax regime
What parameters show whether you can apply a particular tax system or not? We list it.
- Annual revenue volume. Let's say, for the simplified tax system it is 200,000 million rubles, for PSN - 60 million rubles, for NPD - 2.4 million rubles, and for OSNO there are no restrictions.
- Number of employees. On a simplified basis you can work with a staff of up to 130 people, on a patent - up to 15 people, on NPD you cannot hire staff at all, and on OSNO there are again no restrictions.
- Organizational and legal form - individual entrepreneur, LLC, etc. For example, individual entrepreneurs can work on PSN and NPD, but LLC cannot.
- Activities. You can work with OSNO for any type of activity, but each special mode has a list of types for which it can be used. This is spelled out in the Tax Code and regional laws; we will talk about this in more detail when we talk about each special regime.
There are other tolerances for special regimes: the cost of fixed assets, the presence of branches, etc. We will also talk about this later.
Which companies are classified as microenterprises?
Micro-enterprises include: LLCs, individual entrepreneurs, peasant farms, cooperatives that employ less than 15 people. There are other mandatory criteria:
- income for the previous period amounted to no more than 120 million rubles (excluding VAT);
- at least 51% of the capital belongs to individuals or other SMEs (small businesses);
- companies not related to SMP own no more than 49% of shares;
- the share owned by the state, NPOs or constituent entities of the Russian Federation cannot exceed 25% in total.
Small businesses are provided with benefits and various government support measures. Therefore, some businessmen deliberately try to assign a similar status to their organization. Thus, in the field of taxation and accounting, micro-enterprises are allowed the following:
- submit simplified reporting, consisting of only two mandatory forms: a balance sheet and a statement of financial results;
- do not create a reserve for vacation pay;
- correct errors in reports even after submitting the document to the Federal Tax Service;
- do not draw up internal labor regulations;
- do not approve the shift schedule.
The head of the organization can conduct simplified accounting. To do this, it is enough for him to issue an appropriate order.
How to choose a tax regime
Step 1. “Filter” all possible regimes by organizational and legal form. For example, you have an LLC: OSNO and USN are suitable. If you have an individual entrepreneur, any of the modes will do.
Step 2. We look at annual revenue. If according to the business plan you have to earn 45 million rubles, then the NPD will no longer be suitable, but the patent, simplified version and OSNO will do.
Step 3. We count the employees on staff. For example, you have 60 employees: the patent and NPD are no longer required, what remains is simplification and OSNO.
Step 4. We cut off tax regimes by type of activity: check the tolerances for your type. Let's say that insurers do not work on the simplified tax system.
Step 5. We check the remaining criteria: for example, a company with branches or participation of another company in the authorized capital of more than 25% cannot apply the simplified tax system.
Step 6. If you still have a choice before this step, calculate your tax burden. To do this, look at what taxes are paid in each applicable tax regime and calculate the amounts based on your planned or current income. Then compare them and choose the most favorable tax regime.
The choice of taxation system can be made automatically - using a free calculator from Kontur.Accounting. The calculator will help you cut out unsuitable regimes, tell you how to fill out the fields for calculation, and show the tax burden for each system. All you have to do is choose the profitable mode.
USN: taxes and reports, for whom it suits
Simplified is one of the most understandable and profitable special regimes for small businesses; the rules for working and switching to the simplified tax system are in Chapter. 26.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Under the simplified system, they pay one tax (however, if a company has transport and land, then transport and land taxes are paid separately). Every quarter, so-called “tax advances” are transferred, and at the end of the year, the remaining tax is calculated and paid. But there is only one tax return - it is submitted once a year: organizations until March 31, individual entrepreneurs - until April 30.
Another advantage of the system is that the authorities of your region can reduce the tax rate under the simplified tax system for some types of business, then the savings will be even more noticeable.
There is no need to work with VAT on the simplified tax system. Therefore, it is not profitable for other companies that pay VAT to buy goods and services from companies or individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system. So the “Osnoshniks” try not to work with the “Simplers”.
Tolerances and restrictions when working on the simplified tax system:
- annual income - no more than 200 million rubles;
- number of employees - no more than 130;
- cost of fixed assets - no more than 150 million rubles;
- the authorized capital of the company should contain no more than 25% of the contribution of another organization;
- the company should not have branches;
- Manufacturers of excisable goods cannot work on a simplified basis, extract minerals, work with securities, or give loans: in Art. 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation lists everyone who is not allowed to work for the simplified tax system.
The rules for calculating simplified taxes depend on the object of taxation. This is the amount on which tax is paid. There are two options on the simplified tax system:
- income;
- income minus expenses.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
What reporting needs to be submitted and what taxes do LLCs pay using the simplified tax system?
Taxes
Taxes are money that the government charges you. Not to be confused with reporting.
To understand the tax payment system, you need to distinguish between payment periods:
• the reporting period is 3 months, that is, a quarter
• tax period - calendar year
Under the simplified taxation system, you need to pay advance payments at the end of each reporting period, that is, quarterly, 3 times a year, and the annual tax is paid for the fourth quarter - at the end of the tax period. In essence, the annual tax is simply the 4th advance payment. There is no need to submit reports on payment calculations in simplified form.
Quarterly advance payments are made by new organizations and those companies whose monthly revenue does not exceed 1 million rubles, and per quarter - 3 million rubles. If sales revenue exceeds these limits, then the company is obliged to switch to monthly advance payments.
Taxes are calculated on an accrual basis:
- Income or profit are summed up for the entire past period (for six months, 9 months and a year) - this is the tax base ,
- The tax amount is calculated from the result,
- Taxes paid in previous reporting periods are deducted from this amount.
- What's left needs to be paid.
The amount of the advance payment and annual tax is calculated using a single formula:
Single tax = (Tax base * tax rate%) - previously paid advance payments
If, based on the results of the period, the company breaks even, you need to pay a minimum tax - 1% of income.
Which type of “simplified” is more profitable depends on how the company operates. The example below reflects situations in which different types of simplified taxation system are beneficial.
| simplified tax system 6% (income) | simplified tax system 15% (profit) | |
| Calculation of advance payment for 1 quarter (3 months) | Company income = 50,000 rubles Expense = 10,000 rubles Company profit = 40,000 rubles Tax = 50,000 * 6% = 3,000 rubles Net profit for 3 months = 37,000 rubles | Income = 50,000 rubles Expense = 10,000 rubles Company profit = 40,000 rubles Tax = 40,000 * 15% = 6,000 rubles Net profit for 3 months = 34,000 rubles |
| Calculation of advance payment for the 2nd quarter (6 months) | Company income for 6 months = 100,000 rubles (we earned the first 50,000 in the 1st quarter, the same amount in the second) Total company expenses for 2 quarters = 50,000 rubles (10,000 – 1st quarter, 40,000 – 2nd quarter) Profit = 50,000 rubles Cumulative tax = 100,000 * 6% = 6,000 rubles Tax payable (less previously paid) = 6000 – 3000 = 3000 rubles Net profit for 6 months = profit - tax = 47,000 rubles. | Company income for 6 months = 100,000 rubles (we earned the first 50,000 in the 1st quarter, the same amount in the second) Total company expenses for 2 quarters = 50,000 rubles (10,000 – 1st quarter, 40,000 – 2nd quarter) Profit = 50,000 rubles Cumulative tax = 50,000 * 15% = 7,500 rubles Tax payable (less previously paid) = 7500 – 6000 = 1500 rubles Net profit for 6 months = 48,500 rubles |
| Calculation of advance payment for the 3rd quarter (9 months) | Company income for 9 months = 300,000 (50,000 – 1st quarter, 50,000 – 2nd quarter, 200,000 – 3rd quarter) Total company expenses for 3 quarters = 300,000 rubles (10,000 – 1st quarter, 40,000 – 2nd quarter, 250,000 – 3rd quarter). Profit = 0 rubles Cumulative tax = 300,000 *6% = 18,000 rubles Tax payable = 18,000 – 3000 – 3000 = 12,000 rubles Net profit = - 12,000 rubles | Company income for 9 months = 300,000 (50,000 – 1st quarter, 50,000 – 2nd quarter, 200,000 – 3rd quarter) Total company expenses for 3 quarters = 300,000 rubles (10,000 – 1st quarter, 40,000 – 2nd quarter, 250,000 – 3rd quarter). Profit = 0 rubles Cumulative tax = 0 * 15% = 0 rubles Tax payable (minimum tax, 1% of income) = 300,000 * 1% = 3,000 rubles Net profit = - 3000 rubles |
| Annual tax | The company’s total income for the year amounted to 400,000 rubles: 1 sq. — 50,000, 2 sq. — 50,000, 3 sq. — 200,000, 4 sq. — 100,000 rub. Total expenses for the year amounted to 350,000 rubles: 1 sq. — 10,000, 2 sq. — 40,000, 3 sq. — 250,000, 4 sq. - 50,000. Annual profit of the company: 50,000 rubles Cumulative annual tax = 400,000 * 6% = 24,000 rubles Annual tax payable = 24,000 – 12,000 – 3000 – 3000 = 6000 rubles Net annual profit: 50,000 – 6000 = 44,000 rubles. | The company’s total income for the year amounted to 400,000 rubles: 1 sq. — 50,000, 2 sq. — 50,000, 3 sq. — 200,000, 4 sq. — 100,000 rub. Total expenses for the year amounted to 350,000 rubles: 1 sq. — 10,000, 2 sq. — 40,000, 3 sq. — 250,000, 4 sq. - 50,000. Annual profit of the company: 50,000 rubles Cumulative annual tax = 50,000 * 15% = 7,500 rubles Annual tax payable = 7500 – 3000 – 1500 – 6000 = - 3000 rubles - overpayment. The overpayment can be applied to the next quarter or returned. Net annual profit: 50,000 – 0 = 50,000 rubles. |
If no activity was carried out, then there is no need to pay taxes. But you will have to submit reports in any case.
USN “Income”
The tax rate is from 1 to 6% depending on the region and type of activity. This option is usually beneficial if your expenses are difficult to verify or your expenses are less than 60% of your income. If the company's annual income is from 150 to 200 million rubles or the number of employees is from 100 to 130 people, the rate rises to 8%.
Insurance premiums paid can be deducted from the tax amount: these are individual entrepreneurs’ contributions “for themselves” and contributions for employees. Here we talk in more detail about reducing the tax on the amount of contributions.
You can keep records and submit reports to the simplified tax system “Income” yourself to save on an accountant. It is better to do this not in Excel tables, but in a special program or service. For example, the Kontur.Accounting service will calculate taxes, fill out a book of income and expenses and a tax return, and warn about the timing of payments and reporting. For employees - calculates and prepares salaries, contributions, personal income tax, reports.
USN “Income minus expenses”
The tax rate is from 5 to 15% depending on the region and type of activity. It will be beneficial if your expenses are easily supported by documents and they account for more than 60% of your income. If the company's annual income is from 150 to 200 million rubles or the number of employees is from 100 to 130 people, the rate rises to 20%.
Paid insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs and employees can be included in expenses. But not all expenses reduce the tax base on which taxes are paid. To recognize an expense there are requirements:
- the expense is justified and made for the purpose of generating income;
- consumption is mentioned in the list from Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- you received from the supplier what you paid for and paid in full;
- there are documents that confirm the expense;
- if expenses are related to goods for resale, then they can be written off only after the sale of these goods.
In order not to get confused when taking into account the costs of the simplified tax system, it is better to keep records in a special service or involve an accountant. Let's say, the web service Kontur.Accounting takes into account expenses according to all the rules, calculates payments, fills out KUDiR and declaration, generates payments, reminds about the dates of payments and reports. The service has a salary block for working with employees. And with the help of management reports, the manager will be able to control finances.
Taxes on tax regimes
Insurance premiums and personal income tax
In all regimes, it is necessary to pay insurance contributions to the pension fund (PFR), social insurance fund (FSS) and compulsory health insurance fund (MHIF).
And also transfer personal income tax for employees. The base rates are as follows:
- 22% of the wage fund (payroll = take-home salary + personal income tax) in the Pension Fund.
- 5.1% of the payroll in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- 2.9% of the payroll in the Social Insurance Fund.
- 0.2-8.5% of the payroll in the Social Insurance Fund for injuries. The injury rate depends on the type of activity. For example, for an IT company the rate is 0.2%, and for coal miners - 8.5%. The rate for injuries depends on the OKVED (type of activity) of the organization or individual entrepreneur.
- 13% personal income tax on the payroll amount.
From April 1, 2022 (clause 9 of Article 2 No. 102-FZ dated April 1, 2020), reduced insurance premium rates were introduced for the small and medium-sized enterprise sector for amounts above the minimum wage (12,792 rubles as of January 1, 2022).
Rates for small and medium-sized businesses for amounts above 12,792 are as follows:
- 10% of the wage fund (payroll = take-home salary + personal income tax) to the Pension Fund.
- 5% of the salary in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- 0% of the salary in the Social Insurance Fund.
- The injury rates remain.
For example, an employee wants to receive 100,000 rubles a month. In this case:
- 100,000 / 0.87 = 114,942 rubles, where 14,942 rubles is personal income tax.
- 12,792 × 30.2%2) × 15.2% = 3,863 + 15,527 = 19,390 rubles of insurance premiums
- 100,000 + 14,942 + 19,390 = 134,332 rubles, with 100,000 rubles per employee you will have to pay 34,332 rubles in taxes.
For some companies, premium rates may be reduced even further. For example, for IT companies, if the IT company receives accreditation and benefits from the Ministry of Digital Development (clause 5 of Article 1 No. 265-FZ of July 31, 2020).
In this case, the company will have the following insurance premium rates:
- 6% of the wage fund (payroll = take-home salary + personal income tax) in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
- 0.1% of the salary in the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- 1.5% of the salary in the Social Insurance Fund.
In this case, the company will save ~10,000 rubles per month from the developer’s take-home salary of 100,000 rubles/month.
Individual entrepreneurs also pay contributions to funds for themselves at the following rates (Article 430 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- In the Pension Fund of Russia - 32,448 rubles per year (if income does not exceed 300 thousand rubles per year, otherwise, plus 1% of the difference between the income received and 300 thousand rubles).
- In the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 8,426 rubles per year.
If you are an individual entrepreneur, then you will have to pay insurance premiums of ~40,000 per year in any case, even if you have 0 rubles in revenue.
Transport, land and property tax
These taxes arise when an LLC or individual entrepreneur owns transport, land or property (LLCs and individual entrepreneurs on the Unified Agricultural Tax are exempt from property tax).
The amount of transport tax depends on the engine power (Article 361 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), the number of horsepower and the period of ownership of the transport. The more horsepower, the higher the tax. You can calculate the tax on the tax website. Regions can set their own tax rates. The highest tariffs are in Moscow.
Land tax depends on the cadastral value of the land, the tax rate, the size of the share of the plot and the period of ownership. The higher the cadastral value of the plot, the higher the tax.
Property tax depends on the cadastral value of the property, the tax rate and the amount of the deduction. The higher the value of the property, the higher the tax amount.
Land, transport and property taxes must be paid every quarter.
From 2022, companies and individual entrepreneurs do not need to submit declarations on transport and land (No. 63-FZ of April 15, 2022). The tax will be calculated by the tax office. However, you will still need to check the tax authorities’ calculations.
A property declaration is also required to be prepared once a year.
General taxation system (GTS)
OSN is the most labor-intensive regime in terms of accounting and the size of the tax burden due to VAT and high income tax. Also, companies on the simplified tax system attract much more attention from the tax authorities compared to companies on the simplified tax system.
Therefore, accounting within the framework of the general system is the most expensive and cannot be done without the help of an accountant. If you are just starting out and have almost zero turnover, then outsourced accounting will cost 15-25,000 rubles/month, depending on the region.
In this system, the following taxes must be calculated and paid:
- Income tax (for individual entrepreneurs personal income tax)
- VAT
A special feature of OSN is that accounting is carried out using the accrual method. That is, income and expenses are taken into account on the date of the transaction, regardless of when the money arrived in the current account. The disadvantage of this method is the risk of cash gaps.
For example, a company issued a deed (invoice or other closing document) for 120 thousand rubles in January (including 20 thousand rubles VAT), and the customer paid for the purchase only in March. Under the accrual method, the transaction is considered to have occurred in January. Therefore, the tax in the amount of 20 thousand rubles will need to be paid in January, and not in March, when the money actually arrived. As a result, there is a cash gap - the money has not yet arrived, but the tax needs to be paid.
Below we will look at income tax and VAT.
Income tax
The tax is calculated using the following logic:
- Tax payable = ([Organization's income] - [Organization's expenses]) × 20%
The more expenses, the less the tax.
For OSN, the list of income and expenses is open (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 253 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and there is no clear list of what is included in expenses and what is not included. The main thing is that the expenses are:
- Confirmed by documents.
- Economically justified.
- Produced for the purpose of making a profit for the organization.
Therefore, both accounting and tax authorities have flexibility in determining income and expenses.
If you receive a loss, you do not need to pay tax. The loss can be carried forward to the next tax period and reduce the tax amount next year.
Some companies have the right to take advantage of reduced rates (Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For example, regions can reduce the income tax rate to 15.5%.
Also, IT companies that have received accreditation from the Ministry of Digital Development will pay only 3% of profits from 2021. Participants of the Skolkovo project are completely exempt from paying tax (Article 246.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Individual entrepreneurs on OSN pay personal income tax in the amount of 13% instead of income tax.
The tax must be transferred to the budget once a quarter (Article 286 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), however, if the organization received revenue of more than 15 million rubles in a quarter, then the tax will need to be transferred monthly.
Tax reporting is submitted every quarter.
You can read more about income tax in our article.
Value added tax (VAT)
The tax is calculated using the following logic:
- VAT payable = [Output VAT] - [Input VAT]
The higher the input VAT, the lower the tax.
The amount of VAT depends on the VAT rate and the amount of sale or purchase. The standard VAT rate is 20% (Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, you bought design services from a company on OSN:
- Total cost = 100,000 × 20% + 100,000 = 120,000 rubles, where 100,000 is company services, and 20,000 rubles is VAT.
If you sell a product, then you also increase the cost of the product by 20% for the end consumer. For example, you are engaged in the wholesale trade of rolled metal:
Cost of rolled metal = 200,000 × 20% + 200,000 = 240,000 rubles, where 200,000 rubles is the cost of rolled metal, and 40,000 rubles is VAT.
The amount of VAT payable will be calculated in the following way:
- VAT amount = [Output VAT] - [Input VAT] = 40,000 - 20,000 = 20,000 rubles to be paid to the budget.
VAT is passed on to the end consumer - it is an indirect tax. Those. In essence, this is not a tax on the company, but on your customers.
Also, some transactions may not be subject to VAT (Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or not be recognized as an object of taxation. For example, if you export goods, then the VAT rate is 0% (clause 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and if you export services, then they are not recognized as an object of VAT taxation (clause 1 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the amount of input VAT turns out to be greater than the amount of output VAT, then you can make compensation from the budget for this difference.
For example:
- Output VAT = 100 rubles
- Input VAT = 200 rubles
Amount of VAT payable = 100 - 200 = - 100 rubles
You can apply for compensation and receive 100 rubles from the budget.
Therefore, if you are engaged in exporting, then OSN can be very beneficial for you. Because your output VAT will be zero, and input VAT can be obtained if you buy goods and services from contractors on the OSN. In this case, the state may pay you extra.
The tax is paid monthly, in the amount of 1/3 of the tax amount for the quarter. Reporting is submitted every quarter.
You can read more about VAT in our article.
When to apply OSN and how to reduce tax
OSN is beneficial in the following cases:
- If the company operates for export, since in this case the VAT rate will be 0% if these are goods and not subject to VAT if these are services. You will be able to reimburse VAT from the budget and receive money from the state.
- If most of your clients need VAT. In this case, you will be able to deduct input VAT and reduce the amount of VAT payable.
To reduce taxes on OSN, you need to do the following:
- Work with companies on OSN to receive input VAT and reduce the total VAT payable.
- Find out about the possibility of reducing income tax or exemption from VAT.
- Reduce the time difference between the sale (preparation of the document) and the actual receipt of funds into the current account in order to avoid cash gaps.
- Complete documents correctly and on time. If you receive a document from a counterparty, then immediately check it for the presence of all signatures, seals and the correctness of the details, and also sign and stamp it on your part. The tax office may request this document in the future, and if you cannot provide the correct tax document, it will deduct expenses from the tax base and your tax will increase. This may also result in fines and penalties.
Simplified taxation system
Accounting is simpler, and the tax burden on the simplified tax system is lower than on the special tax system. Because the company will not pay income tax and VAT. The company will only pay the simplified tax system. Therefore, companies that use the simplified tax system receive less attention from tax authorities. Because There are much fewer opportunities for additional charges compared to companies on the OSN.
Income and expenses on the simplified tax system are accounted for using the cash method - income and expenses are recognized on the date of receipt or debit from the current account. For example, a company issued a deed or invoice in the first quarter for 500 thousand rubles, and the funds were received in the second quarter. This means that the tax base will increase by 500 thousand rubles in the second quarter.
Unlike the OSN, the situation of state lending does not happen. Those. taxes are paid on actual income and expenses received into the current account. However, documents to confirm expenses are also needed, as for OSN.
If your company is on the simplified tax system, and your buyer asks to charge VAT so that your client can accept it for deduction, then you can also make sales with VAT (clause 1, clause 5, article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, you will need to prepare and submit a VAT return, as well as transfer the VAT amount to the budget. In this case, you will not be able to deduct input VAT.
However, for your client such a maneuver will be illogical, because... As a result, the costs will be similar both without VAT and with VAT. You will add the amount of VAT on top of your service:
- Without VAT, your client’s expenses = 100 rubles.
- With VAT, your client’s expenses = 120 rubles, where 20 rubles are VAT, which can be deducted (reduce taxes by 20 rubles).
Comparison of sales with VAT on the simplified tax system, with VAT on the simplified tax system and without VAT on the simplified tax system.
A company can choose 2 types of simplified tax system: income (6%) or income minus expenses (15%). They differ in the complexity of accounting and the way taxes are calculated.
Also in 2022, the limits on the number of employees and turnover of companies that can apply the simplified tax system were increased (Federal Law dated July 31, 2020 No. 266-FZ):
STS limits before 2022 and after 2022.
Perhaps in the future the limits will also increase.
Tax according to the simplified tax system is paid every quarter, and reports are submitted once a year.
We will look at the simplified tax system for income and income minus expenses in more detail below.
simplified taxation system income (6%)
The tax is calculated using the following logic:
- Tax simplified tax system 6% payable = [Company income] × 6% - [Amount of insurance premiums paid to the budget]
In essence it is a turnover tax. In this case, the tax can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums. If you have an individual entrepreneur and no employees, then you can reduce the simplified tax system by the full amount of insurance premiums ~40,000 rubles. If you have employees, then you can reduce the amount of the simplified tax system by no more than 50% with the help of insurance contributions (clause 3.1 of article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, the simplified tax system is 6% payable if you have employees:
- Income for the year = 10 million rubles.
- Amount of insurance premiums for the year = 1 million rubles.
- STS tax 6% per year = 10,000,000 × 6% - 300,000 = 300,000 rubles.
- Out of 1 million rubles of insurance premiums, only 300,000 rubles can be deducted, because the total amount of the simplified tax system is 600,000 rubles.
- You will pay a minimum of 3% of turnover.
The simplified tax system is 6% payable if you are an individual entrepreneur and have no employees:
- Income = 1.5 million rubles
- STS tax 6% = 1,500,000 × 6% - 40,874 - (1,500,000 - 300,000) × 1% = 37,126 tax rubles.
- In this case, all insurance premiums reduce the amount of the simplified tax system (USN) by 6%.
- Tax burden of the simplified tax system in this case = 37,126 / 1,500,000 = 2.5%
The tax authorities pay minimal attention to this taxation system, because the tax amount does not depend on expenses.
Also, regions can establish reduced simplified tax rates (up to 1%) for companies from certain areas of activity. For example, IT companies in Ulyanovsk can apply a 1% rate if the company has received accreditation from the Ministry of Digital Development.
You can do accounting for individual entrepreneurs in this mode yourself using the online accounting departments of banks. It is free from most banks.
Accounting for an LLC will have to be done with the participation of an accountant, because... in this case, it is necessary to submit a balance sheet.
However, if you are going to do the accounting yourself, then consult with an accountant on what to define as income. Because not all income that you actually receive into your current account will be income for the tax authorities. You may overpay your taxes.
If you want to outsource your accounting, it will cost 2000-5000 rubles per month for an individual entrepreneur and 5000-15000 rubles per month for an LLC.
simplified tax system income minus expenses (15%)
The tax is calculated as follows:
- Amount of tax simplified tax system 15% = ([Income of the organization] - [Expenses of the organization]) × 15%
For example:
- Income = 20 million rubles
- Expenses = 15 million rubles
- Tax amount 15% = (200,000) × 15% = 750,000 rubles
In this case, the logic for calculating tax is similar to calculating income tax. However, the simplified tax system contains an exact list of expenses that, in the opinion of the tax authorities, are considered expenses (Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, not all income and expenses that appear on a bank statement are income and expenses for the tax authorities.
Therefore, you should carefully study the transactions and, if necessary, prepare the documents correctly so that they are included in the list of expenses. Because of the expense side, the tax office will pay more attention to the company, so you can’t do without an accountant.
You will also need to ensure that the primary documentation is completed correctly so that the tax office does not charge additional taxes, fines and penalties if the documents are requested.
If you receive a loss, then you will need to pay 1% of the turnover in any case (clause 6 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). You will not be able to carry forward the loss to the next reporting period, like a company on OSN.
Typically, companies try to keep their expenses as close to 1% as possible in order to pay minimal taxes.
Regions can also set a reduced rate for the simplified tax system for income minus expenses of up to 5%. For example, in the Moscow region, a rate of 10% is established for the simplified tax system for income minus expenses if a company or individual entrepreneur produces furniture. For a complete list, follow the link on the tax website.
To maintain company records using the simplified tax system of 15%, you cannot do without an accountant. If you are just opening, outsourced accounting will cost 10-20,000 rubles per month, depending on the region.
Which simplified tax system to choose and how to pay less taxes
If the share of your expenses is more than 60% of revenue, then it is more profitable to choose the simplified tax system of 15%. If the share of expenses is less than 60% of revenue, then the simplified tax system of 6% is more profitable.
This is calculated from the equation:
- A × 6% < (A - Q × A) × 15%, where A is revenue, Q is the share of expenses from revenue.
- Q < 60%, with the share of expenses from revenue being 60% or less, the amount of tax for the simplified tax system is 15% greater than the amount of tax for the simplified tax system of 6%.
For example, two companies are engaged in the installation and maintenance of security systems. The first company carries out installation, its annual revenue is 10 million rubles, expenses (labor, fuel, equipment, materials, etc.) are 7 million rubles. The second company provides security system maintenance. Its revenue is 9 million rubles, expenses (labor, fuel, consumables) are 2 million rubles. Let's calculate taxes.
Comparison of the tax burden on the simplified tax system of 15% and the simplified tax system of 6%.
If you do not work for export and your clients do not need VAT, then choose the simplified tax system. At the end of the article, you can download our tax model in Excel, enter your values and calculate the tax amount.
How to pay less taxes:
- Check the availability of benefits under the simplified tax system in your region, or check the availability of benefits for your type of activity in another region. For example, an IT company from Moscow can register in Ulyanovsk and pay 1% of the simplified tax system for income.
- Download our calculator, indicate your income and expenses and calculate the amount of tax on the simplified tax system on income and income minus expenses. Choose a profitable simplified tax system.
- If you are on the simplified tax system for income minus expenses, then follow the wording in contracts and documents so that you can legally accept expenses and reduce taxes.
- Make sure the primary format is correct. If the document is executed incorrectly and the tax office requests this document, the tax office will charge additional taxes, fines and penalties.
- If you have income on the simplified tax system, then reduce the amount of tax using insurance contributions and do not forget to check with the accountant that he has taken everything into account.
Unified Agricultural Tax (USAT)
Unified agricultural tax can only be used by companies operating in the agricultural sector. The share of revenue from the production or sale of agricultural products must account for at least 70% (Article 346.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Under this regime, companies and individual entrepreneurs must pay a single agricultural tax in the amount of 6% of profits. In some regions, preferential rates of 0% are established.
Accounting for income and expenses is carried out using the cash method. It is important that this regime also has an exact list of expenses (Article 346.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), as well as the simplified tax system.
This regime does not exempt from VAT. The legislation provides for the right to exemption from VAT in the following cases (Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- If an LLC or individual entrepreneur sent an application to the tax authority for exemption in the same year from which they switched to the Unified Agricultural Tax regime.
- If income from activities covered by the Unified Agricultural Tax for the previous year was below the established limits (for 2022 - less than 70 million rubles).
In the Unified Agricultural Tax regime, the following reports must be submitted:
- annual tax return according to the Unified Agricultural Tax.
- quarterly VAT return.
Tax under the Unified Agricultural Tax is paid every six months, VAT every quarter.
Patent
The patent taxation system can only be applied by individual entrepreneurs, only in relation to certain types of activities. Their list is indicated in paragraph 2 of Art. 346.43 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Essentially, you are buying permission to operate. The cost of a patent does not depend on the actual income and expenses of your individual entrepreneur. For example, a patent for the provision of hairdressing and cosmetic services (beauty salon) in Moscow for 2022 costs 59,400 rubles for 12 months (for 1 month - 4950 rubles). This amount does not change, even if you have 30 million in revenue for the year or 5 million in revenue.
You give the state ~60,000 one-time and continue to work without worrying about income and expenses. It is better to issue a patent from the 1st day of the month to the last day of the month, so that there are no overlaps at the end of the year. Also, the amount of tax (the cost of a patent) can be reduced by the amount of insurance premiums (clause 1.2 of Article 346.51 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) by analogy with the simplified tax system of 6%.
Moreover, for each type of activity you need to purchase a separate patent. For example, if an entrepreneur provides hairdressing services and has a retail store with a storeroom of less than 150 m2, he will be required to purchase two patents.
In addition, the patent is valid only in the region where it was acquired. For example, you purchased a patent for a beauty salon in Moscow. If you want to open a beauty salon in Yaroslavl, then you will need to purchase a patent in Yaroslavl.
If you provide remote services. For example, you acquired a patent for software development in the Rostov region, and you provide services to a customer from Moscow. The contract must indicate that the place of provision of services is your location (Rostov region).
If you provide services or sell goods that do not fall within the scope of the patent, then this operation will be taxed according to the standard taxation system.
Therefore, when you register an individual entrepreneur, be sure to send an application for the use of the simplified tax system, even if you plan to use a patent. Otherwise, you will find yourself on the OSN, where the tax burden is large.
A patent can be purchased for any number of months (clause 5 of Article 346.45 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The deadline for paying the tax depends on the period for which the patent was acquired (clause 2 of Article 346.51 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
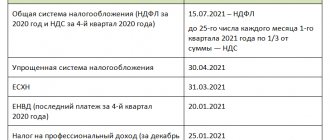
Patent payment deadlines.
If you decide to outsource an accountant, the cost of accounting will be in the region of 1,500-5,000 rubles per month, depending on the region. However, you can do without an accountant if you study the issue in more detail or consult in advance to know about the pitfalls.
BASIC: accounting, reporting, complexity
Small businesses rarely choose OSNO: only if they see benefits in working with VAT payers - many suppliers and buyers are more willing to cooperate with those who also pay value added tax. This tax is paid on OSNO, as well as income tax and corporate property tax if the property owns real estate. If there is transport and land, taxes on them are paid separately. Reporting for each tax is submitted quarterly.
At OSNO you will have to maintain full-fledged accounting and tax accounting - quite complex and painstaking. This is hardly possible without special accounting knowledge, even if you work in a specialized service. So on OSNO, companies and individual entrepreneurs most often work with an accountant.
But still, accounting services simplify your work and eliminate mistakes. For example, in Kontur.Accounting there is a special tool “VAT Calculation”, which helps reduce the tax payable, tells you what documents are missing in the system and what errors were made in accounting.
Keep records of exports and imports in the Kontur.Accounting web service. Simple accounting, payroll and reporting in one service
How will ASN make life easier for taxpayers?
From the very beginning, the automated taxation system was aimed at making it as easy as possible for the “kids” to keep records, submit reports and calculate taxes. The idea was implemented in the following way: individual entrepreneurs and organizations using ASN will be able to legally not maintain accounting and tax records. However, they will need to store primary documents confirming the facts of economic activity for the period specified by the project.
And the most important relief is that special regime officers will be exempt from on-site inspections. But the desk checks have not been cancelled: they will check the full calendar year of activity - 12 tax periods - within three months. Inspections will begin on February 1 of the year following the inspection.
Calculation and payment of contributions and personal income tax from the salaries of employees in the special ASN regime
As you can see, the rates for tax calculation are higher than the standard rates established for the simplified tax system. However, the increase in these values is apparently connected with the purpose of freeing taxpayers from calculating and paying insurance premiums. The abolition of contributions applies to both employees and individual entrepreneurs with their fixed payments. Contribution rates for compulsory medical insurance, compulsory medical insurance, VNIM for all categories of insured persons for those using ASN will become zero. Contributions for injuries are fixed: regardless of the number of employees, the special regime officer will pay 2,040 rubles per year (the specified amount is subject to indexation).
On the income and standard deductions of employees, organizations and individual entrepreneurs will transmit information to the bank, which, in turn, will calculate, withhold and transfer personal income tax from salaries. Only one rate will be applied - 13%. Then the bank will send the received and processed information to the tax authorities. Tax agents will remain responsible for maintaining tax registers for personal income tax.
Submitting reports
The use of an automated taxation system will significantly simplify taxpayers’ reporting to regulatory authorities. The special regime officers were released from surrender:
- regime tax declarations;
- reporting on personal income tax as tax agents (calculation 6-NDFL, including certificates 2-NDFL);
- reporting on insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Federal Tax Service;
- information to the Pension Fund (note that under SZV-M there is an extensive list of exceptions when a report will have to be submitted, but under SZV-TD everyone will need to report);
- statistical reporting.
It is quite possible that companies and individual entrepreneurs will manage mainly without a full-time accountant; they will only need a person who ensures interaction with the bank and the inspectorate.
For entrepreneurs and organizations that still need to submit reports to the Federal Tax Service, funds and other regulatory authorities, K+ specialists have developed the “Accountant Calendar - 2021/2022”. Be sure to check it out so you don't miss the next deadline. You can use demo access to the system. It's free.
Patent: criteria, combination
The patent is similar to the UTII regime, which has been canceled since 2022. Here the amount of tax depends not on actual income, but on potential income. This income is set by regional authorities; the cost of a patent can be calculated on the official website of the tax office.
Working for PSN is easy: you need to make payments for the patent on time and keep a book of income. If you have transport and land, pay taxes on them, and if you have employees, pay personal income tax, contributions and submit personnel reports. Since 2022, it has become possible to reduce the amount of the patent for insurance premiums for yourself and employees, similar to the canceled UTII.
Here are the permissions to work on a patent:
- Only individual entrepreneurs can work on PSN;
- your type of activity must fit under the PSN, each region has its own list (for example, catering, children's development centers, photographic services), check this information with your tax office;
- the entrepreneur has no more than 15 employees;
- annual income - no more than 60 million rubles;
- Individual entrepreneur does not work with excisable goods and goods subject to mandatory labeling.
There is no need to submit patent reports, except for employee reports. Therefore, you can cope with accounting and reporting on PSN yourself. In Kontur.Accounting there is an opportunity to work on a patent.
Combination of tax regimes
Sometimes in business it is beneficial to distinguish two areas and apply a different tax regime for each of them. From 2022, only entrepreneurs can combine different modes. There are two options:
- simplified tax system + patent;
- BASIC + patent.
OSNO and simplified modes cannot be combined; both of these modes are basic and apply to all activities. And NPD cannot be combined with anything.
To summarize: carefully study whether each tax regime is suitable for you in terms of tolerances and criteria, compare the tax burden using our free calculator and work in the most profitable regime for your business. And the web service Kontur.Accounting will help you keep records, calculate salaries and report on any taxation system or when combining them. For the first two weeks, all newcomers work for free.