Paying taxes is the responsibility of any entrepreneur. But you must not only pay, but pay within the time limits established by law. For violation of these deadlines, tax sanctions are provided.
For failure to comply with the deadlines for paying taxes, an entrepreneur is subject to administrative liability - a fine. In addition, the tax itself will still have to be paid, since each “defaulter” will definitely receive a request for payment of taxes, which will indicate the missing amount of tax and late fees.
Fines and penalties are assessed after a tax audit. Before the audit, the tax office cannot demand that you pay taxes. First, an audit is carried out, the arrears are identified, and then measures are taken to pay the missing amount and penalties.
A requirement to pay tax may be issued from the moment the arrears are identified. The maximum period for issuing such a requirement is three months from the date of discovery. If the amount of tax underpayment is 500 rubles or less, then the claim can be made within a year.
If the Federal Tax Service missed the deadline for submitting a claim, it still has the right to collect this arrears from you!
A request for payment of arrears can be issued to an individual entrepreneur personally, can be sent by registered mail, or can be sent electronically via telecommunication channels using an enhanced qualified electronic signature through electronic document management operators or through the taxpayer’s personal account.
Letters from the Federal Tax Service by email should be treated with caution, as this method is used by scammers who, under the guise of the tax office, send files with viruses. The tax office itself does not send regular emails!
If you ignore the tax office’s request to pay taxes, fail to pay the tax itself, or fail to send a document confirming payment within the prescribed period, the tax office will block your current account. To unblock, you will still have to pay tax, penalties and fines, if any, and also personally deal with the tax office, and spend time resolving this issue and unblocking the account.
If you do not agree with the tax office’s demand for payment of tax or the amount of the invoice, then you have the right to appeal it. To appeal, you must contact a higher authority.
Individual entrepreneurs pay taxes on personal property like all individuals: they receive a receipt with the calculated tax amount and a specified deadline for payment. But taxes directly related to business are calculated by individual entrepreneurs independently, and the deadline for paying taxes and advances on them must be monitored personally.
What happens to an individual entrepreneur if you don’t pay taxes?
If taxes are not paid, a penalty is charged for each day of delay. In accordance with the Tax Code, such actions are subject to a fine for late payment for a registered individual entrepreneur. If a sufficient amount has accumulated, more than 900 thousand, criminal penalties may be imposed, especially in the case of deliberate actions.
Didn't pay on time
An entrepreneur, when registering or in the process of work, can choose OSNO or other tax regimes; this determines what taxes he must pay. For each tax contribution there are separate penalties for late payment. As a rule, this is a penalty. The fine for non-payment of taxes for individual entrepreneurs is added if payments are underestimated as a result of intentional or unintentional actions.
Important! If it turns out that the company is in an unfavorable situation, for example, taxes exceed income, it will not be possible to simply forget about paying. The owner of the LLC will solve this issue by selling the enterprise, that is, changing the director and founder. In the case of an individual entrepreneur, this is impossible, since the enterprise is tied to the identity of the owner.
It is important for an individual entrepreneur to know all the intricacies of the legislation so as not to fall into a tax trap. A legal entity is liable for its obligations only for the amount of its authorized capital. If the capital is only 10,000 rubles (this is the minimum amount since 2014), government agencies will not be able to demand more.
A private entrepreneur is responsible with all his property for his own enterprise. Therefore, bailiffs will be able to come to a businessman’s home to seize property for the amount of the debt. In this sense, opening an LLC is less risky.
Calculation of fines
Late fees
If you repay your debt late, you will also have to pay the assigned penalties. They are calculated according to the algorithm established by Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and depend on three factors:
- amount of debt;
- number of days of delay;
- 1/300 of the currently valid refinancing rate according to the Central Bank.
Punishment for violating deadlines
The state exists at the expense of taxes, so for every payment violation there is a fine, penalty or even criminal liability. In some cases there are only penalties. For example, from March 2022, if you fail to make timely tax payments for pension and health insurance for yourself, the individual entrepreneur will only pay penalties, but not a fine. Plus, of course, the underpaid amount.
Individual entrepreneur on a patent - what taxes to pay, mandatory contributions
But here you need to take into account which system the merchant has chosen. The most taxes are charged under OSNO, or “classic”. Under the classical tax system, the most is paid. Therefore, there will be more fines and penalties. If not only taxes are not paid, but also tax returns are not sent within the appropriate time frame, additional fines will be added. Even in the simplest taxation structure - a patent system - you will have to pay for the patent, insurance premiums for yourself, for the staff, and transfer personal income tax for hired employees.
Note! Failure to pay any of these taxes on time will result in penalties.
Even failure to submit reports to statistics on time becomes the reason for penalties, and not in the form of penalties, but immediately from 10 thousand rubles. Illegal engagement in commercial activities without registration with the tax authorities entails a fine of 10% of income, but not less than 40 thousand rubles. Whereas individual entrepreneur registration can be free if documents are submitted through the MFC. Tax debts in the amount of 900 thousand rubles are subject to criminal liability. In any case, it is easier to pay taxes on an individual entrepreneur “than to save.”
Penalty for failure to submit a declaration
Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes sanctions for late submission of reports. To understand the consequences of failure to submit a declaration under the simplified tax system, several parameters should be taken into account:
- taxpayer category - organization or individual entrepreneur;
- are you a payer of the tax levied in connection with the application of the simplified tax system, have you filed an application for simplification in a timely manner, has this document been registered by the tax service in the prescribed manner;
- whether economic activity was carried out during the tax period;
- the offense was committed for the first time or repeatedly.
The amount of tax accrued for payment is the main criterion on which the amount of the fine for late declaration of the simplified tax system accrued to an organization or entrepreneur depends.
Reporting on taxes levied in connection with the application of the simplified system is submitted by March 31 of the year following the end of the tax period. This deadline is established for organizations, and individual entrepreneurs are required to report by April 30. If activities were carried out during the reporting period, then the fine for violating the deadline for submitting a declaration under the simplified tax system will be 5% of the tax amount. The minimum amount is 1000 rubles, the maximum is 30% of the tax base.
If there is a delay of more than 10 days, the tax authority, in addition to imposing a fine for failure to submit a tax return under the simplified tax system in 2022, has the right to suspend transactions on the taxpayer’s accounts (clause 3 of Article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Federal Tax Service No. ED-4-15/25663 dated 11.12. 2014). A request is sent to the bank to block the account, and any expense transactions, except for payments to the budget, will be unavailable until the obligation to submit the report is fulfilled.
There are additional deadlines to keep in mind:
- if the right to use the simplified system is lost, the report must be submitted by the 25th day of the first month of the next quarter;
- in case of voluntary termination of activity - until the 25th day of the next month.
In order to independently calculate the fine for late filing of a declaration under the simplified tax system for 2022, you should check whether the tax is calculated correctly in accordance with the selected object of taxation. For the “Revenue” object the rate is set to 6%, and if the “Revenue minus expenses” object is selected - 15%. The amount of tax on which the fine is calculated is taken from page 273 or page 280 of section 2.2 of the report:
If the data on page 273 is calculated correctly, it is easy to calculate what fine you will have to pay for not filing a simplified tax return:
45000*5%=2250 rub.
Accrual of penalties
Simplified taxation system for individual entrepreneurs - what taxes need to be paid
Typically, if the return is filed on time, the tax office only charges penalties on the unpaid portion. Penalties are calculated as follows:
- If we consider what the fine is for an individual entrepreneur if he does not pay the tax on time, then if the delay is no more than 30 days, the required amount is multiplied by the Central Bank rate. The resulting number is then divided by 300 and multiplied by the number of days overdue.
- If there is a delay of 31 days or more, the underpaid amount is divided by 150, multiplied by the Central Bank rate, and by the number of days after the thirty-first day inclusive, added with the amount for 30 days of delay.
- The Central Bank rate as of July 17, 2022 is 7.5%, it can always be clarified on the website cbr.ru.
- Days are counted as follows: starting from the date following the one when payment was required until the date of payment of penalties, inclusive. This applies to taxes and contributions to the Funds - Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund.
Tax return
Example: the underpayment of tax amounted to 1000 rubles. The last day for payment was June 30, and the missing amount was paid only on July 31. In 30 days (1000*7.5%*30)/300=7.5 rub. And for the last, thirty-first day, (1000*7.5%*1)/150=0.5 rub. We add up these amounts and get 8 rubles. It's usually easier to use online calculators so you don't have to count by hand.
The BCC for paying penalties differs from the BCC for taxes. Therefore, you need to fill out the payment form correctly so that you don’t have to deal with this additionally later.
Note! In 2022, amendments were adopted to the Tax Code stating that penalties cannot exceed the amount of arrears. That is, if 100 rubles were underpaid to the budget, more than 100 rubles cannot be charged as a penalty.
Penalty
Taxpayers must pay taxes on time, that is, within the deadlines established by tax legislation for each tax (clause 1, article 45, clause 1, article 57 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the established period has expired and you have not paid the tax (advance payment), the inspectorate will charge penalties for the period of delay (clause 2 of Article 57, clause 3 of Article 58 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Penalties are charged from the day following the deadline for tax payment until the date of its actual transfer, inclusive. In this case, penalties are charged for each day of delay based on 1/300 of the Bank of Russia refinancing rate.
EXAMPLE OF ACCRUAL OF PENES An accountant for Aktiv LLC had to pay a “simplified” tax at the end of the year in the amount of 112,000 rubles. no later than March 31st. Let's assume that this day was a working day, so there was no official postponement of the tax payment deadline. The company paid the tax only on April 7. Therefore, penalties must be accrued from April 1 to April 7, that is, 7 calendar days. The refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia at that time was 10.5%. The amount of penalties will be equal to: RUB 112,000. × 10.5% × 1/300 × 7 days. = 274.4 rub.
If at the end of the year the amount of calculated tax turned out to be less than the amount of advance payments due during this year, then penalties accrued for non-payment of advance payments can be proportionately reduced. Moreover, this rule applies to “simplified” with any object of taxation (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 5, 2016 No. ZN-4-1 / [email protected] , Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 16, 2013 No. 03-02-08/33518 , dated January 19, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/9).
AN EXAMPLE OF REDUCING PENS An individual entrepreneur who does not have employees applies the simplified tax system on income. Advance payments for “simplified” tax based on the results of the reporting periods - the first quarter, half a year and 9 months - were accrued by the entrepreneur, but not paid. Let’s say the total amount of these payments was 60,000 rubles. At the end of the year, the amount of calculated tax was 75,000 rubles. The individual entrepreneur reduced the amount of tax on fixed insurance contributions to the Pension Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund paid for himself, that is, by 35,664.66 rubles. As a result, the amount of tax was less than the amount of advance payments calculated based on the results of the reporting periods and amounted to 39,335.34 rubles. (RUB 75,000 – RUB 35,664.66) Consequently, penalties for late payment of advance payments must be accrued in the following amounts: - RUB 9,833.84. (RUB 39,335.34: 12 months × 3 months) – due on April 25 (for the first quarter);—RUB 19,667.67. (RUB 39,335.34: 12 months × 6 months) – according to the payment deadline of July 25 (for half a year);—RUB 29,501.51. (RUB 39,335.34: 12 months × 9 months) – due for payment on October 25 (for 9 months).
According to the Ministry of Finance, this procedure can also be applied to the payment of the minimum tax (letter dated October 30, 2015 No. 03-11-06/2/62714).
Financiers make this conclusion based on the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 No. 57. Thus, paragraph 14 of the resolution states that if, at the end of the tax period, the amount of calculated tax was less than the amount of advance payments, then the courts should proceed from the fact that penalties accrued for late payment of advance payments must be proportionately reduced.
Consequently, if at the end of the year the “simplified person” must pay the minimum tax, and the amount of advance payments calculated at the end of each reporting period is greater than the amount of this tax, then penalties for non-payment (or late payment) of advances should be reduced proportionately, that is, in proportion to the amount of the minimum tax
If you were unable to repay the arrears due to the fact that the tax authority seized your property or transactions on bank accounts were suspended by a court decision, then penalties for the arrears are not charged. The usual “freezing” of an account does not exempt you from penalties.
After the arrears arise, the tax office will wait for some time until you pay off the tax debt and pay penalties.
If you don't do this, the inspectors will take active action. They can:
- collect tax forcibly at the expense of the company’s money or property;
- block the company's current accounts;
- seize the company's property.
Read about how to calculate and, if necessary, reduce penalties for late payment of advance payments under the simplified tax system in the “STS in practice” berator.
Concealing the income of an individual entrepreneur
What happens if you don’t submit your individual entrepreneur’s declaration on time - what is the fine?
If an audit, on-site or desk-based, determines that the tax base is understated, the regulatory authority will issue a fine, penalties for underpayment, and the tax amount itself will have to be paid extra. When inspectors manage to prove a deliberate understatement of the tax base, the fine is 40% of the lost tax. If officials believe that the understatement occurred unintentionally, the fine will be 20% of the missing amount.
If it is proven that an entrepreneur is concealing property or finances, through which taxes and other things should be collected, the individual entrepreneur faces a fine of 200 thousand rubles or forced labor for a period of three years. Thus, this is already Article 199.2 of the Criminal Code as amended, which came into force on July 1, 2019. The case of deliberate evasion of the obligations of a tax agent also falls under the Criminal Code. If it is proven that an entrepreneur deliberately does not pay taxes on employees, he may be subject to a significant fine or sent to prison.
Payment evasion
Criminal liability of individual entrepreneurs
Falsifying documentation of a private entrepreneur and submitting reports with false data to the Federal Tax Service is a criminal offense. If, as a result of evasion of the taxpayer’s obligations, non-payment of the fee occurs on a large or especially large scale, the citizen is punished in accordance with Article 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
In case of large amounts of debt, one of the following measures is provided:
- forced labor for up to 12 months inclusive;
- fine from 100 thousand to 300 thousand rubles;
- imprisonment for a period of up to 12 months;
- arrest for six months;
- a penalty in the aggregate of profits received by a person over 1–2 years.
If the debt is in a particularly large amount, the penalty may be:
- imprisonment for 1–3 years;
- a fine in the aggregate of the person’s profits for 1.5–3 years;
- forced labor for a period from 12 months to 3 years;
- collection of a fine from 200 thousand to 500 thousand rubles.
If you have committed this offense for the first time, it is possible to avoid punishment. It is enough to pay the full amount of the fee, assigned penalties and fines.
Re-registration of a car to another owner - https://urmozg.ru/documenty/pereoformlenie-avtomobilya-na-drugogo-vladelca/. How the inheritance is divided between children - read here.
How to get a mortgage using two documents from a bank?
Does the individual entrepreneur hide his actual income and expenses? This is a separate violation for which the punishment is determined according to Article 199.2 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
A citizen can expect a fine in the amount of 200 thousand to 500 thousand rubles or the total profit for 1.5–3 years, forced labor for a period of up to 5 years or imprisonment for the same period. In this case, the judge may rule on the impossibility of an individual entrepreneur to hold a certain position or carry out certain types of activities.
Is there a statute of limitations for tax violations?
It happens that a person hopes that his debts will be forgotten and he won’t have to pay them. Don't count on it. The statute of limitations is of primary importance. It is counted from the day the tax violation was committed, or from the end of the tax period when the violation was committed. If three or more years have passed before the decision to prosecute, the person cannot be prosecuted.
For example, the tax base was underestimated in the reporting, and tax was not received in the amount of 300 rubles. The responsible person, that is, the individual entrepreneur, cannot be held liable if three years have passed. But if a person interfered with an inspection by the fiscal authorities, then the statute of limitations is suspended.
Additional Information! When the liability is criminal, the statute of limitations is 2 years. But in June 2019, the Supreme Court proposed to abolish the statute of limitations for tax crimes. It remains to be seen whether this will become the norm.
Statute of limitations
Thus, when opening an individual entrepreneur, it is better to be sure in advance that the future enterprise will meet all payments. After all, liability is provided not only for missing the payment date, but also for filing a declaration late.
Set of socks, Omsa socks
349 ₽ More details
Set of socks, Omsa socks
349 ₽ More details
Professional side cutters
Good faith of the taxpayer
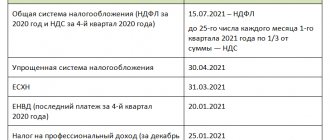
If the activities of an individual entrepreneur involve large turnover (more than 150 million per tax period), or for some other reason the entrepreneur decided not to apply preferential tax regimes and remained on the general tax system, in this case he will have to keep more careful accounting, quarterly report on VAT and declare income annually
for calculating personal income tax, the amount of which is 13%, and from January 1, 2022, from an amount of income exceeding 5,000,000 rubles - 15%.
You will have to pay VAT and advance payments for personal income tax quarterly, and you should also remember the deadlines for paying other taxes and insurance contributions.
When applying the simplified taxation system, the taxpayer makes quarterly advance payments.
Under any taxation system, entrepreneurs pay insurance premiums in a fixed amount until December 31 of the current year
, and if the income exceeds 300,000 rubles, then the individual entrepreneur pays an additional 1% of the amount exceeding 300,000 rubles until July 1 of the next year.
In all cases, according to the law, the entrepreneur independently calculates and takes care of the timely payment of taxes and insurance premiums, as well as the timely submission of a tax return.
If the individual entrepreneur has doubts regarding the procedure and timing of payment
taxes, the correctness of their application of tax regimes, it is better to obtain advice in advance from the territorial tax authority. Moreover, according to the law, the tax authority is obliged to inform the taxpayer free of charge (including in writing) about taxes and fees, the procedure for their calculation and payment, the rights and obligations of the taxpayer, as well as provide forms of tax declarations (calculations) and even explain the procedure for filling them out .