The cash flow statement process can be one of the most challenging issues, whether you are using US GAAP (if you are in the US) or IFRS (if you are in one of the more than 120 countries around the world. applying IFRS).
Many people have problems preparing cash flow because:
- This is the only accounting report generated on a cash basis rather than an accrual basis;
- Report items must be adjusted to exclude non-cash transactions, which can be quite difficult.
It may seem very complicated, but make no mistake, people make far more serious mistakes in the accounting process than they do in cash flow.
Let's look at the indirect method of preparing a cash flow statement in accordance with IAS 7. This method only works if you are aware of the following issues:
- You already know what a cash flow statement is and its components (main activities, investments, financial activities and results).
- You understand the basics of cash flow, the relationships between major financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, etc.), accounting itself, etc.
- You have access to various credentials. Sometimes you will need to make some adjustments, and you will be much more comfortable if you can quickly access the information you need.
- You remain calm and can concentrate on this wonderful task without nerves or stress.
[cm. See also full text of IAS 7]
Let's look at an example of a systematic approach for preparing a cash flow statement in Excel .
Keep in mind, this is only a demonstration of how cash flow can be done indirectly "by hand", step by step, and not an explanation of the details of individual adjustments or other technical details.
See also:
- CFA - Preparation of the Cash Flow Statement (Part 1): Relationship to the Balance Sheet and Operating Activities.
- CFA - Preparation of cash flow statement (Part 2): investment and financing activities, total cash flow.
- CFA - Direct and indirect methods of presenting cash flow from operating activities.
Investment operations
Cash flows from investment transactions include the purchase and sale of:
- various assets - equipment, vehicles, unfinished capital construction projects, etc.;
- shares (participatory interests) in other organizations, debt securities.
Read in the berator “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant”
Cash flows from investment operations
The data for filling out this section is taken from debit turnover on accounts 50, 51, 52, 58 subaccount “Cash equivalents” (minus received VAT) in correspondence with accounts 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” or 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors "
What should you pay attention to?
- Receipts in the form of dividends and interest on debt financial investments also belong to investment activities.
- Interest payments are shown as part of investment transactions if the company includes them in the cost of investment assets. If not included, they are reflected as part of current operations.
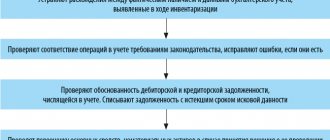
Structure and content of the cash flow statement
The report form was approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. The rules for drawing up are established by PBU 23/2011 “Cash Flow Statement”.
The report has three sections.
The first reflects cash flows from current operations. These are revenues and payments from the ordinary activities of the organization. Based on the results of such operations, as a rule, profit (loss) from sales is formed.
The second reflects cash flows from investment operations. These include the purchase and sale of vehicles, equipment, etc. Another example is financial investments other than the purchase of cash equivalents and investments intended for resale in the short term.
The third section shows flows from financial transactions. These are contributions from the founders, proceeds from the issue of shares, bank loans, etc.
Check the financial condition of your organization and its counterparties
The difference between a DDS report and a cash budget
The report reflects the fact of the operation, and the budget contains plans (PDDS) and projected indicators. The cash flow budget (CFB) is made up mainly by large enterprises to prevent cash gaps.
It is important for the manager to provide the current activities of the organization with free money for timely payment of obligations so that business processes are not interrupted. BDS is a cash flow forecast.
Report structure
For a user who does not have an economic education, the report will seem complicated at first. ODDS contains 3 sections; the code lines show monetary transactions based on 3 key indicators of the enterprise’s economic activity (described later in the article).
Not all cash movements are included in the report. Not included:
- currency exchange transactions;
- the amount received and deposited in the bank and credited to the company’s account;
- exchange of other liquid assets for money (equivalents);
- movements within the company between accounts in different banks.
Important information! The report includes financial transactions; the currency of the state in which these schemes were carried out is not important. In this case, all information in the ODDS is included in rubles per unit. changes approved for the balance sheet.
By Operations
The main activity (current) relates to events occurring in the economic life of the enterprise. The goal of any commercial company is to earn profit. Therefore, the main activity is aimed at receiving revenue from the sale of goods, works, and services. The flows or finances related to the main (operational) work are as follows:
- receipt of funds from customers;
- income from the transfer of property for short-term rent;
- settlements with counterparties for goods posted to the warehouse;
- transfers to the contractor for the accepted volumes;
- payment of wages to employees;
- payment of loan obligations received by the company from lenders, including interest.
ODDS does not include credit and borrowed funds spent on the purchase of fixed assets and intangible assets.
For investment transactions
This category includes cash flows related to the disposal and receipt of non-current assets (CA). For example:
- settlements with counterparties for the purchase or development of VA;
- payment of interest on loans received and loans spent on the acquisition of non-current assets;
- revenue from the sale of VA;
- issuance and repayment of loans;
- payments for the acquisition of shares and participation in the business of third-party companies and the repurchase of shares;
ODDS reflects income from dividend payments and interest on the securities of other legal entities.
For financial transactions
This includes events related to the contribution of money by the company’s founders to the authorized capital, receipt and return of borrowed funds, transfers of dividends to owners, settlements with them upon the sale of shares of the management company, proceeds from the issue of securities, and payments upon redemption.
Final indicators
Separate accounting is generated for each type of activity. Russian legislation provides for a direct method of preparing ODDS. To calculate receipts and payments, data is taken from the accounting accounts of cash and cash equivalents. Adjustments are not taken into account; how much money the organization received or spent is included in the report.
For each individual line of business, the balance of financial flows is displayed, added to the opening balance, and the amount remaining at the end of the period is calculated.
How to fill out Form 4 lines for 2022 - instructions
The cash flow statement consists of two parts:
- Introductory, which indicates basic information about the legal entity.
- Tabular, reflecting cash flow for the calendar year.
The introductory section shows the following information:
- the title of the report, reflecting the essence of the document.
- reporting period – 2022
- full name of the enterprise, main type of economic activity, details (codes);
- date of sending financial statements;
Unit of measurement of ODDS indicators: thousand rubles only.
Filling the table row by row
The report table is compiled for the full year 2022. The form must also contain indicators for the previous year 2022.
Comparing values for different reporting periods will help establish the facts that influenced the movement of financial flows. Receipts of money and payments of DS are taken into account in 3 areas described earlier in this article.
Rice. 1 Example of filling out the ODDS
The table shows the structure of the DDS report by type of cash flows reflected during the reporting period. All payments are indicated in parentheses, since these are expense transactions (minus).
| Line code | The name of indicators |
| Financial flows from the company's operating activities | |
| 4 110 | Cash flows from current operations, total |
| 4 111 | Including: from the sale of products, goods, services, works |
| 4 112 | Money received for rent, license, commissions, royalties and similar income |
| 4 113 | Resale of existing investments |
| 4 119 | Other cash receipts not reflected in 4,111 – 4,113 |
| 4 120 | The total amount of payments made for the main activity is summed up by lines 4,121 to 4,129 |
| 4 121 | Including: payments to counterparties for capitalized goods and materials and services |
| 4122 | Transfers of wages to employees |
| 4 123 | Interest payments on company obligations (debt) |
| 4 124 | Paid income tax |
| 4 125 | Payments of insurance premiums to the Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund |
| 4 126 | Other taxes not included in lines 4,124 and 4,125 |
| 4 129 | Other money transfers for the reporting period |
| 4 100 | The balance of cash flows from operating activities. The sum of the lines is 4,110 – 4,120. |
| Cash flows from investing activities | |
| 4 210 | Total amount of receipts, addition of line indicators from 4,211 to 4,219 |
| 4 211 | Proceeds from the sale of VA, except for those indicated on line 4,210 |
| 4 212 | Sold shares of third-party companies (shares) |
| 4 213 | Loans previously provided to borrowers were returned, sales of claims, bonds and more |
| 4 214 | Interest received for the loan provided, income in the form of dividends, |
| 4 219 | Other types of income |
| 4 220 | The total amount of payments under this section, summing up indicators from 4,221 to 4,229 |
| 4 221 | Including: payments related to the purchase, creation and modernization of VA |
| 4 222 | Purchased shares of third-party companies (participatory interests) |
| 4 223 | Loans were issued at interest, bonds and rights of claim under assignment agreements were purchased |
| 4 224 | Interest paid, other obligations on the investment package |
| 4 229 | Other types of payments |
| 4 200 | The rest of the money from investment work |
| Cash capital from financing activities | |
| 4 310 | Total amount of receipts, summing lines 4,311 – 4,319 |
| 4 311 | Credits and loans received |
| 4 312 | The founders of the company made contributions to the authorized capital |
| 4 313 | Proceeds from the issue of securities or increased participation interests in other organizations |
| 4 314 | Share premium from bonds, redemptions of bills, and other debt securities |
| 4 319 | Other cash receipts |
| 4 320 | The total amount of payments made while conducting financial activities. Summing rows 4,321 – 4,329 |
| 4 321 | Payments for the repurchase of shares, participation interests from owners or the withdrawal of founders from the membership of the company |
| 4 322 | Dividends or other payments paid to owners when distributing net profit |
| 4 323 | Repayment of loans, repayment or redemption of debt instruments |
| 4 329 | Other payments |
| 4 300 | Cash balance from financing activities, summing lines 4,310 to 4,320 |
| 4 400 | Balance of cash flows for the reporting period, sum of lines 4,100, 4,200 and 4,300 |
| 4 450 | Balance of money at the beginning of the calendar year |
| 4 500 | The same for the end of the reporting year. Amount line 4,450 and 4,400 |
The cash flow statement form for 2022 can be downloaded on our website. Additionally, the form is attached as a separate document in Excel format - sample.
ODDS (sample report)
ODDS (filling example)
What is the procedure for filling out sections
The basic rules for drawing up an ODDS are given in PBU 23/2011. When forming the ODDS, take into account a number of nuances:
- Receipts from the sale of goods and transfers to suppliers are reflected without VAT.
- Value added tax and excise taxes are reflected in total and in a separate line - in current operations. If the VAT charged to buyers exceeds the input VAT, then reflect the difference in line 4119, and if it does not exceed, then in line 4129.
- Employee remuneration, income tax and other salary deductions (insurance contributions) are entered in line 4122.
- Income tax is recorded in line 4124 “Organizational income tax.”
- The remaining taxes are recorded in total in line 4125.
See the table for how to fill out the DDS report by section:
| ODDS section title | The order of filling them out and deciphering the lines in form 4 (as it was called before), in 2022 this is the OKUD form 0710005 |
| For current transactions | We indicate cash flows from current operations:
|
| For investment transactions | We determine the flows from investment activities:
|
| For financial transactions | We calculate flows from financial transactions:
|
| Final indicators | In line 4400 we indicate the balance (the difference between income and expenses) for the reporting year. In line 4450 we determine the balance of cash and equivalents at the beginning of the period, and in line 4500 - at the end of the year. In line 4490 we write down the magnitude of the impact of changes in the foreign currency exchange rate to the ruble. |
Where to get data for the DDS report
Inga:
“The main sources of information for DDS are a bank account statement and a cashier’s reporting form if you work with cash. It is usually developed by a financial manager.
Basic information this form should contain:
- how much money was in the cash register at the beginning of the day
- how much was received at the end of the day
- how much goods were sold for?
- how much was paid in cash
— how many payments were made by bank card?
In the DDS report, all money is distributed to wallets - these are the places where the company’s funds are located: current account, cash register, wallets in various electronic payment systems, if you work with them.
In the DDS report templates that are available on the Internet, a separate sheet is provided for wallets. It shows how much money the company has now and where it is: so much in the account, and so much in the cash register. And the line about each transaction reflects its date, how much money came or went, from which wallet, under what item of income or expense and to what activity of the company this item relates.
For example: “06/15/2021, $5000, current account, purchase of goods, operating activities.”
What report generation methods are used?
Direct or indirect methods are used for reporting.
Straight
When using the direct method, cash flows are taken into account as a calculation of the company's cash outflows and inflows. Net financial flow is defined as receipts from the main activity minus expenses for the purchase of goods, works and services, operating costs, tax payments, loan interest, dividends, etc.
Indirect
The indirect method is the accounting of cash according to the income statement and balance sheet. The movement of money is reconciled with the profit that the organization received from conducting its main economic activities. Items such as depreciation, provisions and impairments are added to net income because no cash is involved in such transactions.
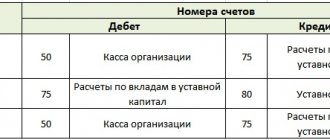
Example of a table for DDS
Let's draw up a table using the example of a company that is engaged in wholesale sales of goods, as well as the provision of services. In addition, the company rents out its existing office space.
The online university “Netology” will help businessmen learn how to build business processes and manage finances.
Take the “Finance for Entrepreneur” course with an extensive program and you will receive all the necessary knowledge to run your own business.
Have an easy year everyone and successful work with management reporting!