Composition of annual financial statements
The composition of the annual financial statements is fully regulated by Art. 14 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
Annual financial statements, in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 14 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ dated December 6, 2011, consists of a report of financial results and an appendix to it, as well as a balance sheet.
The category of applications includes (clauses 2, 4 of Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n):
- Report regarding cash flows;
- Report on changes in capital;
- Report on the intended use of funds (required for non-profit organizations);
- Other explanations or applications.
The annual financial statements have a clear form, which is approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n.
What do the annual financial statements for 2018 consist of?
The composition of the annual financial statements is regulated by Art. 14 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and looks like this:
- The balance sheet, which is one of the most important accounting documents and reflects the financial and economic condition of an organization or individual entrepreneur. The balance consists of 5 sections:
- Non-current assets (state of fixed assets, intangible assets).
- Current assets (accounts receivable up to 1 year, short-term financial investments, etc.).
- Capital and reserves (authorized capital, additional capital, etc.).
- Long-term liabilities (accounts payable from 1 year, etc.).
- Short-term liabilities (for example, loans for up to a year).
Read more about the contents of the balance sheet and the rules for filling it out in this publication . You can also download its template here.
- The financial results statement, which is an important document reflecting the indicator of net profit or loss, formed taking into account the following indicators:
- revenue;
- cost;
- expenses - administrative, commercial, interest payable, etc.;
- income - from participation in other companies, etc.;
- current income tax and adjustments related to discrepancies between accounting and tax accounting data.
- explanations for these forms - do not have a set format and are necessary to disclose general indicators given in two main forms;
See details here .
- cash flow statement;
- statement of changes in equity;
- report on the intended use of funds.
More details about the use of the listed reports and the procedure for filling them out are described in the material “Filling out forms 3, 4 and 6 of the balance sheet” . Here you will find forms of these documents.
The annual financial statements may also include an auditor's report.
This article will help anyone who needs it to figure it out.
See also: Can the tax office impose a fine if an audit report is not submitted?”
All organizations and entrepreneurs are required to prepare annual accounting statements, with the exception of those persons who have the opportunity to use a simplified type of annual accounting statements (or not prepare them at all), namely:
- small business;
“Balance Sheet for Small Enterprises (Features)” will help you understand when this category has the right to draw up a simplified balance sheet, and get acquainted with the nuances of filling it out .
- non-profit enterprises;
- participants of the Skolkovo project.
Basic regulations for the preparation of annual financial statements
The most important requirement is complete reliability of the data. In other words, each indicator must be reliable, so that whether an internal or external user, there is no doubt about the results of business activities.
Data must meet timeliness criteria, which significantly affects the quality of the annual report. Data must be reflected in the reporting period in which they actually occurred.
The principle of completeness, according to which financial statements should display data as completely as possible.
All reporting indicators must be comparable. This means that data from declarations and registers must have a logical relationship.
When completeness of data is missing for any reason, then this fact must be indicated in the explanatory note.
Main users of financial statements
An enterprise must have a consolidated form of accounting information, which is what annual financial statements are.
Based on this, accounting information must have target users who will use it for various purposes. Therefore, users are divided into external and internal.
The category of external users consists of government bodies: the Federal Tax Service, the Social Insurance Fund, the Pension Fund, and the Federal State Statistics Service. Legal entities and individuals are also considered external users, because accounting statements must necessarily comply with the principles of publicity and openness.
Internal users are considered to be higher-level organizations (if any), company managers, and various management departments (if the company is large).
Features of preparing financial statements
Features of the preparation and presentation of accounting (financial) statements:
- when reorganizing a legal entity - Art. 16 Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ;
- upon liquidation of a legal entity - Art. 17 Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ;
- the composition, features of the preparation and presentation of accounting (financial) statements of public sector organizations are established by the Budget Code, Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2010 N 191n (clause 4 of Article 14 of the Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ);
- The composition, features of the preparation and presentation of the accounting (financial) statements of the Central Bank are established by the Federal Law of July 10, 2002 N 86-FZ (Clause 5 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ).
Mandatory annual financial statements of the organization for 2020 in 2022
The end of March is approaching, so all accountants in the country are preparing for the important task of submitting annual financial statements. In addition to the well-known balance sheet, it is also necessary to submit an application to it, which is required by the Federal Tax Service. Further details about the applications themselves and deadlines.
The set of annual reports consists of a report of financial results, a balance sheet and several appendices (Part 1 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). The nuances and subtleties are well covered in PBU 4/99.
Different types of applications:
- cash flow statement;
- statement regarding changes in capital;
- a note with an explanation (clauses 2 and 4 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 23, 2013 No. 03-02-07/2/18285);
- current report on the intended use of funds (required only for non-profit organizations. 2 Article 14 of Law No. 402-FZ).
The reporting deadline is 03/31/2021. There is no need to submit it separately, because everything is submitted in one package of documents. The simplified accounting procedure is designed for small businesses.
GENERAL PROCEDURE FOR PREPARATION OF ANNUAL REPORTS
Accounting (financial) statements are information about the financial position of an economic entity as of the reporting date, the financial result of its activities and cash flows for the reporting period, systematized in accordance with the requirements established by the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” "(as amended on July 26, 2019; hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 402-FZ). The obligation of organizations to prepare a Report is stated in paragraph 1 of Art. 3 of this Law.
To ensure the reliability of the Report, organizations at the end of the reporting year:
Note!
It is mandatory to conduct an inventory before preparing annual financial statements[1].
After completing the listed activities, you can prepare a Report. General requirements for the Report[2]:
• information in reporting must be reliable. This requirement follows from the basic rule of accounting in the Russian Federation: all entries in accounting accounts and accounting entries are compiled on the basis of primary documents drawn up in accordance with Art. 9 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ.
Accounting (financial) statements must be prepared on the basis of data contained in accounting registers, as well as information determined by federal and industry standards[3];
• reporting should include performance indicators of all divisions of an economic entity, including its branches and representative offices, regardless of their location[4];
• reporting is prepared in the currency of the Russian Federation, i.e. in Russian rubles[5];
• reporting is considered completed after it is signed by the head of the economic entity[6];
• reporting is approved and published in accordance with the procedure and cases established by federal laws.
Note!
If federal laws and (or) constituent documents of an economic entity provide for the approval of the accounting (financial) statements of the economic entity, it is not allowed to make corrections to them after their approval[7].
Publicity of reporting
For a certain range of companies, publication of financial statements is a mandatory procedure. After all, all interested parties must have free access to data that characterizes the activities of the enterprise (Clause 9, Article 13 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
Whether or not it is necessary to publish an organization’s statements can be found out from the law that regulates the company’s activities. For example, we can take self-regulating companies that are required by law to publish reports (clause 11, clause 2, article 7 of Federal Law No. 315-FZ of December 1, 2007).
Also, joint stock companies are required to disclose data from their annual reports (clause 1, article 92 of Law No. 208-FZ of December 26, 1995).
The deadline by which everything must be published is June 1 (according to clause 46 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 6, 1999 No. 43N).
Frequency of preparation of accounting (financial) statements
An economic entity must compile annual accounting (financial) statements (Clause 2, Article 13 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ).
Interim accounting (financial) statements (for a reporting period of less than a year) are prepared by an economic entity in cases where legislation, agreements, constituent documents or decisions of the owner of the economic entity establish the obligation to submit them (Clause 4, Article 13 of Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402 -FZ).
Features of the balance sheet
According to the manual, the balance sheet (aka F-1) consists of liabilities and assets, including sections, in each of which there are lines containing data on certain types of property or liabilities.
The asset includes 2 sections:
- Fixed assets
Here you can find information about intangible assets, R&D, fixed assets, long-term financial investments, that is, about property that is not quickly sold.
- Current assets
They are called short-term assets or quickly realizable: accounts receivable with a maturity of no more than 1 year: inventories, cash, short-term financial investments.
The passive contains 3 sections:
- Reserves and capital
The section reflects data on the organization’s capital (additional, reserve, authorized), as well as retained earnings (uncovered loss).
- long term duties
If the maturity is more than 12 months, then it is a long-term liability (estimated, deferred, borrowed).
- Short-term liabilities
This section displays information on obligations that have a maturity of less than a year, as well as accounts payable, borrowed funds, estimated and other obligations.
Balance sheet figures must be provided as of one of the following dates:
- reporting date (in any case, this is December 31 of the reporting year);
- December 31 of the previous year;
- December 31 of the year, before the previous one.
The balance lines are coded, and the code itself is taken from Appendix 4 to Order No. 66n.
An example of correctly filling out a balance sheet
For example, Flagi LLC was founded in 2022. The director and chief accountant in one person, at the end of the year, compiled a current balance sheet based on the balance sheet for the accounting accounts. Due to the fact that this is the first year of activity, there are simply no indicators for the past 2 years. Available account balances are well presented in the table.
| Account debit balance | Amount, thousand rubles | Account credit balance | Amount, thousand rubles |
| 01 | 100 | 02 | 14 |
| 10 | 74 | 60 | 40 |
| 19 | 37 | 62 | 45 |
| 50 | 15 | 66 | 39 |
| 51 | 88 | 69 | 14 |
| 70 | 37 | ||
| 80 | 10 | ||
| 84 | 115 |
The difference between accounts 01 and 02 is entered in line 1150 of the balance sheet, namely, the residual value of fixed assets is reflected.
Available balances on account 10 are recorded in line 1210. VAT must be taken into account in line 1220. All funds are displayed in line 1250 of the balance sheet asset (15 + 88 = 103).
There is a separate line 1310 for the authorized capital, and line 1370 for indicators of retained earnings.
The balance of account 66 (loans) is illustrated in line 1510. All debt to creditors is in line 1520 (40 + 45 +14 +37 = 136).
At the final stage of filling out the balance, you need to compare lines 1600 and 1700 - they must be equal. In the example given, the balance sheet total is 300 thousand rubles.
Income statement
Many people call this report Form No. 2. The approved form does not have line codes, so you enter them yourself.
Some changes have also been made to the income statement template. Some lines were excluded, and some received new names. The changes will come into force with the reporting for 2020.
When drawing up a balance sheet, you can take account balances as a basis. Account turnover will be needed for the financial results report.
Below is a brief summary of each line:
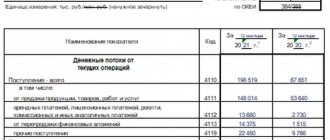
Code 2110 - turnover on the credit of account 90 “Revenue”. If we assume that Flags LLC managed to earn 11,000 thousand rubles.
Code 2120 - turnover on the debit of account 90. The cost of goods, work, products sold, etc. is recorded in this place. Let’s say that Flagi LLC allocated costs for production costs in the amount of 7,000 thousand rubles.
Code 2100 is the difference between lines 2110 and 2120. It turns out that in our example the calculation is as follows: 11,000 - 7,000 = 5,000.
Code 2210 - turnover on the debit of account 90. In this line we will write down the commercial expenses (account 44) of Flagi LLC, which amounted to 1,500 thousand rubles.
Code 2220 - turnover on the debit of account 90 “Cost of sales” in correspondence with account 26. The accountant will enter the amount of 1,300 thousand rubles into the report.
Code 2200 = line 2100 - 2210 - 2220. The profit of Flagi LLC will be 2,200 thousand rubles. (5,000 - 1,500 - 1,300).
Code 2340 - turnover on the credit of account 91 (amounts on lines 2310 and 2320 are not taken into account).
Code 2350 - turnover on the debit of account 91 minus line 2330.
Code 2300 = line 2200 + line 2310 + line 2320 + line 2340 - line 2330 - line 2350.
Code 2410 - accrued income tax (20% of line 2300). Flags LLC has a profit of 144 thousand rubles. This means that the tax is 29 thousand rubles. (144 x 20%).
Code 2400 = 2300 - 2410 - 2460. You also need to take into account lines 2430 and 2450 (either subtract or add depending on the sign of the line).
Appendixes to the balance sheet and income statement
Experts know that forms No. 3, 4 and 6 of the accounting report are part of the annual financial statements and at the same time appendices to the main forms (financial results and balance sheet):
- a report showing changes in capital or Form 3;
- a report showing cash flow or Form 4;
- a report showing the intended use of funds or form 6.
The forms of the main reporting forms and application forms are officially approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia.
Simplified accounting reporting
Simplified annual accounting (financial) statements consist of (clause 6 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n):
- balance sheet;
- financial results report;
- report on the intended use of funds (only for non-profit organizations);
- appendices to the balance sheet, statement of financial results, report on the intended use of funds, which provide only the most important information, without knowledge of which it is impossible to assess the financial position of the organization or the financial results of its activities.
Statement of changes in equity
To show changes in capital, there is Form 3 in the balance sheet. This displays information regarding the organization’s equity capital, which includes:
- Extra capital;
- retained earnings;
- authorized (share) capital;
- other reserves.
The report also displays data on own shares that were purchased from shareholders.
Form number 3 has 3 sections:
- Movement of capital
This table clearly illustrates changes in capital over 2 years - decrease or increase, what influenced it.
- Adjustments related to changes in accounting policies and correction of errors
The section contains information about adjustments to capital that are associated with various changes in accounting policies. In turn, changes may be caused by errors that were present in the reports of previous years.
- Net assets
The section contains information about the net assets of the enterprise for the previous 2 years and reporting (according to the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 28, 2014 No. 84n).
Forms of accounting (financial) statements
The forms of annual accounting (financial) statements are established:
- for simplified accounting (financial) statements - Appendix No. 5 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n;
- for accounting (financial) statements prepared in the general manner - appendices No. 1 and 2 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n.
Interim accounting statements are prepared in accordance with the forms established by law, contracts, constituent documents or decisions of the owner of an economic entity (clause 3 of article 14 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ; clause 49 of PBU 4/99).
Report on the targeted expenditure of funds
The sixth form of balance sheet is intended for legal entities that have received targeted funding or non-profit organizations.
This form of report for non-profit organizations is the main one, because it fully discloses information about the intended use of funds. The balance sheet contains indicators of the balance of funds, expenditures and receipts during the reporting period, as well as balances at the end of the year. Form No. 6 can be filled out in two ways: simplified and complete.
Error correction
Sometimes there may be errors in accounting that can significantly distort the data. When an error is found before reporting is generated, then it is corrected by the date of the reporting year, but there are nuances:
- The accountant found an error in the reporting year. Then the reversing entries will be entered by the month of discovery.
- The accountant found a mistake in the new year. In this case, the correction is made in December.
The reporting has already been submitted, then errors should be corrected this year. The postings will contain account 84. It is worth knowing that reporting is not resubmitted. Adjustments will need to be made for the current year, by correcting the opening balance, as well as other reports.
Detailed instructions are available in PBU 22/2010.
Corrections have been made to the accounting (financial) statements
The rules for making corrections to financial statements are established by PBU 22/2010.
Features of preparation and presentation of accounting (financial) statements
Accounting (financial) statements are considered prepared after signing a copy of it on paper by the head of an economic entity (Clause 8, Article 13 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ).
Interim accounting (financial) statements are approved in the manner established by law, contracts, constituent documents or decisions of the owner of an economic entity (clause 3 of article 14 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ; clause 49 of PBU 4/99).
In most cases, annual accounting (financial) statements are subject to approval by the highest management body of the company, and in some cases - mandatory publication (clause 9, article 13 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ; clause 6, clause 2, art. 33 of the Law “On LLC”; paragraph 11, paragraph 1, article 48 of the Law “On JSC”, etc.).
A trade secret regime cannot be established in relation to accounting (financial) statements (Clause 11, Article 13 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011).
1C: Accounting 8
“1C: Accounting 8” is the most popular accounting program that can take accounting automation to a whole new level. A convenient product and services connected to it will allow you to effectively solve the problems of the accounting department of any business!
- Support of different tax systems, maintaining accounting and tax records, submitting reports;
- Inventory accounting, batch accounting, settlements with counterparties, extracting primary documents;
- Payroll calculation, accounting of cash transactions;
- Integration with other 1C programs and websites;
- Working with electronic certificates of incapacity for work (ELS).
Try 30 days free Order
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter