The property rights of the enterprise are extremely extensive. The company's capital can include both tangible and intangible objects, financial assets, and cash equivalents. To implement a company's activities, values that do not belong to it are often used. Such objects can be transferred under a leasing agreement. They must be reflected in accounting.
Is property recorded in off-balance sheet accounts subject ?
What are off-balance sheet accounts?
Off-balance sheet accounts (AB) are intended to store information about the objects used by the company. Their key feature is that the company does not have ownership rights to these objects. They are temporarily part of the company. Provided on the basis of various agreements. These objects may include:
- rented premises, warehouses;
- valuables transferred for safekeeping;
- raw materials accepted for processing;
- equipment adopted for the purpose of installation work.
How can a tenant account for leased objects (premises, equipment, other property) on off-balance sheet account 001?
The principle of property separation and off-balance sheet accounts
The organization of off-balance sheet accounts is based on the principle of property separation. It states that the accounting of an organization's assets should not coincide with the accounting of the assets of its owners, as well as the assets of other organizations under the care of this organization. The same principle applies not only to assets, but also to liabilities.
Objects temporarily included in the assets, provided under certain agreements, do not belong to the enterprise. However, during a certain period of time, it is the enterprise that is responsible for them, which means it must take them into account in a certain way. But such values cannot be mixed together with those owned by right of ownership within the same accounting accounts.
When and how to take into account inventories on off-balance sheet accounts ?
Off-balance sheet accounts are auxiliary accounts within the framework of accounting. They become relevant if you need to obtain information not contained in balance sheet accounts. This feature explains their name. Balances from off-balance sheet accounts will not be included in the balance sheet. They are displayed behind the total of this indicator. That is, they are recorded on the balance sheet.
IMPORTANT! Information from the accounts in question does not affect financial performance. For this reason, they will not appear in the company's financial statements.
What are off-balance sheet accounts for?
Off-balance sheet accounts perform the following functions:
- Accounting for the availability of property and tracking transactions with it. Accounting may also concern objects that belong to the enterprise, but their value is written off as expenses.
- Collection of data necessary for the formation of explanations for the main balance sheet and financial statements.
- Control over the operation of property to which the enterprise does not have ownership rights.
- Control over the safety of the objects in question.
- Supporting role to monitor the execution of property papers without delays. In particular, documents are drawn up on the receipt of objects and their disposal.
- Full organization of accounting in this area.
Properly executed off-balance sheet accounts allow you to obtain all the data on objects that are located on the territory of the enterprise, but do not belong to it. Information is necessary to analyze the company's creditworthiness and determine its financial stability.
What is an off-balance sheet in accounting?
Property, valuables and some assets that are transferred to an organization for temporary use or for safekeeping should not be included in accounting on the balance sheet.
Property and financial assets are recorded in special accounting accounts off the balance sheet. The answer to the question of what an off-balance sheet account in accounting is can be found in Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n. This is the name of special accounting accounts that reflect information about assets and liabilities that do not belong to the organization. In total, eleven off-balance sheet accounts are used in accounting:
- Account 001 “Leased fixed assets”.
- Account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.”
- Account 003 “Materials accepted for processing.”
- Account 004 “Goods accepted for commission.”
- Account 005 “Equipment accepted for installation.”
- Account 006 “Strict reporting forms”.
- Account 007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss.”
- Account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received.”
- Account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued.”
- Account 010 “Depreciation of fixed assets”.
- Account 011 “Fixed assets leased out”.
Types of off-balance sheet accounts and their accounting
The required type of off-balance sheet account is determined depending on what kind of object is subject to accounting. There are the following types of ES:
- 001 “Fixed assets leased.” Their cost must be confirmed by an agreement concluded with the lessor.
- 002 “Valuables taken under safekeeping.” Typically, an agreement is concluded in relation to these objects, after the fulfillment of the terms of which the values become the property of the enterprise. Until this moment, the company's objects will not belong to the company. The condition is certain deductions. The postings must indicate their size.
- 003 “Raw materials taken for processing.” Materials for processing can be indicated on off-balance sheet accounts only if they were transferred by the customer and the manufacturer does not pay their cost.
- 004 “Materials for commission.” The products that were taken by the commission agent for sale are indicated.
- 005 “Equipment intended for the performance of installation services.” The equipment used to perform installation services is indicated.
Off-balance sheet accounts reflect assets owned by the enterprise that have been written off as expenses:
- 006 “Reporting forms”. May include various receipts and subscriptions.
- 007 “Bad debts written off at a loss.” Displayed on accounts for five years. It is assumed that during this time the financial position of the debtor may change.
Off-balance sheet accounts are relevant for collecting information necessary as additional information to the explanations of the statements:
- 008 “Collateral received.” Needed to store data on transferred guarantees to ensure compliance with conditions;
- 009 “Issued collateral.” Relevant for collecting information on issued guarantees to ensure payments.
- 011 “Funds received for rent.” This account is placed in the reporting of both the lessor and the tenant.
All account data is indicated in a special accounting plan. An enterprise can open other accounts that are not in the plan if this is required to support its activities.
An organization has the right to open a sub-account to an existing off-balance sheet account or introduce a new account if it is not provided for in the plan. The main thing is that this change is properly spelled out in the accounting policies.
IMPORTANT! Organizing off-balance sheet accounts is extremely important. If, as part of a tax audit, objects are discovered that do not appear in the reporting, they will be written off as non-operating income. That is, they will be subject to income tax.
Features of accounting on the AP
Off-balance sheet accounts are presented in the form of a table with two columns. One of them displays debit, the other – credit. Accounting for APs is carried out using a simplified system. No double entry required. That is, you don’t have to write the same amount in debit and credit. The following transactions must be indicated in the debit column:
- getting objects;
- acquisition or issuance of security.
The loan column displays:
- disposal of the object;
- termination of security.
The debit will show the income, and the credit will show the expense.
Off-balance sheet accounting of someone else's property
Sometimes there is a need to take into account assets that do not belong to the company on the balance sheet.
These can be leased fixed assets, goods under a contract for commission or safekeeping, etc. Tenants must account for the received property in account 001 “Leased fixed assets” (paragraph 7, clause 32 of PBU 6/01, clause 27 of PBU 4/99). If such records are not kept, the company may be fined (Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The receipt of leased funds is reflected in the debit of account 001, the return to the lessor is reflected in the credit of the account. Leased property is recorded at the cost specified in the lease agreement. If the contract does not indicate the cost of the object, then it can be taken into account without the price.
Commission agents reflect the goods accepted for commission in the debit of account 004. The type, cost and quantity of goods can be viewed in the acceptance certificates. The commission agents reflect the sold and returned goods on the credit of account 004.
accepted for safekeeping are recorded by suppliers and buyers on account 002. Suppliers of goods reflect on account 002 the goods paid for, but not removed by the buyer for reasons beyond the control of the parties. Such records are kept when the buyer left the goods for safekeeping. Buyers use account 002 when accepting goods for storage if:
- the goods have not been paid for, and according to the terms of the supply agreement, they cannot be used until payment is made;
- The title to the goods still belongs to the supplier.
Important
The taxpayer cannot deduct VAT while inventory items are taken into account off the balance sheet. Controllers believe that if the buyer does not have the right to use these goods in transactions subject to value added tax, then he does not have the right to deduct the tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 22, 2016 No. 03-07-11/48963).
Transactions with off-balance sheet accounts
On off-balance sheet accounts, just like on regular ones, procedures for registering and writing off values are carried out. You can also make sales from off-balance sheet accounts. There are some nuances to take into account.
How to put an asset into an off-balance sheet account
The legislation does not regulate the accounting of individual off-balance sheet values, leaving the accounting department to independently choose a strategy, specifying it in the accounting policy. An organization can open an additional account for, for example, low-value property, assigning it a number next to the planned ones and reflecting this in the policy. It is convenient to account for low-value assets in off-balance sheet accounts because:
- such assets will not get lost among the “voluminous” balance sheet assets;
- property is assigned to a specific employee responsible for it.
Sales from an off-balance sheet account
If management decides to sell an asset held in an off-balance sheet account that they previously used and continue to do so, they must write off the asset as a credit to the corresponding off-balance sheet account. The funds received from the sale must be reflected as income from sales and VAT must be added. At the same time, in tax accounting, this operation will entail the reflection of income included in the income tax base.
ATTENTION! Since the initial cost of the asset was already taken into account at the time of commissioning, it is not reflected in accounting or tax accounting, otherwise distortions in financial results are possible.
Write off an asset from an off-balance sheet account
Objects can not only be accounted for in off-balance sheet accounts, but, if necessary, can be written off from them. This happens if the asset has become completely unusable, or it is about to be sold, for these reasons it is no longer used in the activities of the enterprise. Information about the transaction is entered into a special journal of material assets, which is maintained specifically for objects of off-balance sheet accounts. The following information is required:
- name of the asset;
- date of its commissioning;
- price;
- inventory number;
- person responsible for it (full name, position);
- write-off date (added after this operation).
After the date of write-off is entered in the journal, the enterprise can no longer use the specified asset, which is confirmed by a special act.
Reflection of the transfer of property from account 21 to 1C: BGU 8
To restore the balance of fixed assets accounted for in off-balance sheet account 21, use the document Write-off of fixed assets, intangible assets, legal assets with the type of write-off Write-off of own fixed assets in oper. accounting (21) and the flag enabled: Restore to balance . the Restore on balance flag, the Restore on balance tab appears .
On the Fixed Assets, Intangible Assets, Regulatory Assets , fixed assets are selected that are written off from off-balance sheet account 21. On the Balance Restoration , data on fixed assets that are written off from off-balance sheet account 21 are indicated.
On the Accounting transaction , select the standard transaction Write-off of fixed assets with restoration on the balance sheet and in the additional details indicate the full working account 401.10.172. The gratuitous transfer of a fixed asset is formalized by the document Transfer of fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts with the type of transfer - Transfer of own fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts on the balance sheet (101, 102, 103) and the standard transaction Gratuitous transfer to organizations of fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts (401.20.280) .
More on the topic: Reflection of settlements under an agency agreement in the accounting of budgetary institutions
Published 05/19/2021
Postings to off-balance sheet accounts using an example
Two enterprises entered into an agreement with each other for the supply of goods. One of the parties provides security for payment in the form of equipment pledged. The cost of the equipment is 200,000 rubles. Payment under the contract was not made, and therefore another enterprise receives the equipment at its disposal and then sells it. These transactions will be reflected using the following entries:
- DT 008 “Payment Security” 200,000 rubles;
- KT 008 “Write-off of collateral” 200,000 rubles;
- DT 002 “Accounting for valuables received under a pledge agreement.” Document – pledge agreement;
- KT 002 “Sale of valuables.” Document – act of acceptance and transfer;
- DT 51 CT 91 “Income from sales.” The document is a bank statement.
From this diagram you can extract information about the movement of values and the transaction amount. All operations are confirmed by primary documentation.
What limit to set
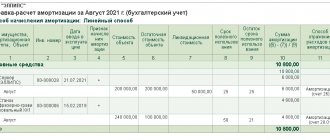
Fixed assets include assets that meet the cost limit that the company sets itself (clause 5 of FSBU 6/2020).
When determining the limit, it is important to remember that its value should not be significant for the organization. For example, it could be 100,000 rubles, as in tax accounting, or even more if this does not distort information about the company’s assets.
The limit can be set in two ways:
- for a set of OS objects. In this case, the limit is determined in relation to the entire group of non-essential assets. There are no cost limits for individual units of assets;
- for individual OS objects.
If the accounting policy does not establish a cost limit, then all property that meets the criteria of fixed assets, regardless of cost, should be classified as depreciable property and depreciated “by default.”
Off-balance sheet accounts in budgetary organizations
If the organization is classified as a budget organization, off-balance sheet values are recorded in it according to a simplified scheme - there is no need to keep corresponding records. When property is capitalized, the necessary entry is made in the debit of a certain off-balance sheet account. At the time of write-off, this entry is made against the loan. It is allowed to introduce additional off-balance sheet accounts for greater reliability of management accounting, naturally, indicating them when developing accounting policies.
So. Off-balance sheet accounts allow you to display information about property that is located on the territory of the enterprise, but does not belong to its property. Other data is also stored on the AP. Having off-balance sheet accounts during tax audits will allow you to avoid making unnecessary tax deductions. It is also a source of important information about the company's activities. The information allows you to track operations carried out by the enterprise.
Repeated closure of the month for December due to the transition to FSBU 6
We advise you to first conduct a repeat Closing of the month for December 2021 on a copy of the database and compare the accounting data with the data on which the Accounting Statements for 2021 . Adjustments when re-closing the month may affect balances on accounts 02, 84.
After all the documents related to the transition to FAS 6 have been entered into the 1C program, perform a repeat Closing of the month for December :
- cancel skipping the operation Transition to FSBU 6 ;
- perform the operation Transition to FSBU 6 and the remaining unperformed operations after it.
If, in parallel, a standard document is being carried out : Transferring OS to low-value equipment associated with the transition to FAS 6 for OS below the limit, you must:
- carry out this document;
- perform the Month Closing for December 2021 , starting with the operation Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets ;
- at the end, take the steps indicated in the Write-off in the accounting book for expenses of the cost of the operating system.
What off-balance sheet accounts are intended for accounting for inventory items?
The very definition of off-balance sheet accounts specified in the instructions to the Chart of Accounts (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n) indicates that these are accounts that are not taken into account in the organization’s balance sheet; their indicators are not involved in assessing the financial position of an economic entity. The chart of accounts and its instructions provide for 11 off-balance sheet accounts, 3 of which are intended for accounting for inventory items:
- Account 002 - it records inventory items that are in the organization’s warehouse, but are not already or not yet its property.
- Account 003 is intended to account for raw materials and materials that the manufacturing organization receives from the customer for processing.
- Account 004 is used by commission agent organizations to account for goods accepted under the terms of a commission agreement.
You can get acquainted with the off-balance sheet accounts provided for in the Chart of Accounts and the features of their use in the article “Rules for maintaining accounting records on off-balance sheet accounts.”
The following is typical for all property off-balance sheet accounts: the receipt of assets is reflected only in debit, write-off only in credit, there is no correspondence in off-balance sheet accounts.
How to transfer materials to an off-balance sheet account?
Paragraph 4 clause 5 PBU 6/01 indicates the need for proper accounting of property written off as expenses as inventories. And paragraph 5 of PBU 1/2008 talks about organizing accounting policies in such a way that assets and liabilities belonging to the organization are accounted for separately from others.
However, to account for material assets, the cost of which has already been written off as expenses, there are off-balance sheet accounts 002, 003 and 004. Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts also provide for the possibility of introducing additional off-balance sheet accounts. Thus, to account for materials that continue to be in the organization and used in its business activities, it is possible to provide an additional account on the balance sheet, and the regulations for its use can be fixed in the accounting policies. Such an off-balance sheet account may be account 012 “Material assets in operation.”
In the accounting program “1C: Accounting”, popular among accountants, for example, an MC account with a number of sub-accounts has been introduced for similar purposes:
- MC02 “Working clothes in operation”;
- MC03 “Special equipment in operation”;
- MC04 “Inventory and household supplies in operation.”
After the property is capitalized and put into operation, its value is written off as the organization’s expenses, and the property itself, assigned to the responsible persons, will be listed on the balance sheet. When this property ceases to be used for one reason or another, it will need to be written off from the off-balance sheet account in which it was recorded.
At the same time, analytical accounting of materials is carried out according to nomenclature and storage locations, which makes it possible to control the availability and use of these values, and in the case of additional costs associated with their use, to justify these costs.
When transferring material assets into operation, the relevant documents are issued, for example, a demand invoice (form M-11), and the following entries are made:
- Dt 20, 26, 44 (cost accounts) Kt 10 “Materials”;
- Dt 012 (MC).
In the event of complete depreciation of the property recorded off the balance sheet, or its disposal for other reasons, a document for write-off is drawn up and a posting is recorded on the credit of the off-balance sheet account: Kt 012 (MC).
Regulations for accounting for values recorded on the balance sheet and monitoring them, as well as a list of documents used for these purposes, must be developed by the organization itself and consolidated in its accounting policies.
How to sell materials from an off-balance account?
To sell property recorded off the balance sheet, its contractual value is determined. When selling, an entry for the sale of other property is generated:
- Dt 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” Kt 91 “Other income and expenses.”
If an organization operates on OSNO, VAT is charged upon the sale of an asset:
- 91 “Other income and expenses” Kt 68 “Calculations for VAT”.
The disposal of property is carried out according to the credit of the off-balance sheet account of its accounting:
- Kt 012 (MC).
Moreover, the cost of such property is zero due to the fact that it has already been taken into account in the organization’s costs when transferring it into operation. Funds from the sale of this property are the income of the organization.
IMPORTANT! To generate documents for sale and the corresponding entries in the accounting program, it is often necessary to restore the property being sold in the organization’s assets, if the functionality of the program does not provide for transactions for the sale of property recorded off the balance sheet. For this purpose, inventory items to be sold are restored to the account from which they were previously written off, at a symbolic cost - for example, 1 kopeck.