All intangible assets owned by the organization are subject to accounting. In order to record the fact of their ownership, there is an intangible asset accounting card.
- Form and sample
- Online viewing
- Free download
- Safely
FILES
Intangible assets may include licenses, trademarks (exclusive rights to use something), databases and other information objects of intellectual property.
The legislative framework
The document was adopted by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee No. 71a of October 30, 1997. There is a footnote to this effect in the paper itself in the upper right corner (it also states that the card has been assigned the interindustry form NMA-1).
In 2013, all forms of primary documents became recommendations. For this reason, when creating a document, deviations from the given forms are allowed. Each such change must be justified and documented. The form remains in use due to the conservatism of the organizers of enterprises, as well as because of its informativeness and convenience.
We fill out the acceptance certificate for the transfer of intangible assets (level 2)
There is no standard form for the act of acceptance and transfer of an intangible asset. Therefore, you can develop it yourself. But to make your task easier, we suggest using the form of the act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets - form No. OS-1 as an initial sample.
In the act, indicate: the initial cost of the asset, its useful life, and the procedure for calculating depreciation.
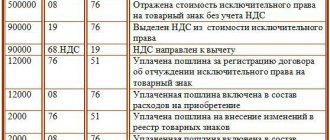
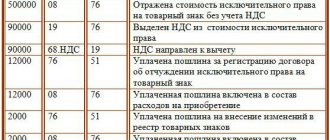
Based on the act, make the following entries:
DEBIT 08 CREDIT 60 (70, 75-1, 76, 98-2, …)
– costs associated with the acquisition (creation) of an intangible asset are taken into account;
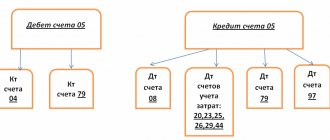
DEBIT 04 CREDIT 08
– the intangible asset is accepted for accounting.
For the intangible asset accepted for registration, create an inventory card according to form No. Intangible asset-1 in one copy. You can use the unified form approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated October 30, 1997 No. 71a.
Keep in mind that in column 8 “Depreciation rate, % or estimated rate” of the inventory card, the rate at which depreciation will be charged on intangible assets throughout its useful life. Depreciation on intangible assets is calculated:
- in a linear way;
- reducing balance method;
- by writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products produced.
Fill in Column 8 if depreciation will be calculated using the straight-line method or the reducing balance method.
If depreciation on an intangible asset will be calculated by writing off the cost in proportion to the volume of products produced, then make a corresponding note in this column.
Columns 13–17 should be filled in when the intangible asset is written off from the organization’s balance sheet (for example, sold).
In the section “Brief description of the object of intangible assets,” indicate the main characteristics of the intangible asset that are not mentioned in the documentation attached to it.
Partner news
How much money do you need to be completely happy?
The powers of “unauthorized persons”: how to confirm and how to refute
New form of DAM from the 1st quarter of 2022
We are challenging the cadastral value from January 1, 2022
Changes in property tax: clarifications from the Federal Tax Service
New amounts of sick leave, maternity and child benefits in 2019
Scans are not a basis for deducting VAT
SKUAD for non-payers: tax debts will be collected in a new way
Components of the card
The paper is filled on both sides. On the title side there are:
- Title of the document;
- his number;
- OKUD code;
- OKPO
After this data, in the first lines of the card, you must write down the full name of the company itself, as well as the department in which the document is being filled out.
At the end of the introductory information there is a small table for filling in the date of compilation, transaction code, date and number of the described intangible asset.
Attention! In the vast majority of cases, the object of intangible assets is described in a single copy. This is indicated on the form itself; at the beginning there is space for one name.
Below are two tables to fill out. The first should provide data on:
- structural unit;
- the type of activity specified in the described intangible asset;
- account number;
- analytical accounting code;
- book value;
- period of use;
- volume of financial depreciation;
- estimated rate, percentage of depreciation rate;
- account code and the code of the accounting object itself;
- registration deadlines.
The second table is more extensive and includes columns such as:
- method of acquiring an intangible asset;
- description of the registration document;
- for what reasons, when and at what price it left.
At the very end, a separate line mentions the amount of depreciation of the intangible asset.
Filling out form No. NMA-1
Drawing up a document is a simple operation, but there are rules that guide it:
Each registration card is assigned a registration number in the line “Card No.”, the date of drawing up the document and the acceptance certificate, the full name of the company, OKPO code, as well as the division (shop/department) where the facility is operated are indicated. However, based on the intangibility of property, it is usually used in the activities of an entire enterprise, for example, a brand or trademark of a company, and then there is no need to fill out the line “Structural unit”.
For enterprises using a coding system, the transaction code for the receipt of the asset is entered on the card, and then the date and number of the corresponding document are specified. Subsequently, information is entered about the type of activity for which the asset was acquired, the department responsible for operating the asset, and the balance sheet account (subaccount) in which it will be recorded.
All object parameters are indicated:
- the initial cost, which consists of the costs of purchasing and bringing it to usable formats;
- the period required for full depreciation of property (SPI). Often, SPI is determined by expert means, since a special classifier has not been created, and the specifics of these assets are not always amenable to traditional methods of calculating depreciation. For intangible assets whose useful life is not determined, depreciation rates are set for ten years;
- depreciation rate in % or estimated rate;
- monthly depreciation amount;
- an account in which accrued depreciation amounts are accumulated.
For objects for which depreciation is not accrued (for example, received under donation agreements), dashes are placed in the corresponding columns.
The column “Acquisition method” provides information on how the company acquired the assets. Column 12 “Registration document” contains information about the document confirming the right to use intangible assets.
The last block of the table is devoted to information about the disposal/relocation of an object: document number and date, reason for disposal, amount from the sale of the object.
In the lower right corner of the form, in the “Depreciation amount” detail, the amount of monthly deductions is indicated.
The reverse side of the card is devoted to a brief description of the main qualities of the object.
Reverse side of the intangible assets accounting card
There are no tables on the second page of the document. On it, the filler is provided with lines for a brief written description. Moreover, the purpose of the asset is not stated in it, since it should already be contained on the front side of the document.
You can specify here the specific parameters and capabilities of the computer program, terms, and rights. A list of functionality will also be useful. They often list the company whose intellectual property the product was. But too lengthy a description is not welcome.
Important! Information on the brief characteristics should not duplicate or quote technical documentation (instructions, operating rules) for the described object, which is located in the organization.
The final touch on the paper will be the indication of the position of the person filling it out, his personal signature and transcript. It is placed after a comprehensive analysis of the intangible asset.
Subtleties of filling out the card
Responsibilities for filling out and maintaining all accounting cards in proper form rest with the accountant. In the vast majority of cases, it is this employee who signs the final part of the paper. Information to be filled out can come from acceptance certificates, various documents for the posting of the described assets.
Attention! A separate card is drawn up for each item of intangible assets.
Then they are all entered into the general register of cards, and a general statement is formed for all compiled documents.
Certificate of acceptance and transfer of intangible assets
Approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance dated April 22, 2011 N 23
I APPROVED I APPROVED Head of the donating organization Head of the recipient organization ___________ _________ __________ ___________ _________ ___________ (position) (signature) (last name, (position) (signature) (last name, M.P. initials) M .P. initials) __ ____________ 20__ __ ___________ 20__ —— ¦Codes¦ +—-+ Form according to OKUD <**> ¦ ¦ +—-+ UNP <*> according to OKYLP <***> ¦ ¦ —— Delivering organization _________________ _________ (name) ________________________________________________ (name of structural unit) —— UNP according to OKLLP ¦ ¦ —— Recipient organization ______________ _________ (name) ________________________________________________ (name of structural unit) —————— Grounds for drawing up the act ______________________ ¦ number ¦ ¦ (order, instruction, +———-+—-+ agreement) ¦ date ¦ ¦ ————+—— ——————— ———————————— ——— ¦ ¦ Date ¦ ¦ ¦acceptance for accounting¦ ¦ ¦Number¦of compilation ¦ ¦Date +—————————-+—-+ +——+————+ ¦ ¦write-off from accounting¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ——+—————————-+—— ——+————- Account, subaccount, analytical accounting code ACT ————————— —————— about acceptance and transfer ¦ Inventory number ¦ ¦ intangible assets —————————————+—— Object of intangible assets _____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Organization - holder of exclusive rights to the object of intangible assets ___________________________________________________________________ (name ) For information: Foreign currency ______________ ___________ _____________ (name) (rate) (amount) ——————————— <*> Payer’s account number. <**> National Classifier of the Republic of Belarus “Unified Documents”. <***> National classifier of the Republic of Belarus “Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs”. 1. Information on the condition of the intangible asset object as of the date of transfer ————————————————————————— ¦ Date ¦ Actual term ¦ +——————— ——————————+ use ¦ ¦creation or acquisition¦ start of use ¦ (years, months) ¦ +————————-+————————+——— ————-+ ¦ 1 ¦ 2 ¦ 3 ¦ +————————-+————————+———————-+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ———— —————+————————+———————— ————————————————————————— ¦ ¦ Cost . ¦ rub. ¦ assets ¦ ¦ rub.¦ assets with VAT, ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ without VAT <*>, ¦ ¦ ¦ rub. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ rub. ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +—————+————+—————+——+——+—————-+ ¦ 4 ¦ 5 ¦ 6 ¦ 7 ¦ 8 ¦ 9 ¦ +— ————+————+—————+——+——+—————-+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ —————+————+——— ——+——+——+—————— ——————————— <*> Value added tax. 2. Information about the object of intangible assets as of the date of acceptance for accounting ————————————————————————— ¦ Initial ¦ Useful life ¦ Method of calculating depreciation ¦ ¦ cost , rub. ¦ use +————————————+ ¦ ¦ ¦ name ¦ norm ¦ +——————+——————+——————+————— —+ ¦ 1 ¦ 2 ¦ 3 ¦ 4 ¦ +——————+——————+——————+——————+ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ————— —-+——————+——————+—————— Other characteristics _____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Admission Committee Conclusion of the commission: ______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Appendix _______________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Chairman of the Commission ________________ ____________ _____________________ (position) (signature ) (last name, initials) Members of the commission: ________________ ____________ _____________________ (position) (signature) (last name, initials) ________________ ____________ _____________________ Object of intangible assets Handed over ¦Accepted ___________ _________ _______________¦___________ _________ _______________ (position) (signature) (surname, ¦( position) (signature) (surname, initials) ¦ initials) __ ____________ 20__ ¦__ ___________ 20__
Possible mistakes
Loan costs should not be included in the initial cost of the asset. This may include:
- costs of attracting specialists (both internal and external);
- price of materials;
- depreciation of environmental protection;
- patent fees.
But not loans or credits.
If a company has acquired software, and its copyright holder is another organization, then such an asset cannot be registered in the intangible assets accounting card. This only occurs if the exclusive rights to that specific software product or license are transferred.
You should not issue an intangible registration certificate (NMA-1) for the rental service of any program. These cases are noted only on the off-balance sheet account according to the agreement number, which stipulates the relationship of the copyright holder with the user.
Important point! The useful life of the program or license must be reviewed annually.
The same applies to the calculation of depreciation (in particular, the method of carrying out this calculation). It is worth noting that there are intangible assets with an indefinite useful life. They require confirmation each year for factors that prevent these deadlines from being established.
What to fill out when accepting intangible assets
Material assets include, in particular, works of science, literature and art, computer programs, databases, inventions, utility models, selection achievements, inventions, know-how, brand names, trademarks and service marks, etc.
For an asset to be called intangible, it must have a useful life of more than 12 months and its value, as opposed to its physical form, can be reasonably determined. In addition, you need to have a document confirming your organization's exclusive right to this asset (patent, exclusive license, etc.).
Intangible assets do not include:
- organizational costs associated with the formation of a company;
- intellectual and business qualities of employees, their qualifications and ability to work (PBU 14/2007);
- material things in which the results of intellectual activity are expressed (for example, books).
Intangible assets arrive on the basis of an acceptance certificate, which is drawn up by a commission appointed by order of the manager. The commission includes representatives of the company administration, accounting employees, as well as specialists capable of assessing an intangible asset.