Any accountant will tell you that some contractors take a responsible approach to preparing the necessary documents, including invoices, while others do so carelessly. And these others are a headache not for the company, but for the accountant, who has to prove to the counterparty that the document was drawn up with errors and ask them to correct them. We tell you which defects in invoices, according to officials, are not critical, and which still require correction.
An invoice is a document giving the right to deduct input VAT. Therefore, during a tax audit, invoices are always subject to careful study by inspectors. If something is wrong with them, the Federal Tax Service may, based on the results of the inspection, remove part of the deduction, which means that the company will have to pay VAT, penalties and sanctions.
However, not every error on an invoice will disqualify the buyer from the deduction. Only those defects that interfere with the identification of the seller and the buyer, the name of the goods, their value, as well as the tax rate and amount of tax are threatened with unpleasant consequences. This follows directly from paragraph 2 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It would seem that there is a clear rule regarding errors in the invoice. However, in practice, questions and controversial situations still arise. Let's figure it out.
Identification of the parties to the transaction in the invoice
Information by which the seller and buyer can be identified is the name of the organization (or full name of an individual entrepreneur), TIN and address. Therefore, it is worth paying attention to the correctness of these indicators.
Questions usually do not arise with the name of the organization, as well as with the full name. individual entrepreneur. It happens that entrepreneurs, when issuing invoices to their customers, do not indicate their status there. As a result, it looks as if the invoice was drawn up not by an individual entrepreneur, but by an ordinary individual Vasily Ivanov. And Vasily Ivanov, as an individual, in principle, cannot issue invoices, since he is not a VAT payer.
So, such filling should not create negative consequences for the buyer, because it is still possible to identify the seller in this situation. The lack of individual entrepreneur status does not prevent you from understanding who the seller is. Explanations from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation confirm that such filling does not indicate violations in the invoice (letter dated 05/07/2018 No. 03-07-14/30461).
The following clarification from officials concerns filling out information about the name of the purchasing organization. In the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01/09/2017 No. SD-4-3/ [email protected] attention is drawn to the fact that the purchasing organization will not be able to claim VAT for deduction if this line does not indicate its details, but the surname of its employee, which product was purchased. We think that this situation is very rare, but if you do encounter it, then keep in mind that such a design is a gross mistake.
As for the address, the address that is contained in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs must be indicated. This is stated in subparagraph “d” of paragraph 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137). However, it is not scary if the organization’s address indicated in the invoice uses a different sequence of words than in the register. According to officials, such filling cannot be an obstacle to obtaining a VAT deduction (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 23, 2018 No. 03-07-11/84720).
Will minor changes in the spelling of an address be considered a serious violation (for example, using lowercase letters instead of capital ones, abbreviating the words “city”, “street”, replacing the word “premises” with the word “office”, etc.)? No, it will not. The address itself is correct. Officials also do not see anything illegal in this (letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 17, 2018 No. 03-07-14/58351, dated April 2, 2018 No. 03-07-14/21045, dated January 29, 2018 No. 03-07-09/4554 ).
Due to minor distortions in the spelling of the address of the seller or buyer, tax authorities do not have the right to withdraw the deduction.
Identification of the “item of sale” in the invoice
As mentioned above, errors that make it difficult to identify the name of the product (work, service) are grounds for declaring the deduction illegal. Therefore, incorrect indication of the name of a product (work, service) is considered a serious violation, due to which the buyer will be deducted the “input” VAT on completely legal grounds (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2015 No. 03-03-06/1/47252). But incomplete information about the name of the goods (works, services) cannot become a reason for withdrawing a deduction, however, provided that such filling out the invoice will not prevent the tax authorities from identifying the “item of sale” (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2016 No. 03-07 -09/67406, dated 05/10/2011 No. 03-07-09/10).
What information can help identify a product, work or service? For example, details of the contract in accordance with which the implementation is carried out. Therefore, if the name of the subject of the transaction is not fully reflected in the invoice, it is advisable to also provide a link to the details of the contract or invoice.
But if the document does not disclose the very name of the product or the nature of the work or services, but only contains a link to the details of the contract (for example, services under contract No. __ dated ______), then such registration may cause claims from the verifiers. And in practice, similar precedents arose. True, in such cases the court, as a rule, takes the side of the taxpayers (see, for example, Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated December 1, 2014 No. A40-52708/14).
Identification of amounts in the invoice
The cost of goods (works, services), tax rate and VAT amount in the invoice must also be filled out correctly. Errors in them are a serious violation, the consequence of which may be the removal of the VAT deduction by the inspectors.
For example, if the tax rate is in error, the seller must correct the invoice accordingly. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation recalled this in a letter dated November 6, 2018 No. 03-07-11/79611. If there are no corrections, then for the buyer this is fraught with deprivation of the deduction.
What about cost accuracy? For example, from clause 3 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 follows that the cost indicators of the invoice are indicated in rubles and kopecks. Does this mean that if this order is violated (for example, by rounding), the buyer will lose the deduction?
Let us turn to the explanatory letters of the departments. In a number of letters, officials of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation cite this rule, adding that rounding the amount is unacceptable (letters dated September 27, 2018 No. 03-07-14/69147, dated February 17, 2014 No. 03-07-09/6395 and dated January 29, 2014 No. 03 -02-07/1/3444.). However, the authors of the letters do not draw any conclusion about the consequences of such a violation. We believe that rounding does not make it impossible to identify cost indicators. But we do not exclude the risk of claims from tax authorities.
But on the following situation, officials from different departments do not have a common opinion. We are talking about reflecting the graphic sign of the ruble in the invoice instead of the code and name of the currency. Capital tax officials believe that such filling deprives the buyer of the right to deduction (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 22, 2016 No. 16-15/028574), and representatives of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation are more loyal. In their opinion, expressed in letter No. 03-07-11/21095 dated April 13, 2016, such preparation does not prevent the use of the deduction.
We believe this approach is more correct, because such filling does not interfere with identifying the cost indicators of the invoice. If disputes arise with tax authorities, you must refer to this letter from the Ministry of Finance. Most likely, it will convince local inspectors of the legality of the deduction.
Let's go to refusal
Taking into account all of the above, if an error is made in calculating the cost of goods, as well as the tax itself in the invoice, the inspectorate has the right to refuse to accept VAT for deduction.
Of course, errors can be different, but a fairly common situation is when in a document compiled using software, discrepancies in the calculation of the tax amount can amount to, for example, 0.1 kopecks, but the total amount of the calculated VAT calculation is indicated correctly. If, upon acceptance of tax deduction under such a document, the final tax amount clearly corresponds to the rate, then the Federal Tax Service will have no formal grounds for refusing the deduction. As an example, we can cite the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated January 19, 2012 No. A56-17988/2011. The inspectorate refused the company because there were discrepancies in the information contained in the invoices. The reason for the discrepancies was the rounding done by the accountant's program. The court found that, according to the inspectorate’s calculations, the deduction could have been claimed in a larger amount, therefore, the reflection of incorrect data in the documents did not lead to an overestimation of the deduction amount. The arbitrators concluded that the deduction of value added tax was legal.
On a note
89 percent is the safe share of VAT deductions in 2015, the national average. If a company claims a higher percentage of deductions, then it most likely cannot avoid a tax audit.
Let's look at another common mistake: the invoice shows the wrong tax rate, but the final VAT amount is determined correctly. In this situation, it would seem that the fiscal authorities should refuse the deduction in any case. But, as in the previous case, the organization should proceed from the fact that the amount of the tax deduction is determined correctly. This conclusion is confirmed by arbitration practice. For example, the FAS Moscow District, in a resolution dated November 13, 2012 in case No. A40-19351/12-115-48, came to the conclusion that a technical error in the VAT rate indicated in invoices did not lead to incorrect calculation of tax or incorrect deduction statement. Of course, we cannot but be pleased with this approach of the arbitrators on the issue of VAT deduction. However, we should not forget that legal disputes with fiscal authorities are in any case a waste of time and nerves. Of course, with sufficient control over the indicators of invoices received by the organization, the errors in question can be identified at the stage of receiving the paper. Otherwise, this violation will lead to a recalculation of the taxable base based on the results of the audit.
Minor defects in invoices
All other defects that do not interfere with the identification of the above information should not become a reason for the inspectors to remove the VAT deduction. Here are examples of such errors that, according to officials, are not serious.
| Description of the defect | Confirmation letters | Note |
| The invoice was issued late, that is, after the expiration of five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services) | Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 25, 2016 No. 03-07-11/2722, dated April 25, 2018 No. 03-07-09/28071 | The day of shipment is included in the five-day period established for issuing an invoice (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 18, 2018 No. 03-07-14/74899) |
| An error was made when filling out line 4 “Consignee and his address” of the invoice | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2019 No. 03-07-11/10765 | The officials’ conclusion can be extended to a situation where the error is also contained in line 3 “Consignor and his address” |
| The invoice contains additional information about the actual addresses of the seller or buyer, which differ from the addresses specified in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs | Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 2017 No. 03-07-09/85517 | Information about the actual address is indicated as additional information. That is, the invoice must necessarily contain an address corresponding to the one indicated in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities (USRIP) |
How to correct errors in invoices
How to correct invoices if the errors in them are serious and affect the receipt of a deduction?
Firstly, the one who compiled the invoice, that is, the seller or contractor, must correct it. Secondly, corrections are made by drawing up a new, corrected invoice, that is, nothing needs to be done with the “source” (one copy of it still remains with the buyer unchanged).
When issuing a revised invoice, the seller/performer must use the same form as for the original invoice. Fill it out in the same way as the original invoice, but with the correct information. In this case, the serial number and date of correction are added to line 1a. As for line 1, when issuing a revised invoice, data from line 1 of the “source” is transferred to it.
This procedure follows from clause 7 of the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
Results
Once you receive an invoice and discover an error in it, do not rush to demand that it be corrected. First, check whether this error prevents VAT deduction. You need to contact the counterparty only if the answer to this question is positive. For information about when you need to correct an invoice, read the article “You made a mistake on an invoice - what and how to correct it.”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Registering the corrected invoice in the purchase ledger
The buyer's procedure depends on which tax period (quarter) the seller will draw up the corrected invoice.
If for the quarter in which the original document was drawn up, then the course of action is as follows. In the purchase ledger, you must first cancel the original entry. This is done like this: the indicators of the original invoice are re-registered, but the values are given with a minus sign. After this, the data of the corrected document is recorded in the purchase ledger as usual.
The situation is more complicated when the quarter in which the original invoice was received and recorded in the purchase ledger has ended. And if a VAT return has already been submitted for this quarter, then you cannot do without an updated declaration.
The buyer should draw up an additional sheet to the purchase book for the quarter in which the “source” was registered. In this sheet, he needs to cancel the entry on the original invoice, re-reflecting its indicators with a minus sign. As a result of this, the amount of “input” VAT for this quarter will be reduced, which will entail the need for an updated declaration in which the amount of the deduction will be reduced. And the corrected invoice should be recorded in the purchase ledger for the quarter in which it was received. It is in this quarter that the deduction on the original invoice becomes eligible.
This procedure follows from clause 9 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger, approved. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137.
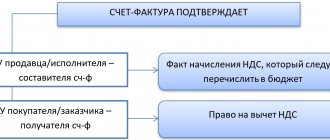
What is the purpose of an invoice and what are the consequences of mistakes made in it?
An invoice is the primary tax accounting document for VAT, issued by the seller - a VAT payer when selling products, works, services, etc.
ATTENTION! Invoices are required to be issued by persons exempt from VAT under Art. 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Also, in certain cases (for example, when importing goods from abroad), the document is also required to be drawn up by persons who are not payers of the specified tax, for example, simplifiers or imputators.
The compiler must highlight the amount of VAT payable to the budget on the transaction. The buyer, in turn, if he is a VAT payer, can deduct the amount of tax specified in the received invoice. This is the main purpose of this document (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Considering that a deduction is an opportunity to reduce VAT payable to the budget, serious requirements are imposed on invoices as documents confirming the right to deduction. By violating them, the seller deprives the buyer of the opportunity to legally reduce the amount of tax. We will talk about all these requirements further.