Accounting policies include methods of accounting, as well as forms of primary documents used in the company. Management has the right to reflect a specific type of document or accounting method if there are several options at the legislative level. At the same time, the company must strictly comply with the provisions specified in the accounting policy, otherwise inspectors may apply penalties during the inspection. We will discuss how to correctly draw up an accounting policy for 2022 in the article.
The concept of accounting policy
The accounting policy is an internal regulatory document of the organization, which contains the method of accounting, the procedure for reflecting individual transactions, as well as the forms of primary documentation.
The document reflects the method of calculating depreciation, the procedure for calculating the reserve for the payment of vacation pay, what primary documents are used when shipping goods and other important aspects of accounting.
The company must determine for itself what standards to adhere to for accounting or tax purposes.
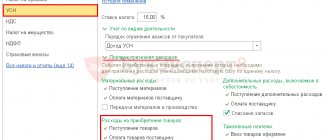
So, for example, when calculating the amount of depreciation in tax accounting, it is allowed to use a depreciation bonus, which can be written off to current expenses in the amount of 10%.
According to accounting standards, any organization is required to create reserves for upcoming vacations, with the exception of small enterprises, while the methodology for calculating the reserves has not been established, so the company can independently decide: to make the calculations personally for each employee or for departments as a whole.
The company can decide for itself: to use exclusively unified forms for accounting or to independently develop certain types of primary documents. For example, vacation schedule, staffing table and other documentation.
Accounting policies must meet the following requirements:
- completeness of reflection of the facts of economic life
- timely recording of transactions
- correspondence of the turnover of analytical and synthetic accounting based on the results of each month
In the accounting policy, it is necessary to establish a working chart of accounts with a list of accounts that the company will use in accounting.
If tax legislation allows the use of several accounting methods for the same transaction, the company must reflect one of them in its accounting policy.
The company must strictly comply with the provisions of its accounting policies; this is precisely the position taken by the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation in its Determination No. 167-O dated May 12, 2005.
Accounting policy according to accounting
Order No.
On approval of the accounting policy of Cozy House LLC for accounting purposes
Moscow December 31, 2022
I ORDER
The following accounting policy of Cozy House LLC will come into effect from January 1, 2022:
1. Accounting shall be carried out through double entry in the accounting accounts in accordance with the Chart of Accounts, approved. By order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n. The working chart of accounts is presented in Appendix No. 1.
2. As primary accounting documents for recording facts of economic life, use approved unified forms of primary accounting documentation approved by the Resolutions of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation, as well as independently developed forms presented in Appendix No. 2;
3. Data contained in primary accounting documents are subject to timely registration and accumulation in accounting registers. The forms of accounting registers were developed by the organization independently and are presented in Appendix No. 3;
4. Carry out an inventory of property and liabilities in cases provided for by law, including annually when preparing annual financial statements;
5. Maintain accounting records using a specialized accounting computer program 1C;
6. Maintain accounting records according to the following rules:
1. Accounting and qualification of assets
1.1. Accounting and qualification of assets is carried out depending on the period of their use, taking into account the cost criterion. Costs for the acquisition, creation, improvement of an asset are recognized:
- stocks, if the period of use is up to 12 months;
- fixed assets, if the period of use is more than 12 months;
- expenses of the period in which they are incurred, if the value of the asset is immaterial (hereinafter referred to as immaterial assets).
1.2. Non-essential assets include objects whose value is not significant for financial statements:
- objects worth up to 100,000 rubles, if their useful life is more than 12 months;
- objects, regardless of the period of use and cost: special means of production: special tools, special devices, special equipment, special clothing;
- household equipment and devices;
- furniture;
- inventories for management needs.
1.3. Accounting for non-essential assets is maintained on account 10.21 “Low-valued equipment and inventories” according to the following subaccounts:
- 10.21.1 “Purchase of low-value equipment and supplies”;
- 10.21.2 “Disposal of low-value equipment and inventories.” At the time of acquisition (creation) of assets:
- Dt 10.21.1 Kt 60 – capitalization of assets;
- Dt cost account Kt 10.21.2 – recognition of the cost of assets in expenses; The cost account corresponds to the cost account where depreciation of non-essential assets would be included. At the time of transfer of non-essential assets into operation:
- Dt 10.21.2 Kt 10.21.1 – transfer of assets into operation;
- Dt MTs.ХХХ – capitalization for the balance sheet of assets.
1.4. Reflection of the consequences of changes in accounting policies in connection with the transition to FAS 5/2019 “Inventories2” is carried out prospectively without retrospective recalculation of indicators.
2. Accounting for fixed assets
2.1. Objects with a service life of more than 12 months and a cost of more than 100,000 rubles. are taken into account as part of fixed assets;
2.2. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method for all fixed assets;
2.3. Fixed assets are not revalued.
3. Accounting for intangible assets
3.1. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis for all intangible assets.
4. Accounting for inventories (materials, goods)
4.1. Inventories include assets used within 12 months:
- for the production of products, performance of work, provision of services, as well as for sale in the normal course of business.
They are accounted for at actual cost and are reflected in account 10 “Materials”.
4.2. Inventories intended for management needs are recognized as non-essential assets. These include:
- office stationery and accessories;
- water and materials to ensure normal working conditions;
- materials for household needs, maintaining order.
The costs of their acquisition and creation are taken into account in accordance with clause 1.3.
4.3. The costs of purchasing and procuring goods to central warehouses are included in the cost of goods and are taken into account in account 41 “Goods”.
4.4. Goods in wholesale and retail trade are accounted for at actual cost on account 41 “Goods2.
4.5. The actual cost of inventories when acquired with non-cash funds corresponds to the book value of the transferred assets.
4.6. Subsequent valuation of inventories at the reporting date is carried out at actual cost. There is no annual test for impairment of inventories.
4.7. When inventories are disposed of, they are valued using the FIFO method.
5. Accounting for work in progress and finished products
5.1. Direct costs for production of products, performance of work, provision of services include:
- material costs (raw materials and materials) used in the production of products, works, services;
- costs of wages and other payments to production workers (including insurance contributions from salaries);
- depreciation of fixed assets used directly in production;
- other costs that are directly related to the production of specific products, works, services.
These costs are determined in accordance with specifications, technological maps, control measurement reports and other documents confirming the composition of costs necessary for the production of products, provision of services, and performance of work. They are taken into account on account 20 “Main production”.
5.2. The distribution of total direct costs between types of finished products (works, services) is carried out in proportion to the sum of all direct costs for a specific finished product (works, services);
5.3. Indirect production costs include general production, general shop costs that are indirectly involved in the production process, performance of work, and provision of services. They are accounted for in account 25 “General production expenses”2 and at the end of the month they are distributed into direct costs (Dt 20 “Main production” Kt 25) in proportion to the amount of all direct costs;
5.4. Excessive costs are taken into account under the article “Excessive costs” in Dt 20 (25). They admit:
- expenses at the end of the month as a result of improper organization of the production process, i.e. are not included in the cost of WIP, GP - Dt 90.02 Kt 20.01, 25;
- are included in the cost of work in progress and GP if losses are caused by the technological process Dt 20.01 Kt 20.01, 25, 28.
5.5. Accounting for finished products is maintained on account 43 “Finished products” without using account 40 “Release of finished products”. The evaluation of finished products during their production is carried out at the planned output price, which is determined by order of the head of the organization. And at the end of the month (in reporting), the assessment is carried out at actual cost (based on the sum of actual direct and indirect costs);
5.6. Accounting for semi-finished products of own production is carried out separately, similar to accounting for finished products on account 21 “Semi-finished products of own production”;
5.7. Work in progress (WIP) is accounted for on account 20.01 “Main production” and is assessed in the reporting at the amount of direct costs (excluding indirect ones).
6. Accounting for settlements with employees and contractors
6.1. All settlements with employees for amounts allocated for administrative, economic and other expenses for the needs of the organization are carried out on account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”, regardless of whether they were issued for reporting or were compensated to employees after their reporting;
6.2. Accounting for tickets issued in electronic form purchased by an organization for employee business trips is kept in account 76.14 “Purchase of tickets for business trips.”
7. Accounting for income and expenses
7.1. Management costs include costs not associated with the production of products, works, and services. They are accounted for in account 26 “General business expenses” and at the end of the month are fully recognized as expenses (Dt 90.08 “Administrative expenses” Kt 26);
7.2. Costs associated with the sale of products, works and services (including packaging and transportation costs) are recorded in account 44.02 “Business expenses in organizations engaged in industrial and other production activities” and at the end of the month are written off in full to the debit of the account 90.07 “Sale expenses”;
7.3. Income and expenses associated with the provision of property for rent are recorded as other income and expenses accordingly in account 91 “Other income and expenses”.
8. Accounting for state aid
8.1. The organization accepts budget funds for accounting as funds are actually received;
8.2. Future income related to the receipt of budget funds to finance capital expenditures is presented separately in the reporting. In the balance sheet as a separate item as part of long-term liabilities. In the financial results statement, amounts included in financial results are treated as a separate item within other income.
9. Accounting for interest on loans
9.1. Interest on borrowed funds is included in other expenses, including when acquiring (creating) an investment asset.
10. Bug fixes
10.1. An error that leads to a change in the total amount of assets (liabilities), as well as income (expenses) in the statements by more than 10% or leads to a change in a group of balance sheet items or income statement in the amount of 200 thousand rubles or more is considered significant. inclusive.
10.2. A significant error identified after approval of the financial statements is corrected by entries in correspondence with account 91 “Other income and expenses” without retrospective recalculation of indicators.
11. Estimated values
11.1. The creation of reserves for doubtful debts is carried out for each doubtful debt separately according to the methodology specified in Appendix No. 5 to the accounting policy.
12. Accounting regulations do not apply
12.1. PBU 12/2010 “Information by segments”;
12.2. PBU 18/02 “Accounting for corporate income tax calculations”;
12.3. PBU 2/2008 “Accounting for construction contracts”;
12.4. PBU 8/2010 “Estimated liabilities, contingent liabilities and contingent assets”;
12.5. PBU 11/2008 “Information about related parties”;
12.6. PBU 16/2002 “Information on discontinued activities.”
13. Form of presentation of financial statements
13.1. The organization submits annual financial statements in the simplified form provided for in Appendix No. 5 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. If it is required to disclose significant events that formed the reporting indicators, then such disclosure in any form is reflected in the form of Explanations to the annual reports.
CEO /
Appendix No. 1. Working chart of accounts
View the working chart of accounts
Appendix No. 2. Primary accounting documents
Appendix No. 2 to the Order “On approval of the accounting policy of Cozy House LLC for accounting purposes”
Primary accounting documents
1. The Company uses the following primary accounting documents according to unified forms:
- For accounting of fixed assets - forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2003 N 7;
- For recording working hours and settlements with personnel for wages - forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 N 1;
- For accounting of materials - forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 1997 N 71a;
- For settlements with accountable persons - form N AO-1, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated 01.08.2001 N 55
- When transporting goods - the form of the consignment note approved by Appendix 4 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 21, 2020 N 2200 (Appendix N 2);
- For accounting of cash transactions - forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 N 88;
- For the shipment of goods - form N TORG-12, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 N 132;
- For the shipment of goods, provision of services, performance of work - the UPD form proposed in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated October 21, 2013 N ММВ-20-3 / [email protected] (Appendix No. 1 to the order);
- For recording inventory results - forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 N 88; When using unified forms, it is necessary to fill in all the details specified in Federal Law dated December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting”. Other details are filled in as necessary.
2. The Company uses the following primary accounting documents in accordance with independently developed forms:
- For accounting for the write-off of materials – Act on the write-off of materials;
- For accounting of work or services performed - Certificate of work performed (services rendered);
- To reflect other facts of economic life - Accounting certificate.
3. The above forms of unified and developed documents are recommended for use, and can be added or changed by order of the manager. The forms of primary accounting documents for execution of certain transactions can also be agreed upon with the counterparty when concluding agreements with them.
CEO /
Appendix No. 3. Accounting registers
Appendix No. 3 to the Order “On approval of the accounting policies of Cozy House LLC for accounting purposes”
Accounting registers
The Company uses the following accounting registers in accordance with independently developed forms:
- To generate summary data – Balance Sheet.
- To generate detailed data on an accounting account - Account balance sheet or Account analysis.
The forms are recommended for use and can be added or changed by order of the manager.
CEO /
The procedure for drawing up accounting policies
At the legislative level, there is no clear regulation on the issue of who exactly should draw up the accounting policy, as well as the requirements for it.
In most cases, responsibility falls on the company's chief (or sole) accountant, who is responsible for ensuring that the approved accounting policies meet the needs of the organization and are also correctly executed.
The only requirement for companies is to draw up an internal order approving the accounting policies signed by the manager (PBU 1/2008). Its absence may entail financial sanctions from the inspection authorities, since some business transactions may be recognized as incorrectly executed. The order is drawn up in free form indicating the list of persons responsible for the accounting policy; the following details are required: number, date and signature of the manager.
As a rule, accounting policies are formed separately for tax and accounting, where each section is named in accordance with the object or method of accounting: “Fixed assets”, “Wages”, “Calculation method”, etc.
Accounting
The accounting policy of individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system “Income” in terms of accounting does not differ from its registration by businessmen and organizations operating under other regimes. Basic requirements for the preparation of this document include mention of the following points:
- Maintenance is carried out on the basis of Federal Law No. 402-FZ and PBU.
- The accounting uses the chart of accounts approved by Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000.
- Responsible for the accounting policy of individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system “Income” and maintaining accounting records is the entrepreneur indicating his full name.
- Unified forms of primary documents are used (must be listed).
- Manual (or automated) control of the control unit is used.
- The possibility of correcting accounting errors of previous periods in the reporting period and the methods for these corrections are indicated.
- In the case of production, methods for assessing initial goods and materials used in the manufacture of products are reflected.
- The procedure for accounting for income and expenses is described (if the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” is applied).
Timing for approval of accounting policies
When starting its activities, a company approves an accounting policy, which it can adhere to throughout the entire period of business until liquidation or make the necessary adjustments at the end of the reporting or tax period.
Approval deadlines differ for accounting and tax accounting:
- for accounting purposes - within 90 days from the date of registration or until January 1 when making changes to a previously approved document (PBU 1/2008)
- for VAT accounting - until the end of the first reporting period, the rules apply to activities from the moment of creation (clause 12 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
- for accounting for income tax - the deadlines are not defined, but must be applied before the end of the current tax period (Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)
Changes to accounting policies are permitted in the following cases:
- a new type of activity or new transactions not previously listed in the accounting policy
- implementation of new amendments to tax legislation
- changing the accounting method to a more efficient one
Accounting policy in 2022
When drawing up an accounting policy for the next year, the company must take into account the following points:
- in connection with the abolition of UTII, it is necessary to decide which taxation system will be used for accounting; if the choice falls on the simplified tax system, then before the end of 2022 you must notify the tax office of your decision (see in more detail Which regime to switch to after UTII?)
- from next year, more companies will be able to apply for the use of the simplified tax system due to an increase in the maximum values of mandatory limits
- for SMEs in 2022, reduced rates of insurance premiums will be applied for wages above the minimum wage, which also affect the size of the reserve for vacation pay
- from next year it is allowed to adhere to the requirements of the Federal Standard “Fixed Assets” instead of PBU6/01
- IT companies can apply a reduced rate on insurance premiums and income tax (see more details Income Tax. Changes for 2022)
- The form of the waybill has changed, the accounting policy must reflect the method of registration: paper or electronic