The widespread introduction of online cash registers has led to a significant increase in expenses for the maintenance and servicing of cash registers. Whatever technology is used in the company: stand-alone devices or fiscal recorders that require connection to a computer system, it contains a fiscal drive that stores transaction data. It must be reflected in accounting.
Fiscal drives, in accordance with the law, require periodic replacement. The accountant is also required to reflect these transactions in the accounting data.
What types of FN are there?
The validity period of the FN can be 13, 15 and 36 months. However, these numbers do not mean that the drive will last for the specified time. The maximum time limits are written on the device. In reality, the period will depend on the characteristics of the company.
For many types of activities and taxation systems, the legislation allows the use of storage devices with a validity period of 13 months or more. As a rule, businessmen, in an attempt to save money, purchase functional units with maximum operating duration. However, in most cases, it is not possible to forget about the drive in the online cash register for 36 months. Why?
There are two reasons for this:
- The specified period does not always coincide with reality. For example, at a cash register that does not send information to the OFD, the device will work less than 19 months for 36 months.
- The memory capabilities of the drives are the same. If 200 or more receipts are processed per day, a single FN will not be enough for a long period of time. In such a situation, it is safer to purchase a financial fund for 13 or 15 months.
Thus, purchasing a financial fund for three years is not always advisable. However, not all entrepreneurs have a choice.
Still have questions?
Leave a request and we will advise you
Accounting for cash register equipment as part of fixed assets
To classify cash register equipment as fixed assets, the following conditions must be met:
- subject of labor - an independent object that is not a spare part of other equipment;
- useful life more than a year;
- used in the process of entrepreneurial activity for the purpose of making profit;
- the initial cost criterion is at least 100 thousand rubles.
If the company’s accounting policy decides to take cash registers into account as part of fixed assets, then the initial cost will be collected from the main costs incurred:
- cash register cost;
- costs of information and consulting services;
- cost of work on setting up and installing equipment, delivery, etc.
In accounting, the formation of the initial cost of fixed assets is displayed on active account 08: debit - price formation, credit - transfer of the asset to the fixed assets and start of use:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 – expenses for the purchase of a cash register and fiscal storage device are taken into account;
- Dt 08 Kt 26 – general business services are written off;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 – the cost of the fixed asset is fully formed, the asset is transferred for use.
Case Study 1
Limited Liability Company "Rus", in order to modernize the cashier's workplace, acquired a new autonomous cash register with a fiscal storage device. The acquisition cost is 33.4 thousand rubles, including VAT 18% 5094.92 rubles. The company also incurred additional costs for purchasing an activation key for 36 months and connecting the cash register to the fiscal data operator. The total cost of additional settings amounted to 8,600 rubles, including VAT 18% of 1,311.87 rubles.
The accounting policy of Rus LLC stipulates that cash registers should be accepted in accounting as part of fixed assets if their initial cost is above 30 thousand rubles.
Accounting entries for business transactions:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 – 28,305.08 rub. – the purchase of equipment from the supplier is taken into account.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – 5094.92 rub. – accounting for input VAT.
- Dt 08 Kt 60 – 7288.13 rubles – the company’s costs for setting up the cash register.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – 1311.87 rub. – input VAT from the supplier.
- Dt 68 Kt 19 – 6406.79 rub. – value added tax is accepted for deduction.
- Dt 01 Kt 08 – 35,593.21 rub. – the purchased cash register is included in the company’s fixed assets.
As part of fixed assets
The company decided to consider cash register equipment as a fixed asset in accounting. The cost of a cash register as a fixed asset in accounting can be formed:
- from the cost of the cash register, including the fiscal accumulator;
- from consulting services;
- from services for installation and debugging of equipment.
Example
A cash register with a fiscal drive was purchased at a cost of 46,000 rubles. plus VAT 20% and it was configured by a third-party company, services costing 12,000 rubles. plus VAT 20%.
The postings will be like this:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 RUB 46,000.00 – purchased a cash register;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 9200.00 rub. – input VAT on purchase;
- Dt 08 Kt 60 RUB 12,000.00 – services for setting up a cash register;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 RUB 2400.00 – input VAT on services;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 RUB 11,600.00 (9200+2400) – VAT deductible;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 – 58,000.00 rub. – capitalized by cash register as OS.
10 months after purchase, the FN’s memory was full and it was replaced. The useful life of the device is 72 months. Depreciation per month - 58000.00/72 = 805.56. In 10 months depreciation amounted to 805.56*10 = 8055.60 rubles.
A new drive was purchased for 5,000 rubles, incl. VAT - 833.33 rubles, services for its replacement by a third-party company amounted to 2000 rubles, incl. VAT – 333.33 rub.
The operations will be reflected in the accounting system as follows:
- Dt 10 Kt 60 4166.67 rub. – purchased from FN suppliers;
- Dt 08 Kt 10 4166.67 rub. – the purchased FN is included in the company’s expenses;
- Dt 08 Kt 60 1666.67 rub. — services for replacing the FN are included in the company’s expenses;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 1166.66 (833.33+333.33) rub. – input VAT;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 1166.66 rub. – to deduct VAT;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 5833.34 rub. – increase in the cost of cash registers;
- Dt 60 Kt 51 7000.00 rub. – payment to service providers and FN.
Depreciation: (58000 + 5833.34 - 8055.60)/(72-10) = 899.64 rubles. Dt 26 (or 44) Kt 02,899.64 – depreciation.
Important! After replacement, a used drive is stored for 5 years.
Accounting for cash registers as part of inventories
In addition to including equipment as part of fixed assets, many companies capitalize equipment to account 10 as part of the inventory and immediately write off the cost of commissioning to the corresponding cost accounts. In this case, information about the fiscal accumulator and cash register can be taken into account in an off-balance sheet account or checked during detailed analytical accounting of the account. 10.
Case Study 2
Limited Liability Company "Kaktus" as part of modernization acquired the fiscal registrar "ATOL" worth 32 thousand rubles (including VAT 18% 4881.36 rubles). The costs of concluding an agreement with the OFD and calling technical specialists amounted to 15 thousand rubles, including VAT 18% 2288.14 rubles. The company is a small trading enterprise.
The accounting department of Cactus LLC compiled the following transactions:
- Dt 10 Kt 60 – 27118.64 rub. – receipt of goods from the supplier.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – 4881.36 rub. – VAT included.
- Dt 44 Kt 60 – 12,711.86 rub. – costs for calling specialists are included in sales costs.
- Dt 19 Kt 60 – 2288.14 rub. – tax accounting.
- Dt 68 Kt 19 – 7169.50 rub. – VAT is accepted for deduction.
- Dt 44 Kt 10 – 27,118.64 rub. – the cash register is put into operation.
Fiscal storage. Accounting.
1.
- Expenses for ordinary activities form:
expenses associated with the acquisition of raw materials, materials, goods and other inventories;
expenses arising directly in the process of processing (refinement) of inventories for the purposes of production, performance of work and provision of services and their sale, as well as sale (resale) of goods (expenses for the maintenance and operation of fixed assets and other non-current assets, as well as to maintain them in good condition, commercial expenses, administrative expenses, etc.).
- Expenses are recognized in the reporting period in which they occurred, regardless of the time of actual payment of funds and other form of implementation (assuming the temporary certainty of the facts of economic activity).
Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/06/1999 N 33n (as amended on 04/06/2015) “On approval of the Accounting Regulations “Organization Expenses” PBU 10/99″ {ConsultantPlus}
2.
Modern cash register equipment contains a fiscal drive inside the case (Clause 1, Article 4 of Federal Law No. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003 “On the use of cash register equipment when making payments in the Russian Federation” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 54-FZ) ). Fiscal storage is a software and hardware encryption (cryptographic) means of protecting fiscal data in a sealed case containing fiscal keys (Article 1.1 of Law No. 54-FZ).
Users of cash register systems are required to regularly replace fiscal drives (Clause 2, Article 5 of Law No. 54-FZ). An organization can make a replacement either independently or with the help of third parties. Many cash register models do not require special skills to replace the fiscal drive (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 15, 2018 N 03-11-11/16093).
The procedure for accounting for the replacement of a fiscal accumulator depends on how the cash register was taken into account: as fixed assets or as part of inventories.
| CCP is accounted for as a fixed asset |
The organization sets the cost criteria for recognition of fixed assets itself in its accounting policies, but not more than 40 thousand rubles. (Clause 5 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Fixed Assets” PBU 6/01, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 N 26n (hereinafter referred to as PBU 6/01)).
If the cost of a cash register exceeds this threshold, then it is recognized as a fixed asset.
The fiscal drive is used as part of a cash register, therefore it is not an independent OS object.
Replacing the fiscal drive does not change the operational characteristics of the cash register. These are the costs of maintaining fixed assets and maintaining them in working condition (clause 66 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 N 91n). Costs for the fiscal drive are taken into account as consumables with subsequent write-off for the costs of maintaining and operating the OS, as well as for maintaining them in good condition (clause 2 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for inventories” PBU 5/01, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance Russia dated 06/09/2001 N 44n; clause 26, PBU 6/01; clause 5, Accounting Regulations “Organization Expenses” PBU 10/99, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/06/1999 N 33n (hereinafter - PBU 10/99)). These expenses are reflected in the reporting period in which they occurred (clause 18 of PBU 10/99).
If the cash register is not an operating system, then the costs of the fiscal accumulator are also taken into account as part of expenses for ordinary activities in the reporting period in which they occurred (clause 5, PBU 10/99).
Accounting records are made in accordance with the Instructions for the application of the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n.
| Accounting for replacement of a fiscal drive | |||
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit | Base |
| Purchased a fiscal storage device | 10 | 60 | Packing list |
| The fiscal drive has been put into production | 44 (20, etc.) | 10 | Request-invoice |
| Work to replace the fiscal drive was carried out by a third party | 44 (20, etc.) | 60 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of works (services) |
| VAT presented by the supplier and contractor is reflected | 19 | 60 | Invoices |
| The submitted VAT is accepted for deduction | 68 | 19 | Invoices |
| Payment has been made to the supplier and contractor | 60 | 51 (50) | Bank statement on the current account (expenditure cash order) |
Question: How are the costs of replacing a fiscal drive reflected in accounting? (Expert Consultation, 2020) {ConsultantPlus}
Replacement of fiscal drive, accounting
The fiscal drive is an integral part of the cash register, ensuring the formation of a fiscal sign, recording and storing data, encrypting information for transferring information to the OFD.
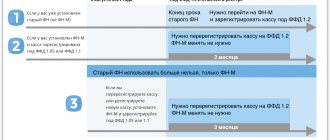
When using cash register equipment, the drive needs to be replaced:
- due to expiration;
- when changing the owner of cash register equipment;
- The drive memory is full before the expiration date;
- breakdown of the cash register or failure of the element.
Accounting for replacing an item will also depend on the cash accounting method chosen by the enterprise.
CCP refers to the company's fixed assets. In this case, the replacement of the fiscal drive will occur as part of the modernization of the asset:
- Dt 10 Kt 60 – purchase of a new FN.
- Dt 08 (sub-account for accounting for modernization costs) Kt 10 - the costs of purchasing and installing the element are taken into account.
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - an increase in the value of the asset as a result of replacing the drive will be reflected in the OS card.
The cash register does not belong to the company's fixed assets: the costs of the new fiscal drive will be immediately charged to the appropriate accounts:
- Dt 10 Kt 60 – purchase of FN.
- Dt 26 (44) Kt 10 – write-off of costs.
What to do after replacing the fiscal drive
Let's consider what to do after replacing the fiscal drive. The owner of the cash register is required not only to activate the new module, but also to re-register the online cash register with the tax service.
Activation of a new FN
Launch the registration program again and select “Re-registration” from the menu. Synchronize the time with your computer and click on the “Next” button. The date entry document will be printed.
At the next stage, indicate the reason for re-registration of the cash register. From the list presented, select “Replacement of FN” and click on the “Next” button. Check the information about the cash register is correct and make adjustments if necessary.
Click “Next” to save the changes and wait for the online cash register to generate and print the fiscalization report. At the same time, a notification about the successful completion of the operation should appear in the program window.