Income in kind and “non-natural”
People's income can be represented not only in the form of money, but also in kind. For example, individuals can receive in-kind income in the form of:
- food and personal hygiene products, clothing for those in need;
- products that are grown and produced by personal farming;
- production from hunting, fishing, picking berries and mushrooms in the forest, etc.
Question: A branch employee received income in the form of wages in kind from the parent organization. How to reflect this income in reporting forms 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL and to which budget is the personal income tax transferred? That is, income should be included in reporting at the location of the organization (head office) or at the location of the branch? The branch and head office are located in different regions. View answer
At the same time, the word “natural” is used not so much in the sense of “natural, natural”, but rather “intended not for sale, but for one’s own consumption.”
How to tax income in kind ?
IMPORTANT! From a tax point of view, such income, along with cash income, is also subject to accounting (that is, income tax is paid on it as well). This is written about in the Tax Code (Article 210). There (Article 226) it is established that firms, entrepreneurs, private lawyers and notaries must themselves calculate and pay personal income tax from the payer (most often we are talking about their employee who receives part of the salary in kind).
Who is the tax agent for non-cash income?
Income in kind is subject to income tax. Tax agents for all types of income in kind are (clause 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- legal entities and individual entrepreneurs;
- privately practicing notaries and lawyers;
- separate divisions of foreign organizations operating on the territory of the Russian Federation.
If they paid income in kind to the employee (or the person with whom the GPC agreement was concluded), they are required to pay taxes:
- calculate;
- withhold from the employee’s (taxpayer’s) income;
- transfer to the budget.
If for any reason the agent is unable to withhold personal income tax, he is obliged to notify the taxpayer himself and his Federal Tax Service about this in writing no later than March 1 of the year following the year in which such income was received by the taxpayer. To do this, a 2-NDFL certificate with attribute “2” is submitted to the employee (clause 5 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting for natural income
Special instructions have been developed for the accountant to take into account the employee’s natural income. They are given below:
- The natural share in income can be maximum equal to 20% of his salary, taking into account income tax (Article 131 of the Labor Code). But in this case, income that is not a type of salary (Article 129 of the Labor Code) is not taken into account - for example, travel allowances.
- If the employee receives part of the income in kind, then it is necessary to take into account the rules prescribed in paragraph 54 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2004 No. 2:
- the right to payment in kind is prescribed in an additional agreement to the employment contract or in a collective agreement;
- the employee voluntarily refuses money in favor of food or other goods, of which he has drawn up a written confirmation;
- goods issued as income in kind can only be intended for private use (for example, it is not allowed to give out part of the salary in the form of fittings);
- the cost of goods should not be higher than the price prevailing on the market.
- On the amount of income in kind, the amount of accrued VAT depends on what type of product it is paid for (rate 10% or 18%).
- The delivery of goods is accompanied by the delivery of a regular invoice, but the invoice is created in one copy and is not given to the employee.
- If the share of net profit from the sale of agricultural products produced in the company exceeds 70%, then the payment of wages to employees in the form of these products may not be accompanied by the accrual of VAT (clause 1, clause 1, article 146, clause 20, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
- Income in kind is subject to income tax and insurance contributions (clause 1, clause 1, article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation); in this case, insurance premiums are calculated based on the current market value of goods (Article 105.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and VAT and excise taxes are already taken into account in this amount.
- The price indicated in the documents is recognized as a market price if the Federal Tax Service was unable to provide evidence that this is not the case, and in the case where the taxpayer did not independently change the amount of tax (clause 6 of Article 105.3 of the Tax Code).
- Receipts in kind are taken into account regardless of the taxation system (general or simplified): see Art. 255, pp. 6 clause 1 art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letters of the Ministry of Finance dated May 27, 2016 N 03-03-07/30694, dated November 20, 2015 N 03-03-05/67502.
How to pay wages in kind ?
IMPORTANT! Salaries in kind cannot be paid with the following goods or financial obligations:
- alcohol and drugs;
- toxic, poisonous substances;
- ammunition and weapons;
- promissory notes;
- coupons.
The procedure for processing salary payments in kind.
According to the provisions of Article 130 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the system of basic state guarantees for remuneration of workers includes:
- limitation of remuneration in kind.
In accordance with the provisions of Article 131 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, wages are paid in cash in the currency of the Russian Federation (in rubles).
In accordance with a collective agreement or an employment contract, upon a written application from an employee, remuneration may be made in other forms that do not contradict the legislation of the Russian Federation and international treaties of the Russian Federation.
Payment of wages in kind may be in the form of products produced by the organization or other property and goods owned by the company.
It is also possible to provide the employee with the services he needs.
It must be taken into account that the property and goods with which wages are paid must be intended for the personal consumption of the employee and his family, and they must be issued at a reasonable price.
At the same time, the share of wages paid in non-monetary form cannot exceed 20% of the accrued monthly wage
In addition, payment of wages is not allowed
- in booms,
- coupons,
- in the form of debt obligations,
- receipts,
- in the form of alcoholic drinks,
- drugs,
- poisonous, harmful and other toxic substances,
- weapons,
- ammunition,
- other items for which prohibitions or restrictions on their free circulation have been established.
In order to comply with the requirements of current legislation, in the case of payment of wages to employees in kind, the employing organization must prepare an appropriate package of documents establishing the rules for paying wages in kind.
Such documents, for example, may include:
- Regulations on employee remuneration,
- Collective agreement,
- Employment contract,
- And so on.
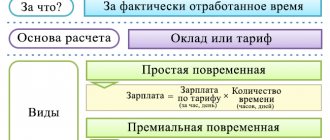
Wiring diagram
To correctly record the natural part of income, you should use the entries shown in the table:
| Wiring | Operation |
| D 20 (26, 44) - K 70 | payroll |
| D 70 - K 90 | issuance of goods as wages, including VAT on their cost |
| D 90 - K 68 | VAT accrual on the cost of transferred goods |
| D 90 - K 41 (43) | write-off of the cost of transferred goods |
Reflection of natural income in form 6-NDFL
Comments on filling out this form are contained in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 08/01/2016 No. BS-4-11/13984. Briefly the rules are:
- on 020 we write the amount of non-cash income received;
- 040 – income tax on this income;
- 070 – income tax on the rest of the salary;
- 100 – date of receipt of the natural part of the salary;
- 110 – date of receipt of the rest;
- 130 – the amount of the natural part of income.
IMPORTANT! Federal Law No. 212 contains a list of non-monetary receipts from which insurance premiums are not charged. These include:
- travel costs to and from work for persons working in the far north;
- costs of training employees in special professional educational programs;
- the amount of costs for uniforms required by law for some employees
- compensation payments to citizens (subsidies for food, utilities, free housing, etc.).
What is provided in natural form
Payment in kind can be made with any property that can be useful or suitable for use by the employee for personal purposes. The following may be issued in kind:
- Finished products;
- Product;
- OS;
- Materials;
- Raw materials, etc.
If the goods that are issued in the form of wages exceed their market value, then such a payment may be considered unreasonable. At the same time, market means the cost of goods, which is established in the employer’s region at the time of payment of wages (
Income in kind and preferential meals for employees
It happens that an organization holds a festive event, which includes free refreshments for employees. In short, in these situations, workers receive additional income in kind. However, you do not have to pay income tax on it. The corresponding position was stated by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in a Letter dated March 6, 2013. No. 03-04-06/6715.
The essence of the recommendation is that if a company cannot assess the benefit from the benefits received by employees, as well as personalize it, then personal income tax is not charged.
It’s a different matter if we are talking about an organized food system for employees (preferential or completely free). In this case, the company is obliged to keep records on the basis of coupons issued to employees or using a special journal where their visits to the canteen are recorded.
There is another system - employees can be given cards with which they pay for food, and at the end of the month, waste is recorded based on actual consumption.
Types of income
The procedure for taxation of income paid in kind is established by Article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Such income, in particular, includes:
- the cost of goods (work, services, property rights) fully or partially paid by the organization for an employee in his interests. For example, the cost of free meals or training not provided for by law (subclause 1, clause 2, article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the cost of goods (work, services) provided to an employee free of charge or with partial payment. For example, the cost of gifts, gift certificates or gift cards exceeding RUB 4,000. per year (subparagraph 2, paragraph 2, article 211, subparagraph 28, article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2012 No. 03-04-05/9-809, dated April 4, 2011 No. 03 -03-06/1/207);
- the cost of goods (work, services) issued as payment for labor (subclause 3, clause 2, article 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The cost of goods (work, services) that an organization pays for an employee in its own interests is not subject to taxation if the receipt of these goods (work, services) by the employee is directly related to the performance of his job duties. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 11 of paragraph 3 of Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, payment of bills from restaurants, visits to which is included in the program of entertainment events accompanying business negotiations conducted by the organization, is not subject to personal income tax. The basis for exempting such income from personal income tax may be an order to conduct such events and a list of employees who must take part in them. This was stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 3, 2015 No. 03-04-06/11078.
Income in kind and travel of employees
If work involves business travel or if additional expenses are necessary when traveling to work and home (for example, the office is located outside the city), the company is obliged to reimburse all travel costs. Often employees are provided with a travel ticket or compensation for the actual number of trips made. These funds are not income, which means they are not taxed. Therefore, it is incorrect to count them as income in kind.
IMPORTANT! Business travel expenses do not fall into this category. They are compensated by the employer in the manner prescribed by Article 168 of the Labor Code.
In general, accounting for the non-natural part of income does not take much time and effort. You just need to follow the instructions exactly and take into account the latest changes in relevant laws.