Accounting implications
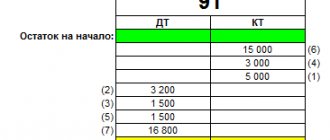
51 positions of the Chart of Accounts are necessary in order to summarize information on the availability and movement of monetary resources in the national currency of the Russian Federation on demand deposits of companies that are opened in commercial banks.
In the debit part, the receipt of financial resources on a demand deposit of the organization in whose name this deposit was opened should be recorded. In turn, the credit part contains data on the write-off of resources.
If for some reason this or that amount was incorrectly reflected as a debit or credit, and this was revealed when checking bank statements, then such amounts are recorded in position 76, called “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.”
The amounts for the debit and credit parts of the designated position are reflected on the basis of statements received from the bank and payment documents attached to them.
As for analytics, it should be conducted for each bank demand deposit of the company separately.
How are transactions carried out on 51 accounts?
51 is the active register. This means that debits record inflows and credit records outflows. Both receipts and expenses are carried out on the basis of supporting documentation: statements, payment orders.
If some amounts were erroneously reflected in the debit or credit of 51 accounts. (the accountant discovered an error when checking the statement), they are reflected in register 76, using the subaccount “Calculations for claims”. To register erroneous deposits to the account, use the following entry: Dt 51 Kt 76.
Reporting for 51 registers is as follows:
- balance sheet - a document that reflects the turnover and balances of the account;
- analysis - all information about transactions on the account. 51 for a certain period of time;
- account card 51 (what this is becomes clear from the user instructions for accounting programs) - detailing of transactions by sampling dates and correspondence analytics.
If a journal-order accounting system is used, then the accountant draws up a journal-order for account 51 using Form No. 2. The journal is filled out on the basis of bank statements with the results of the corresponding registers - one or more statements from a credit institution. If there are several extracts, then it is necessary to indicate the start and end dates of such documents. Statement No. 2 is attached to the back of ZhO No. 2. It records the debit turnover of the account. 51.
ConsultantPlus experts have figured out how to fill out journal order No. 2. Use these instructions for free.
Existing types of payments
So, when opening a bank deposit, a bank account agreement is signed between the company and the credit institution, according to which the latter undertakes to accept and accept financial resources received in the name of the client, carry out the instructions of the account owner to write off monetary resources from the account or issue them, as well as perform other operations according to the account. The bank receives a commission for cash and settlement services to clients.
Depending on the payment procedure chosen between the counterparties for a particular transaction, cash and non-cash payments are distinguished. In the first case, financial resources are used in kind, i.e. in the form of banknotes. As for non-cash payments, they are made through accounts opened with a credit institution.
If we talk about citizens of the Russian Federation, then this category has no restrictions in choosing the procedure for making payments. But with legal entities and individual entrepreneurs the situation is somewhat different. Thus, in accordance with current legislation, in each transaction carried out, the limit for settlements using cash today is 60.0 thousand rubles.
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation and other regulatory and legal acts regulating banking activities allow the use of four key forms of non-cash payments:
- settlements using payment orders, when, on the instructions of the account owner, funds within the balance on it are transferred in favor of a counterparty who can be serviced by the same or another financial and credit institution;
- letter of credit form of payment;
- collection form;
- payments by checks.
Payment of interest under a loan agreement: postings
To write off interest on a loan, entries are made to the Debit account 91 to the subaccount “Other related expenses”. To post “interest accrued on a short-term loan,” we use Account Credit 66.
Example:
- Payment of interest: Debit 66, Credit 51;
- Accounting for interest as expenses: Debit 91.2, Credit 66.
The organization that issued the loan records the interest received as “Other income” in Debit 76 of account, Credit 51 (or 50 if there was cash).
An example of accounting for an interest-bearing loan by an organization:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Base |
| 51 | 66 | Short-term loan without interest received by the organization | 100 000 | Bank statement |
| 91.2 | 66 | Interest accrual for the first calendar period (month) | 500 | Accounting certificate |
| 66 | 51 | Interest paid for the first calendar period | 500 | Outgoing payment order |
| 91.2 | 66 | Interest accrual for the second calendar period (month) | 400 | Accounting certificate |
| 66 | 51 | Interest paid for the second calendar period | 400 | Outgoing payment order |
| 66 | 51 | Repayment of a credit | 100000 | Outgoing payment order |
The organization can issue itself or receive borrowed funds. According to the terms of loans, short-term and long-term are distinguished. Another nuance that affects accounting is whether the loan is provided without payment for the use of funds (interest-free) or whether interest must be paid (interest-bearing). In this article we will look at examples of postings for loans issued and received.
A legal entity, individual entrepreneur and individual can receive a loan. In turn, the organization can temporarily issue funds and property for use, both to other companies and to individuals (its employees, founders, strangers).
Typical accounting entries
The overwhelming number of transactions in 51 positions represent settlements between buyers and suppliers, which are carried out in accordance with concluded agreements. At the same time, typical accounting entries for such transactions look like this:
1) Dt 51
Kt 62 – crediting of funds for goods received or services provided;
2) Dt 51
Kt 60 – return of previously paid funds from suppliers;
3) Dt 51
Kt 43 – crediting of funds received for the transportation of goods;
4) Dt 51
Kt 76 – receipt of funds from other counterparties;
5) Dt 60
Kt 51 – payment to suppliers and contractors for goods or services received;
6) Dt 51
Kt 90 – crediting of proceeds from the sale of goods or services, etc.
What is reflected in account 51
Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n dated October 31, 2000 indicates what 51 accounts in the accounting department are - a current account.
This register is used to collect, record and analyze information about the movement of money in ruble equivalent on bank accounts. According to the account 51 keep synthetic records of bank account accounts that are opened by the organization in various credit institutions. The Ministry of Finance regulations also provide an analysis of 51 accounts: what this means in accounting and how analytics is carried out. Accounting 51 allows you to control ruble transactions and bank transactions of the enterprise. It takes into account all mutual settlements of the company through bank accounts:
- with staff (payment of salaries on cards);
- with suppliers and contractors, customers and buyers (payment under agreements and contracts);
- with the budget (transfer of taxes, fees, contributions), etc.
In this way, analytics is carried out on accounts. 51 - in the context of counterparties and types of transfers, that is, all operations of the enterprise.
Case Study
Let’s imagine a situation in which a certain LLC decided to transfer available funds in the amount of 3.0 million rubles to a deposit. for a period of 1 year. The interest rate on the deposit is 11.2% per annum, and interest is capitalized. In addition, funds in the amount of 45.0 thousand rubles were withdrawn from the company's current account, which were intended for internal business expenses.
In this situation, all these transactions will be reflected in accounting as follows:
1) Dt 55.03
Kt 51 – 3.0 million rubles, transfer of funds to deposit;
2) Dt 76
Kt 55.03 – 34.5 thousand rubles, accrued interest on the deposit;
3) Dt 51
Kt 55.03 – 34.5 thousand rubles, crediting accrued interest to the current account;
4) Dt 51
Kt 55.03 – 3.0 million rubles, return of funds from the deposit;
5) Dt 50
Kt 51 – 45.0 thousand rubles, funds were withdrawn from the company’s demand deposit.
Loans received: postings
Any organization can not only issue, but also take a loan. How to account for a loan in accounting? We'll look at the wiring further.
Loans issued by the company can be short-term - up to 1 year and long-term - over 1 year.
For short-term loans we use account 66. Entry:
- Receipt under the loan agreement - postings: Debit 50 (cash loan from the cash desk), 51 (non-cash from the current account), 52 (foreign currency loans), Credit 66;
- Return: reverse posting – Debit 66, Credit 50,51, 52.
If the organization incurred some additional costs associated with obtaining a loan (for example, the loan had to be insured or a commission had to be paid), then this amount is written off to Debit 91.2, Credit 66.
For long-term loans, account 67 is used, but the easiest way is to record the loan as short-term, at 66, and after 12 months transfer it to 67.
Example of accounting for an interest-free loan:
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Base |
| 51 | 66 | Short-term loan without interest received by the organization | 100 000 | Bank statement |
| 66 | 50 | Repayment of a short-term loan | 100 000 | Outgoing payment order |
| 51 | 67 | Long-term loan received by the organization | 1 000 000 | Bank statement |
| 60 | 51 | Payment of legal services for processing loan documents | 3 000 | Outgoing payment order |
| 91.2 | 67 | Costs for legal services are taken into account as expenses associated with obtaining a loan. | 3 000 | Act of executed works |
| 67 | 51 | Repayment of a long-term loan | 1 000 000 | Outgoing payment order |
Accounting for loans from the lender - entries for issuing loans
If a company issues a loan to another organization, then the transactions will be as follows:
- Debit 58 Credit 51 (50, 52, 40 ...) – entry for the loan issued.
As can be seen from the posting, a loan can be provided not only in the form of a sum of money, but also in the form of property (materials, fixed assets, etc.). The amount that will be taken into account in this case is the value of goods/materials, etc.
When issuing an interest-free loan to a legal entity, the amount is taken into account in the debit of account 76 and the credit of the account for issuing funds or property (50, 51,10, 40, etc.).
Loan repayment is documented by posting:
- Debit 51 (50, 40...) Credit 58 (76).
Regarding the taxation of loans with VAT, there are two opposing points of view. The first is based on the fact that there is a transfer of ownership, which is an implementation (Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Sales are subject to VAT. The opposite point of view: when receiving and returning a loan in the form of goods, there is no object of VAT taxation.
Entries for VAT accounting on loans in kind:
- Debit 91.2 Credit 68 VAT – when issuing a loan
- Debit 19 Credit 58 (76) – accounting for input VAT when repaying the loan.
The issuance of a loan to an employee of an organization is documented by posting:
- Debit 73 Credit 50 (51).
The return is processed by return posting.
Example:
The organization issued an interest-free loan to a legal entity in the amount of 320,000 rubles.
Postings for issuing a loan:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 76 | 51 | Issuing an interest-free loan | 320 000 | Payment order ref. |
| 51 | 76 | Loan repayment | 320 000 | Bank statement |
Postings for obtaining a loan
The period for issuing short-term loans does not exceed 1 year. When an organization receives funds from a credit institution, founder, etc. they are accounted for in account 66. The loan can be received in cash, by transfer to an account, or in foreign currency. The following entries will be made accordingly:
- Debit 50 (51, 52) Credit 66 - entries for receiving a loan.
When repaying the debt, the posting is reversed:
- Debit 66 Credit 50 (51.52).
The payment amount and frequency are specified in the terms of the contract.
When a company incurs additional costs when obtaining a loan, they are recorded in 91 accounts:
- Debit 91.2 Credit 66.
Long-term loans are provided for a period of more than a year. Accounting account – 67. The loan can be accounted for in this account, or after the repayment period becomes less than 12 months, transfer it to account 66:
- Debit 67 Credit 66.
Example of loan receipt transactions:
The organization received two loans: one for 6 months in the amount of 150,000 rubles, and the second for 36 months in the amount of 680,000 rubles. When applying for a long-term loan, the lawyer’s services were paid - 5,000 rubles.
Postings:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 51 | 66 | Short-term loan received | 150 000 | Bank statement |
| 66 | 50 | Short-term loan repaid after 6 months | 150 000 | Payment order ref. |
| 51 | 67 | Long-term loan received | 680 000 | Bank statement |
| 60 | 51 | Paid lawyer's services | 5 000 | Payment order ref. |
| 91.2 | 67 | Legal services included as expenses | 5 000 | Certificate of completion |
| 67 | 51 | Long-term loan repaid | 680 000 | Payment order ref. |