Account balance sheet
The “Account balance sheet” report is intended for generating a balance sheet for a selected account for a certain period of time.
In terms of the information displayed, the report resembles a fragment of the Turnover Balance Sheet report.
The report can be generated with detail by subaccounts or by analytical accounting objects (subaccounts).
Data can be displayed with an additional breakdown by time periods: month, year, etc.
You can display the expanded balance in the report. In this case, the expanded balance is calculated for each grouping level and for the account as a whole.
What it is?
As you know, accounting account 51 refers to the cash section (Section V), which is part of the Chart of Accounts, approved by a special regulatory act of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation (we are talking about order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000).
It is designed to record the receipt, expenditure and balance of non-cash money in the bank account of a business entity.
A characteristic feature of account 51 is the fact that it is used as an active synthetic accounting account, which records all incoming and outgoing transactions made in Russian rubles with non-cash funds of the organization.
The receipt (deposit) of non-cash money in rubles on the bank account of the organization is always recorded by the accountant under debit 51. The expenditure (write-off) of non-cash money in rubles from the bank account of the company is always reflected by the accountant under credit 51.
The corresponding transactions are generated on the basis of a bank account statement, to which supporting documents are usually attached (payments, checks, collection orders, other papers). The bank statement and its annexes are considered primary documentation.
Balance account 51 shows the actual cash balance in the company's bank account.
Analytical accounting of account 51 may provide detailing of transactions and balances for each of the current accounts opened by the organization in different financial institutions.
A detailed picture of the movement and balances of money in the bank current accounts of a business entity for certain periods of time can be obtained by generating and analyzing the card.
For this card, the following information is taken into account and systematized, characterizing the dynamics of non-cash money in a r/account for a specific time period:
- balance recorded at the beginning of the analyzed period;
- debit turnover (receipt of money);
- credit turnover (spending money);
- balance recorded at the end of the analyzed period.
Filling procedure
Account card 51 is a table that indicates data on balances and cash movements for a specific account of an organization for a certain period of time.
It is noteworthy that this table mentions the primary documents that justify each incoming or outgoing transaction.
This card is filled out by entering the following information into the table:
- name of the business entity;
- name of the card indicating the accounting period;
- initial balance (debit balance) of non-cash funds;
- for each incoming and outgoing transaction, the period, confirming document, debit analytics, credit analytics, correspondence of the necessary accounts, the amount of the transaction are separately indicated, and the change in the current balance of non-cash funds caused by the corresponding transaction is also reflected;
- total debit/credit turnover 51;
- the final balance (debit balance) of non-cash funds.
Download free sample and form
filling - link.
| LLC "AVB" Account card 51. Accounting period – 01/11/2019 | ||||||||
| Accounting period | Confirmation document | Analytics | Debit | Credit | Current balance | |||
| Debit | Credit | Check | Sum | Check | Sum | |||
| Opening balance | Debit 7000 | |||||||
| 11.01.2019 | Parish 323 dated 01/11/2019. Payment for the consignment of goods according to invoice No. 32 dated January 10, 2019. | Bank name, account | Start LLC, invoice No. 32 dated January 10, 2019. Parish 323 dated 01/11/2019. | 51 | 5000 | 62 | — | Debit 12000 |
| 11.01.2019 | Payment 256 from 01/11/2019. Calculation under supply agreement No. 23 dated 01/09/2019. | Finish LLC, supply agreement No. 23 dated 01/09/2019. Incoming invoice No. 11-23 dated 01/09/2019. | Bank name, account | 60/01 | — | 51 | 3000 | Debit 9000 |
| 11.01.2019 | Payment 258 from 01/11/2019. Payment of bank commission according to receipt No. 127 dated January 11, 2019. | Payment for banking services | Bank name, account | 91/02 | — | 51 | 10 | Debit 8990 |
| Total turnover, final balance | — | 5000 | — | 3010 | Debit 8990 | |||
Account Analysis
The “Account Analysis” report is designed to present data on turnover between the selected account and all other accounts for a certain period.
In terms of the content of the information displayed, the report is similar to the Account Turnover report. The difference lies in the form of presentation of information.
The report can be generated with detail by subaccounts or by analytical accounting objects (subaccounts).
Data can be displayed with an additional breakdown by time periods: month, year, etc.
You can display the expanded balance in the report. In this case, the expanded balance is calculated for each grouping level and for the account as a whole.
Account card
The “Account Card” report is intended to present a sample of invoice correspondences, ordered by date, that relate to the selected time period and in which the selected account was used.
The structure of the report is similar to the Subconto Card report.
Each line of the report corresponds to one account correspondence. The report displays summary information: the initial balance of the selected account, as well as the final balance and total turnover.
Data can be displayed with an additional breakdown by time periods: month, year, etc.
What is account card 51
Account 51 is necessary to ensure control and analysis of cash flow, turnover, and other indicators characterizing the financial condition of the company.
The debit of the account reflects cash receipts, and the credit reflects the debiting of money from the current account (payments). The account balance indicates the availability of funds in bank accounts. The basis for recording account transactions are payment documents (orders - payment and collection, checks, announcements for cash deposits, etc.), and information from them is grouped in bank statements.
Analytical accounting is usually organized for each current account separately, as well as by types of transactions performed or counterparties with whom settlements are made. Enterprises have the right to build analytics in the most acceptable way for themselves. Account 51 corresponds with settlement accounts (with suppliers, buyers, personnel, accountable persons, budget, funds, etc.).
The reliability of account data is ensured by a number of documents usually generated in most accounting programs. Their registration allows the user to daily monitor and receive operational information about the availability of funds in the current account, payments made and the status of settlements with counterparties. One such form is the 51 account card.
It provides information about the balance of funds at the beginning of the period under review, provides a detailed list of completed transactions in strict chronological order, after each of which the account balance is displayed.
Subconto analysis
The “Subconto Analysis” report is intended to present data on the selected type of subconto: opening and closing balances, turnover for the period according to accounts. A report can be generated not only by a selected subconto or several subcontos, but also by a subconto value or a subconto value attribute.
The report is generated with details on accounts. The report settings allow you to specify additional detail for subaccounts.
Data can be displayed broken down by time periods: month, year, etc.
You can display the expanded balance in the report. In this case, the expanded balance is calculated for each grouping level.
You can set the following settings in the report:
- Indicators
- Grouping
- Selection
- Sorting
- Decor
- Additional data
- Diagram
Accounting registers
Let us recall that accounting registers are a type of accounting documents intended for registration, systematization and accumulation of information contained in primary documents accepted for accounting (Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). Accounting registers are not only the basis for the summary reflection of information on accounting accounts. Accounting registers are used to prepare financial statements.
According to their purpose, accounting registers are divided into chronological and systematic registers, and according to the degree of generalization of information into synthetic registers and analytical accounting registers. For example, in contrast to chronological ones, systematic accounting registers are designed to summarize information about accounting objects for a certain period, presenting summary data on turnover and balances in the context of synthetic accounts.
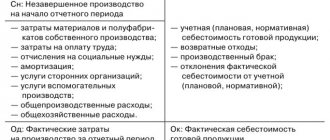
Let us show what accounting registers are with an example. One of the most common synthetic accounting registers, widely used by accountants when preparing a balance sheet, is the balance sheet. In this register, for a certain period, for each synthetic account, information is provided on the balance at the beginning of the period, turnover for the period and balance at the end of the period. Naturally, information on balances and turnover is presented separately by debit and credit of the corresponding accounts:
| Check | Balance at the beginning of the period | Period transactions | balance at the end of period | |||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | |
| 01 | ||||||
| … | ||||||
| 99 | ||||||
| Total | ||||||
Subconto card
The “Subconto Card” report is intended to present a sample of invoice correspondences, ordered by date, that relate to the selected time period and in which the selected type of subconto was used.
The structure of the report is similar to the Account Card report.
Each line of the report corresponds to one account correspondence. The report displays summary information: the initial balance of the selected account, as well as the final balance and total turnover.
Data can be displayed with an additional breakdown by time periods: month, year, etc.
Examples of working with 1C reports
For example: “Account card” and “Account analysis”. “Account Analysis” allows you to analyze account turnover.
Example of analysis of account 60 for the year:
The Account Card report provides details down to the posting. You can pick up the primary and compare it with the details:
main book
The “General Ledger” report allows you to display information for each account (subaccount) about the balance at the beginning and end of the period, the turnover of the account with other accounts (subaccounts) for the selected period of time. The report is generated based on accounting data.
The report is generated by clicking the Generate .
To generate a more compact report with a hidden header, click the Header .
Report generation parameters can be set using the Settings :
- In the Period , you can specify the period for generating the report: month, year, etc. If you need to display data in the report for periods in which there were no movements in the accounting accounts, then you need to check the All periods .
- To detail the data by subaccounts or by subaccounts of correspondent accounts, you need to select the By subaccounts or By subaccounts of correspondent accounts .
- To display the expanded balance, you need to select the Expanded balance . Additional parameters can be set on the Expanded balance , for example, specify by subaccounts or according to the account analytics, the expanded balance should be displayed in the report. By clicking the Default , you can fill in the settings that are set by default in the report and, if necessary, adjust them.
- When printing, you can display the data of each account (subaccount) on a separate sheet. To do this, you need to check the Split into sheets box .
Express accounting check
An express check of accounting in the 1C Accounting 8 program helps to obtain summary or detailed information about the state of the information base data at any time.
An express check is a set of checks grouped by accounting sections. Each check ensures that there are no errors in the infobase data. Control may consist in compliance of credentials with certain provisions of the law or in compliance of data with internal algorithms embedded in the program.
As a result of the express check, a report is generated that shows the total number of checks performed and the number of checks during which errors were detected. The report can be printed or saved to a file.
The results of the express check can be displayed with details up to the accounting section or before each check. The report can show comments for each check performed:
- subject of control - what exactly the current inspection checks;
- the result of the check - whether errors were found during the check;
- possible causes of errors;
- recommendations for troubleshooting.
The list of checks performed can be limited ( Show/hide settings ). To prevent a check or check section from being performed, you need to uncheck the box.
Analytical accounting card in 1C 8.3
To store data on debtors and creditors, with information about each transaction in primary documents, form card No. RT-12 is used.
It is necessary to take into account that in the version of the program “1C: Enterprise Accounting 3.0” this card is not present in the report form. But it can be compiled from data contained in standard program reports. All necessary reports are located in the “Reports” - “Standard Reports” menu.
The reports are presented in various forms, but this does not prevent you from using them in your work.
Account card
The program provides the opportunity to generate an “Account Card”. The card contains detailed information about the movement of documents on the selected account. For example, let’s generate data on counterparties. Select account No. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” and create an account card. The “Show settings” button, which exists in each 1C report, allows you to assign additional selection, for example, to find a specific counterparty.
In the account settings there is a basic set of data filters that will be in the report:
- counterparties;
- contracts;
- documents of settlements with the counterparty.
If this set is not enough for work, the “Add” button allows you to include additional indicators in the filter. The selected data can be saved in the report settings using the “Save settings...” button.
If necessary, you can view any primary document in the 1C analytical report by double-clicking it.
Posting report
Data for several accounts is simultaneously generated using the “Posting Report” function. The “Show settings” function in “Selection” is also involved in selecting the desired indicators. By setting the “Comparison type” field to “Equal”, select the desired account, and in the “Subconto” field, find the required counterparty.
The following values can be applied when setting the selection.
The user can use the "List of Values" function to select specific values, for example, accounts 60.01 or 60.02.
When generating any report in the 1C program, you can set similar conditions.
Please note that you need to select an account with a subaccount that forms the posting (in our example, subaccounts 60.01 and 60.02). If you do not do this, the report will be empty. This differs from the account card, where it is enough to indicate the group account.
Analytical reports from the “Standard reports” group are generated in a similar way.
Universal report
The “Universal Report” allows you to select analytical information for working with an analytical accounting card. It is located in the “Reports” - “Standard Reports” section. To collect such information, select the “Accounting Registers” section of the report. The Settings button sets various filters for this report.
The “Add selection” field specifies selections for data generation.
To detail the selection fields, use the “+” button. Thus, it is possible to select any data in the report settings.
The “Structure” tab is used to specify the data that the user needs in the report. The data is grouped in the “Detailed records” field.
This adds fields with the necessary information.
After completing the settings, the detail line will look like this:
After completing the settings and clicking the “Close and Generate” button, the user receives the generated report.
The 1C: Enterprise Accounting 3.0 program lacks some unified forms. It is possible to compile them yourself by processing analytical data from standard reports.
Still have questions? Order a free consultation with our specialists!
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter
Other articles on the topic:
#1C:Accounting
All articles
Loading the price list in 1C 8.3 Reserves for vacation pay in 1C: Accounting
No time to read? We'll send it to you by email!
Order help from a 1C specialist
Log in to leave a comment
Use your social media account to leave a comment or review!
Report “Analysis of the state of tax accounting for income tax”
The report is intended to identify possible errors in tax accounting data and take into account differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities.
The report contains an analytical analysis of the state of tax accounting and accounting for differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities, which is carried out by comparing data from accounting, tax accounting and accounting for differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities.
The report needs to be generated only after performing routine month-end closing operations.
The report indicators are grouped by economic content and presented in the form of graphic diagrams (block diagrams). Connections between blocks are reflected by arrows. The arrows illustrate the “transition” of value from one accounting object to another. The arrows come from blocks symbolizing objects being written off (their value decreases) and enter blocks symbolizing objects whose value is increasing.
Connections between circuits are indicated in two ways:
- using automatic transitions from one scheme to another;
- on the general diagram.
The transition from one scheme to another is made by double-clicking on the block with the indicators of interest. If the decoding of the requested indicator does not imply a transition to another scheme, then a transaction report opens, containing all the accounts for which this indicator was generated. Each account can be detailed by documents. To do this, you need to select the Expand by command panel documents checkbox. The document can be opened directly from the report and adjusted if necessary.
A general picture of the location of the schemes and the connections between the schemes can be found in the section “Structure of the tax base”. The structure of the tax base is available when opening a report and using the button of the same name on the command panel of any scheme and decoding table. Using the structure of the tax base, you can go to the accounting section of interest.
The “Production” diagram reflects production costs for the production of finished products and services provided to third-party customers. Expenses attributed to the cost of services provided to in-house production units are not reflected in the report.
In the “Cost of Assets” diagram, in the block “Cost of goods, RBP, written off as expenses and depreciation”, the value of assets written off for reasons other than sales (write-off for own needs, write-off for other expenses, returns to suppliers, etc.) is reflected. .
On the “Expenses for ordinary activities” diagram, in the block “Cost of goods, RBP, written off as expenses and depreciation”, the cost of assets written off as expenses for ordinary activities is reflected.
In the “Expenses for ordinary activities” diagram and in the “Production” diagram, a discrepancy between the data in the “Direct costs” block for multi-process production is allowed if at some production stage the reclassification of costs from direct to indirect and vice versa is allowed. The same rule applies to the “Indirect costs” block.
In the “Tax” diagram, the analysis of the state of tax accounting is carried out by comparing the amount of income tax according to tax accounting data (profit statement) and according to accounting data, taking into account the recognition and write-off of permanent and deferred tax assets and liabilities (profit and loss statement). If the amount of income tax according to accounting data coincides with the amount of income tax according to tax accounting data, then tax accounting is regarded as correct.
The blocks illustrate the value of the organization's assets, liabilities, income and expenses according to the following data:
- accounting (yellow background),
- tax accounting (blue background),
- accounting for permanent differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities (pink background),
- accounting for temporary differences in the valuation of assets and liabilities (green background).
If for the indicators of one block the rule “ Value assessment according to accounting data = Value assessment according to tax accounting data + Permanent and temporary differences ” is not followed, then the block is surrounded by a red frame. This is a signal of accounting errors. It is recommended to consider the history of the formation of block indicators, find out the reason for non-compliance with the rule and eliminate it.
The report is not intended to analyze data on income and expenses related to activities with a special taxation procedure. With the exception of those expenses that are classified as activities with a special taxation procedure, as a result of distribution according to income received. The report is not intended to analyze income that is not taken into account when determining the tax base (Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Report “Analysis of the state of tax accounting for VAT”
The report is intended for checking in the 1C Accounting 8 program the correctness of filling out the purchase book, sales book and VAT declaration. The report shows the amount of VAT accruals and deductions by type of business transaction.
The report needs to be generated only after completing regulatory VAT operations.
The report consists of a general scheme of the tax base and explanations of individual blocks of this scheme.
To return to the report scheme from the transcripts, click the Tax base structure .
Each block reflecting the accrual or deduction of VAT contains two indicators:
- amount of calculated VAT (yellow background),
- amount of uncalculated VAT (gray background).
If a block contains entries with errors, a red exclamation mark is displayed next to it.
The sum of each report block can be decrypted.
Report “Availability of invoices”
The report is designed to monitor the availability of invoices received from suppliers.
When generating a report, you can set the following parameters:
- Availability of invoice - possible values: Yes - when building the report, documents for which invoices are generated are taken into account,
- No - documents for which invoices were not generated are taken into account,
- It doesn’t matter - all documents that can be used to generate invoices are taken into account.
- Depending on the value of the Selection , the report is generated either based on the documents specified in the List of documents , or based on all documents except those specified in the List of documents .
The results of report generation are displayed in the Result :
- Document-basis - displays the document on the basis of which the invoice is generated.
- Invoice – an invoice generated on the basis of a document. If the invoice details are specified directly in the base document, then the name of the base document is displayed.
- Posted —indicates that the invoice has been posted.
Types of registers
In fact, accounting registers are order journals and various cards, certificates and statements, for example, the most important one is the balance sheet (“chessboard”), based on the data of which a balance sheet is compiled. Therefore, it is logical that accounting registers are divided into:
- systematic;
- chronological;
- combined (synchronistic).
The first ones are maintained according to certain accounting accounts and an example of them can be called the balance sheet or the general ledger. Systematic documents also include cards in which the accountant records any events in economic life. Chronological ones are used to record events of economic activity for a certain period of time, most often a month. This is how most order journals are maintained. These two types of accounting registers complement each other; there is even the so-called Mendes rule:
The sum of turnovers in chronological registers is equal to the turnovers in the debit or credit of systematic registers.
Therefore, in practice, for the convenience of accountants, combined type registration documents are often used. For example, a journal is a general ledger common in small companies.
According to the degree of information generalization, there are analytical and synthetic accounting registers. A striking example of synthetic accounting documents is the same balance sheet. In it, the accountant records information for each synthetic account for a certain period about balances at the beginning and end of the period, as well as turnover for the period. This document looks like this:
The accountant records analytical information, that is, not only the transaction details, but also a summary of its contents, in special statements or cards. For example, this could be accounting for materials, goods, fixed assets, or settlements with counterparties. It will show what accounting registers are, an example of an analytical unified inventory card of fixed assets:
Report “Tax Audit Risk Assessment”.
The form contains report management commands, a “quick” user settings field, and a report result field.
When opened, the “quick” user settings field displays the current list of parameters (the current settings option) by which data can be selected for generating a report. The list of “quick” user settings includes only those parameters that are defined for this during configuration, as well as those for which the “ Quick access ” mode is specified in the user settings of each such parameter. By checking or unchecking options, and changing comparison conditions and comparison values, you can quickly obtain different slices of data.
To edit the full list of current settings, execute the “ Settings ” command. In the form that opens, the selection conditions for generating the report are created. The list may contain additional parameters.
To use existing settings, execute the command “ All actions - Select setting ”. In the list, select the desired setting and click the “ Select ” button. The selection command is present only if the report or configuration has the “ Storage of custom report settings ” property set.
The report may contain several options for report settings defined during configuration. To select the desired option, use the “ Select Option ” command. In the list, select the desired option and click the “ Select ” button. The list will contain those settings that were previously saved by the “ All actions - Save settings ” command.
If the values of all parameter settings are intended to be used to build a report in the future (possibly if the user has the “ Save user data ” right), then a version of these settings can be saved. To do this, execute the command “ All actions - Save option ”. In the form that opens, specify the name of the option and click the “ Save ” button.
If you need to change an existing option, run the command “ All actions - Change option ”. In the form that opens, select an option and click the “ Select ” button. Make the required changes and save the result.
If changes have been made to the “quick” user settings field and you want to return to the “standard” values (values that are saved for the current settings option), run the command “ All actions - Set standard settings ”.
To build a report, click the “ Generate ” button.
The result is displayed in the field of the spreadsheet document. In the upper part of which the values of the selection parameters used for this construction are indicated.
The report result can be saved in the 1C Accounting 8 program and also printed.
Next Previous
These features are available to both users of local versions and cloud solutions, for example 1C:Fresh, 1C:Ready Workplace (WWW) . To purchase boxed versions or rent the 1C:Accounting 8 program in the cloud, please call +7(499)390-31-58, or e-mail: [email protected]
We recommend that you read the sections
Cash accounting in 1C Accounting
| How to create a user with “Administrator” rights in 1C Accounting 8.3 |
| Directories. Documentation. Operations. |
| Interface Taxi 1C Accounting 8.3 How to switch to bookmarks, 1C Accounting 7.7 |
| 1C Accounting setting up accounting parameters |
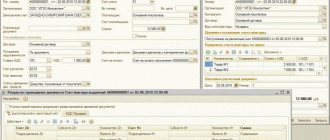
What additional fields can be displayed in the account card in 1C: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0?
Published 02.09.2021 14:20 Author: Administrator 1C programs have many reports, with skillful handling of which the user can obtain information in various sections and with the necessary detail. One of the innovations in version 3.0.94 was the implementation of additional fields in the account card. Let's figure out how this functionality can be used in the 1C program: Enterprise Accounting ed. 3.0, and what information the user can obtain using this feature.
The “Account Card” report is located in the “Standard reports” block of the “Reports” menu section.
To further customize the report, click the “Show Settings” button.
Having previously selected an account on the “Additional Fields” tab, use the “Add” button to set additional report details.
Let's look at examples.
Select an account for analysis (in our example, let it be account 41 “Products”) and add an additional field for analytics from the list of available fields, revealing possible corresponding sub-accounts with pluses.
Please note that all fields are listed alphabetically, which makes it easier to find the desired value.
Let's take the value of the TIN field as an example.
The selected field appears in the detail list. Click "Generate".
As a result, an additional line with the TIN value of the product supplier appeared in the report in the “Kt Analytics” column.
Similarly, you can add other values you need, for example, address, phone, email of the supplier.
Please note that fields that begin in Latin, for example, E-mail, are located at the beginning of the list of available fields.
As a result of the setup, the specified information is added to the report analytics.
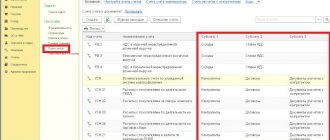
Next example.
Similarly, you can make the settings when generating a card for account 26 “General business expenses”, supplementing the data about the counterparty - the service provider assigned to the selected expense account.
As in the previous example, additional information appeared in the “CT Analytics” column according to the settings. In this option, this is the INN and E-mail of the service provider.
One more example. If you keep records by item groups, you can add this type of analytics to the analysis of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”.
In this case, the corresponding account 41 “Goods” will have an additional mark, by which you can find out which product group the supply of goods belongs to in the “Analytics Dt” column. In our example, these are “Products for landscaping and landscaping” and “Main product group”.
You can enter any additional information you are interested in on the account card. If the information is not displayed, then the fields are not filled in or are not available for this account.
For example, when generating an invoice card for analyzing the supply of goods (account 41 “Goods”), we will display additional fields “Article” and “Country of Origin” in the report.
These fields are filled in on the product card. Otherwise, the information will not be reflected in the report.
Generate a report.
In the “Analytics Dt” column, under the product name “Orchid Flowers”, additional information about the country of origin has appeared and the product article number has been displayed. In the second line, where “Ready lunch Standard” is indicated, no additional information is displayed, because This data is not on the product card.
Using this principle, you can experiment with settings with other accounts (for example, 10 “Materials”, subaccounts of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, etc.), selecting the information you need for the report in the analytics.
Author of the article: Olga Kruglova
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
Comments
0 Irina Plotnikova 09.09.2021 21:33 I quote Elena:
Thank you, it turned out to be very useful. Is it possible to display some kind of report so that you can see for a certain day the invoices issued to customers, paid, as well as by item, what is presented in these invoices?
Elena, good afternoon.
Part of your question can be solved in a standard way. You issue an invoice to the client, then he pays it, you upload bank statements into the program. In the receipt to the current account, indicate the type of operation “Receipt from the buyer”, a field will appear where you can select the desired account. After that, go to the “Sales” - “Customer Accounts” section. A list of accounts will appear in front of you. Those invoices that you have added up in your bank statement will appear in the “Payment” column in green with the words “Paid.” In the payment invoice itself, below in the “Comments” field, you can write a short list of the items being sold. Then if you display a list of invoices in the “Sales” - “Invoices to Customers” section, you will see this comment. this is the only option. If there is not enough such functionality, then you need to write processing from programmers. Quote 0 Elena 09/08/2021 20:08 Thank you, it turned out to be very useful. Is it possible to display some kind of report so that you can see for a certain day the invoices issued to customers, paid, as well as by item, what is presented in these invoices?
Quote
Update list of comments
JComments