In 2022, amendments were made to Instruction No. 157n (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 14, 2020 No. 198n). Already now it is necessary to take into account the property that employees use even during non-working hours, all medical products, and not just medicines.
In what cases will posting 0.401.10.172 help, when you should not use the “red reversal”, what new accounts have appeared - about this and more in more detail.
- Accounts
- Innovations in analytical accounting
- Fixed assets
- Material reserves
- Land
- Calculations for financing transactions from budgets
- Other accounting objects
- Rights to use intangible assets
- What amendments need to be taken into account from 2022?
- Technical amendments to the Instructions
- Procedure for transition to new rules
Accounts
Own analytical codes of synthetic accounts and off-balance sheet accounts can be entered into the working chart of accounts only taking into account the requirements of the body to which the institution submits reports (consolidation entity). The order to change the Instructions does not indicate what to do with already established additional accounts. The requirements are expected to be met for all accounts that are reported after the amendments become effective.
Divide deferred income by date of recognition in the financial result. Account the amounts you plan to include as current year income in your 401.41 account. Reflect the remaining amounts on account 401.49 “Deferred income to be recognized in subsequent years.”
On off-balance sheet account 27, among other things, take into account fixed assets for the personal use of employees. This is property that they use also outside the institution and outside of working hours. Previously, the Instructions did not talk about off-balance sheet accounting of such objects, so the issue was controversial.
According to account 105.01, in addition to medicines, take into account all medical products that the institution uses for medical purposes. The purpose of the account was brought into line with code 341 KOSGU.
For some amendments, there are discrepancies in the application dates. Thus, accounts 114.87 and 114.88 were introduced into the Unified Chart of Accounts and Instruction No. 157n to account for the reserve for reducing the value of inventories. According to the standard, these reserves must be reflected from 2020, however, new accounts are valid from accounting for 2022. According to amendments to the charts of accounts No. 162n, No. 174n and No. 183n, these accounts must be applied from reporting for 2022. Thus, the innovation must be introduced starting this year.
Features of budget accounting
Just as in commercial companies, in the public sector the organization of accounting is guided by the Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 129-FZ.
In addition, enterprises use the Instructions for accounting of institutions and organizations on a budget (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 107 n), the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, the Chart of Accounts for budgetary accounting and instructions for its application, adopted by the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 16, 2010. No174н.
Perhaps the most important distinguishing feature of accounting in budgetary organizations is the use of a special Chart of Accounts, which includes the so-called budget classification, consisting of 26 categories.
Each of these categories carries information about the organization. For example, in categories 1 to 17 the classification of income and expenses, as well as sources of subsidies, are coded. Bit 18 contains data on types of activities, each of which is also assigned a specific number.
Look, number 1 is indicated when organizations work with funds that are in temporary use, 2 - are engaged in activities that generate income for the institution, number 3 is indicated if budgetary activities are carried out.
We will look at the budget chart of accounts in more detail in our next article.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that the reporting of public sector employees differs from companies engaged in commercial activities.
The general composition of budget reporting is determined by clause 3 of Art. 264.1 BC RF.
“Balance sheet of a state (municipal) institution” (f.0503730);
By and large, the essence and structure of the balance sheet is similar to the balance sheet of commercial organizations. It also reflects the organization's property - assets
, and collateral -
liabilities
.
However, due to the specifics of budget accounting, the balance sheet of budgetary institutions consists of financial
and
non-financial assets
. Liabilities are not divided into short-term and long-term.
But with regards to property, on the contrary, the budget balance sheet deciphers the initial cost, residual value, depreciation in more detail, and especially valuable property is highlighted separately.
“Report on the financial results of the institution” (f.0503721);
The report implies a more detailed classification of income and expenses. Budget funds
are allocated to a separate block .
There are also other forms of reporting that are unique to budgetary organizations.
Filing reports also has its own specifics and a special procedure, enshrined in Instruction No. 33n
Recipients of budget funds report to a higher organization, that is, to the founder. In turn, the latter is obliged to generate consolidated (consolidated) reporting for transfer of the corresponding budget to the financial authority (according to clause 11 of Instruction No. 33n).
I will note some more information regarding budget accounting, such as the peculiarities of accounting for fixed assets, cash accounting, as well as accounting for settlements with debtors and creditors, industry-specific accounting features, which I will certainly talk about in the following articles.
Fixed assets
Restore objects on the balance sheet by posting to account 0.401.10.172. The instructions gave two cases when such wiring is done.
First situation:
An object that no longer meets the criteria of an asset was written off to off-balance sheet account 02. At the same time, the owner of the property demanded that the property be used for a different purpose or transferred to another institution.
Second situation:
the property is accounted for in off-balance sheet account 21 and the owner demanded that the property be transferred free of charge to another copyright holder.
When transferring fixed assets to employees for personal use, reflect the property in off-balance sheet account 27. Similar objects worth more than 10 thousand rubles. continue to account for 0.101.00.000, reflecting the internal movement on it.
If, after dismantling the inventory group, an asset is taken into account again, assign it a new inventory number. Do not use the inventory number of the complex of objects and the internal inventory numbers of objects within the group in the future.
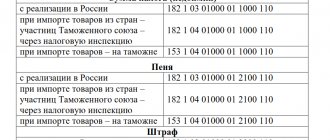
Instruction 174n as amended for 2022 - changes in the chart of accounts (account 101)
Let's look at the main changes in account 101 00 000 “Fixed Assets”:
1. New wiring has appeared. When fixed assets are transferred for financial lease (gratuitous perpetual use) by the lessor (lender), the disposal of fixed assets classified as non-operating (financial) environment objects is reflected in the following entries:
| DEBIT account 0 401 10 172 “Income from transactions with assets” of the corresponding analytical accounting accounts: |
| 0 104 00 000 “Depreciation” |
| 0 114 00 000 “Impairment of non-financial assets” |
| CREDIT of the corresponding analytical accounting accounts account 0 101 00 000 “Fixed assets” |
2. A new group 00 “Fixed assets – property in concession” and analytical accounting accounts were introduced:
| Analytical accounting account | Account names |
| 0 101 91 000 | “Residential premises = property in concession” |
| 0 101 92 000 | “Non-residential premises (buildings and structures) – property in concession” |
| 0 101 94 000 | “Machinery and equipment – concession property” |
| 0 101 95 000 | “Vehicles – concession property” |
| 0 101 97 000 | “Biological resources – property in concession” |
| 0 101 98 000 | “Other fixed assets – property in concession” |
3. The group of accounting accounts 0 101 40 000 “Fixed assets – leased items” and analytical accounts for it (0 101 (41 – 48) 000) are excluded.
4. The following accounts have been excluded:
| Analytical accounting account | Account name |
| 0 101 18 000 | “Other fixed assets – real estate of the institution” |
| 0 101 21 000 | “Residential premises are particularly valuable movable property of an institution” |
| 0 101 23 000 | “Structures are especially valuable movable property of an institution” |
| 0 101 31 000 | “Residential premises – other movable property of the institution” |
| 0 101 43 000 | “Structures – leased items” |
5. Certain account names have been changed:
| Account name in the old version | Name of the account in the new edition |
| 0 101 26 000 “Industrial and business equipment - especially valuable movable property of the institution” | 0 101 26 000 “Industrial and economic equipment - especially valuable movable property of the institution” |
| 0 101 27 000 “The library collection is a particularly valuable movable property of the institution” | 0 101 27 000 “Biological resources are particularly valuable movable property of the institution” |
| 0 101 33 000 “Structures – other movable property of the institution” | 0 101 33 000 “Investment real estate” – other movable property of the institution |
| 0 101 36 000 “Industrial and business equipment - other movable property of the institution” | 0 101 36 000 “Industrial and economic inventory - other movable property of the institution” |
| 0 101 37 000 “Library collection – other movable property of the institution” | 0 101 37 000 “Biological resources – other movable property of the institution” |
Material reserves
Restore objects accounted for off-balance sheet accounts 02, 03 and 07 to account 0.105.00.000 by posting to account 0.401.10.172. Do this if the owner has demanded that the supplies be transferred free of charge to another institution.
In a similar manner, take into account the return of inventories that were in the personal use of employees and were listed on off-balance sheet account 27.
Attribute the cost of consumed material reserves, among other things, to accounts 0.401.20.214, 0.401.20.223, 0.401.20.263, 0.401.20.265 and 0.401.20.267.
When changing the purpose of the inventory, change its accounting group by internally moving the debit and credit of account 0.105.00.000.
Accrue the reserve for the reduction in the cost of goods, finished and biological products by posting to the debit of account 0.401.20.274 and the credit of accounts 0.114.87.440, 0.114.88.440. When these inventories are disposed of or their planned selling (distribution) price increases, reduce the reserve by reverse posting. In relation to inventories that were sold at reduced prices during the reporting period, write off the balances from accounts 0.105.07.440, 0.105.08.440 to reduce the reserve for the debit of accounts 0.114.87.440, 0.114.88.440.
Calculations for financing transactions from budgets
Reflect transactions with interbudgetary transfers, subsidies to budgetary and autonomous institutions with the entries that the Ministry of Finance provided in system Letters dated January 15 and February 4, 2022. These correspondence were recorded in the instructions for the charts of accounts.
Regarding subsidies to budgetary and autonomous institutions, it was also prescribed that such institutions reflect the income of the current period based on information about the fulfillment of the conditions for the provision of funds. Such information may be a subsidy report, notice (f. 0504805) or another document that is enshrined in the agreement. The Ministry of Finance also explained in what situation each of these documents should be used. Previously, the guidelines for the notification form were also clarified.
For recipients of targeted interbudgetary transfers, we have additionally changed the account on which the balances of unused funds from the previous year are formed for return. Such amounts should be reflected in account 0.303.05.000, and not in account 0.205.00.000. Note that a similar procedure is used by budgetary and autonomous institutions when reflecting the balances of last year’s subsidies for return.
Instruction 174n as amended for 2022 - changes in the chart of accounts (account 104)
Account 104 00 000 “Depreciation” for accounting for depreciation charges has been adjusted to a significant extent:
1. Accounts excluded:
| Analytical accounting account | Name |
| 0 104 18 000 | Depreciation of other fixed assets – real estate of the institution |
| 0 104 21 000 | Depreciation of residential premises – especially valuable movable property of an institution |
| 0 104 23 000 | Depreciation of structures - especially valuable movable property of the institution |
| 0 104 31 000 | Depreciation of residential premises - other movable property of the institution |
| 0 104 43 000 | Depreciation of structures – leased items |
2. The name of the accounting group for account 0 104 40 000 has changed. Now the name is “Depreciation of rights to use assets”, previously it was “Depreciation of leased items”.
3. A new accounting group for account 0 104 40 000 “Depreciation of property in concession” was introduced.
4. New budget accounting entries have appeared:
| Operation | DEBIT | CREDIT |
| Termination of the right to use assets upon early termination of the agreement under which operating lease items were taken into account (disposal of an accounting item) must be reflected in the amount of accumulated depreciation of the right to use assets. | ... corresponding analytical accounting accounts account 0 104 40 000 “Depreciation of rights to use assets” | ... corresponding analytical accounting accounts account 0 111 40 000 “Rights to use non-financial assets” |
| Termination of the right to use an asset (subject to full execution of the contract) (disposal of an accounting object) must be reflected in the amount of the book value of the right to use the assets. | ... corresponding analytical accounting accounts account 0 104 40 000 “Depreciation of rights to use assets” | ... corresponding analytical accounting accounts account 0 111 40 000 “Rights to use non-financial assets” |
Other accounting objects
If, according to one estimate, you create a complex of non-financial asset objects, reflect the disassembly of investments by internal movement in the debit and credit of account 0.106.00.000.
In case of early termination of a lease or gratuitous use agreement, write off the account balances 0.111.40.000, 0.205.20.000, 0.302.20.000, 0.401.40.000, 0.401.50.000 with entries opposite to those that you reflected when recognizing the objects in accounting. Do not use the “red reversal” method. Similar amendments were made to the “Rent” standard this year.
Reversal of losses from impairment of non-financial assets is reflected in the debit of account 0.114.00.000 and the credit of account 0.401.20.274.
Budgetary and autonomous institutions reflect the decrease in the value of real estate and especially valuable movable property on account 0.210.06.000 on the credit of account 0.401.10.172. Their founders reduce the indicator for account 0.204.33.000 by debiting account 0.401.10.172. The “red reversal” method is not used.
Divide the indicators of account 205.00 in the analytical accounting registers not only by counterparties, but also by the legal basis for the occurrence of income (for example, under contracts). Accounting can be maintained by groups of counterparties, but only on the condition that you maintain personalized accounting outside of balance sheet accounts (management accounting). At the same time, at least at each reporting date, reconcile the accounting and management accounting data.
In account 302.00, reflect payments for purchases of goods, works, and services in the context of legal grounds (contracts). You can still take into account payroll calculations for a group of counterparties if you keep personalized records outside of balance sheet accounts and reconcile the data for each reporting date.
Maintain analytical accounting for accounts 206.00, 208.00 and 302.00, including by account numbers of monetary obligations (if any).
The procedure for analytical accounting for off-balance sheet accounts 08 and 20 has been clarified. For example, for off-balance sheet account 20, take into account accounts payable in the context of classification codes for income, expenses, sources of financing budget deficits, as well as counterparties and financial institutions.
In account numbers 0.304.66.000 and 0.304.76.000, indicate the KOSGU code, based on the type of your institution: state-owned provide codes 731 and 831, budgetary and autonomous - codes 732 and 832 KOSGU. Note that a similar procedure applies to accounts 0.304.86.000 and 0.304.96.000.
The authorized bodies account for investments in treasury property under a new account 0.106.50.000. Analytical codes for types of property have also been introduced for it. Please note that the amendments to the Unified Chart of Accounts and Instruction No. 157n provide for different dates for the start of application of this account. Taking into account the changes in the chart of accounts No. 162n, the innovation needs to be introduced from 2022.
Classification of amendments
Instruction 157n, as amended for 2022, imposes new requirements for accounting. The amendments are caused by changes in legislation and can be grouped as follows:
- changes in instruction 157n caused by the adoption of five new public finance accounting standards, which came into force on January 1, 2020. The instructions include some points directly borrowed from these standards; new account codes have appeared in the chart of accounts, new wording has been removed, and outdated ones have been excluded. Amendments have also been made regarding the procedure for applying the codes;
- amendments that eliminate contradictions between the instructions and other regulations; some terms in it are outdated;
- clarifying the procedure for maintaining centralized accounting, formalizing the transfer of powers for maintaining accounting;
- changes related to the introduction of new forms of registers;
- the system of analytical accounting of assets has been streamlined.
The amendments are not only of a formal nature, but also clarify the procedure for authorizing expenses, expand the functions of the subject of consolidated reporting, etc.
What amendments need to be taken into account from 2022?
The adjustments are mainly related to the entry into force of new standards.
For example, when accounting according to the “Intangible Assets” standard for accounts 102.00, 104.00, 106.00, 114.00, use uniform analytical codes for the types of synthetic accounts:
- N—scientific research (research and development);
- R - experimental design and technological developments;
- I - software and databases;
- D - other intellectual property items.
Own analytical codes can be provided by agreement with the founder only for objects from group D.
Transactions with intangible assets received under a license agreement are recorded in accounts 111.60, 106.60 and 104.60. The analytical codes of the types are the same: N, R, I, D. Do not use off-balance sheet account 01 to account for such objects anymore.
On account 114.60, take into account the impairment of the rights to use intangible assets. Now it reflects the depreciation of non-produced assets, but from the new year an account of 114.70 is provided for these purposes.
Other accounts were also introduced, for example, to correct errors of previous years identified by controllers:
- 304.66 “Other calculations of the year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities”;
- 304.76 “Other calculations of previous years identified through control measures”;
- 401.16 “Income of the financial year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities”;
- 401.17 “Income of previous financial years identified through control measures”;
- 401.26 “Expenses of the financial year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities”;
- 401.27 “Expenses of previous financial years identified through control activities.”
Accounts 304.84 and 304.94 for correcting errors of previous years in intradepartmental calculations are excluded.
From 2022, the Instructions provide for account 106.50 to account for investments in treasury property. It was introduced into the Unified Chart of Accounts only in 2021. According to Chart of Accounts No. 162n, the start date for using the account also falls on next year. Thus, the innovation must be introduced starting in 2022.
The rules for compiling a cash book have been clarified. If you maintain and store it in electronic form with a qualified electronic signature, at the same time use the new electronic form of the journal for recording incoming and outgoing cash orders (f. 0504093).
We adjusted the requirements for analytical accounting on some balance sheet and off-balance sheet accounts. Institutions and bodies have the right to take these amendments into account during 2022. The decision must be enshrined in the accounting policies.
Innovations in analytical accounting affected balance sheet accounts 107.00, 108.00, 210.05, 502.00. So, on account 502.01, keep records in the context of the accounting numbers of budget obligations, in account 502.02 - in the context of the accounting numbers of monetary obligations (if any). For account 502.07 in the analytical accounting registers, reflect the purchase identification number.
In off-balance sheet accounting, the requirements for analytics have been updated for accounts 01, 02, 04, 05, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27. For example, for the last three accounts, conduct analytics, including by KOSGU codes.
Updated instruction No. 157n
The Ministry of Finance sent an order for registration with changes to the Unified Chart of Accounts and Instruction No. 157n. Some amendments must begin to apply no later than reporting on January 1, 2021.
What amendments need to be taken into account from the reporting as of January 1, 2021
Changes in accounts and their purpose
Your own analytical codes of synthetic accounts and off-balance sheet accounts can be entered into the working chart of accounts only taking into account the requirements of the body to which you submit reports (consolidation entity). The instruction change order does not indicate what to do with the additional accounts already established. We believe that the requirements must be met in relation to all accounts that are reflected in the financial statements after the amendments enter into force. We recommend that you reconcile all accounts you entered before filing your 2022 returns.
At the end of the year on accounts with balances, there is no need to reset the KOSGU codes under subarticles of articles 560, 660, 730 and 830.
Future income must be divided according to the dates of recognition in accounting. The amounts that will be reflected in the financial result of the current year are recorded in account 401 41. The remaining amounts are reflected in account 401 49 “Deferred income for recognition in subsequent years.”
In off-balance sheet account 27, among other things, fixed assets for the personal use of employees are taken into account. This is property that they use also outside the institution and outside of working hours. Currently, the instructions do not indicate off-balance sheet accounting of such objects, so the issue is moot.
According to account 105 01, in addition to medicines, all medical products that the institution uses for medical purposes are taken into account. Thus, the purpose of the account will correspond to code 341 KOSGU.
Innovations in analytical accounting
They will adjust the requirements for analytical accounting for many balance sheet accounts. Let's look at some amendments.
If, after the inventory group has been destaffed, an asset is accepted for accounting again, it must be assigned a new inventory number. The inventory number of the complex of objects and the internal inventory numbers of objects within the group are not used in the future.
The indicators of account 205 00 in the analytical accounting registers must be divided not only by counterparties, but also by the legal basis for the occurrence of income (for example, under contracts). Accounting can be maintained by groups of counterparties, but only on the condition that you maintain personalized accounting outside of balance sheet accounts (management accounting). At the same time, at each reporting date it is necessary to reconcile the accounting and management accounting data.
In account 302 00, settlements for purchases of goods, works, and services must be reflected in the context of legal grounds (contracts). Payments for wages can still be taken into account for a group of counterparties if personalized accounting is maintained outside the balance sheet accounts and the data is reconciled at each reporting date. The analytical accounting procedure will also be clarified for some off-balance sheet accounts. For example, they will indicate that in off-balance sheet account 20, accounts payable must be taken into account in the context of classification codes for income, expenses, sources of financing budget deficits, as well as counterparties and financial institutions.
Technical amendments to the instructions
Some of the amendments provide for accounting procedures that institutions and bodies could already apply in practice.
For example, they will establish the obligation to take into account non-produced assets in account 103 00 in the context of responsible persons, location and identification numbers (cadastral, register, accounting). Institutions and bodies may have already reflected this data in the inventory card. With regard to account 105 05, it will be indicated that only supplies that the institution uses for the purposes of labor protection, compliance with safety regulations, civil defense and emergency protection should be classified as special clothing.
It will be possible to reflect the BSO on account 105 06. An exception will be made for forms that are issued from the warehouse for registration to employees or that were received last, bypassing the warehouse. Such forms will be recorded in off-balance sheet account 03. The Ministry of Finance has already prescribed the use of this approach in accounting.
The Ministry of Finance had similar requirements for off-balance sheet accounting of gifts. They will also be fixed in the instructions for off-balance sheet account 07. Amendments will also be provided for transactions carried out by a small number of public sector organizations. For example, they will introduce missing accounts to account for concessions and operations under long-term construction contracts.
Procedure for transition to new rules
The order to change the instructions only states that the new rules must be applied when preparing reports for 2022. We believe that the entries should be reflected in accounting on the same day as the final transactions.
Institutions and bodies will be given the right to introduce innovations in analytical accounting during 2022. The decision on this must be fixed in the accounting policy.
What amendments need to be taken into account from 2022
Innovations are mainly associated with the entry into force of new standards.
For example, for accounting according to the “Intangible Assets” standard for accounts 102 00, 104 00, 106 00, 114 00, unified analytical codes for the types of synthetic accounts will be introduced:
- N—scientific research (research and development);
- R - experimental design and technological developments;
- I - software and databases;
- D - other intellectual property items.
Your own analytical codes can be provided by agreement with the founder only for objects from group D.
To account for intangible assets that an institution uses under a license agreement, accounts 111 60, 106 60 and 104 60 will be introduced. Such assets will no longer be reflected in off-balance sheet account 01.
On account 114 60 it is necessary to take into account the impairment of the rights to use intangible assets. Now it reflects the depreciation of non-produced assets, but for these purposes an account 114 70 will be provided.
Other accounts will appear, for example, to correct errors of previous years identified by controllers:
- 304 66 “Other calculations of the year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities”;
- 304 76 “Other calculations of previous years identified through control measures”;
- 401 16 “Income of the financial year preceding the reporting year, identified through control measures”;
- 401 17 “Income of previous financial years identified through control measures”;
- 401 26 “Expenses of the financial year preceding the reporting year, identified through control activities”;
- 401 27 “Expenses of previous financial years identified through control activities.”
Accounts 304 84 and 304 94 will be excluded for correcting errors of previous years in intradepartmental calculations.
Technical amendments to the Instructions
Some of the amendments provide for accounting procedures that institutions and bodies could already apply in practice.
For example, on account 103.00, non-produced assets are taken into account by responsible persons, location and identification numbers (cadastral, registry, accounting). Institutions and bodies could have previously reflected this data in the inventory card.
Workwear in account 105.05 includes only supplies that the institution uses for the purposes of labor protection, compliance with safety regulations, civil defense and emergency protection.
Account 105.06 also reflects BSO. An exception is forms that are issued from the warehouse for processing by employees or that were received last, bypassing the warehouse. Such forms are recorded in off-balance sheet account 03. The Ministry of Finance has already prescribed the use of this approach in accounting.
The Ministry of Finance had similar requirements for off-balance sheet accounting of gifts. They were also included in the instructions for off-balance sheet account 07.
Amendments have also been made for transactions carried out by a small number of public sector organizations. For example, we introduced missing accounts to account for concessions and operations under long-term construction contracts.