Who must submit a VAT return?
Filing a VAT report is the responsibility of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who:
- do not work under special regimes and made sales with value added tax over the past quarter;
- act as a tax agent;
- work under special regimes and are exempt from tax in accordance with Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but issued invoices to contractors with it.
If the company was not associated with tax for the quarter, then there should be no exemption from filing reports. A nil return must be filed.
Filing a VAT return
The VAT declaration is a mandatory reporting form for organizations and individual entrepreneurs that:
- are recognized as VAT payers;
- are tax agents for VAT;
- conduct intermediary activities, during which they issue invoices on their own behalf with the allocated amount of VAT;
- They work in special modes, but issue invoices with the VAT amount filled in.
In addition, VAT tax returns are submitted using a special form:
- importers of goods from EAEU countries;
- foreign organizations that or through which sell electronic services in Russia.
The VAT declaration is submitted to the inspectorate at the place of registration of the company (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). There is no need to submit a report on the location of separate units.
The declaration is submitted electronically using TKS. The Federal Tax Service considers reports submitted on paper to be unsubmitted. There are two exceptions to this rule:
- tax agents who are not VAT payers and do not conduct intermediary activities with the issuance of invoices on their own behalf (clause 5 of Article 174 and clause 3 of Article 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Except for buyers of recyclable materials, they do not fall under this exception;
- foreign organizations that provide electronic services in Russia, and foreign tax agents. They submit returns electronically through the taxpayer’s personal account.
Where and when to submit the declaration
Reporting is submitted to the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation. In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 80 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it can be submitted electronically or on paper. The obligation to submit electronically via TKS is assigned to the following categories of taxpayers:
- with an average number of employees over the past year of more than 100 people;
- only to established or reorganized companies with more than 100 employees.
Tax agents can submit reports in paper form.
The deadlines for submitting VAT reports imply submission no later than the 25th day of the month following the end of the quarter.
Procedure for submitting income tax returns
It is necessary to report profit in the form approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 23, 2019 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
If the average number of personnel does not exceed 100 people, then the declaration can be submitted on paper.
The deadline for submitting the declaration for the first half of 2022 is no later than July 28, 2020 (Clause 4 of Article 289 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Please note: the deadline for submitting semi-annual reports, unlike reports for 2022 and the first quarter of this year, has not been postponed.
At the same time, the specific deadlines for submitting the declaration for the reporting periods depend on how the advances :
- monthly, based on actual profit: advance payments are paid and the declaration is submitted monthly until the 28th, the reporting periods in this case will be a month, 2 months, 3 months and so on until the end of the calendar year;
- quarterly: advance payments are determined based on the results of the quarter, half a year, 9 months.
What liability follows for failure to submit a declaration?
If the deadlines are violated, the Federal Tax Service has the right to issue a fine to the company. The amount is calculated based on the amount of tax to be paid: 5% for each month. The fine has a set minimum (1 thousand rubles) and a maximum - it is 30% of the calculated VAT.
Tax authorities also apply additional sanctions. Thus, a delay in the VAT return for more than 10 days risks blocking transactions on the current account for a business. Tax officials also impose penalties in the amount of 1/300 of the Central Bank key rate, which are calculated every day.
The Astral Report 5.0 service will always remind you about the deadlines for submitting your VAT report. This is a convenient platform for maintaining records, exchanging documentation with counterparties and sending reports to regulatory agencies. You can fill out a VAT return in Astral Report 5.0 in a few minutes. The service will provide the current form of the form, and you can transfer the necessary information from the database loaded into the program.
Tax agent reporting on profits
Russian organizations are recognized as tax agents for income tax if they pay:
- interest on state and municipal securities to Russian organizations and foreign organizations with permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 286 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- income to foreign organizations that have permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation, not related to the activities of such representative offices (clause 4 of Article 286, subclause 1 of clause 4 of Article 282, clause 6 of Article 282.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- individual income to foreign organizations that do not have permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 309, clause 1 of Article 310 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- dividends to other Russian organizations (clause 3 of Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or foreign organizations with permanent representative offices in the Russian Federation (clause 3 of Article 275, clause 6 of Article 282.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For information on how dividends are reflected in the declaration, read the article “How to correctly calculate the tax on dividends?” .
Agents submit income tax calculations at the end of each reporting (tax) period in which they paid income (clauses 1, 3, 4 of Article 289, Article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ConsultantPlus experts explained how to fill out and when to submit a profit-making declaration to a foreign organization. If you do not have access to the system, get trial online access and upgrade to the Ready Solution for free.
Changes to the VAT return from 2022
From the 1st quarter of 2022, a new VAT tax return form will be used. Accordingly, taxpayers are required to use the new electronic format and the new established procedure for filling out the declaration. The changes are caused by the exemption from VAT for a number of transactions, the emergence of the right to use the declarative nature of the VAT refund procedure for a number of organizations and the emergence of duties as a tax agent when purchasing goods, works or services from foreign companies, in cases where the place of sale is the territory of the Russian Federation.
Innovations in the VAT return form from the 4th quarter of 2022
In 2022, the VAT report has undergone adjustments.
Important
Changes to the VAT return were made by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 19, 2020 No. ED-7-3/591
.
Below we summarize what should be taken into account when filling out a VAT return starting from the 4th quarter of 2022.
We described in detail about the changes to the VAT return, including explanations on the SZPK, in the article “New form of the VAT return for the 4th quarter of 2022: overview of changes.”
Instructions for filling out a VAT return
| Declaration section | What you need to indicate | Notes |
| Title page | Basic information about the organization. Clarification of the period for which the report is submitted. | All organizations and individual entrepreneurs must fill out this form. If an adjustment is sent, its number should be indicated in the appropriate field (002, 003) |
| Section 1 | The amount of tax that the taxpayer estimates should be transferred to the state treasury. | Please indicate the correct OKTMO and KBK codes. It is recommended that you fill in the numbers in the other sections before completing this section as it is summary in nature. |
| Section 2 | The amount of tax calculated for transfer to the state budget according to the tax agent. | This part is provided by tax agents for each organization for which they perform similar functions. |
| Section 3 | Calculation of tax deductions for transactions taxed at the rates from paragraphs. 1-4 articles 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. | These sections, as well as annexes, should be completed if the organization carried out the operations specified in them. If there were no such sheets during the reporting period, then these sheets should simply be excluded from the document. |
| Sections 4-6 | Calculation of tax on the sale of goods or the sale of services or work for which a zero rate has been established, which has already been confirmed by documents or not yet. | |
| Section 7 | Information about transactions that are exempt from this type of taxation. | |
| Section 8-9 | Data from the books of purchases and sales for transactions for the reporting quarter is recorded here. | Data must be entered from the relevant journals. This section is intended to be completed by intermediaries, including those who are not VAT payers. |
| Section 10 | Transfer information from the invoice journal | |
| Section 11 | Display information from the log of received invoices | |
| Section 12 | Include data from invoices issued by persons from the list of clause 5 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. | Fill in those non-payers of VAT who, when preparing invoices, allocate the tax on a separate line. |
In a zero VAT return, only the title and the first section are filled out.
The procedure for entering data into VAT reporting
Like most tax reports, it is more convenient to fill out the VAT return from the end . That is, we first fill out the sheets and sections in which we enter data for calculating the tax, and only then those sections in which results - Section 1 and the title page.
Title page
The title traditionally indicates general information about the business entity submitting the declaration, the reporting period and the tax authority to which the declaration is submitted.
Section 1 and Section 2
The results of the tax calculation are shown here: whether it needs to be paid to the budget or reimbursed, and in what amount.
These sections indicate OKTMO, KBK.
Please note: it is in Section 1 that new fields to indicate:
- participation or non-participation in the SZPK;
- amounts of tax to be paid or reimbursed by SZPK participants.
Section 1 is easy : the formula for calculating the indicator entered in the lines is indicated under the corresponding lines. We remind you that this should be completed last . Section 2 is completed by tax agent . It includes as many sections 2 in the declaration as for how many persons the organization (IP) acts as a tax agent.
Section 3
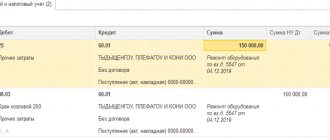
This section is the main section of the declaration, since it is here that the final tax amounts are calculated.
Here they reflect:
In the appendices to section 3 the following is recorded:
- recoverable tax amounts for previous calendar years;
- the amount of tax of a foreign organization that operates through its representative offices.
Sections 4 – 6
Sections are devoted to those transactions that are subject to a zero VAT rate.
Section 7
not subject to are reflected here - for each such transaction in accordance with the code.
Failure to complete this section does not lead to a distortion of the tax base and the calculated tax. However, it cannot . If you had to fill out the section, but didn’t do it, you may be liable under the Tax Code or the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation:
- failure to submit a document – a fine of 200 rubles (for each document) under clause 1 of Art. 126 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- administrative fine for an official - from 300 to 500 rubles under Part 1 of Art. 15.6 Code of Administrative Offences.
Sections 8 – 12
Sections - contain information from those registers maintained by VAT taxpayers (and not only) during the reporting period.
For a typical version of filling out a VAT return for the 4th quarter of 2020 (title page, section 1 and section 3) see here:
How to prepare a VAT return for submission. Tips on how to avoid a desk audit for VAT.
To ensure that the VAT reporting campaign does not become stressful for an accountant, in this article we will analyze all stages of VAT preparation, starting with the preparation of the declaration and ending with its analysis. So, some information regarding VAT tax regulation.
Taxable period.
The tax period for all VAT taxpayers is a quarter. This is stated in Art. 163 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Deadlines for submitting the declaration.
At the end of the quarter, you are required to report VAT. To do this, you must submit a VAT return to the tax authorities. The 25th day of the month
following the reporting quarter is the last day for submitting a declaration without penalties.
So the deadlines are as follows: for the 1st quarter
- you should send reports before
April 25
, for
the 2nd quarter
- before
July 25
, for
the 3rd quarter
- before
October 25
, and, therefore, the deadline for filing a VAT return for the
4th quarter
- will be
January 25.
(Clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
Payment deadlines.
You have the right to transfer VAT to the budget after the end of the quarter during the first three months in equal installments also until the 25th
.
For example, you can pay VAT for the 4th quarter of 2015 in equal installments (1/3 of the total amount of VAT payable) until January 25, until February 25 and until March 25
, according to (clause 1 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Declaration submission form.
Taking into account clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, you should know that all VAT tax returns are submitted exclusively in electronic form. Otherwise, the document will be considered not submitted with all the ensuing consequences. What consequences can we expect?
Fines.
A company that erroneously submitted a VAT report in paper form: 1.
will be fined under Art.
119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The recovery will be 5%
of the amount of tax payable for each overdue month (full and incomplete), but not less than 1000 rubles.
and no more than 30% of the specified amount. 2.
Moreover, the organization faces blocking of the account if it is late in submitting reports by more than 10 days. This right of tax officials is directly enshrined in the law (clause 3 of article 76 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Structure of a tax return.
The VAT return was adopted by Order No. 558 of October 29, 2014.
The VAT tax return adopted by Order No. 558 of October 29, 2014 includes 12 sections. But that doesn't mean you have to fill them all out. Here, as in many other reports, the rule applies: we submit only those sheets for which we have completed data.
The tax inspectorate requires
♦ Title page
♦ “Section 1” with the specified amount of tax to be paid according to the calculation data.
If there is no revenue in the reporting quarter?
These rules also apply to those taxpayers who do not have quarterly revenue.
In this case, they submit a “zero” declaration. Let's move on to review other sections:
“Section 2” is devoted to the VAT of the tax agent,
therefore, only companies charged with tax agent functions fill it out.
“Section 3” - contains the calculation of the tax payable, after which it is transferred to “Section 1”. For information on how to correctly calculate VAT, read the article “How to calculate VAT. Calculation example."
“Sections 4,5,6”
- for organizations that carried out export transactions taxed at a rate of 0% during the reporting period.
“Section 7”
- here we show transactions that are not subject to taxation.
Naturally, if there are none, then the section is not filled out and is not submitted. “Section 8”
- is filled out by taxpayers claiming tax deductions for VAT, in other words, data
from the purchase book
.
IN
to section 8, companies record information from additional sheets to the purchase book.
"Section 9"
— contains data
from the sales book
for the corresponding period.
In this case, each entry in the sales book must correspond to a separate sheet of section 9. Similar to section 8, if there are additional sheets from the sales book, then the organization enters them in Appendix 1 to section 9.
“Sections 10,11”
- relevant for those organizations that, by virtue of clause 5.2 of Art. 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is obliged to maintain and submit to the inspection a log of issued and received invoices.
"Section 12"
— information from invoices, as well as UTII payers who accidentally issued invoices, are transferred to this section.
Important tips on how not to attract the attention of tax authorities to your VAT return.
Tip #1. Check your revenue figures with your income statement.
Before you send the report, it is necessary to analyze it in order to reduce the likelihood of errors and discrepancies in the declaration, as well as to avoid claims from the tax authorities, up to a documentary check.
So, tax officials verify all data using control ratios, both within the declaration and compared with external reports. Namely, with a profit declaration. What indicators of the two declarations should be compared.
Since we charge VAT on revenue, the amounts of revenue in the VAT return and in the income tax return must be identical. If for some reason these figures do not agree, then it is advisable for you to immediately write an explanation of the reason for the discrepancy, or wait for a request for explanations from the tax office.
Tip #2. Check the row metrics in section 1.3
Further, if in “Section 1” you showed a tax refund from the budget, then a desk audit is inevitable. This rule is provided for in clause 8 of Article 88 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Lines 130 and 90 of Section 3.
Let's move on to "section 3". Here, the inspectors are interested in lines 130
and
90.
On line
130
, the buyer takes into account the deduction of VAT from advances paid, and on line
90
, the VAT restored from these advances after the goods are accepted for registration.
Tax workers calculate the tax amounts and periods for which the organization is ready to deduct VAT from the advance and, subsequently, restore it. If inspectors record even the slightest discrepancy in the indicated amounts, they demand an explanation.
Line 170 of Section 3.
Another indicator is line 170
, it contains the amount of VAT on advances received and subject to deduction from the seller.
This figure cannot exceed the sum of column 5 along lines 010,020,030,040.
Tip #3. Check with your counterparties
I would like to give one more important piece of advice on preliminary self-checking of the declaration. Before creating “section 8”, it is worth checking with the counterparties issuing the invoice data.
A situation may occur when inspectors discover invoices for which the company applied for a deduction, and your counterparty did not reflect the sale in its declaration in “section 9”.
In this case, they will require clarification and will also be required to provide all documents regarding these transactions. In particular, they may ask for contracts, invoices (acts), invoices, balance sheets, account turnover, bank statements, etc.
Last tip.
In order to be confident in the correctness of tax calculations and reporting and be able to minimize the risks of a desk audit for VAT and income tax, I strongly advise you to take the course: “Practice of filling out VAT and income tax returns 2015 +1C 8.3.”
Here, together with your teacher, you will examine in detail the procedure for filling out VAT and profit returns for different reporting periods using complex examples from practice.
The course is taught by Botova E.V., a member of the NP “International Association of Certified Accountants”, a member of the association of “Professional Accountants in Russia”.
Watch the lesson from
the course “3 Tips on How to Avoid a Desk VAT Audit”
Peculiarities of tax calculation and calculation of its amount payable
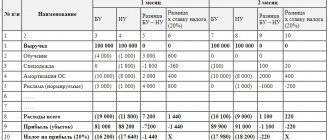
When calculating the total amount of tax to be paid or reduced for the year in the declaration, you need to remember that in this calculation:
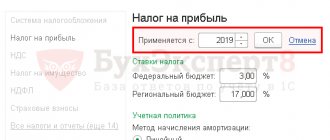
- tax distribution between budgets in 2022 - 2022 is carried out in a ratio specially established for this (3% to the federal budget, 17% to the regional budget);
- it is necessary to take into account all advances accrued for the period, reducing by them the total amount of tax, defined as a percentage of the entire tax base;
- if there are losses in the years preceding the reporting year, then data about them must be entered in Appendix No. 4 to sheet 02;
- legal entities with separate divisions will have to fill out a declaration in a special order, using Appendix No. 5, included in sheet 02;
- there is no need to calculate and enter data in the section and in the lines allocated to reflect the amounts of advances accrued for future periods.
There are updates to the 2021 income tax return form itself. About them - in the material “There will be changes in the income tax return.”
Property tax payment deadlines will be updated
At the moment, property tax and advances on it are paid in the manner and within the time limits established by the legislation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Thus, the timing of tax remittances may vary significantly depending on the region.
From 2022, Russia will introduce uniform deadlines for paying corporate property tax and advances on it.
According to the updated version of paragraph 1 of Art. 383 of the Tax Code, property tax will need to be paid no later than March 1 of the year following the previous tax period. Advances on it will need to be paid no later than the last day of the month following the previous reporting period.
At the same time, regional authorities will lose the right to determine these deadlines through the legislation of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. However, they will still be able to influence the timing of payment of advances on property taxes. Thus, they will also be able to establish for certain categories of taxpayers the right not to calculate and not pay advances on property tax during the tax period (clause 6 of Article 382 of the Tax Code).