If the cooperation between the employer and employee is assumed to be permanent or on a more or less long-term basis, then an employment contract is concluded to formalize it. But if the employer is more interested in the result than in the process of cooperation, and moreover, the interaction is planned to be one-time, then the relationship moves into the civil legal plane: a contract is signed.
- Form and sample
- Online viewing
- Free download
- Safely
Relying on the Law
An agreement according to which the customer (employer) gives the contractor (employee) a certain task with subsequent payment for the result is a contract .
The provisions that regulate this type of relationship are enshrined not in the Labor Code, but in the Civil Code (Chapter 37-38 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, specialized legal acts are applicable to certain types of contracts, such as consumer protection, federal laws relating to architectural, investment activities, etc.
Internal labor regulations
Each full-time employee works at a time agreed with the operating hours of the organization itself . Therefore, he is obliged to work according to the company's rules. Come and leave work at the appointed time, have lunch and rest, and take technical breaks. Absence from work without a good reason is permitted only on non-working days: holidays and weekends established by the staffing schedule.
The full-time employee remains under the control of the employer throughout the working day.
Persons working under GPC agreements are not required to obey the customer’s internal rules . They do not obey the officials of the organization and its regulations.
The contractor can work at night, when the entire staff of the organization is resting, and sleep well during working hours. Weekends also do not affect the work process in any way. The main thing is to submit the result of the work on time.
Contract with character
Features and differences between a work contract and other types of approval documents:
- Consensuality . A contract is concluded from the moment the parties agreed on the terms and sealed the promise to fulfill them with signatures. No further actions are required to initiate the contract.
- Reciprocity . Both parties are legally equal. The basis of contracts of this type is initial mutual trust and good conscience.
- Remuneration . Both parties, having fulfilled the agreement, receive a certain profit.
- Divisibility of an object . If the result obtained can be divided into several equal independent parts, the subject of the contract is considered divisible. An indivisible object implies the singularity of the result of the contractor’s actions.
Contracts can be different, most often the following are concluded:
- building;
- domestic;
- design;
- municipal or state;
- for scientific research.
A work contract is in many ways similar to other obligations, which provide for the performance of certain actions, but it has many unique features that make such a document a separate form of agreement.
| № | Type of agreement | Similarities with a contract | Difference | |
| Another agreement | Work agreement | |||
| 1 | Contract of sale | Under the contract, a thing (material object) is transferred | You can transfer not only objects, but also rights, real estate, property complexes, as well as energy | Only things (created or transformed) can be transferred |
| Only the transfer of the subject of the contract is regulated | The process of manufacturing or transforming a thing is regulated | |||
| Subjects of the contract - Things that have generic characteristics | The subjects of the contract are individually determined | |||
| 2 | Service agreement | The contractor performs certain actions as requested by the customer | The activity may not have a tangible result (training, treatment, etc.) | Only the material result of activity |
| 3 | Employment contract | You can conclude one instead of the other, only with different legal consequences | Internal labor regulations of the team | The organization of the contractor's work does not matter |
| Guaranteed salary regardless of work results | Payment upon delivery of results | |||
| Standardized working day | Final deadlines matter | |||
| Employer's material base | The means of production belong to the contractor | |||
| Social benefits (vacation, sick leave, pension) | None | |||
| What the employee creates belongs to the employer | Before transfer, the owner of the thing is the contractor | |||
Personal income tax and insurance premiums
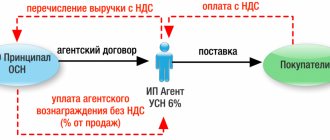
The employer acts as a tax agent in both cases . He withholds and pays 13% to the tax office on a monthly basis from the salaries of employees working under any type of contract.
This does not apply to contracts concluded with individual entrepreneurs. Entrepreneurs pay taxes themselves. To avoid tax claims, ask the individual entrepreneur for documents about his status.
Both types of employees may qualify for tax deductions. True, contractors can apply to the customer for it only while the contract is in force.
For employees under an employment contract, the employer pays monthly insurance contributions in the amount of 30% of the salary - to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund and the Federal Compulsory Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund. Additionally, he is obliged to transfer contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases at the rate applicable to the organization.
For employees under a GPC agreement, contributions must also be paid, but in a smaller amount . Contributions to the Social Insurance Fund in case of temporary disability or maternity are not accrued, and contributions for injuries are paid only if this is provided for in the contract. So 27.1% of the salary is transferred to the Federal Tax Service.
Contributions to the Pension Fund are paid in any case, and under any agreement, the pension savings of the employee or performer grow.
View from different sides
There are 2 parties to the contract: the customer and the contractor . They can be both individuals and legal entities, as well as individual entrepreneurs (in any combination of each other).
The law does not prohibit the involvement of additional performers - subcontractors . Then the first contractor will act as a general contractor, responsible to the customer, while the subcontractors are already responsible to him. If the subject of the contract is divisible, each subcontractor is responsible for its share. In case of indivisibility, the liability of subcontractors is joint and several.
REFERENCE! The relationship between the general contractor and subcontractors is regulated by a separate document - a subcontract agreement.
Working conditions: workplace and materials
According to the employment contract, the employer provides the employee with proper working conditions . It highlights the work area, computer, tools, uniform, materials and instruments. Conducts safety training.
According to the GPC agreement, the customer is not responsible for the contractor’s workplace . The contractor himself selects and equips his workplace. The customer can transfer tools and materials for the work to the contractor, and then this is written in the contract. If there is no such clause in the contract, the contractor works with his own tools and materials.
Without which there will be no contract
In a work contract, the essential elements include the subject of the contract and the deadlines for completion. Another element that does not affect materiality is the price, sometimes drawn up as an estimate. Let's take a closer look at these elements.
What subject are we talking about?
A work contract implies a specific subject - the result for which the contract was concluded. The achieved result must be material, separable from both sides. In addition, it must be possible to guarantee the quality of the result; it must depend on objective factors.
FOR EXAMPLE: the quality of the built foundation for a house depends on the materials used, it must comply with certain SNiPs, GOSTs and have a warranty period (that is, the foundation must last a certain period). But an English language course, even if taught by the best teachers using certified manuals, will not necessarily be mastered by students. Therefore, the latter cannot be the subject of a contract, unlike the former.
So, the subject of a contract can only be a thing or a property of this thing:
- a newly created material object (for example, a manufactured table);
- a new property of an already finished item (for example, an improved or repaired device);
- another result that has materiality (for example, developed documentation).
Enter deadlines
The deadlines specified in the text are essential - without them, the contract will not be valid. It is necessary to mark the start and end dates of the work. It is permissible to establish intermediate stages, especially in long-term contracts. Meeting the allotted time is the contractor’s problem. But, if stipulated by the conditions, the dates can be moved at the initiative of both parties.
Completion of the contract sooner than specified is at the discretion of the contractor. If the contract has a clause on urgency, delays will be paid additionally.
IMPORTANT! When the customer sees that the contractor will definitely not meet the deadline due to a late start or insufficient pace of work, it is permissible to refuse the contract and demand compensation for damages.
The other side also has the right to be paid for the results of work on time. If the customer delays accepting the work, avoiding contacts with the contractor, then the latter has the right, after informing the customer twice, to sell the result of his work a month after the deadline, taking the due amount for himself and sending the rest of the amount to the customer’s account.
Everything has a price
For construction contracts, cost is not a mandatory condition. Instead of putting down numbers, you can indicate how the remuneration is set: usually it is labor costs plus payment for the work. The price may not be indicated: in this case, the calculation takes place at similar prices for similar work.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The price is not necessarily fixed in monetary terms: by agreement, the contractor may be provided with a certain service or certain property may be transferred.
If the contract is large-scale, long-term and involves different types of work, it is more logical to document the cost with an estimate. Any party can create it. If the parties have not decided on the approximate estimate, it is taken into account as firm by default - that is, it is unacceptable to deviate from its provisions in the direction of exceeding it.
NOTE! A contractor who exceeds the firm estimate may be refused further cooperation (with compensation for the part of the work performed). But if the overexpenditure is associated with objective reasons, for example, an increase in the cost of consumables, the contractor has the same rights (Article 451 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
I have rights, but I also have obligations
The contractor is obliged:
- comply with contractual deadlines and budgets;
- use your own forces, means and materials for work, unless otherwise specified in the contract, while guaranteeing the proper quality of tools, equipment and materials;
- perform the work efficiently (if the standards and warranty periods are not specified in the contract, then the usual requirements for this category of items apply);
- inform the customer about all circumstances that could affect the result (changes in the quality of materials, deadlines, estimates), suspending work until the customer clarifies the situation.
What can a contractor expect:
- customer refusal and compensation;
- if the quality is lower than required - refusal, requirement to replace the subject of the contract, correction of defects, price reduction, reimbursement of correction costs;
- if the contractor did not promptly inform the customer about the changed circumstances and continued performance without approval, then reference to these circumstances will not be taken into account.
The customer is obliged:
- in the case where the contract provides for a change in the quality of the thing, the subject of the contract must be provided in a timely manner and in proper condition;
- if the provision lies with the customer, then everything necessary must also be provided on time;
- respond to contractor requests in a timely manner;
- timely accept work according to the delivery and acceptance procedure;
- make a payment.
What does the customer risk:
- compensation to the contractor in case of unilateral refusal to work;
- suspension of work without timely provision (if agreed upon);
- rescheduling or increasing the cost of work (if there are problems with facilitating the work);
- without checking the quality during transmission, appeal to obvious shortcomings of the work.
Remuneration: regular or one-time
Employees on staff regularly receive salaries in the agreed amounts . According to the rules of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, salaries must be transferred at least twice a month - an advance payment and the main part. For failure to comply with payment deadlines, the employer issues compensation to the employee. It is charged for each overdue day as 1/300 of the refinancing rate.
If an employee works properly and fully performs his functions, he cannot be paid a salary below the minimum wage. In 2020, the minimum wage increases to 12,130 rubles.
Employees under a GPC contract will receive remuneration when they provide the customer with the result of the work performed . So the contractor can receive payment even once every six months, if such a period was required to complete the order.
The GPA can include the delivery of work in stages or the payment of advances. Then the customer will pay regularly, after accepting part of the work performed.
We accept the finished result
The paper that records the completion of the work by the contractor and the satisfaction of the customer with it is called the act of acceptance of the work performed. It is mandatory only for construction contracts (clause 4, Article 753 of the Civil Code), but is also used in other agreements. This document can serve as evidence in case of legal disputes. The specifics of the contents of the act are recorded in the contract and appendices:
- form of the agreement (not defined by law);
- procedure for signing by the parties;
- timing of signing;
- persons authorized to sign;
- liability of the parties for non-signing.
Mutual responsibility of the parties: employer and employee, customer and contractor
The employer is obliged to make the following payments in favor of the employee:
- average earnings for the period during which he was illegally deprived of the opportunity to work;
- compensation for damage to health and property;
- compensation for moral damage
- interest for late wages.
The employee, in turn, bears financial responsibility to the organization within the framework of his monthly earnings. For violation of discipline, he may be subject to a reprimand, reprimand or dismissal.
The customer of work or services is obliged to compensate the contractor for losses caused by improper performance of duties. The performer is responsible to the customer in the same way.
The contractor cannot be brought to disciplinary liability.
Manual for drawing up a work acceptance certificate
Clause 1 of Article 720 of the Civil Code states that inspection of the work result and its acceptance must be carried out by the customer in the presence of the contractor, and at the same time they sign the corresponding act. In order for the procedure to go smoothly, you need to pay attention to the proper preparation of the document. We provide step-by-step instructions.
- Name . The document is called “Work Acceptance Certificate”, then you need to indicate which ones, and also provide the details of the relevant contract.
- Date of preparation . It may differ from the final date for completion of work specified in the contract. It is better to agree on the date of acceptance and transfer in the text of the contract separately.
- Details of the parties . Names and details of legal entities, full names of individuals.
- Job information . Information about the type, volume and timing of the contract.
- Calculations . Indication of the amount of monetary or other measure of payment to the contractor.
- Signatures . Persons who completed the act of acceptance and transfer of work or authorized to do so by the customer and contractor, indicating their positions, surnames and initials.
- Seal . It is not provided for by law, but is a business custom; moreover, it contains the customer’s details.
IMPORTANT! If the act does not contain at least one of the listed points, it may be declared invalid.
Claims from tax authorities
Since 2022, the Federal Tax Service has been administering insurance premiums. She is interested in requalifying the GPC contract as a labor contract for the purpose of additional calculation of insurance premiums in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity.
Most often, the tax office goes to court when an organization enters into a GPC agreement with an individual entrepreneur or self-employed person. Since these categories pay personal income tax and insurance premiums on their own, the organization does not assume the obligations of a tax agent and saves on taxes and contributions.
Recently, a fraudulent scheme has spread. In order to reduce payments, employers offer employees to register as individual entrepreneurs or self-employed and enter into a GPC agreement with them. In order to assess additional taxes, the Federal Tax Service applies to the court with a claim to recognize the GPC agreement as an employment contract.
Example: during an on-site inspection, the Federal Tax Service found out that the organization was working with individual entrepreneurs under GPC agreements in order to understate the tax base and receive benefits for personal income tax and VAT. At the same time, individual entrepreneurs were its employees and performed labor functions. In this regard, the tax authorities reclassified the contracts as employment contracts and assessed additional VAT, income tax, personal income tax, fines and penalties to the company. The executing entrepreneurs did not agree with this and filed a lawsuit. The courts of three instances rejected the entrepreneurs because the individual entrepreneurs worked in the organization’s office 40 hours a week, performed labor functions and did not pay rent. At the same time, individual entrepreneurs received monthly remunerations regardless of the amount of work performed.
So even the disagreement of the performers to requalify the contract does not protect against risks.
It is easier to defend your position if the GPC agreement is concluded with an individual, and not an individual entrepreneur or self-employed person, especially with the support of an employee. In court, he must declare that he himself wanted to enter into a GPC agreement with the organization, and not an employment agreement. Citizens have the right to freely dispose of their work and independently choose the procedure for registration - an employment contract or a civil law contract.
There are a number of other court decisions where employers were able to defend the GPA and prevent retraining. The tax authorities were not helped by their arguments. For example:
- The GPC agreement provided for work and services that were assigned to full-time employees of the company and corresponded to their job functions.
- Over the course of several months, an organization enters into an agreement with the same individual to perform one type of work or service.
- The performer who worked under the GPC agreement was later included in the organization’s staff.
The presence in the GPC agreement of one or two circumstances that are not typical for this type of relationship does not prove their labor nature. Evidence can only be a combination of several signs of an employment relationship.
In disputes between legal entities and the tax office, the Federal Tax Service often wins. At the same time, even drawing up an agreement with an individual entrepreneur or self-employed person does not always become a decisive factor.
A striking example: the court recognized the contract concluded by the employer as not a civil contract, but a labor contract, since it immediately provided for many factors indicating the labor nature of the relationship. These include personal performance of clearly defined job duties for a long period of time, compliance with internal work regulations and safety precautions. During this entire period, the performer receives a fixed remuneration twice a month and bears financial responsibility.
What if the job doesn’t suit you?
If deficiencies are identified during the acceptance of work, the customer can include them in the act (clause 2 of Article 720 of the Civil Code). If this is technically difficult (for example, such a section or column is not provided), the act should not be signed. The reasons for refusing to sign - discovery of deficiencies - must be stated in a separate document, which is sent or handed to the contractor.
If the defects are hidden and only revealed during the operation of the delivered subject of the contract, the customer has the right to declare them within the period established by law.
A signed acceptance certificate deprives the customer of the opportunity to declare obvious deficiencies.
Orders and claims from regulatory authorities
Dissatisfied employees can contact the State Labor Inspectorate (SIT) with a complaint against the employer. The GIT can learn about violations of the organization not only from employees. Government agencies can report this: the prosecutor’s office, the police, the Federal Tax Service, and so on. If the State Tax Inspectorate finds out that the employer is hiding behind a civil process agreement instead of a labor agreement, it will issue him an order to eliminate the violation. The employer can either comply with it or try to appeal it in court.
There is no point in going to court if there really is a violation. If there is doubt about the nature of the relationship, the court interprets it as a labor relationship (Part 3 of Article 19.1 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Until January 1, 2014, the State Labor Inspectorate could not independently go to court with a demand to recognize the relationship as an employment relationship. Now the State Tax Inspectorate can conduct an inspection, prepare materials based on its results and take them to court with a claim to re-qualify the contract. In this case, the opinion of the employee himself is not taken into account. In this case, the court will study all the information and make a decision.
GIT does not often go to court to re-qualify contracts with individual entrepreneurs. The status of an entrepreneur implies greater security when working with customers and the possibility of not complying with internal regulations.