The tax base
As a general rule, profit is the income received minus the expenses allowed by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The tax base is calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the tax period, which corresponds to one calendar year.
That is, the tax base is calculated for the period from January 1 to December 31 of the current year.
The accountant has the right to accept all income and all expenses for accounting only on the basis of primary documents confirming either income or expenses. Requirements for primary documents are regulated by Article 9 of the Law “On Accounting”.
Organizational expenses in the tax base based on profit
Expenses are recognized as justified and documented expenses. For example, employee salaries, purchase of raw materials and materials, depreciation of fixed assets, advertising and entertainment expenses, legal expenses, IT expenses and so on.
For a complete list of expenses and the rules for accounting for them in the tax base for profits, see the “Practical Encyclopedia of an Accountant” berator.
The costs of paying dividends, contributions to the authorized capital, repaying loans, etc. are not taken into account as expenses.
Methods for calculating income tax
A company can choose one of two methods for determining revenue.
Accrual method
The date of recognition of income/expense does not depend on the date of actual receipt/write-off of funds.
Income and expenses are recognized in the period in which they relate.
Cash method
Income is recognized on the date of actual receipt, that is, the receipt of money in the company's account. And expenses - according to the date of actual payment, that is, debiting money from the account.
Formula for calculating income tax
INCOME TAX = TAX BASE * TAX RATE
To calculate the tax base for income tax, an accountant must know:
- The period for which the tax base is determined.
- The amount of income from sales received in the reporting (tax) period.
- The amount of expenses incurred in the reporting (tax) period that reduces the amount of income from sales.
- Profit (loss) from sales.
- The amount of non-operating income.
- Profit (loss) from non-operating operations.
- Total: tax base for the reporting (tax) period.
The amount of loss to be carried forward can be excluded from the tax base.
If a company conducts several types of activities with different income tax rates, the tax base must be calculated separately for each type of activity.
Recognition of income and expenses
The moment of recognition of income and expenses is the period in which the receipts or expenses taken into account when calculating fees are posted. This is important for calculating income tax for dummies. The moment of recognition directly depends on the method of recognition of income and expenses. There are cash method and accrual method.
If an organization has chosen the cash method, then it must record income when it is immediately received, and expenses when funds are written off. Under the cash method, tax payments are reflected on the days of receipt. write-offs. The cash method cannot be used by banking organizations. The organization has the right to recognize profitability (costs) upon receipt (write-off) in the case where revenue is recorded in the amount of no more than 1 million rubles for each quarter (the last 4 quarters are taken into account). If revenues exceed this threshold, then the company must switch to the accrual method.
Under the accrual method, all income and expenses are recorded in accounting when they arise, and tax payments are reflected on dates confirmed by primary documents. The actual date of payment does not matter.
An institution has the right to annually choose the method of recognizing income and expenses and notify the tax office about this by December 31 of the current year.
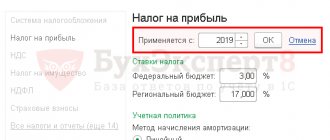
Income tax rate
Basic rate
20%
- 2%
to the federal budget (
3%
in 2022 - 2024); - 18%
to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation (
17%
in 2022 - 2024).
The tax amount calculated at a rate of 18% is credited to the Moscow city budget, 2% to the federal budget.
Regional authorities can lower the tax rate for certain categories of taxpayers, but not more than 13.5% (12.5% in 2017 - 2022).
The rate may be even lower:
- for residents of special economic zones (clause 1, clause 1.7 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for participants in regional investment projects (clause 3 of article 284.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 3 of article 284.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for residents of the territory of rapid socio-economic development or the free port of Vladivostok (clause 1.8 of article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, article 284.4 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Results
The amount and basic conditions for the application of income tax rates are established in Art.
284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In the period 2017-2018, a number of changes were made to it, significant only for a certain circle of taxpayers. The income tax rate in 2022 has not changed and is 3% for the federal budget and 17% for the regional budget. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to calculate monthly advance payment for income tax
The amount of the monthly advance payment that must be paid in the next reporting period is calculated based on the amount of the advance payment calculated for the previous reporting period.
The monthly advance payment for the first quarter of the year is equal to the monthly advance payment calculated for the fourth quarter of the previous tax period.
New organizations pay quarterly advance payments rather than monthly ones until a full quarter has passed from the date of their registration.
Then you need to clarify the amount of sales revenue excluding VAT. If it is less than 1 million rubles per month or 3 million rubles per quarter, the company can continue to pay quarterly advance payments. If your revenue is higher, you need to switch to monthly advance payments from the next month.
How to calculate your quarterly advance income tax payment
The advance payment for the quarter is equal to the amount of tax for the quarter minus the tax paid for the previous quarter.
In what cases can only quarterly advance payments of income tax be made?
Federal Law No. 121-FZ of April 22, 2022 raised the income limit under which only quarterly advances on income tax can be paid from 15 million rubles to 25 million rubles
Companies whose sales income for the second, third, fourth quarters of 2022 and the first quarter of 2022 did not exceed an average of 25 million rubles per quarter can switch to paying only quarterly advances. You can already pay them based on the results of the reporting periods of 2020. And when drawing up a declaration for the first quarter of 2022, do not charge monthly advances for the second quarter of 2022.
Quarterly income tax payments
Article 56 of the BC RF. Tax revenues of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (current version)
1. Tax revenues from the following regional taxes are subject to credit to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation:
corporate property tax - according to the norm of 100 percent;
tax on gambling business - according to the standard 100 percent;
transport tax - according to the standard 100 percent.
2. Tax revenues from the following federal taxes and fees, including those provided for by special tax regimes, are subject to crediting to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation:
corporate income tax at the rate established for crediting the specified tax to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - according to the standard of 100 percent;
tax on the profits of organizations when implementing production sharing agreements concluded before the entry into force of the Federal Law “On Production Sharing Agreements” and not providing for special tax rates for crediting the specified tax to the federal budget and budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - according to the standard of 75 percent;
personal income tax (except for personal income tax in relation to income specified in paragraphs thirty-five, thirty-six and thirty-nine of Article 50 of this Code and paragraphs five and fifty-four of this paragraph) - according to the standard of 85 percent;
personal income tax paid by foreign citizens in the form of a fixed advance payment when they carry out labor activities on the territory of the Russian Federation on the basis of a patent - according to the standard of 100 percent;
excise taxes on ethyl alcohol from food or non-food raw materials - according to the standard of 100 percent;
excise taxes on alcohol-containing products - according to the standard of 100 percent;
excise taxes on motor gasoline, straight-run gasoline, diesel fuel, motor oils for diesel and (or) carburetor (injection) engines produced in the Russian Federation - according to the standard of 88 percent;
the paragraph became invalid as of January 1, 2022. — Federal Law of November 29, 2021 N 384-FZ;
excise duties on alcoholic products with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol over 9 percent, with the exception of beer, wines, fruit wines, sparkling wines (champagne), wine drinks produced without the addition of rectified ethyl alcohol produced from food raw materials, and (or) alcoholized grape or other fruit must, and (or) wine distillate, and (or) fruit distillate - according to the standard 84 percent;
excise taxes on alcoholic products with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol over 9 percent, including beer, wines, fruit wines, sparkling wines (champagnes), wine drinks made without the addition of rectified ethyl alcohol produced from food raw materials, and (or) alcoholized grape or other fruit must, and (or) wine distillate, and (or) fruit distillate - according to the standard 100 percent;
the paragraph is no longer valid. — Federal Law of September 22, 2009 N 218-FZ;
excise taxes on alcoholic products with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol up to 9 percent inclusive - according to the standard of 100 percent;
excise taxes on wine materials, grape must, fruit must - according to the standard of 100 percent;
tax on the extraction of common minerals - according to the norm of 100 percent;
tax on mineral extraction (with the exception of minerals for which a rental coefficient other than 1 is established for taxation, minerals in the form of hydrocarbons, natural diamonds and common minerals, coking coal, iron ores, apatite-magnetite, apatite- staffelite and low-iron apatite ores, multi-component complex ore, in respect of which a taxation coefficient has been established that characterizes the cost of valuable components in the ore) - according to the standard of 60 percent;
tax on mineral extraction in the form of natural diamonds - according to the standard of 100 percent;
regular payments for the extraction of mineral resources (royalties) upon implementation of production sharing agreements in the form of hydrocarbon raw materials (with the exception of natural gas) - according to the standard of 5 percent;
fee for the use of objects of aquatic biological resources (excluding inland water bodies) - according to the standard of 80 percent;
fee for the use of objects of aquatic biological resources (for inland water bodies) - according to the standard of 80 percent;
fee for the use of wildlife objects - according to the standard 100 percent;
tax levied in connection with the application of the simplified taxation system, including the minimum tax - according to the standard of 100 percent;
The paragraph became invalid on January 1, 2013. — Federal Law of June 25, 2012 N 94-FZ;
the paragraph became invalid as of January 1, 2022. — Federal Law of November 30, 2016 N 409-FZ;
The paragraph became invalid on January 1, 2013. — Federal Law of June 25, 2012 N 94-FZ;
state duty (to be credited at the place of state registration, commission of legally significant actions or issuance of documents), with the exception of the state duty provided for in paragraphs forty-eighth and fiftieth of this paragraph - according to the standard of 100 percent:
in cases considered by the constitutional (statutory) courts of the relevant constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
for the performance of notarial acts by notaries of state notary offices and (or) officials of executive authorities authorized in accordance with the legislative acts of the Russian Federation and (or) legislative acts of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to perform notarial acts;
for state registration of interregional, regional and local public associations, branches of public associations, as well as for state registration of changes to their constituent documents;
for state registration of regional branches of political parties;
for the state registration of an agreement on the pledge of vehicles, including the issuance of a certificate, as well as for the issuance of a duplicate certificate of state registration of an agreement on the pledge of vehicles to replace the lost or deteriorated in terms of registration of the pledge of tractors, self-propelled road-building machines and other machines and trailers him;
for the issuance of a qualification certificate granting the right to carry out cadastral activities;
for issuing a certificate of state accreditation of the regional sports federation;
for issuing a certificate of a tour guide (guide) or a guide-interpreter providing services on tourist routes;
for state registration of a mass media, for making changes to the registration record of a mass media (including those related to changes in subject matter or specialization), the products of which are intended for distribution primarily in the territory of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation, the territory of a municipal entity;
for state registration of a mass media, for making changes to the registration record of a mass media (including those related to changes in subject matter or specialization), the products of which are intended for distribution primarily throughout the entire territory of the Russian Federation, beyond its borders, in the territories of two or more subjects of the Russian Federation;
for actions of authorized bodies related to licensing the use of subsoil plots of local significance;
for the actions of authorized bodies related to the licensing of the procurement, processing and sale of non-ferrous metal scrap, with the licensing of the procurement, processing and sale of ferrous metal scrap;
for the provision of licenses for the retail sale of alcoholic beverages issued by executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation;
for actions of executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation related to licensing of educational activities carried out within the limits of the delegated powers of the Russian Federation in the field of education;
for the actions of executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation related to state accreditation of educational activities carried out within the delegated powers of the Russian Federation in the field of education;
for granting a license for the production, storage and supply of alcohol-containing non-food products in terms of those produced from confiscated ethyl alcohol, alcohol and alcohol-containing products that do not comply with national standards and technical regulations, or obtained from processing waste from the production of ethyl alcohol and alcohol products;
for the issuance by executive bodies of state power of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation authorized in the field of control (supervision) of accreditation certificates in order to recognize the competence of the organization in the relevant field of science, technology and economic activity to participate in control activities;
for the actions of executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in affixing an apostille on state documents on education, on academic degrees and academic titles within the delegated powers of the Russian Federation in the field of education;
for the issuance by an authorized executive body of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation of a special permit for the movement on roads of vehicles transporting dangerous, heavy and (or) large-sized cargo;
Paragraphs thirty-six to thirty-eight became invalid as of January 1, 2013. — Federal Law of December 3, 2012 N 244-FZ;
for actions of authorized bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation related to licensing of business activities for the management of apartment buildings;
state duty (to be credited at the place of state registration, commission of legally significant actions or issuance of documents) for the performance by federal executive authorities of legally significant actions in the event of filing an application and (or) documents necessary for their implementation to the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services - according to the standard 50 percent;
The paragraph became invalid on January 1, 2015. — Federal Law of October 22, 2014 N 311-FZ;
state duty (to be credited at the place of state registration, performance of legally significant actions or issuance of documents) for the performance by federal executive authorities of legally significant actions in the case of filing an application and (or) documents necessary for their implementation in electronic form and issuing documents through a multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services - according to the standard of 25 percent;
tax on professional income - according to the standard 63 percent;
state duty (to be credited at the place of state registration, commission of legally significant actions or issuance of documents) for the commission by authorized executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation of legally significant actions related to the state registration of attractions - according to the standard of 100 percent;
personal income tax in the part of the tax amount exceeding 650 thousand rubles, related to the part of the tax base exceeding 5 million rubles - according to the standard of 74 percent;
tax on the extraction of mineral resources, in respect of which a rental coefficient other than 1 is established during taxation - according to the standard of 17 percent;
tax on the extraction of minerals in the form of coking coal - according to the standard of 30 percent;
tax on mineral extraction in the form of iron ore (except for oxidized ferruginous quartzites) - according to the standard of 17 percent;
tax on the extraction of minerals in the form of apatite-magnetite, apatite-staffelite and low-iron apatite ores - according to the standard of 17 percent;
tax on the extraction of mineral resources in the form of multi-component complex ore, in respect of which a taxation coefficient is established that characterizes the cost of valuable components in the ore - according to the standard of 17 percent;
excise tax on liquid steel is 17 percent.
2.1. In the current financial year, tax revenues from excise taxes on motor gasoline, straight-run gasoline, diesel fuel, motor oils for diesel and (or) carburetor (injection) engines, subject to credit to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in accordance with the standard established by this article, are sent to the territorial body of the Federal Treasury to the authorized territorial body of the Federal Treasury for their distribution and transfer at least once every 10 days to treasury accounts for the implementation and reflection of operations for accounting and distribution of receipts of territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury in accordance with the standards established by the federal law on the federal budget for current financial year.
Tax revenues from the specified excise taxes transferred by the authorized territorial body of the Federal Treasury in the current financial year to treasury accounts for the implementation and reflection of operations for accounting and distribution of revenues of the territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury are distributed by the territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury between the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets, taking into account those established by the laws of the constituent entities Russian Federation differentiated standards for contributions to local budgets.
2.2. In the current financial year, tax revenues from excise taxes on alcoholic products with a volume fraction of ethyl alcohol over 9 percent, with the exception of beer, wines, fruit wines, sparkling wines (champagne), wine drinks made without the addition of rectified ethyl alcohol produced from food raw materials, and (or) alcoholized grape or other fruit must, and (or) wine distillate, and (or) fruit distillate, subject to credit to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in accordance with the standard established by this article, are distributed by territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury between the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation Federation in accordance with the federal law on the federal budget.
2.3. In the current financial year, tax revenues from excise taxes on ethyl alcohol from food or non-food raw materials, excise taxes on alcohol-containing products, subject to credit to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in accordance with the standard established by this article, in the amount of 50 percent of the volume of these revenues are distributed by territorial bodies of the Federal Treasury between the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation in accordance with the federal law on the federal budget.
2.4. No longer in force on January 1, 2022. — Federal Law of November 29, 2021 N 384-FZ.
3. Tax revenues from federal taxes and fees, taxes provided for by special tax regimes, subject in accordance with this Code to be credited to local budgets and budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation, shall be credited to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation - the federal cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol. , as well as income from trade taxes payable in the territories of these constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
4. Tax revenues from regional taxes established by the state authorities of the region (region), which includes the autonomous okrug, are subject to credit to the budget of the region (region). Tax revenues from regional taxes established by government bodies of the autonomous region are subject to credit to the budget of the autonomous region.
Unless otherwise established by the federal law on the federal budget and an agreement between the state authorities of the territory (region), which includes the autonomous district, and the state authorities of the corresponding autonomous region, tax revenues specified in paragraph 2 of this article are subject to credit to the regional budget (region), with the exception of the personal income tax at the rate of 15 percent, subject to credit to the budget of the Autonomous Okrug, transferred in full by the state authorities of the Autonomous Okrug to the relevant local budgets in the manner prescribed by Article 58 of this Code.
5. The tax revenues specified in this article may be transferred in whole or in part by state authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation to the relevant local budgets in the manner prescribed by Article 58 of this Code.
Income tax return
The tax return is submitted to the Federal Tax Service no later than 28 days from the end of the corresponding reporting period.
The annual income tax return must be submitted no later than March 28 of the year following the expired tax period.
The declaration is submitted to the tax office:
- at the location of the organization;
- at the location of each separate division of the organization.
Most accounting programs support auto-filling of the declaration and ensuring that the form itself is up to date.
If the accounting department does not use an accounting program, the tax return form can be downloaded electronically on the Federal Tax Service website or filled out through the taxpayer’s personal account, which can also be registered on the Federal Tax Service website.
The Federal Tax Service accepts tax returns in electronic form.
Effective tax rate as an opportunity to exclude profits from taxation
Law No. 150-FZ of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation dated 06/08/2015 amended Art. 25.13-1, which regulates the conditions for removing from the tax base income received by a controlled foreign company (hereinafter referred to as the CFC). One of the reasons for this is the effective profit tax rate of at least 75% of the weighted average rate for this type of payment.
To determine the effective tax rate, two indicators must be used:
- the amount of income tax of a foreign legal entity, determined in accordance with the regulatory framework of a foreign state (a detailed description of the components of this indicator is given in subparagraph 1, paragraph 2, article 25.13-1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the amount of profit of a foreign organization determined according to the requirements of Art. 309.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The weighted average rate is calculated according to the formula fixed in subparagraph. 2 p. 2 art. 25.13-1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
So, if a foreign company has a positive profit, it is necessary to express the ratio of the effective and weighted average profit rates.
Read more about effective and weighted average tax rates in this material.
Deadlines for payment of taxes and advance payments
| What do we pay? | Payment deadlines |
| Income tax at the end of the year | No later than March 28 of the year of the following year (that is, the next year after the expired tax period) |
Advance payments at the end of the reporting period:
| No later than the 28th day of the month following the month for which the advance payment amount is calculated. No later than the 28th day of the month following the expired reporting period. |
| Monthly advance payments | Every month no later than the 28th day of the current month |
| Tax on income from state and municipal securities subject to taxation by the recipient of the income | Within 10 days after the end of the month in which the income was received |