Salary in cash and non-monetary form
The employer must pay the employee’s labor (Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Article 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation indicates that wages are paid in cash in the currency of the Russian Federation (rubles) and, in some cases, in foreign currency and in non-monetary form.
Payment for work in non-monetary form can be made in accordance with a collective agreement or employment contract upon the written application of the employee. At the same time, payment in kind cannot exceed 20% of the accrued monthly salary.
When resolving disputes arising in connection with the payment of wages in kind to an employee, one should take into account Article 4 of the ILO Convention No. 95 of 01.07.1949 on the protection of wages, ratified by Decree of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the USSR of 31.01.1961 No. 31.
It states that payment of wages in this form can be recognized as justified if the following legally significant circumstances are proven:
- the employee voluntarily wished and confirmed with a written statement the receipt of wages in non-monetary form;
- wages paid in non-monetary form do not exceed 20% of accrued monthly earnings;
- payment of wages in kind is common or desirable in a given industry or profession (for example, the agricultural sector of the economy);
- payments of this kind are suitable for the personal consumption of the employee and his family or bring him a certain kind of benefit;
- When paying wages to an employee in kind, the requirements of reasonableness and fairness are met with respect to the value of the goods transferred to him as wages, i.e. their value in any case should not exceed the level of market prices prevailing for these goods in a given area during the period calculation of payments.
It may happen that the goods and services received by the employee are so beneficial to him that he expresses a desire to purchase them as part of his salary in a larger amount than 20%. The employer has the right to meet such a wish, but not as remuneration, but as payment for wages, essentially selling these goods or services to his employee as a counterparty.
If an employee receives goods or services from an employer not as remuneration (and does not violate the requirements of Article 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Article 4 of ILO Convention No. 95), then the transfer of goods and provision of services with the deduction of their cost from the salary for the employer turns out to be a normal sale. The counterparty in this transaction is the employee.
Payment for goods and services purchased by him must be confirmed by a cash receipt, even in cases where the cost of goods and services is withheld from the salary. Such withholding is not “withholding” in the sense of Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and is not subject to restrictions.
Meals for posting employees - compensation for the cost of meals for employees
Often, an enterprise does not provide free lunches to staff, but simply compensates them for the cost of food. The chart of accounts provides for the use of:
- account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” - it reflects the implementation of payments to personnel not related to wages and compensation of expenses of accountable persons (payment of compensation for the cost of food from funds taken at the cash desk will be reflected in the DEBIT of account 73 in correspondence with the account 50 "Cashier");
- sch. 91 “Other income and expenses” subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses” - to reflect non-operating expenses.
Let's look at an example of how an accountant records the company's expenses associated with paying employees compensation for the cost of lunches.
Let’s imagine that employees of Oblaka LLC receive monthly compensation for the cost of food in the amount of 1,500 rubles: DEBIT
| 91-2 | 99-2 | 73 | 73 |
Using online cash registers for salary deductions
Cash register is used on the territory of the Russian Federation by all organizations and individual entrepreneurs when making payments, except for cases established by law (clause 1, article 1.2 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making payments in the Russian Federation ").
Settlements in accordance with Article 1.1 of Law No. 54-FZ are considered to be the acceptance (receipt) and payment of funds in cash and (or) by bank transfer for goods, work, services, including in the form of advance payment and offset of the cost of goods, work , services, or providing or receiving other consideration for goods, works, services.
Based on paragraph 4 of Article 4 of Federal Law No. 192-FZ dated 07/03/2018, organizations and individual entrepreneurs, when making settlements with individuals when providing or receiving other consideration for goods, work, services, must use cash register systems from 07/01/2019.
Thus, the employer is obliged to use an online cash register if the cost of:
- goods sold to him (see the concept of “payment” given in Article 1.1 of Law No. 54-FZ, explanations in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 30, 2018 No. 03-01-15/86884);
- services provided to him (see paragraph 4 of Article 4 of Law No. 192-FZ, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 25, 2019 No. 03-01-15/4355);
- issued uniform (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 12, 2018 No. 03-01-15/90372).
There is no need to punch checks when the employee is compensated for the cost of goods or services and then deducted from wages. For example, in cases where the organization:
- pays employees for mobile communications and deducts expenses for it from their salaries (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 25, 2019 No. 03-01-15/4355);
- purchases a work book form (insert in the work book), and then the employee reimburses these expenses (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 25, 2019 No. 03-01-15/4355);
- pays for parking spaces for employees’ personal cars and deducts reimbursement of these expenses from salaries (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 4, 2018 No. 03-01-15/87763).
You should not use cash register systems in many other cases, including when issuing funds on account. Employees return unspent accountable funds to the organization's cash desk. Letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 11, 2018 No. 03-01-15/65050 and dated February 8, 2019 No. 03-01-15/7892 indicate that such transactions are also not considered settlements for the purposes of applying Law No. 54-FZ.
The innovation associated with the use of cash register systems when deducting from wages does not introduce any changes from an accounting point of view.
The sale of goods or services does not change. The use of cash register only ensures the efficiency of recording a trade transaction that occurred at the time of payment of wages. The obligation to register deductions from wages for payment of goods and services by cash register check does not cancel the obligation to issue a check when transferring goods or services. Thus, the check is punched twice if the transfer of goods or services does not coincide with the moment of deduction of the cost from the salary.
Meals for posting employees - meals for employees are provided for in the labor (collective) agreement
A different situation with taxation of the cost of free meals at an enterprise arises when the provision of meals to employees is regulated by a labor or collective agreement.
Income tax
The costs incurred by the enterprise for organizing meals for employees are not taken into account when calculating the taxable base for income tax, since lunches are provided free of charge (or at a reduced cost) and are not provided for the purpose of providing special meals to certain categories of employees (clause 25 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
Unified social tax
Payments to employees are not subject to UST if the taxpayer company does not have these payments as expenses taken into account when calculating income tax. Since free meals are not issued on the basis of an employment contract, the cost of meals cannot be subject to a single social tax. That is, insurance contributions to the Pension Fund should not be paid from the cost of food. However, according to Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the expenses of a taxpayer company may include any labor costs, including accruals in kind. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the size of the income tax base on the cost of food only if it is provided for by labor or collective agreements.
If a manufacturing company, or a firm provides services or performs paid work, the cost of food for tax purposes is taken into account separately for production personnel and administrative and management specialists. This is done because the provision of food is related to wages, and it can be attributed to direct or indirect expenses of the company.
The enterprise's expenses for remuneration of production personnel are direct expenses, part of which is not written off at the end of the period, but relates to work in progress. The costs of paying managers are indirect and are written off in full at the end of the tax period to form the income tax base.
Cash receipt for deduction from salary in “1C:ZUP 8” (rev. 3)
In the 1C: Salaries and Personnel Management program, edition 3, in accordance with legal requirements, starting with version 3.1.10.78, the ability to mark deductions, which may be the basis for issuing cash receipts, has been added, and to transfer this information to the accounting program.
For deductions with the purpose Other deductions in favor of third parties
,
Deduction for settlements for other transactions
and the type of salary transaction
Deduction for other transactions with employees
on the
Accounting
, a flag has been added.
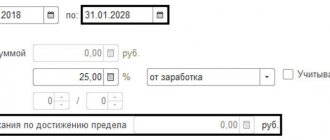
This is the basis for issuing a cash receipt
(Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Setting up a hold
When at least one deduction requires the issuance of a cash receipt and the corresponding flag is set in the settings, in the document Reflection of salaries in accounting
On the
Withheld salary
, additional columns appear:
Receipt
,
Description of deduction for check
.
The columns are filled in automatically from the document Retention for other transactions
, which registers the employee's deduction.
Example
The employer (canteen) provides a service outside the framework of labor relations: it provides lunches to its employees and deducts their cost from the employees’ salaries.
In the 1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8 program, edition 3, “Deduction for lunches”
with the flag set
Is the basis for issuing a cash receipt
(Fig. 1).
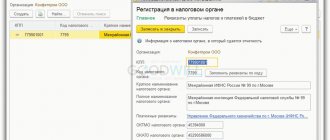
For employee S.S. Gorbunkov registered a document Retention for other transactions
in the
Retention field – “Retention for lunches”
(Fig. 2).
Retention
field is available when the program has several different types of retention configured. If one type of retention is configured, it is assumed by default.
Rice. 2. Document “Retention for other transactions”
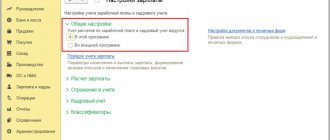
After salary calculation, the document Reflection of salary in accounting
(Fig. 3).
Fields Check
and
Detention Description for the check
are filled in automatically in the document.
Rice. 3. Document “Reflection of salaries in accounting” in “1C: Salaries and personnel management 8” (ed. 3).
In the process of synchronizing “1C: Salaries and HR Management 8” (rev. 3) with the program “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0) document Reflection of salaries in accounting
transferred to “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0).
Synchronization of "1C: ZUP 8" (rev. 3) with "1C: Accounting 8" (rev. 3)
Synchronization of programs must be previously configured.
The setup can be done in any of the programs: “1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8” (rev. 3) or “1C: Accounting 8” (rev. 3.0).
To do this, in the Administration menu - Data synchronization
you should set the
Data synchronization
on the link
Setting up data synchronization
.
In this case, in the second program, symmetrical settings occur automatically.
When synchronizing programs, data from reference books and documents is synchronized. In this case, only those directory elements that are used in the synchronized documents are synchronized: Reflection of salaries in accounting
and documents on payment and transfer of wages.
Synchronization can occur according to a schedule or by clicking the Synchronize
.