What is taken into account on account 26 in accounting
Account 26 “General business expenses” is used to summarize information about the organization’s administrative expenses. This refers to costs not directly related to the production process. Examples of such costs are the costs of financing the activities of the organization’s functional services:
- economic department;
- accounting;
- sales department;
- technical supply department;
- security;
- directorates;
- secretariat and others.
Account 26 “General business expenses” is active. The debit of the account collects all expenses associated with the maintenance and management of the enterprise as a whole. At the end of the month, the entire amount is written off and distributed from the loan. Therefore, there is no balance in this account at the end of the month. It is not shown on the balance sheet.
What do general business expenses include?
Which costs are included in general business expenses depends on the nature of the company's activities, the industry in which it operates, and the rules defined in its accounting policies.
The main cost items included in the OR:
- wage fund (payroll) for management personnel, that is, the directorate, accounting department, office, secretariat;
- insurance premiums accrued to the payroll of the organization's management apparatus;
- depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets used exclusively for administrative and economic needs;
- costs for repairing non-production OS;
- rental of non-production premises;
- information and consulting services;
- materials purchased for management purposes;
- entertainment expenses;
- retraining of personnel;
- security company services;
- costs associated with recruitment;
- BY;
- communication services and Internet;
- travel expenses.
Postings to accounts 20 and 90: select the method of writing off expenses
General business expenses can be written off in one of two ways. Postings for writing off general business expenses, depending on the chosen method, are presented in the figure:
The chosen procedure for writing off general business expenses must be fixed in the accounting policy.
This publication will help you cope with the preparation of accounting policies for 2022.
There you will also need to indicate the indicator in proportion to which general business expenses will be distributed to the cost of different types of products if they are written off as a debit to account 20 “Main production”. This could be the salary of key production workers, revenue, production volume and other indicators.
We will show the technology of distribution and write-off of general business expenses using an example.
Accounting for general business expenses
The OP accounting is carried out in the debit of account 26. The account has no balance, so at the end of the month the OP is completely written off to account 90 “Sales”.
Thus, during the month, the debit of the account accumulates amounts from the credit of accounts 02, 60, 76, 70, 69. At the end of the month, the amounts are written off to account 90.
If the organization’s activities are not related to the production process, for example, the company is engaged in agency or forwarding, account 26 can be used as the main one, that is, it is on it that all expenses are reflected, and then written off to account 90.
But trading companies should not use account 26, since they must reflect their costs on account 44.
Operations for accounting for general business expenses of budget accounting are reflected in account 109 80 according to the chart of accounts approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n. These are the same administrative and management expenses - salaries and insurance premiums of management personnel accrued on it, travel expenses, costs for communication services, utility bills.
General business expenses of the institution incurred during the month are charged to account 109 60, and in terms of non-distributable expenses - to account 401 20.
ORs are not included in the cost of work in progress.
Analytics is carried out in a multigraph card according to form 0504054, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n, by type of finished products produced, work performed, services by type of expense (clause 139 of the instructions to the chart of accounts of Order No. 157n).
Write-off of general business expenses to the cost of production: posting
In accounting, general business expenses are written off by posting D/t 20 (90) K/t 26, with two options possible:
- To the debit of the account. 20 transfer of accumulated costs from the credit account. 26 – in full for one type of finished product (GP), or distributing OCR by type of GP. In this case, OCR forms the “full” cost of production and writes it off at the end of the period.
- To the debit of the account. 90/2 “Cost of sales” - if the company conducts non-production activities (for example, accounting support services, consulting, etc.). With this method of accounting, a “reduced” cost price of the enterprise is formed, and the technical and chemical works are completely written off for sales, regardless of the sales indicator in the reporting period.
Distribution of general business expenses
Typically, RR is immediately written off as expenses for the current period. They are not included in the cost price (clause 18 of FSBU 5/2019). This method is called direct costing, or the reduced cost method. In this case, expenses are written off as semi-fixed expenses to the debit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount 90-2 “Cost of sales”.
The fact is that starting from 2022, instead of the previous PBU 5/01, FSBU 5/2019 is used. Thanks to the new standard, ORs are now not included in work in progress and finished products. This event put an end to the possibility of forming a full cost price. Thus, direct hosting became the only possible option for accounting for PR. Writing off general business expenses to cost of sales using this method is accompanied by the posting: Debit 90 Credit 26.
We will tell you more about all the important nuances of the new FSBUs and PBUs at a free webinar on October 5: you can sign up right now.
An example of the formation of product costs using the direct hosting method
Let’s say that within a month, materials for production were released from the warehouse to workshop No. 1:
- products “A” - in the amount of 325 thousand rubles;
- products “B” - in the amount of 100 thousand rubles.
At the beginning of the month there was no balance of work in progress and finished goods.
During the month, 50 products “A” and 45 products “B” were produced.
The balance of work in progress at the end of the month was:
- products “A” - 15 pieces worth 150 thousand rubles;
- products “B” - 5 pieces for the amount of 20 thousand rubles.
On the last date of the month accrued:
- depreciation of production equipment in workshop No. 1 - 55 thousand rubles;
- wages and insurance premiums for employees of workshop No. 1 - 220,675.68 rubles;
- general production expenses - 383,783.80 rubles;
- general business expenses - 170 thousand rubles.
Intrashop indirect costs are distributed in proportion to the standard cost of production. The standard cost of product “A” is 10 thousand rubles, product “B” is 4 thousand rubles. General production is distributed among departments in proportion to the cost of fixed assets; the share of production in workshop No. 1 is 0.25.
1. We calculate the amount of general production and OR attributable to workshop No. 1. At the same time, we do not distribute OR, since we use the direct costing method. The amount of overhead costs attributable to workshop No. 1 is 95,945.95 rubles (383,783.80 rubles x 0.25)
2. We calculate the coefficient of distribution of indirect costs by product.
| Name of product | Standard unit cost (RUB) | Output | Distribution coefficient (gr. 4 / sum of rows of gr. 4) | |
| Quantity (pcs.) | Standard cost (RUB) (gr. 2 x gr. 3) | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Product "A" | 10 thousand | 50 | 500 thousand | 0,74 |
| Product "B" | 4 thousand | 45 | 180 thousand | 0,26 |
3. We distribute indirect costs among products.
| Products | Distribution coefficient | Depreciation (RUB) | Salary and contributions (RUB) | General production expenses (RUB) | Total indirect costs (RUB) |
| Workshop No. 1 | 1,0 | 55 thousand | 220 675,68 | 95 945,95 | 371 621,63 |
| Product "A" | 0,74 | 40 700 | 163 300 | 71 000 | 275 000,00 |
| Product "B" | 0,26 | 14 300 | 57 375,68 | 24 945,95 | 96 621,63 |
4. We calculate the total amount of costs and production costs for products.
| Products | WIP at the beginning of the month (RUB) | Direct costs per month (RUB) | Indirect costs per month (RUB) | Total costsper month (rub.) (D count. 20), gr. 3 gr. 4 | WIP at the end of the month (RUB) | Cost of manufactured products (RUB) (D count. 43), gr.2 gr. 5 - gr. 6 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| Product "A" | 0 | 325 thousand | 275 thousand | 600 thousand | 150 thousand | 450 thousand |
| Product "B" | 0 | 100 thousand | 96 621,63 | 196 621,63 | 20 thousand | 176 621,63 |
5. We calculate the cost per unit of production.
| Products | Cost of manufactured products | Number of products released | Unit cost (RUB) (group 3 / group 2) |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Product "A" | 450 thousand | 50 | 9 thousand |
| Product "B" | 176 621,63 | 45 | 3 924,93 |
Closing
To determine active or passive account 26, you need to pay attention to how costs are reflected on it. They are distributed as a debit and written off as a credit to the cost accounts for the main production. Thus, account 26 in the accounting department is active. It closes monthly. All balances are transferred to the cost of production. The balance at the end of the period should be zero.
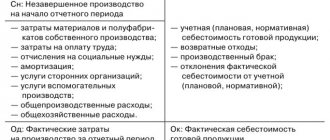
There are two ways to form costs:
- At actual cost (full).
- Direct costing or at reduced cost.
An enterprise can use only one method in its activities, which must be fixed in its accounting policies. It will not be possible to change it. Closing the account 26 will depend on the chosen method.
If the organization uses the formation method at actual cost, then in this case general business expenses will be closed to account 20 “Main production”. If the company has service or auxiliary workshops that provide services to third parties, then the costs must be divided between accounts 23 “Auxiliary production” and 29 “Service production and facilities”. The procedure for writing off and distributing general business cost bases must also be reflected in the accounting policy. The accounting entry in this case will look like this:
Dt20 (23, 29) - Kt26
How to close the 26th account if the company has chosen the direct costing method. Everything is very simple. General business expenses when working at a reduced cost will be taken into account in account 90.2 “Cost of sales”. Wiring sample:
Dt90.2 - Kt26
In accounting, problems sometimes arise with writing off general business expenses. Why is account 26 not closed? Most likely he has an opening balance, which he shouldn't have. There are several reasons that, by eliminating them, can solve this impossible question:
- First of all, you need to check the accounting policy settings in the accounting program. It should indicate the method of cost formation at the enterprise, as well as information on how general business costs are distributed.
- The second possible reason may be incorrect analytical accounting for general business expenses. You should check the correctness of the distribution of costs by type of item, as well as by division of the company. Most likely, an error will be discovered in the details of the operations performed.
The accountant closes the month
. What to do if there was no revenue during the reporting month. There is also a way out. You need to create a sale for 1 kopeck and send it to a fake counterparty. After this, you can close general business expenses from account 26 to account 20 “Main production”. After this, all that remains is to manually reverse the extra penny at the end of the year.
An example of how to close account 26 manually by posting:
Dt26 - Kt02 - depreciation on fixed assets has been accrued.
Dt26 - Kt10 - inventories are written off.
Dt26 - Kt70 - wages accrued to the administrative and economic apparatus.
Dt26 - Kt68 (69) - insurance payments have been calculated.
Dt20 (21, 29, 90) - Kt26 - costs have been written off.
Important! If general business expenses are taken into account in tax accounting as indirect, then temporary differences invariably arise. They must also be written off by postings.
Postings 26 of the accounting account
Examples of accounting entries for account 26:
| Contents of operation | Account debit | Account credit |
| Depreciation was accrued for fixed assets and intangible assets for general business purposes | 26 | 05, 02 |
| Write-off of materials used for general business needs | 26 | 10 |
| Entertainment expenses included | 26 | 60 |
| Costs for audit services are taken into account | 26 | 60 |
| Repair costs reflected | 26 | 60 |
| The cost of materials used during repairs has been written off | 26 | 10-5 |
| Salaries accrued to management personnel | 26 | 70 |
| Insurance premiums are calculated from the salaries of management personnel | 26 | 69 |
| Rent for the use of premises and vehicles | 26 | 76 |
| The cost of fire fighting equipment is taken into account | 26 | 60 |
| General business expenses were written off when accounting for finished products (works, services) using the direct costing method | 90-2 | 26 |