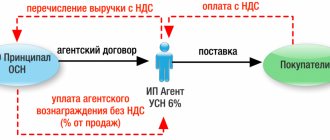
What is an agency agreement
An agency agreement is a form of intermediary agreement in which the customer entrusts a task to the contractor.
As a rule, this is the sale or purchase of goods, works and services. In an agency agreement, the customer is the principal and the contractor is the agent. The peculiarity of an agency agreement is that tasks are performed both on behalf of the principal and on behalf of the agent, but always at the expense of the principal. Based on the completion of the contract, the agent receives a reward. The customer can specify in the contract a fixed amount, a percentage of the transaction amount, or promise to transfer the profit received from the sale or savings on the purchase as a reward.
Accounting for the principal
In accounting for an agency agreement on behalf of both the principal and the agent, the costs of its execution are accounted for by the principal.
All expenses of the agent for the execution of the contract with the principal are accounted for in account 76. Accounting for VAT on contract services is reflected only by the principal, even if the services are provided on behalf of the agent. The agent takes into account VAT only on the agency fee.
An example of accounting for services under an agency agreement for a principal with postings
Master LLC, which owns residential premises, entered into an agency agreement with Vector LLC. According to the terms of the agreement, “Vector”, on its own behalf, leases the premises of a shopping and entertainment center owned by “Master”.
The contract specifies a fixed amount of agent remuneration in the amount of 500,000 rubles. At the end of December 2016, the amount of sales (rent) for all premises amounted to RUB 12,600,000, including VAT of RUB 1,922,033.
The terms of the agency agreement provide for the withholding of the amount of remuneration by the agent when transferring proceeds.
Postings under the agency agreement with the principal Master LLC:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 62.1 | 90.1 | Revenue from sales (rent) is reflected | 12 600 000 | Implementation Act |
| 90.3 | 68(VAT) | VAT charged on sales (12,600,000*18/118) | 1 922 033 | Invoice issued |
| 20 | 60(76) | The amount of the agent's remuneration is reflected (500,000 - 500,000*18/118) | 423 729 | Accounting information |
| 19 | 60(76) | VAT on the amount of the agent's remuneration (423,729*18%) | 76 271 | Accounting information |
| 68(VAT) | 19 | VAT is accepted for deduction | 76 271 | Book of purchases |
| 51 | 62.1 | Receipt of funds from rent minus agent's remuneration is reflected | 12 100 000 | Bank statement |
| 76 | 62.1 | The offset of the agent's remuneration against payment is reflected | 500 000 | Accounting information |
Another option for accounting for agent remuneration would be to transfer the remuneration directly to the agent:
| Dt | CT | Operation description | Amount, rub. | Document |
| 60(76) | 51 | Remuneration transferred to the agent | 500 000 | Payment order ref. |
| 51 | 62.1 | Receipt of rental income | 12 500 000 | Bank statement |
VAT on an agency agreement with the principal
Let's figure out how to work with VAT and invoices when selling and purchasing goods under an agency agreement. The procedure depends on whose name the transaction is executed: the customer or the contractor. There are four possible situations in total.
VAT on the principal when selling goods
If goods are sold on behalf of the customer , then VAT must be charged, invoices issued and registered in the standard manner. Proceed in the same way as when working without intermediaries:
- Charge VAT on the day the agent delivers the goods to the buyer. If there was an advance payment, then VAT is charged twice: on the day of the advance and on the day of transfer.
- Issue an invoice five calendar days from the date of shipment or receipt of advance payment.
- Record the invoice in the sales ledger. At the end of the same quarter, include VAT in your return.
The tax is paid based on the results of the quarter - before the 25th day of the month following the reporting period.
If the product is sold on behalf of an agent , then you will not have to interact with the buyer. The agent himself will issue all the invoices to him, and will give you copies of them or information from them in another convenient form that you agree on. Based on the copies received, charge VAT and re-invoice the agent. There are three steps in total:
- Charge VAT on the day of shipment, and if you receive an advance payment, charge the tax twice - upon receipt of the advance payment and upon shipment.
- Re-invoice the agent within five days. In its lines 2, 2a and 2b, enter your data; in line 1, enter the number that corresponds to your order of invoices. Take the remaining data from the copy received from the agent. Please remember that the date on the reissued document must match the date on the buyer's invoice.
- Register the reissued invoice in the sales ledger in the quarter in which you made the shipment or received the advance. When registering, indicate the buyer’s information in columns 7 and 8, and your agent’s information in columns 9 and 10.
Fix in the agency agreement a condition on the period within which the agent must provide you with information about shipments and advances or invoices issued to buyers. This is necessary so as not to be late in calculating tax and issuing an invoice.
VAT from the principal when purchasing goods
When purchasing items on your behalf, the seller will issue an invoice directly to you. Register it in the purchase ledger in the standard manner and accept the input VAT for deduction.
When purchasing goods on behalf of an agent, he will receive an invoice from the seller in his name and reissue it to you. Register the reissued invoice in the purchase book. Do this in the quarter in which you have met all the conditions for accepting input VAT for deduction, or in the next quarter if you want to transfer the deduction. In columns 9 and 10, indicate the seller’s information, in columns 11 and 12, the agent’s information.
If several invoices are issued or received on the same day, they can be replaced by one consolidated invoice, which summarizes the information from all documents.
Results
In order not to make mistakes with transactions under an agency agreement, it is necessary to study its terms - on the basis of which documents to reflect transactions in accounting, what algorithms are used to calculate agency fees, etc.
The main account for recording transactions is 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” in correspondence with accounts 51 (for payments), 68/2 (for VAT accounting), 44 (for registering purchased goods), etc. More
complete You can find information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
VAT on an agency agreement with an agent
On the part of the contractor, the procedure for working with VAT and invoices again depends on whose name the transaction is executed: in the name of the agent or in the name of the customer. Let's consider four situations.
VAT at the agent when selling goods
If you are selling goods on behalf of a principal , then you have minimal responsibilities. The principal himself will calculate VAT and issue invoices to buyers. Your responsibility will only be to issue the agency fee.
If you sell goods on your own behalf , you must issue and register an invoice in the name of the buyer in the accounting book. Draw up the document in two copies within 5 days from the date of transfer of goods to the buyer (reception of advance payment). Give one copy to the buyer, the other to the customer under the contract. Based on the received copy, the principal will issue you an invoice with the same indicators. It must be recorded in Part 2 of the invoice journal; nothing needs to be entered in the purchase ledger.
Record the invoice issued to the buyer of the principal's goods in the first part of the invoice journal.
VAT from the agent when purchasing goods
If you are purchasing goods on behalf of a principal , you cannot deduct input VAT since the purchased goods do not become your property. The seller will immediately issue invoices for the goods in the name of the principal, so there will be no need to re-issue anything.
If you buy goods on your own behalf , you cannot deduct input VAT either. But in this case, invoices received from the seller will have to be reissued and recorded in the accounting journal. Proceed in the following order:
- Register the invoices received from the seller in part 2 of the accounting journal for the quarter in which they were compiled.
- Reissue the invoice and transfer it to the principal. In line 1, indicate the serial number of the account according to your numbering, in lines 2, 2a and 2b the seller’s details, in line 5 the payment details, and in lines 6, 6a and 6b the principal’s details. Take all other indicators from the seller's invoice.
- Provide the principal with certified copies of invoices received from the seller.
- Record the invoice reissued to the principal in Part 1 of the accounting journal.
The agent can purchase goods from the seller not only for the principal, but also for himself or other customers. In this case, in the copy of the invoice, the quantity of goods purchased will not match the one that the agent issues to the customer. This is normal, since other people's goods are excluded from the document.
1C Accounting 8 edition 3.0 - Implementation of agency services
In accordance with Ch. 52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, under an agency agreement, one party (agent) undertakes, for a fee, to perform, on behalf of the other party, the principal (principal), legal and other actions on its own behalf, but at the expense of the principal, or on behalf and at the expense of the principal.
Let's look at an example. The organization (Agent) entered into an agency agreement with the principal to provide services on its own behalf.
The agency fee is 5% of the cost of services sold and is deducted from funds transferred by buyers.
To be able to reflect agency transactions in the 1C Accounting 8 edition 3.0 program, you need to configure the program. Why, in the Program Functionality on the “Trade” tab, enable the necessary items by checkboxes. In our case, this is the sale of goods or services of principals (principals) (Fig. 1)
Picture 1.
To implement the above example in the program, we will need the following documents: 1. Implementation (Act, invoice). 2. Report to the committent.
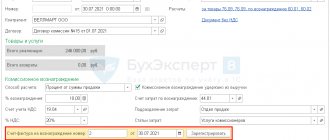
In the “Sales” section, we will create a Sales document (Act, invoice) with the type of operation “Goods, services, commission”. In the “Head” of the document, fill in the details of the Counterparty and the contract - the type of contract “With the buyer”. In the tabular part on the “Agency Services” tab we will indicate the nomenclature - the service, its cost, VAT rate. In the counterparty and agreement field, we indicate the principal and the agency agreement (The type of agreement should be “With the principal (principal) for sale”). The contract can specify the option for calculating the agency fee. The settlement account is automatically set to 76.09 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.” Let's review the document. We will issue an invoice (Fig. 2).
Figure 2.
If the agent sells goods (work, services) of the principal on his own behalf, then the invoice is issued by the intermediary in 2 copies on his own behalf. One copy of this document is handed over to the buyer, and the second is filed in the journal of issued invoices without registering it in the sales book.
After the sale of services, the agent must submit a transaction report to the principal. To perform this operation, as well as to reflect the commission, we need to create a document Report to the Principal, which is located in the “Purchases” section. On the “Home” tab, select the principal and the agency agreement. The commission calculation method will be entered automatically because... We initially specified it in the contract. It is necessary to create, accounting accounts will be automatically filled based on the “Item Accounting Accounts” register. On the goods and services tab, fill out the tabular part using the “Fill in - Fill in sold under the contract” button. We will issue an invoice for the remuneration and look at the document entries. We see that our revenue has been reflected and VAT has been charged. The document settings are shown in (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
Upon receipt of the report from the agent, the principal must issue invoices for each buyer. The agent must receive a copy of the invoices and register them in the journal of received and issued invoices by the date of receipt.
Invoices - invoices received from the principal are created on the basis of a report to the principal. In the invoice document received, you must indicate the number and date, and in the invoice field issued to buyers, select the invoice issued by the agent to the buyer upon sale. (Fig. 4)
Figure 4.
Now we need to generate reports and make sure that our actions are correct. In the “Reports” section we will create a Journal of received and issued invoices (Fig. 5) and a sales book (Fig. 6).
Figure 5.
Figure 6.
Registration of transfer of products to the agent
Based on paragraph 1 of Art. 971 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and clause 1 of Art. 996 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, things transferred by the principal to the agent remain the property of the principal.
Considering the above, when the principal’s products are transferred to the agent, they are not disposed of by the principal.
The operation of transferring goods for storage, in particular, to an agent for subsequent sale, is a fact of economic life within the meaning of Art. 3 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 N 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as Law N 402-FZ) and is subject to appropriate reflection in the accounting accounts (Part 3 of Article 10 of Law N 402-FZ).
The procedure for accounting for finished products is regulated by PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories” and the Guidelines for the accounting of inventories, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 N 119n (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines).
According to the second paragraph of clause 208 of the Methodological Instructions, the basis for issuing an invoice for the release of finished products in a warehouse is an order from the head of the organization or a person authorized by him, as well as an agreement with the buyer (customer).
In this case, the basis for releasing products from the organization’s warehouse will be an agency agreement.
The invoice for the release of finished products must contain the mandatory details established by clause 2 of Art. 9 of Law N 402-FZ, and may reflect additional indicators, such as:
— the main characteristics of the shipped (dispensed) products (goods), including product (product) code, grade, size, brand, etc.;
— name of the structural unit of the organization that produces finished products;
— name of the agent and reason for leave.
Guidelines as a standard form of an invoice recommend using form N M-15 “Invoice for the release of materials to the third party”, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee dated October 30, 1997 N 71a (see also letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 7, 2006 N 03-11-05/96 and dated 04/04/2006 N 03-11-04/3/186 and Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 04/28/2006 N 20-12/35854). Based on this unified form, an organization can develop its own invoice form.
In our opinion, when shipping finished products, the organization also has the right to use a consignment note (the TORG-12 form, which was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of December 25, 1998 N 132, can be taken as the basis for its development) marked “under an agency agreement” and a consignment note according to the unified form N 1-T (approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated November 28, 1997 N 78, hereinafter referred to as TTN) in the case of transfer of goods to the carrier for delivery to the warehouse of the commission agent. Along with the TTN, the form of the consignment note is used, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 15, 2011 N 272.
In accordance with the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations and the Instructions for its application (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n, hereinafter referred to as the Chart of Accounts and Instructions) to summarize information on the availability and movement of shipped products (goods), revenue from the sale of which for a certain time cannot be recognized in accounting, account 45 “Goods shipped” is intended.
Taking into account the above, at the time of transfer of finished products to the agent, the following entry is made in the principal’s accounting:
Debit 45 Credit 43
— finished products were shipped to the agent for sale.
How to show an agency scheme on the simplified tax system and acquiring
You are an agent. Selling goods or services of the principal
You deduct remuneration from the money received from the client. Its size is written in the agency agreement
Take into account the agency fee in the simplified tax system when you receive payment from a client.
Create a receipt from a customer in Elba:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: payment amount from the client
- Take into account in taxes: amount of agency fee
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the client
The principal transfers the remuneration separately: based on sales results or in advance
Take into account the agency fee in the simplified tax system on the day you receive payment from the principal.
Create a receipt from a customer in Elba:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: payment amount from the client
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the client
Create a receipt from the principal in Elbe:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: amount of remuneration from the principal
- Take into account in taxes: the same amount of remuneration
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the principal
You withhold remuneration from the money received from the client, but the amount of remuneration is not fixed in the contract, but is determined by the agent’s report
Take into account the entire amount received from the client in the simplified tax system. When the principal approves the amount of remuneration in the agent's report, adjust the income.
Create a receipt from a customer in Elba:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: payment amount from the client
- Take into account in taxes: the same amount of payment from the client
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the client
Adjust the income after the agent's report is approved:
- Money → Receipt “other” → Accrual of remuneration under the agency agreement
- Take into account in taxes: the difference between the amount of remuneration and payment from the client with a minus sign
- Date of receipt: the day the principal approves the agent’s report.
This way, a corrective entry will appear in KUDiR - only agency fees will be taken into account in taxes.
Expenses of the simplified tax system: we transfer the proceeds to the principal
On the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, it is important to correctly take into account expenses. Transferring proceeds to the principal is not an expense.
Create a write-off for the principal in Elba:
- Money → Bank write-off → Payments under an agency agreement
- Amount: the amount of payment from the client or revenue minus the agent's commission
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Write-off date: day of transfer of proceeds to the principal
Only for LLC: accounting
1. When selling on behalf of the principal
- Commissioned goods: in Elbe it will not be possible to account for such goods - they require a special off-balance sheet accounting account 004. Take into account such goods, incoming invoices from the principal and outgoing invoices for clients in a separate Excel file.
- When selling commission services: before generating financial statements, check that the outgoing and incoming commission acts.
2. When preparing financial statements for the year, accrue agency fees in accounting:
- open the task “Prepare and send financial statements” → step “Reflect the missing transactions using accounting statements” → “Add accounting statements”
- type of transaction: “Sale of goods and services of the principal under an agency agreement”
first entry: Debit 76 Principal - Credit 99, amount: agency fee
second entry: Debit 76 Client - Credit 76 Principal, amount: the entire amount of the client’s payment
- date: when the agent's report was signed
For example, you sell consignment goods on behalf of the principal and retain the commission immediately. The accounting entries will be:
You are an agent. Buying goods or services for the principal
Your client, the principal, hires you to purchase goods or services. You receive a reward for the work done. Look at the transaction diagram in our help.
You keep the reward yourself. Its size is fixed in the contract
Often the principal transfers money for the purchase and the amount of the agent’s commission in one amount - from which you yourself deduct the reward.
The principal instructed you to place an advertisement on Yandex.Direct and transferred 15,000 ₽. Of this amount, you spend 10,000₽ to pay Yandex and retain 5,000₽ - the income in the simplified tax system will be the size of your commission of 5,000₽.
Create a receipt of money from the principal in Elbe:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: the entire amount received from the principal
- Take into account taxes: only the amount of the agency fee
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the principal
The principal transfers the remuneration separately. Its size is fixed in the contract
Sometimes the principal transfers the remuneration and the amount for the execution of the order in separate payments.
The Principal transferred the Money to execute the order:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: amount to execute the order
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the principal
The principal transferred the agent's remuneration:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: reward amount
- Take into account in taxes: amount of remuneration
- Receipt date: day of receipt of remuneration from the principal
You do not know the amount of the reward in advance and withhold it from the money received for the execution of the order
When receiving money from the principal, take into account the entire amount in the simplified tax system. When the principal approves the amount of remuneration in the agent's report, adjust the income.
Received money from the principal:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: receipt amount
- Take into account in taxes: the same amount of receipt
- Receipt date: the day the money was received from the principal
Adjust the income after the agent's report is approved:
- Money → Receipt “other” → Accrual of remuneration under the agency agreement
- Take into account in taxes: the difference between the amount of remuneration and receipts from the principal with a minus sign
- Date of receipt: the day the principal approved the report
An adjusting entry will appear in KUDiR; only agency fees will be taken into account in taxes.
Only for LLC: accounting
When preparing financial statements for the year, accrue agency fees in accounting:
— “Prepare and send financial statements” → step “Reflect missing transactions using accounting statements” → “Add accounting statements”
— type of transaction: “Purchase of goods and services for the principal under an agency agreement”
- first entry: Debit 76 Principal - Credit 99, amount: agency fee
- second entry: Debit 76 Client - Credit 60 Supplier, amount: amount of payment to the supplier minus agency fees.
— date: when the agent’s report was signed
You can read about the documents for the buyer and the principal and the agent’s report in the help desk.
You are the principal. Selling goods or services through an agent
You entrust the agent with a task: transfer goods to the buyer, sell your services, receive money for goods, or find clients. Look at the transaction diagram in the article about agency agreements.
In taxes, take into account the entire amount of the client's payment, even if the agent withheld the commission and transferred part of the proceeds to you. The date of receipt of income depends on the terms of the agency agreement.
The agent sells on his own behalf and receives money from the client
Include income in the simplified tax system on the day the money arrives from the agent.
Show in Elba the receipt of money from the agent:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
- Amount: receipt amount
- Take into account in taxes: the full amount of the client's payment without reduction for the agent's commission
- Date of receipt: the day the money was received from the agent
The agent sells on your behalf and receives money from the client
Take into account the income in the simplified tax system on the day the client paid the agent.
Show the client's payment in the simplified tax system income:
- Money → Receipt “other” → Not specified
- Take into account in taxes: the full amount of the client’s payment
- Receipt date: the day the agent received the money from the client
Create a receipt of money from an agent in Elba:
- Money → Receipt → by Bank → Sales under agency agreement
- Amount: receipt amount
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Date of receipt: the day the money was received from the agent
The agent does not participate in settlements
Take into account the income in the simplified tax system on the day you receive money from the client.
Create a receipt of money from a client in Elba:
- Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Payment for goods and services by clients
- Amount: receipt amount
- Take into account in taxes: the full amount of the client’s payment
- Receipt date: the day the agent received the money from the client
Expenses of the simplified tax system: when to take into account the agent's commission in expenses
If you are using the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, write down the amount of the agent’s commission as expenses.
The date depends on the method of payment of remuneration:
The agent withheld a commission from the money received from the buyer
Show the agency fee in the simplified tax system expenses:
- Money → Write-off “other” → Not specified
- Amount: 0
- Take into account in taxes: amount of remuneration
- Date: date of approval of the agent’s report or act for agency remuneration
You transferred the reward in a separate amount
Create a write-off in Elba for the payment of agency fees:
- Money → Bank write-off → Payments under an agency agreement
- Amount: reward amount
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Date: date of payment of the agent's remuneration
Additionally, show the agency fee in the expenses of the simplified tax system:
- Money → Write-off “other” → Not specified
- Take into account in taxes: amount of remuneration
- Date: compare the dates of payment of remuneration and approval of the agent’s report or act for agency remuneration and select the latest one
When to take into account the cost of goods in the expenses of the simplified tax system
You have the right to write off the cost of goods sold as expenses based on the sale date specified in the agent’s report.
— Money → Write-off “other” → Write-off of goods sold
— Amount: cost of goods
— Take into account in taxes: cost of goods
— Date: implementation date indicated in the agent’s report
Only for LLC: accounting
The invoice or act is issued by your agent
1. To reflect the transfer of goods to the agent, reflect the write-off act:
— Goods → Select goods → Write off → Used/spoilt → Expense type “Other”, account 45 (Shipped goods)
— The system itself will calculate the amount and construct the wiring 45 - 41
— Date: when the goods were transferred to the agent.
2. When preparing financial statements for the year, write off the cost of goods sold using an accounting statement. Task “Prepare and send financial statements” → step “Reflect missing transactions using accounting statements” → “Add accounting statements”:
— Operation type: “Other”
— Debit 99 Income and expenses — Credit 45, the amount of the cost of goods
— Date: when the agent’s report was signed.
3. When preparing financial statements for the year, accrue agency fees and reflect the transfer of goods or services of the principal in the accounting records. Task “Prepare and send financial statements” → step “Reflect the missing transactions using accounting statements” → “Add an accounting statement”: - Type of operation: “Sale of goods and services to the public through an agent” - First entry: Debit 20 - Credit 76 Agent, amount: agent's fee - Second entry: Debit 76 Agent - Credit 99 amount of client payment - Date: when the agent's report was signed.
You issue the invoice or act yourself
1. Reflect the transfer of goods to the customer in the outgoing invoice for the amount of the sale to the customer. The system itself will construct wiring 99 - 41 and 62 - 99.
2. When preparing financial statements for the year, accrue agency fees and reflect the transfer of goods or services of the principal in the accounting records. Task “Prepare and send financial statements” → step “Reflect the missing transactions using accounting statements” → “Add an accounting statement”: - Operation type: “Sale of goods and services to clients through an agent” - First entry: Debit 20 - Credit 76 Agent, amount: agent's fee - Second entry: Debit 76 Agent - Credit 62 Client, amount: amount of client payment - Date: when the agent's report was signed.
You are the principal. Buying goods or services through an agent
You instruct an agent to buy goods or services: find an intermediary, pay him a fee, and he buys the desired product for you. Look at the transaction diagram in the article about agency agreements.
When to include purchase costs in the simplified tax system expenses
It depends on what exactly you are buying:
1. Product for resale.
On the day the goods are shipped to the final buyer.
2. Services or goods for your own use.
On the last date: when the purchase was paid in full or the agent’s report was signed.
When to take into account agency fees in the expenses of the simplified tax system
On the last date: when the remuneration was transferred or the agent’s report was signed.
1. Reflect in Elba the debiting of money for the execution of the order by the agent:
- Money → Bank write-off → Payments under an agency agreement
- Amount: amount to complete the order
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Date: date of debiting for the execution of the order.
2. Reflect in Elbe the expenses for the agent's remuneration
If you signed the agent's report and then transferred the fee:
- Money → Bank write-off → Payment for goods and services
- Amount: reward amount.
- Take into account in taxes: amount of remuneration
- Date: date of payment of the agent's remuneration
If you transferred the remuneration before approving the agent’s report, first show the write-off for payment of the remuneration, and in taxes reflect the expenses as a write-off under “other”:
- Money → Bank write-off → Payment for goods and services
- Amount: reward amount
- Take into account taxes: zero
- Date: date of payment of the agent's remuneration
+
- Money → Write-off “other” → Not specified
- Take into account in taxes: amount of remuneration
- Date: date of approval of the agent's report
3. Reflect the costs of the product or service in the simplified tax system
Create a write-off in Elba for completing an order:
- Money → Write-off “other” → Not specified
- Take into account in taxes: the amount of purchase costs
- Date: determine the date of consumption according to the rules listed above
4. Reflect the goods in the warehouse
If the supplier has issued an invoice in your name, add it to Documents → Inbox.
If there is no invoice, add the goods to the warehouse based on the acceptance certificate from the agent: Goods → Add → “By acceptance certificate.”
If you purchased a service through an agent, and the service provider issued a deed in your name, add it to Documents → Inbox.
Only for LLC: accounting
When preparing financial statements for the year, write off the agent's debt to you:
— open the task “Prepare and send financial statements” → step “Reflect missing transactions using accounting statements” → “Add accounting statements”
— operation type: “Other”
— posting: Debit 99 Credit 76
— amount: agency fee
— date: when the agent’s report was signed
If you have already added a deed or invoice from the seller, create an accounting certificate:
— operation type: “Other”
— posting: Debit 60 Credit 76
— amount: the cost of the purchased product or service excluding agency fees
— date: when the agent’s report was signed
You can read about documents for an agent in the article about agency agreements.
Acquiring
Take into account the income in the simplified tax system on the day when the money arrives from the bank. The Ministry of Finance allows this.
See when Elba takes into account acquiring automatically.
If it doesn't work automatically, show it like this:
— Money → Receipt “by the bank” → Sales under an agency agreement
— Amount: amount received
— Take into account in taxes: the full amount of customer payments without reduction by bank commission
— Receipt date: the day the money was received from the bank
— Commission: bank commission. Elba will take this amount into account in expenses if you are on the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”
Answer Profbukh8
Olga Sherst
Elena, hello, with the execution of agency transactions for the purchase of materials for the principal, there are some inconsistencies regarding the input of 1C - because The program normally implements commission sales, not the purchase of goods. I tried to choose the most suitable scheme for you:
1) Posting for receipt of funds from the principal for the purchase of materials:
- Dt 51
- Kt 76.09 - document “Receipt to the current account” - type of agreement “With the principal (principal)”.
2) Posting for the transfer of funds to the supplier for purchased goods
- Dt 60.01
- Kt 51 - document “Write-off from current account”
3) Posting for the acceptance of goods to the warehouse Dt 002 - in theory, it can be formalized by the document “Receipt of goods and services”, but in the future these goods will not be written off from accounting with the document - only “Operations entered manually”, therefore, to automate the process, 1C offers use invoice 004 (which is applied vice versa for goods accepted for commission), but if you put it in the document, then in the future you will be able to transfer the goods to the principal automatically using the document “Sales of goods and services”. There is such an inconsistency in this scheme - but it is the only one. You can, of course, violate the accounting methodology and use off-balance sheet account 004 - this is just an accounting methodology, but the accounting will be automated.
4) The agent’s report to the principal is registered in the document “Report to the principal (principal) on sales”, it indicates:
- on the “Goods and Services” tab you can indicate the materials purchased for the principal
- On the “Remuneration” tab, indicate your remuneration and its accounting accounts; as a result, you should have the following transactions generated:
Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1 - for the amount of commission
Dt 90.03 Kt 68.02 - for the amount of VAT on commission fees
Dt 76.09 Kt 62.01 - for the amount of the withheld remuneration (if it is necessary to offset the remuneration from the transferred amount to the agent)
5) You adjust mutual settlements with the principal for funds spent on purchasing goods from the supplier using the document “Adjustment of debt” - “Carrying out mutual settlements»,
those. collapse the receivables and payables between the principal and the supplier, i.e. wiring must be generated:
- Dt76.09 (principal)
- Kt 60.01 (material supplier).
And then everything will work out!
Best regards, Olga Sherst.
Elena Thank you very much for the diagram in 1C 8.3 and the sequence of operations for an agency agreement, I’ll get to it now.
I really forgot to note that we are using simplified taxation system income and will pay 6% only on the remuneration amount.
I tried in April myself through invoice 02, but for some reason I didn’t get the agent’s report.
Today I'll try it differently. I'll unsubscribe. Thanks again!!!!!!!!!!!
Please rate this question: (
2 ratings, average: 3.50 out of 5)
More than 300 video lessons on working in 1C: Accounting 8, 1C: ZUP are available to registered users
Registered users have access to more than 300 video lessons on working in 1C: Accounting 8, 1C: ZUP
I am already registered
After registering, you will receive a link to the specified address to watch more than 300 video lessons on working in 1C: Accounting 8, 1C: ZUP 8 (free)
By submitting this form, you agree to the Privacy Policy and consent to the processing of personal data
Login to your account
Forgot your password?