How is the amount calculated?
In case of untimely payment of wages or other amounts established by the remuneration system, the employer is obliged to pay compensation to the employee in accordance with Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employer is obliged to pay compensation regardless of whether it is his fault for the delay or not.
Before generating entries for compensation for delayed payment of wages, it must be calculated.
The Labor Code establishes only the required minimum compensation payment. The organization has the right to establish a higher size by approving it in a local regulatory act:
- collective agreement;
- regulations on wages;
- order, disposition, other LNA.
Compensation for delayed payment of wages is calculated for each calendar day of delay, starting from the day following the established day of payment of wages and up to and including the date of repayment of the debt. The minimum amount of compensation is calculated based on 1/150 of the key rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation:
At CLUB.TK LLC, wages are paid no later than the 15th of the next month. For May, manager Ivanov I.I. the salary in the amount of 10,000 rubles was transferred on June 19. The transfer delay was 4 calendar days. The key rate of the Central Bank for the settlement period is 5.5%. The amount of compensation paid to the employee will be:
Employee compensation calculator for late wages
Fill in the amount of debt, the established and actual date of payment of wages. The calculator will calculate the amount of compensation:
What are the consequences of late payment of wages?
Payment to employees for their work must be made at least twice a month.
The periods for advance payment (from the 15th day of the month until its end) and final payment (from the 1st to the 15th day of the month) are regulated by the Labor Code. More precise terms for salary payment are established depending on the capabilities and desires of the employer. If the salary is not paid on time, the employer is obliged to pay the employee interest for the delay (Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In fact, these percentages, calculated as at least one hundred and fiftieth of the key rate of the Central Bank, will be compensation for late paid wages.
In general, the smallest amount of compensation can be calculated using the formula:
Kmin = Unpaid wages on time × Key rate / 150 × Number of days overdue
NOTE! A larger amount of compensation may be stipulated in the wage regulations, employment contract or other local regulatory act.
An example of calculating compensation for delayed payment of wages from ConsultantPlus In the organization, wages for the second half of January 2022 (final payment) should have been paid on February 6, 2022. It was paid on February 11, 2022. The delay in payment was 5 days (from 02/07/2020 to 02/11/2020). The amount of wages not paid to the employee on time is 60,000 rubles, the amount of personal income tax withheld upon payment is 13,000 rubles. See the full example in K+.
What accounting entries appear in accounting when calculating compensation?
Record the accrual and payment in account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations.” Maintain analytical records for each employee. Compensation for late payment of wages and accrued insurance premiums from it is recognized in accounting as another expense and is charged to account 91.
Compensation for late payment of wages: postings
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Compensation accrued for delay in salary transfer | 91 | 73 |
| Insurance premiums accrued | 91 | 69 |
| Compensation payment for delayed salary paid to employee | 73 | 50, 51 |
| Insurance premiums listed | 69 | 51 |
It is risky to recognize compensation for late payment of wages as tax expenses (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2011 No. 03-03-06/2/164).
We pay compensation for delayed wages in 2020-2021 - accounting entries
Currently, it is possible to compensate for delayed salaries either by issuing cash from the cash register or by non-cash payment.
When paying compensation for late payment of wages, the entries may look like this:
- Dt 73 Kt 50 - compensation was paid from the cash desk of the company or individual entrepreneur;
- Dt 73 Kt 51 - compensation is transferred from the current account to the employee’s bank account.
Typically, when paying income to an employee, personal income tax must be withheld. However, the accrual and payment of compensation in the minimum amount or the amount fixed in the employment contract or other local document of the employer does not imply the accrual and withholding of income tax from it (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 06/04/2013 No. ED-4-3 / [email protected] , Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 28, 2017 No. 03-04-05/11096). If compensation is paid in an amount greater than the minimum and this is not taken into account in local documents, then officials say it is necessary to charge personal income tax on the excess amount.
The issue of charging insurance premiums for compensation is controversial. A ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus will help you decide whether to accrue them or not. Get trial access to K+ for free and proceed to the material.
Do I have to pay personal income tax and insurance premiums?
Compensation compensation for untimely transfer of wages to employees is not subject to personal income tax in full (clause 1 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated February 28, 2017 No. 03-04-05/11096).
The imposition of insurance premiums on compensation for non-payment of wages is a controversial issue. The Federal Tax Service and the Ministry of Finance believe that compensation for late payment of wages is subject to insurance contributions (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 03/06/2019 No. 03-15-05/14477), since:
- Paid as part of the employment relationship.
- Not named in non-insurance payments.
If insurance premiums are not paid, regulatory authorities will recognize this as a violation and charge penalties and fines.
On the other hand, there is a Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court dated December 10, 2013 No. 11031/13, which classifies such payments to employees as compensation and non-taxable insurance contributions. The Supreme Arbitration Court considered the provisions of Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009, which became invalid on January 1, 2022. But in fact, the new rules for calculating insurance premiums are similar to the provisions of 212-FZ.
If you are not ready to argue with the tax authorities, then create not only entries for calculating compensation for delayed salaries, but also reflect in your accounting the accrual and payment of insurance premiums from the compensation payment.
On the procedure for accounting for compensation for late payment of wages
From time to time, at any enterprise, conflicts occur between employees and the employer. This situation is most often accompanied by a delay in payment of wages. Such a delay can be both the cause of the conflict and its consequence. But, let’s leave these philosophical reflections on where the cause is and where the effect is, and pay attention to how to take into account the accrual and payment of compensation for delayed wages in accounting and tax accounting. The first question that arises is what compensation for delayed wages is: labor costs or other expenses in the form of fines, penalties, penalties for violation of contract terms. The second question is whether the amounts of such compensation are taken into account in expenses when calculating income tax. Let's figure out whether compensation for late payment of wages is classified as labor costs. The definition of the concept of “wages” is contained in Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In accordance with this article, wages (employee remuneration) are remuneration for labor depending on the employee’s qualifications, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed, as well as compensation payments and incentive payments. That is, compensation payments are wages. And in accordance with Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, interest for late payment of wages is monetary compensation, and, therefore, is wages. Based on this logic, the costs of paying this compensation should be taken into account for accounting purposes of the organization as part of expenses for ordinary activities in accordance with the procedure for accounting for expenses provided for by the accounting policy of the organization. However, there is another position on this issue. Some authors believe that compensation for delayed wages is a type of financial liability of the employer, in fact it represents a sanction for violating the deadline for paying wages and should be taken into account as part of other expenses. There is an ambiguous situation and the accountant, of course, is interested in the question: what to do in this case. Let us take the liberty of recommending that compensation for delayed wages be taken into account as part of other expenses. And the reasons, oddly enough, stem from tax accounting, namely from the answer to the question: are the amounts of such compensation taken into account in expenses when calculating income tax. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain an answer to this question. The official position of the Ministry of Finance of Russia is expressed in Letter dated December 9, 2009 N 03-03-06/2/232 and is that the amounts of compensation paid for delayed wages are not recognized as expenses for tax purposes, since they are not related to the conditions or regime work. Similar conclusions are contained in the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 17, 2008 No. 03-03-05/38. According to experts from the Ministry of Finance, in accordance with Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer’s expenses for wages include compensation charges related to work hours or working conditions. And since compensation for delayed wages is not related to the work schedule or working conditions, it cannot be taken into account for tax purposes. This point of view is also controversial, since compensation for delayed wages can be taken into account as a non-operating expense under subclause 13 of clause 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The validity of this conclusion is confirmed by numerous judicial practice, for example, Resolution of the FAS Volga District dated 08/30/2010 in case No. A55-35672/2009, Resolution of the FAS Volga-Vyatka District dated 08/11/2008 in case No. A29-5775/2007, Resolution of the FAS Ural District dated April 14, 2008 No. F09-2239/08-C3 in case No. A60-14685/07. The courts indicate that compensation paid on the basis of Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is in fact a sanction for violation of contractual obligations. At the same time, subparagraph 13 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not limit the employer’s right to include these amounts in expenses depending on the legal relationship within which the obligation was violated: civil or labor. Our recommendation follows from the above. Namely, since the courts recognize this compensation as a sanction, it is more appropriate to classify it as other expenses, and for tax purposes it is more appropriate not to take it into account from the point of view of ordinary efficiency. The amounts of compensation, as a rule, are disproportionately small compared to the time and money spent on defending one’s point of view in court. Therefore, it is cheaper to agree with the opinion of the Ministry of Finance and not take into account compensation for delayed wages as part of the expenses taken into account for tax purposes. In this case, of course, in each specific case your decision will depend on the conditions of your situation. The last words are yours, dear colleagues.
Consulting on accounting and tax issues
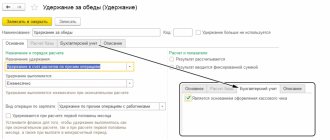
How is payment of compensation for delayed wages processed?
The procedure for documentation is not established by law. Its organization has the right to develop it independently: issue a local normative act (order, regulation), attaching to it a calculation of the amount of compensation payment. The LNA leader approves. Please familiarize the recipients of the compensation with the order against their signature.
IMPORTANT!
The Labor Code obliges workers to pay wages at least twice a month (Article 136 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Full remuneration must be paid no later than the 15th day of the month following the billing month.
How to apply for compensation
Compensation payment for late payment of wages is calculated in accordance with the rules of Article 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Labor legislation has established a minimum amount of compensation. The organization has the right to decide that compensation for delayed wages will be paid in an increased amount. Such a decision is approved in a collective agreement or other LNA. Issue payments by order of the manager and create postings based on it. Familiarize each employee with the order.
Sample order
Administrative and criminal liability for delayed payment of wages.
In addition to the liability provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer bears administrative and criminal liability for non-payment or incomplete payment on time of wages and other amounts within the framework of labor relations.
Administrative responsibility for these acts is established in parts 6, 7 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation - in the form of a warning (draft bill No. 473887-7 proposed to exclude punishment in the form of a warning from Part 6) or a fine. We will show the size of the sanctions in the table.
| Subject of the offense | Amount of fine, rub. | |
| In case of primary violation (Part 6) | In case of repeated violation (Part 7) | |
| Officials | From 10,000 to 20,000 | From 20,000 to 30,000 |
| IP | From 1,000 to 5,000 | From 10,000 to 30,000 |
| Legal entity | From 30,000 to 50,000 | From 50,000 to 100,000 |
Criminal liability for non-payment of wages threatens the manager if he acted out of selfish or other personal interest (Article 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of sanctions is in the table.
| Aspect | Responsibility provided for in Art. 145.1 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation | ||
| Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | |
| Composition of the offense | Partial non-payment of more than three months of salary (and other amounts provided by law) | Complete non-payment of wages (and other amounts established by law) for more than two months or payment of wages for more than two months in an amount below the minimum wage | Non-payment (partial or full) of wages entailed serious consequences |
| Measure of responsibility | Fine up to 120,000 rubles. or in the amount of salary (other income of the convicted person) for a period of up to one year. Deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a period of up to one year. Forced labor for up to two years. Imprisonment for up to one year | Fine from 100,000 to 500,000 rubles. or in the amount of salary (other income of the convicted person) for a period of up to three years. Forced labor for a period of up to three years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a period of up to three years. Imprisonment for a term of up to three years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a term of up to three years | Fine from 200,000 to 500,000 rubles. or in the amount of salary (other income of the convicted person) for a period of one to three years. Imprisonment for a term of two to five years with or without deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or carry out certain activities for a term of up to five years |
An essential point: both administrative and criminal liability can occur only in the presence of guilt (Article 2.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Article 14 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation). Non-payment of wages entails criminal liability only if the organization has funds and the non-payment is due to self-interest or other personal interest of the head of the organization (branch, representative office, separate (structural) unit).
Formula for calculating the amount of interest due
Compensation is calculated individually - based on payments to each employee for days of delay in payment of wages, vacation pay, benefits, calculation upon dismissal, etc., according to the formula:
K = (Z - personal income tax) x KSCB / 150 x D, where
Z - salary due but not paid;
Personal income tax is a tax on the amount of this salary;
KSCB – the current key rate of the Central Bank;
D – number of days of delay
Example
Due to the lack of funds in the company’s account, salaries for the second half of February in the amount of 86,200 rubles (after deducting personal income tax) were paid not on time, 03/05/2020, but only on 03/17/2020, resulting in a delay of 12 calendar days (from 6 to th to March 17th). The amount of compensation is calculated in accordance with the provisions of Art. 236 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, i.e. based on 1/150 of the Central Bank key rate (from 02/10/2020 it is equal to 6%).
The company has 3 employees, the amount of overdue payments and the amount of compensation for each are presented in the table:
| Full name | Salary (rub.) | Central Bank key rate | Number of days overdue | Compensation amount (RUB) (gr.2 x gr.3 / 150 x gr. 4) |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Ivanov I.R. | 30 000 | 6% | 12 | 144,00 |
| Sorokin V.B. | 26 900 | 129,12 | ||
| Ryabova R.M. | 29 300 | 140,64 | ||
| Total: | 86 200 | 413,76 |
Please note that the counting of days of delayed payment begins on the next day from each date approved for payment of wages. That is, if the advance in our example should have been paid on February 20, and it would also have been issued on March 17, then the amount of interest for 26 would have to be added to the amount of accrued compensation for the payment of wages for the second half of February days (from February 21 to March 17) of delay in advance payment for the first half of the month.