Compensation for delayed wages is not payment for labor
The Labor Code and other federal laws establish the payment of various types of compensation to employees.
Some of them are included in the wage system, some are not. Thus, compensation payments to employees in case of violation by the employer of the established deadline for payment of wages (including advance payments, vacation pay, dismissal payments and other payments paid within the time limits specified by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are established by Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is not part of the employee remuneration system and is not recognized as remuneration for work.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Deadlines for payment of salaries and other income
The amount of compensation for late payment of wages can be specified in a collective agreement, local regulation or employment contract. It cannot be lower than 1/150 of the current key rate of the Bank of Russia.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation allows for compensation for delayed payment of wages to be established in an increased amount.
There are additional payments and allowances (they are also often called compensation payments), which are part of the remuneration system and are remuneration for work. These are additional payments for night hours, overtime pay, etc. Compensation for delayed payment of wages is not included in the employee remuneration system and is not recognized as remuneration for labor. They are a measure of the employer’s responsibility for violating the rights of employees to receive timely wages.
The obligation to pay this monetary compensation arises in all cases of delay, regardless of whether the employer is at fault.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Types of employer liability for failure to pay wages on time
How to count
Before we figure out how to calculate compensation for late wages, let’s look at how to calculate the due amount. Compensation funds are accrued for the full period of deferred payment of wages, starting from the date following the payment day established by the institution until the date of actual transfer of remuneration.
The amount of the compensation payment must be fixed in the local regulations of the institution - collective and labor agreements, as well as in the regulations on remuneration.
If the amount of such compensation is not determined by internal regulations, then it is calculated based on the current key rate. At the moment, compensation for delayed wages, 2022 entries are similar to 2022 accounting entries, should not be lower than 1/150 of the key rate. The employer has the right to increase the amount of compensation established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, the procedure for calculating the compensation amount is determined as follows: 1/150 of the refinancing rate for each day of late payment.
The calculation formula established in Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it will be like this:
Personal income tax
All types of compensation payments established by the current legislation of the Russian Federation (within the limits established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation) related to the performance of labor duties by the taxpayer are not subject to personal income tax (clause 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Such compensation payments also include payment of compensation if the employer violates the established deadline for payment of wages. The application of this norm to the amounts paid does not cause any complaints from inspectors (see letter of the Ministry of Finance dated February 28, 2017 No. 03-04-05/11096). Moreover, even compensation for delayed wages, paid in an increased amount (see letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 28, 2008 No. 03-04-05-01/450).
Consequences of failure to meet salary deadlines
Salary delays can occur for several reasons:
- Through the fault of the employee (if inaccurate current account information was provided or the employee was absent on the day the salary was paid);
- Due to the fault of the bank (delays in transfer);
- Due to the employer's fault.
In each case, the consequences for the employer will be different . If the first two were not the employer’s fault, then he will not face any compensation or fines.
In the latter case, the employer is at fault; the extent of liability will depend on the amount of debt, the reasons for non-payment, as well as the length of the delay.
If the delay in wages is more than 15 days, the employee has the right not only to receive compensation, but also not to attend the workplace while maintaining average earnings.
Depending on the reasons and timing of the delay, the employer may face one of the following types of liability :
- Administrative - in the form of a fine on the basis of Article 5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation;
- Disciplinary – removal from official duties under Article 192 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Criminal - suspended sentence or imprisonment for up to 5 years;
- Material – in the form of a penalty for late payment.
However, the employer will never “give up” and issue himself a fine. Therefore, in order for management to respond according to the law, the employee must contact the appropriate authorities.
We will learn about the procedure for suspending work due to non-payment of wages by reading a special article prepared by the editors of our website.
Penalty
The employer does not have the right to postpone the date of payment of wages. The date is fixed in the employment contract and the deadlines for all payments must be strictly observed. Even if the employee himself asks to postpone the day of payment of wages, the employer may pay for this by having to pay a penalty.
A penalty or compensation for delayed salary payments is calculated in accordance with Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Its size is equal to 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate.
In addition to the compensation provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employee of an organization whose wages are delayed may demand compensation for moral damage and lost profits . This is done through the court in a claim procedure.
General information about penalties for late payments is described in a special material. Recommended reading.
Insurance premiums
But as for insurance premiums, the issue remained and remains controversial for a long time.
Opinions vary. Insurance premiums are not charged on the amount of compensation for delayed salary payments. This is the position of the courts, including the highest ones (see, for example, Determination of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of January 10, 2022 No. 303-KG18-22489). The compensation that is paid to the employee on the basis of Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is the financial liability of the employer to the employee. It is paid to employees by law, and its purpose is not payment for work, but the protection of the labor rights of employees. Therefore, amounts of monetary compensation for delayed wages are not subject to insurance premiums. Quite a convincing rationale.
The Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service have a categorically opposite position. And it also cannot but be considered convincing. It is as follows.
Compensation for delayed payment of wages should be subject to insurance contributions, since:
- payment of this monetary compensation does not constitute compensation for the employee’s expenses associated with the performance of his labor duties;
- the list of payments to individuals not subject to insurance premiums is given in Article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and is exhaustive;
- The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for a special rule on inclusion in the specified list of monetary compensation to an employee for violation by the employing organization of the established deadline for payment of wages (see, for example, letters of the Ministry of Finance dated September 24, 2018 No. 03-15-06/68161, dated September 24 2022 No. 03-15-05/68049, etc.).
Let us add that, as a justification for the need to accrue contributions, the inspectors cite the fact that this is a payment within the framework of an employment relationship. And such payments are subject to insurance premiums.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Object of taxation of insurance premiums
Financial liability under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in 2020 (employee compensation)
The financial liability of the organization in the form of payment of compensation for delayed wages is established by Art. 236 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The amount of compensation for delayed wages in 2022 is fixed in the collective or labor agreement. If it is not established by an employment or collective agreement, it is calculated based on 1/150 of the key rate for each day of delay.
Compensation is paid not only for delayed salaries, but also for other payments to the employee: bonuses, vacation pay, additional payments, severance pay. Moreover, regardless of whether the organization is to blame for the delay or not. For example, if the delay occurred due to the fault of the bank, the employer will pay compensation for the fact that the salary was not received on the employee’s card on time.
The period of delay in salary is calculated as the number of days by which the payment is overdue. The first day of delay is the day following the due date for payment of wages. The last day of delay is the date of actual payment of wages (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
And one more rule: the calculation of compensation includes the amount that the employee must receive in hand - without personal income tax and other deductions.
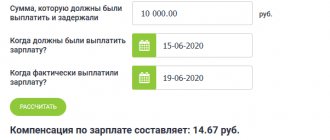
Example
A salary in the amount of 13,050 rubles is due for payment for the second half of December, minus personal income tax. The payment deadline is December 27, 2019, but it was paid on January 9, 2020. Delay from 12/28/2019 to 01/09/2020 - 13 days. The key rate of the Bank of Russia during the overdue period is 6.25%.
Compensation amount = 70.68 rubles. (RUB 13,050 x 6.25% / 150 x 13 days).
Compensation for delayed wages is not subject to personal income tax (Clause 1, Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But the need to impose insurance premiums is a controversial issue. The judges believe that contributions from compensation do not need to be calculated (Decision of the Supreme Court dated December 28, 2016 No. 310-KG16-17515, etc.), but controllers do not agree with them (Letter of the Ministry of Labor dated April 27, 2016 No. 17-4/OOG-701 and etc.).
How to determine size
The amount of compensation for delayed wages in 2022, which is due to employees, directly depends on three indicators:
- Amount of remuneration for work (salary, bonuses, sick leave benefits, additional payments and incentives).
- The date of payment of wages in the organization, established in local acts (collective or employment agreement).
- The actual settlement date (the day on which the employees received the money).
The calculation is made using the formula:
IMPORTANT!
The calculation includes the amount of salary and other remuneration from which personal income tax has already been withheld. If the employee has other types of deductions (writ of execution, union dues), then the amount due for payment in person should be taken into account for the calculation. That is, after all deductions have been made.
What the law says
If the employer has delayed payments in favor of its employees, then, according to Art.
236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, employees are entitled to special compensation for late payment of wages 2022. It is important to note that these funds are assigned regardless of the reason why the transfer deadlines were violated. In addition to compensation money, an unscrupulous employer will be punished under Art. 5.27 Code of Administrative Offences. Thus, the administrative code provides for penalties in the amount of:
- 30,000–50,000 rubles - for legal entities;
- 10,000–20,000 rubles - for responsible officials;
- from 1000 to 5000 rubles - for individual entrepreneurs who are employers.
IMPORTANT!
Compensation money will have to be accrued not only for delayed wages, but also for all types of benefits, vacations and other types of remuneration for work. For example, for compensation, incentive and bonus payments in favor of an employee paid with delay, compensation for delayed salary in 2022 is also calculated.