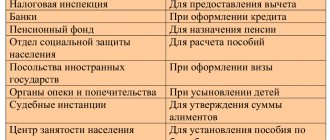
How and who determines the retention period for documents?
Paragraph 1 of Article 17 of the Federal Law of October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ “On Archiving in the Russian Federation” states that organizations and individual entrepreneurs are obliged to ensure the safety of archival documents, including documents on personnel, during their storage periods.
These deadlines are established by federal laws, other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, as well as special lists. First of all, this is a List of standard administrative archival documents generated in the course of the activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating their storage periods (approved by order of the Federal Archives of December 20, 2019 No. 236; hereinafter referred to as List No. 236);
In addition, storage periods are determined by other legal provisions. Thus, the minimum storage time for tax documents is established in the Tax Code, and for accounting documents - in the Accounting Law. And for joint-stock companies, there is also a Regulation on the procedure and periods for storing documents of joint-stock companies (approved by Resolution of the Federal Commission for the Securities Market dated July 16, 2003 No. 03-33/ps).
Important
The inclusion of documents in the archival fund does not depend on the method of their creation and the type of media (Article Law No. 125-FZ). Therefore, it is necessary to ensure the safety of both “paper” and electronic documents. The type of media in most cases does not affect the period during which the document must be preserved. At the same time, legally significant electronic documents can be stored without printing (see “The Ministry of Finance explained how to store electronic invoices”).
Exchange legally significant “primary data” with counterparties via the Internet. Free inbox.
Why keep accounting documents?
Any accountant knows that every document drawn up in a company or received from counterparties has its own value and must be preserved.
Based on the information contained in the primary documents, accounting is carried out and financial statements are prepared. Verification of accounting and accounting data by all regulatory authorities is carried out using primary documents. All primary accounting records and reports must be stored for legally defined periods.
The storage periods for accounting documents are regulated by the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and the approved list of storage periods.
To learn about what groups documents arising in the activities of an organization are divided into and what their storage periods may be, read the article “Basic storage periods for documents in an organization (archive).”
Storage periods for accounting documents
As already mentioned, the storage period is established by Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”. For most accounting papers it is five years. The nuances are related to the procedure for calculating this period.
Thus, for primary accounting documents, accounting registers, accounting reports and audit reports, the countdown of the five-year period begins after the corresponding reporting year (clause 1 of Article No. 402-FZ). And with regard to accounting policies and other documents related to the organization and maintenance of accounting, as well as tools that ensure the reproduction of electronic documents and verification of the authenticity of an electronic signature, the five-year period is counted from the year in which they were last used to prepare the accounting (financial) ) reporting (clause 2 of Art. Law No. 402-FZ).
Get a sample accounting policy for a small LLC Get it for free
Verified supporting documents (cash documents and books, bank documents, counterfoils of cash check books, orders, time sheets, bank notices and transfer requests, acts of acceptance, delivery, write-off of property and materials, receipts, invoices and advance reports, correspondence) are also relied upon store for at least five years, and in the event of disputes or disagreements - until a decision is made on the case, even if it is made outside this period (Article 277 of List No. 236). But the period of storage of documents (protocols, acts, certificates, calculations, statements, conclusions) on revaluation, determination of depreciation, write-off of fixed assets and intangible assets begins to flow only from the moment of disposal of fixed assets and intangible assets (Article 323 of List No. 236).
As a general rule, the storage period for travel documents is 5 years. But this period increases to 50 years if there are no other documents confirming harmful and dangerous working conditions (Article 553 of List No. 236).
Attention
Here and further in the text, the storage period of 50 years established in List No. 236 applies to documents created after January 1, 2003.
Similar documents drawn up before this date cannot be destroyed for 75 years. Fill out waybills indicating the route and mandatory details in a special service
Which documents establish the retention period for expense reports?
Documents related to the economic activities of entities can be divided into 2 categories:
- tax (used when calculating taxes and contributions);
- accounting (supplement tax in terms of keeping records of personnel, assets, control over expenses and in other aspects).
Advance reports are accounting documentation. They belong to the category of primary documents (clause 1 of the resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated 01.08.2001 No. 55).
Read more about the form of advance report established by law in this article.
The main provisions of the legislation establishing the rules for storing advance reports are recorded in:
- Art. 23 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 283 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- Art. 29 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ;
- Order of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 No. 236 (valid from February 18, 2020).
ATTENTION! As of November 30, 2020, the rules for issuing reports have been simplified. Now, in the application for the issuance of accountable money, it is not necessary to indicate the amount of the advance and the period for which the accountable amounts are issued. The requirement to submit an advance report within three days has been removed. Employers were also allowed to issue one order for several cash payments to one or more employees. In this case, you need to indicate the name, amount and period for which the money is issued for each employee.
Find out what other innovations in the procedure for recording cash transactions came into effect on November 30, 2020 in ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the K+ system and go to expert comments on the Central Bank Directive No. 5587-U dated 10/05/2020 for free.
Let's study the key provisions of the noted legal acts in more detail.
Retention periods for personnel documents
Personnel documents completed after January 1, 2003 must be stored for 50 years (Clause 2, Article 22.1 of Law No. 125-FZ). This is the period that applies to employment contracts, as well as all additional agreements to them, including termination agreements; personal files and personal cards of employees (Articles 435, 444, 445 of List No. 236). A half-century storage period is also established for civil contracts with individuals, as well as acts on them (Article 301 of List No. 236).
Important
From September 1, 2022, employers are no longer required to maintain personal cards and familiarize employees with entries in Form No. T-2 (also see “Rostrud: employees no longer have to sign personal cards in Form No. T-2”). What to do with cards that were issued before this date? Rostrud believes that even if an organization decides to abandon maintaining the T-2 form, it is necessary to ensure the storage of old cards as archival documents for 50 (75) years.
Also, all orders and instructions regarding personnel, including documents (memos, certificates, statements) to them, are stored for at least half a century. We are talking about orders for admission, transfer, relocation, combination, part-time work, dismissal, remuneration, certification, advanced training, assignment of class ranks, ranks, titles, encouragement, awards, changes in biographical data, parental leave, leaves without pay (Article 434 of List No. 236). A similar storage period applies to original personal documents (work book, diplomas, certificates, licenses, certificates) that were not claimed by employees upon dismissal (Article 449 of List No. 236 ).
Important
In connection with the transition to electronic work books, the following question often arises: is it necessary to keep a copy of the paper work record if the employee has chosen an electronic work record? Rostrud believes that the employer does not have such an obligation. After issuing the original paper work document to the employee, the employer is freed from the need to store this document.
Draw up local acts using ready-made templates and prepare all personnel reports
There are exceptions to the general rule. For example, documents related to the application of disciplinary sanctions can be destroyed after three years (Articles 454 and 434 of List No. 236). The same storage period is defined for vacation schedules (Article 453 of List No. 236) and consents to the processing of personal data. True, in the latter case, the countdown of the three-year period begins after the expiration of the consent or its revocation (Article 441 of List No. 236).
Please note that this concession does not apply to basic documents (regulations or instructions) on the processing of personal data. They must be stored permanently (Article 440 of List No. 236). You will also always have to take care of orders, instructions and other personnel documents related to the main activity (Article 19 of List No. 236). For example, such documents include orders on approval of the structure of the organization, on the creation of divisions (branches), on taking office, on assigning the duties of the chief accountant to the manager, on early resignation, on the appointment of responsible persons, on the approval and implementation of LNA.
A five-year preservation period is established for work time sheets (if working conditions are dangerous or harmful, this period increases 10 times), orders, instructions and other documents on administrative and economic issues (Articles 402 and 19 of List No. 236).
Also, a five-year period is reserved for storing orders for the provision of annual paid and educational leave, as well as orders for sending on business trips for workers not engaged in work with harmful and dangerous working conditions. If the work is “harmful,” then orders for business trips cannot be destroyed for 50 years (Article 434 of List No. 236).
Compose HR documents using ready-made templates for free
In addition, copies of reports, applications, lists of employees, certificates, extracts from protocols, conclusions, correspondence and other documents on the payment of benefits, payment of sick leave and the issuance of financial assistance are kept for five years (Article 298 of List No. 236). But payrolls and documents for them, payslips for the issuance of wages, benefits, fees, financial assistance and other payments will have to be preserved for a year longer - for six years (Article 295 of List No. 236). Please note that payrolls and payslips should be kept for six years only if the employer maintains personal accounts for employees. Otherwise, these documents must remain preserved for 50 years (Article 295 of List No. 236).
Attention
Documents created within the framework of personnel electronic document management are supposed to be stored “for the period established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on archival matters” (Article 22.3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, employers who have switched to HR EDI are required to ensure the safety of such documents within the above-mentioned periods. Also see “Personnel documents are transferred to electronic form: we read the latest amendments to the Labor Code.” Calculate your salary and benefits according to current rules
Storage period for electronic invoices
Now more and more businessmen are switching to electronic document management, including using electronic invoices. An electronic invoice is equivalent to a paper one (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code), the procedure for its execution is regulated by the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia “On approval of the procedure for issuing and receiving invoices in electronic form via telecommunication channels using an enhanced qualified electronic signature” dated November 10. 2015 No. 174n.
Even before the storage of an electronic invoice is organized, i.e. already during its execution, it is necessary to take into account that it must be signed with a qualified electronic signature (clause 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05.05.2015 No. 07-01-06/25701).
The storage period for electronic invoices is the same as for paper ones - 5 years. Companies are not required to store printed paper copies of electronic invoices (letter of the Federal Tax Service dated 02/06/2014 No. GD-4-3/1984).
Retention periods for tax documents
Accounting and tax accounting data and other documents necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes, including documents confirming receipt of income, expenses, as well as payment (withholding) of taxes, must be stored for five years. These are the rules of subparagraph 8 of paragraph 1 of the article and subparagraph 5 of paragraph 3 of the article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The countdown of the period begins after the end of the tax period in which the document was last used for preparing tax reports, calculating and paying taxes, confirming income received and expenses incurred (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 19, 2017 No. 03-07-11/45829).
Important
An exception is made for documents confirming the amount of loss incurred.
They are supposed to be kept for the entire period when it reduces the tax base of the current tax period by the amounts of previously received losses (clause 4 of Article 283, clause 7 of Article 346.18 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). A four-year shelf life is specified for the purchase ledger and sales ledger, including additional sheets to them. In this case, the countdown is carried out from the date of the last entry in the book (clause 24 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book and clause 22 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved by Government Decree No. 1137 of December 26, 2011). As for invoices, they should be kept for five years (Article 317 of List No. 236).
Carry out automatic reconciliation of invoices with counterparties Connect to the service
A five-year retention period is established for tax returns and calculations for all types of taxes. The exception is individual entrepreneur declarations for the period up to 2002 inclusive. They must be stored for 75 years (Article 310 of List No. 236). But the calculation of insurance premiums cannot be destroyed for 50 years from the date of its preparation (Article 308 of List No. 236).
Documents necessary for the calculation and payment of insurance premiums must be kept for six years (subclause 6, clause 3.4 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Such documents include, in particular, individual accounting cards for the amounts of accrued payments and other remunerations and the amounts of accrued insurance premiums (Article 309 of List No. 236).
Attention
In the absence of personal accounts or payroll records, individual accounting cards will have to be protected for 50 years (Article 309 of List No. 236).
From what point does the storage period for documents used to calculate insurance premiums begin? There is no direct explanation. In our opinion, in this case an analogy with tax documents can be applied. That is, the deadline is counted after the end of the billing period in which the document was last used to calculate and pay contributions and prepare reports on them.
Fill out, check and submit insurance premium calculations online
All correspondence with the tax office (notifications, demands, acts, decisions, resolutions, objections, complaints, applications) is required to be kept for five years. This period is doubled if the complaint is filed based on the results of an on-site or desk inspection (clauses 148 and 314 of List No. 236). All electronic documents with UKEP, and certificates of keys for verifying the electronic signature with which complaints and technological documents are endorsed, must be stored for at least five years. Here, the deadlines are counted from the date of receipt or sending of the relevant document (clause 3 of the Procedure given in Appendix No. 4 to the Federal Tax Service order dated December 20, 2019 No. MMV-7-9 / [email protected] ).
Reference
Contracts for the purchase of goods, works, and services to meet state and municipal needs must be kept for five years after the termination of obligations under them (Article 224 of List No. 236).
Receive notifications about government procurement for small and medium-sized businesses Set up newsletter
Other cases of increasing the shelf life of primary products
If Landscape Design LLC operated with a loss, and then took it into account when calculating income tax, the documents would have to be kept for the entire period of transferring the loss plus 4 years after it was completely written off. In this case, it is impossible to get rid of either the primary document confirming the loss received, or other certificates and calculations on the basis of which this loss was transferred.
For example, accounting and tax documents for a loss received in 2022 and taken into account over the next 10 years will have to be stored until the end of 2035.
Read more about the nuances of accounting for losses in the article “How and for what period can losses be carried forward?” .
The storage period for accounting documents will also have to be increased in the following case. Landscape Design LLC provided services to a customer who did not promptly pay for the work performed and did not respond to letters and complaints. The company was not excluded from the state register, but did not repay its debt. Landscape Design LLC was able to take into account bad receivables only in 2022, and all documents of the organization related to this situation will have to be stored until the end of 2026.
How to switch to a new nomenclature: step-by-step instructions
To organize the current paperwork process and the subsequent transfer of documents for storage, you need a nomenclature of cases. This is a systematized list of the titles of cases entered into office work during the year, indicating the periods of their storage. Such a list is necessary for the correct formation of documents, organization of their recording and safety, as well as quick search.
We must strive to ensure that the nomenclature of cases reflects all the functions and areas of work of the organization or individual entrepreneur. Otherwise, during the paperwork process, documents will inevitably appear that are not included in the nomenclature, which can lead to a violation of the storage order and even loss of documents.
Based on the form of case nomenclature approved by Order of the Ministry of Culture dated March 31, 2015 No. 526, we can recommend the following procedure for transition to the new nomenclature. First, you need to enter the numbering of the organization's structural divisions. These numbers will be required to create a case index, since it includes the serial number of the case, as well as the number of the structural unit.
Reference
With a multi-level internal structure of an organization, you can enter complex indices consisting of groups of numbers separated from each other by a hyphen.
For example, separate numbers can be assigned to departments, divisions within a department, and work groups within a department. The second step when transitioning to a new nomenclature is to develop rules for forming case headings. In this case, one must proceed from the fact that the title in a clear but generalized form should reflect the main content and composition of the case documentation. Therefore, you cannot simply indicate “documents” or “correspondence”. It is necessary to specify “hiring documents” or “correspondence with the Federal Tax Service”.
Attention
You cannot use non-specific wording in the title of the case: “Miscellaneous”, “General correspondence”, “Incoming documents”, etc.
The third stage involves the distribution of all cases by storage period, and the introduction of an appropriate paperwork procedure, in which documents are immediately generated by case, based on the storage period. If, when creating documentation, it is difficult to accurately distribute according to storage periods, then a binary system is introduced: initially, all documents relate to cases of either permanent or temporary storage. And the division of temporary storage cases into specific periods is carried out at the next stage by specialists responsible for managing affairs in the organization.
IMPORTANT
Is it necessary to include electronic documents in the nomenclature?
Clause 96 GOST R 7.0.8-2013 “SIBID. Record keeping and archiving. Terms and definitions" defines an electronic file as an electronic document or a set of electronic documents and metadata for them, formed in accordance with the nomenclature of files. Therefore, electronic files are included in the nomenclature common to paper files. When adding electronic documents to the general nomenclature, you must be guided by the same rules that apply to “paper” documentation. Connect to the Diadoc system for electronic document management with counterparties
What documents are considered cash registers?
Cash register documentation is used to carry out settlements with counterparties and within the organization. These include:
- receipt order (PKO): it is issued when money is received;
- expense order (RKO): formed upon disposal of funds;
- register of PKO and RKO: it keeps records of incoming and outgoing orders;
- advance reports: used to account for accountable funds;
- announcement for cash deposit: fill out when depositing money into the bank to replenish the current account;
- Cash book: used to reflect all income and expense transactions and cash balances;
- a book of accounting for received and issued funds: kept if the company has several cashiers and a senior cashier, transactions on the issuance and receipt of money between them are recorded in it;
- Cashier-operator's journal: operations on the receipt and expenditure of cash for each cash register in the enterprise are entered into it.
Cash register documentation is maintained in both paper and electronic form. The manager appoints a responsible employee for conducting operations and generating documents for the cash desk by a separate order:
Accounting and tax regulations indicate how long documents confirming cash settlements with customers and financial transactions at the cash register must be kept. The storage period for such documentation includes:
- 402-FZ of December 6, 2011 (Article 29); Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 8, part 1, article 23);
- Order of Rosarkhiv No. 236 of December 20, 2019 (clause 277).
In addition, the storage period for cash receipts in the organization and other bank registers is prescribed in the Directives of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014. According to the standards of the Central Bank, all payment registers for the bank and cash desk are stored for 5 years.
Fines for violating the document storage procedure
The most common situation when violation of the procedure or storage period can result in a fine is failure to submit a document at the request of the Federal Tax Service.
Let us remind you that such a request can be sent both during an inspection of the taxpayer himself (on-site or office), and within the framework of an “oncoming” inspection, or without ordering an inspection at all (Article and 93.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; for more details, see “The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate requires documents: for which requests need to be answered, and which ones can be ignored” and “The Federal Tax Service Inspectorate requested data on a counterparty or transaction: when is this legal, and what will happen if the request is not answered”). In all cases, failure to submit or untimely submission of each document that the taxpayer must have will result in a fine of 200 rubles. (Clause 1 of Article 126 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Attention
You can facilitate and speed up the process of sending documents to the inspection using special services, for example, the “Connector Kontur.Extern” web service.
It makes it possible to send tens of thousands of electronic documents to tax authorities at a time. Through the “Connector” you can transfer to the Federal Tax Service any electronic documents created in approved formats (for example, invoices, TORG-12 invoices, etc.), as well as scanned images of any documents created on paper: acts, contracts, payments etc. Connect to the Kontur.Extern system
In addition, the absence of primary documents or invoices may result in tax liability for gross violation of accounting rules. Here the size of the fine depends on the consequences. If the violation did not lead to an understatement of the tax base, then the fine will be 10,000 or 30,000 rubles. (Clause 1 and 2 of Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If, due to the lack of documents, the tax base was underestimated, then the fine will be equal to 20% of the amount of unpaid tax, but not less than 40,000 rubles. (Clause 3 of Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Failure to comply with the storage deadlines for documents may become the basis for bringing the organization and its employees to administrative liability. Sanctions for violation of the rules for storing, compiling or using archival documents (including personnel and accounting) are established in Article 13.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The punishment will be a warning or a fine in the following amount: from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles. for officials; from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles. for legal entities.
For failure to fulfill the obligation to store documents of a JSC or LLC within the time limits provided for by current legislation, organizations are punished more severely. The fine ranges from 2,500 to 5,000 rubles. for officials and from 200,000 to 300,000 rubles. for society itself (parts 1 and 2 of article 13.25 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). And for failure to comply with the storage deadlines for accounting and reporting documents on currency transactions, a fine of 4,000 to 5,000 rubles is provided. for officials and from 40,000 to 50,000 rubles. for organizations (Part 6 of Article 15.25 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). Slightly smaller penalties (from 1,000 to 2,000 rubles for officials and from 10,000 to 20,000 rubles for legal entities) are provided for violation of the terms of storage of accounting documents for foreign economic transactions with goods, information, works, services or results of intellectual activity for purposes of export control (Part 2 of Article 14.20 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation).
Article 29 of Law 402-FZ: the report must be kept for 5 years
In accordance with the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 29 of Law No. 402-FZ, primary documentation, which includes advance reports, must be stored by the subject of economic relations for at least 5 years after the reporting year.
Read more about the criteria for classifying documents as primary in the article “Primary document: requirements for the form and the consequences of violating it.”
Advance reports, as a rule, are supplemented by various receipts, PKOs, sales receipts and other documents certifying the actual payment by the employee for goods and services using accountable funds. These can be classified as other sources that are related to accounting in accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 29 of Law No. 402-FZ. The company must ensure their safety, as in the case of expense reports, for at least 5 years after the reporting year.
The company is obliged to store reports and sources supplementing them in safe conditions (Clause 3 of Article 29 of Law No. 402-FZ). If the company’s manager changes, then he must correctly accept the accounting documents in the manner established by the company (clause 4 of article 29 of Federal Law No. 402).
Storage procedure and rules
Legislative standards define only general recommendations for organizing the storage of documentation in institutions. Individual principles must be enshrined in each economic entity independently. The organization should approve a special procedure or rules for storing accounting documentation. When developing a provision, be guided by:
- Regulations on documents and document flow in accounting, approved by the USSR Ministry of Finance on July 29, 1983 No. 105, which establishes the rules for storing primary documents in state (municipal) institutions.
- Federal Law No. 125-FZ.
- Basic rules for the work of archives of organizations (approved by the Decision of the Board of Rosarkhiv dated 02/06/2002).
- By Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 256n dated December 31, 2016.
- By Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia No. 558 of August 25, 2010.
- Other orders of higher ministries, departments and sectoral orders.
According to general recommendations, the company should identify a responsible employee whose responsibilities will include archival management. To ensure safety, a separate room is usually allocated that meets safety requirements. An archive room or warehouse is equipped with shelving, cabinets or even a safe. For example, if strict reporting forms are stored in the archive.
The rules for working with primary documents should be determined depending on the type of documents. For example, primary forms can be issued not only on paper. The electronic form is becoming increasingly popular. For each category of papers, develop an individual algorithm for storing primary accounting documentation and processing it.
Paper forms
The regulation on the storage of papers must contain specific rules and an algorithm of actions. For example, assign a responsible accounting employee who will deal with the preparation and transfer of primary records to the archive. Also determine the transfer deadline. For example, annually, until April 1.
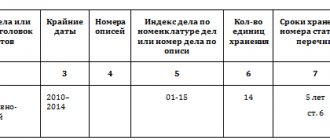
The transfer of the primary document to the archive must be documented. For this purpose, a special inventory is drawn up. The format of the accompanying inventory is developed by the company independently. We recommend using the following details:
- Number in order.
- Case index and title.
- Number of sheets in a folder or file.
- Storage period for primary accounting documentation.
- Date of delivery to the archives department.
- Information about the person in charge (full name, position, signature).
Reception of documentation must also be documented. For this purpose, a corresponding entry is made in a special registration journal. The register columns reveal information about the actual receipt of papers (quantity, name and indexes of cases, persons responsible and date of transfer).
Primary report in electronic form
Electronic forms are stored in a different order. However, the company determines individual rules for storing primary accounting documentation independently. General recommendations are contained in the new FSBU (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 256n). The standards are enshrined in Order of the Ministry of Culture No. 558.
Provide rules for storing primary accounting documentation and implement them at the enterprise:
- Storage of the primary data in electronic format should be done by creating a backup copy of the data.
- The information in the backup copy is formed in chronological order.
- Information should be grouped into categories and types of forms for ease of use.
- A backup copy is created for a separate period of time, the duration of which is determined by the company independently. For example, the reporting quarter, half-year or year.
- Information must be recorded on an external storage medium. For example, a disk, flash drive or external hard drive.
- The information is certified by the electronic signature of an authorized person. For example, ES of the chief accountant.
- External media must be signed. For example, on the front side of the disk, indicate the following details:
- date when the backup was created;
- the period for which the information was prepared;
- type of primary;
- total amount of information;
- serial numbers of accounting journals;
- information about responsible persons.
Copies should be stored in a safe or in another specially equipped room. It is necessary to appoint a responsible employee who will systematically archive and backup information.
Centralized accounting
Accounting can be transferred to a third-party company or, for example, to a centralized accounting department. In this case, an agreement for accounting services is drawn up between the companies. Moreover, the rules and periods for storing accounting documentation must be specified in a separate manner. It is recommended to prepare an additional agreement with the service company.
In the agreement, take into account all the features and requirements for document management and storage of papers. Otherwise, the service company will not be responsible for the safety and correctness of documents.