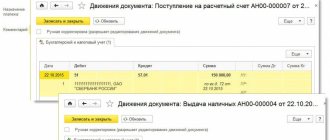
Business entities, taking into account the specifics of their activities, can perform cash transactions while observing the rules of cash discipline. In this article, we will focus on the questions of who is responsible for fulfilling the rules outlined above, how the 50th accounting account works, what the instructions for the designated position of the Chart of Accounts say, what sub-accounts are opened, what standard accounting records are kept. , and also consider one of the examples in practice.
Cash discipline and rules for maintaining it
To begin with, we note that cash transactions are understood as operations within which the receipt, issuance, storage of cash and the generation of relevant documents are carried out. The rules for conducting such operations are regulated by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
According to the designated document, cash discipline means:
- preparation of relevant documents related to cash flow;
- compliance with the requirements regarding the cash balance limit in the cash register;
- limiting the volume of cash payments between legal entities within the framework of each concluded agreement.
The rules outlined above are not relevant to those business entities that operate only through non-cash payments. The obligation to form cash transactions accordingly is not determined by the presence or absence of a cash register, as well as the chosen fiscal regime. In the current circumstances, only one rule works, according to which all those who have cash flows are required to adhere to cash discipline.
If we talk about the formation of documents, then when performing such operations they should be as follows:
- in case of cash receipt, a cash receipt document of the established form is generated. However, if a business entity issues a cash receipt or draws up a cash register receipt for each amount received, then the receipt document should be drawn up for the total amount of funds received during the day;
- When issuing cash, an expense cash order of the established form is issued. When issuing funds, the cashier must make sure that the accountant has endorsed the document and the recipient of the funds has an identification document;
- information on receipts and expenditure documents is entered into the cash book in the established form;
- When salaries, scholarships and other social benefits are issued, a statement can also be drawn up.
If we talk about the standards regarding the cash register limit, then the latter should be understood as the maximum permissible amount of cash that is allowed to be stored in the cash register of the enterprise at the end of each working day. The organization sets the designated limit independently based on the amount of revenue received by issuing an internal order. What is in the cash register in excess of the limit must be transferred to collectors for delivery to the bank. There is an exception to this rule when it comes to payment of wages, as well as holidays and non-working days.
As for the need to limit payments in cash, for business entities this limit is 100,000 rubles. for each signed contract. This rule does not apply to individuals.
Cashier, which account to choose
Sub-accounts to account 50 are opened in accordance with the recommendations in Instruction 94n:
- 50-1, on which all cash movements are to be reflected: receipts from sales, salary payments, cash deposits to the bank, etc. When making payments in foreign currency, it is necessary to organize analytics for each type of currency;
- 50-2 is used if necessary when there are operating rooms, that is, several cash registers remote from the main office, in which the receipt of money for a shift is recorded in the book of the cashier-operator, and not in the cash book;
- 50-3 is used to account for monetary documents in the amount of costs for their acquisition; a separate analytics is created for each type of document.
Using line item 50 in accounting
The indicated position is intended to provide a generalization of data on the available funds in cash at the cash desks of the enterprise and their movement.
The specified account is active, i.e. its debit part reflects the receipt of cash financial resources, and its credit part reflects their payment. At the same time, both third-party organizations and company employees are recognized as participants in such relationships. The following are considered as typical operations for the designated position:
- cash proceeds from the sale of inventory, services or work;
- payment of wages, as well as accountable and other payments to employees as part of the performance of their job duties;
- various types of administrative and economic calculations.
Typical accounting entries
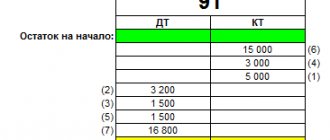
The table below shows standard accounting entries for item 50:
| № | Accounting entry | Purpose of the operation |
| 1 | Dt 50.01 Kt 90.01 | Receipt of proceeds from sales of products to the cash register |
| 2 | Dt 50.01 Kt 90.01 | Crediting income from other transactions to the cash register |
| 3 | Dt 51 Kt 50.01 | Transfer of cash from the cash desk to the bank |
| 4 | Dt 55.01 Kt 50.01 | Transfer of cash from the cash register for crediting to a special company account |
| 5 | Dt 60 Kt 50.01 | Payment to the supplier in cash for the products received |
| 6 | Dt 76 Kt 50.01 | Repayment of debt to other creditors |
| 7 | Dt 04 Kt 50.01 | Purchase of intangible assets |
Typical transactions for account 50 “Cash desk”
Typical transactions for account 50 “Cash desk”
Dt 50 Kt51 Cash withdrawn from the current account was entered into the cash register
Dt50 Kt 55 Cash withdrawn from a special bank account was credited to the cash register
Dt50 Kt60 The supplier returned to the cashier the funds overpaid to him or the advance payment given to him
Dt50 Kt62 Cash received from buyers was credited to the cash register or the buyer made an advance payment
Dt50 Kt71 Unused funds previously issued as a report were returned to the cash desk
Dt50 Kt73-2 Cash received from an employee to compensate for material damage was entered into the cash register
Dt 50 Kt 75-1 Cash contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital was capitalized
Dt 51 Kt 50 Cash was deposited from the cash register to the current account
Dt 55 Kt 50 Cash was deposited from the cash register into a special bank account
Dt 58-1 Kt 50 Shares purchased for cash
Dt 58-2 Kt 50 Debt securities were purchased for cash
Dt 60 Kt 50 The debt to the supplier (contractor) was repaid in cash or an advance was issued in cash
Dt 62 Kt 50 Cash paid in excess by the buyer (customer) was returned or the advance was returned
Dt 69-1 Kt 50-2 Vouchers were issued to employees, paid for from social insurance funds
Dt 70 Kt 50 Wages paid to employees from the cash register
Dt 71 Kt 50 Cash issued on account
Dt 73-1 50 Loan issued to employee
Dt 75-2 Kt 50 Dividends (income) were paid from the cash register to the founder (participant) of the organization
Dt 76-4 Kt 50 Deposited wages paid from the cash register
Dt 94 Kt 50 The shortage of cash in the organization’s cash desk is reflected (during an inventory or audit of the cash register)
Dt 99 Kt 50 Lost cash and monetary documents were written off as losses due to emergency circumstances
Typical transactions for account 51 “Current accounts”
Dt 51 Kt 50 Cash from the organization’s cash desk was deposited into the current account
Dt 51 Kt 51 Funds were transferred from one current account to another
Dt 51 Kt 55 Funds were transferred from a special bank account to a current account
Dt 51 Kt 60 The supplier returned the overpaid funds or advance payment to the bank account
Dt 51 Kt 62 Funds received from the buyer are credited to the current account or an advance is transferred
Dt 51 Kt 66 Cash received under a short-term loan agreement was credited to the current account
Dt 51 Kt 67 Cash received under a long-term loan agreement was credited to the current account
Dt 51 Kt 71 Unused funds previously issued for reporting were returned to the current account
Dt 51 Kt 75-1 Funds were received into the current account as a contribution to the authorized capital
Dt 51 Kt 76-1 Insurance compensation received from the insurance company is credited to the current account
Dt 51 Kt 76-2 Funds are credited to the current account for a recognized (awarded) claim
Dt 51 Kt 90-1 Funds for sold products (goods, works, services) were credited to the current account
Dt 51 Kt 91-1 Funds from the sale of other property received to the current account are reflected in other income
Dt 51 Kt 98-1 Deferred income received in non-cash funds
Dt 51 Kt 99 Non-cash funds were received into the current account as a result of emergency events
Dt 50 Kt 51 Cash withdrawn from the current account was credited to the cash register
Dt 55 Kt 51 Funds were transferred from the current account to a special account in the bank
Dt 58-1 Kt 51 The cost of the acquired shares was paid from the current account
Dt 58-2 Kt 51 Paid from the current account the cost of purchased debt securities
Dt 60 Kt 51 The debt to the supplier (contractor) has been repaid with non-cash funds or an advance has been issued
Dt 62 Kt 51 The funds paid in excess by the buyer were returned from the current account or the advance was returned
Dt 66 Kt 51 Cash was written off from the current account to repay a short-term loan and interest on it
Dt 67 Kt 51 Cash was written off from the current account to repay a long-term loan and interest on it
Dt 68 Kt 51 Taxes and fees to the budget were paid from the current account
Dt 69-1 Kt 51 The unified social tax was paid from the current account in the part subject to credit to the social insurance fund
Dt 69-2Kt 51 The unified social tax was paid from the current account in the part subject to credit to the pension fund
Dt 69-3 Kt 51 The unified social tax was paid from the current account in the part subject to credit to the compulsory health insurance fund
Dt 70 Kt 51 Employees' wages were transferred from the current account
Dt 71 Kt 51 Funds from the current account were issued for reporting
Dt 75-2 Kt 51 Non-cash funds were used to pay dividends to the founder of the organization
Dt 84 Kt 51 Expenses were paid from the current account using retained earnings
Dt 96 Kt 51 Various expenses were paid from the current account at the expense of a previously created reserve
Dt 99 Kt 51 Expenses related to eliminating the consequences of emergency situations were paid from the current account
Typical transactions for account 58 “Financial investments”
Dt 58-1 Kt 51 Purchased shares paid from the current account
Dt 58-2 Kt 51 Purchased debt securities paid from the current account
Dt 58-3 Kt 51 Funds were transferred from the current account under the loan agreement
Dt 51 Kt 58-3 Loan returned to the current account
Dt 91-2 Kt 58-1 The cost of shares disposed of as a result of the sale is included in
other expenses (sale of securities is not the subject of the organization’s activities)
Dt 91-2 Kt 58-2 The cost of debt securities disposed of as a result of sale is included in other expenses (the sale of securities is not the subject of the organization’s activities)
Typical entries for account 59 “Provisions for impairment of investments in securities”
Dt 59 Kt 91-1 The reserve for impairment of investments in securities that was not used at the end of the reporting period is included in other income
Dt 59 Kt 91-1 The reserve for impairment of investments in securities was reduced by the amount of the increase in the market value of securities
Dt 59 Kt 91-1 The amount of the created reserve upon disposal of securities from the organization’s balance sheet is written off
Dt 91-2 Kt 59 A reserve has been created for the impairment of investments in securities
Dt 91-2 Kt 59 The reserve for impairment of investments in securities was increased by the amount of the decrease in the value of securities
Typical transactions for account 07 “Equipment for installation”
Dt 07 Kt 23 The costs of auxiliary production associated with the delivery and setup of equipment are written off to increase its cost
Dt 07 Kt 60 Equipment requiring installation has been capitalized
Dt 07 Kt 66 Interest on short-term loans and borrowings received for the purchase of equipment is taken into account when determining its cost
Dt 07 Kt 67 Similarly for long-term loans and borrowings
Dt 07 Kt 71 Equipment purchased by the accountable person was capitalized; expenses related to the delivery of equipment were paid by the accountable person
Dt 07 Kt 75-1 Equipment contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital was capitalized
Dt 07 Kt 76 Reflects the cost of services provided by third parties for the delivery and storage of equipment
Dt 07 Kt 76-2 The supplier satisfied the claim for shortage or incompleteness of equipment requiring installation
Dt 07 Kt 91-1 Equipment identified during inventory and not previously accounted for in accounting accounts was capitalized
Dt 08 Kt 07 The cost of equipment handed over for installation is taken into account as part of investments in non-current assets
Dt 76-1 Kt 07 The cost of insured equipment as a result of its damage or destruction is written off due to insurance compensation
Dt 91-2 Kt 07 The cost of equipment disposed of as a result of sale, write-off or partial liquidation is included in other expenses
Dt 94 Kt 07 Reflects the shortage of equipment requiring installation
Dt 99 Kt 07 The cost of equipment requiring installation was written off as losses due to emergency circumstances
Typical entries for account 04 “Intangible assets” and account 05
"Amortization of intangible assets"
Debit Credit Contents of business transaction
Dt 04 Kt 08-3 Intangible asset put into operation
Dt 05 Kt 04 Depreciation on an intangible asset disposed of as a result of sale or liquidation is written off to reduce its original cost
Dt 20 Kt 04 Depreciation was accrued on intangible assets used in the main production (without account 05)
Dt 91-2 Kt 04 The residual value of an intangible asset disposed of as a result of sale or write-off is included in other expenses
Dt 20 Kt 05 Depreciation was accrued on intangible assets used in the main production
Dt 23 Kt 05 Similarly in auxiliary production
Dt 25 Kt 05 Similarly for intangible assets for general production purposes
Dt 26 Kt 05 Similar to general purpose
Dt 44 Kt 05 Depreciation was accrued on an intangible asset intended to support the process of selling products
Material assets"
Dt 08 Kt 16 Deviations in the cost of inventories used in long-term investments are taken into account as part of investments in non-current assets
Dt 15 Kt 16 The amount of deviations of the actual cost of capitalized inventories from accounting prices is taken into account (savings, actual cost is less than the accounting price)
Dt 20 Kt 16 The amount of deviations in the cost of inventories transferred to the main production is written off (in case of savings - “red reversal”)
Dt 23 Kt 16 Similarly for auxiliary production
Dt 25 Kt 16 Similarly transferred for general production needs
Dt 26 Kt 16 Similarly for general business needs
Typical transactions for account 50 “Cash desk”
Dt 50 Kt51 Cash withdrawn from the current account was entered into the cash register
Dt50 Kt 55 Cash withdrawn from a special bank account was credited to the cash register
Dt50 Kt60 The supplier returned to the cashier the funds overpaid to him or the advance payment given to him
Dt50 Kt62 Cash received from buyers was credited to the cash register or the buyer made an advance payment
Dt50 Kt71 Unused funds previously issued as a report were returned to the cash desk
Dt50 Kt73-2 Cash received from an employee to compensate for material damage was entered into the cash register
Dt 50 Kt 75-1 Cash contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital was capitalized
Dt 51 Kt 50 Cash was deposited from the cash register to the current account
Dt 55 Kt 50 Cash was deposited from the cash register into a special bank account
Dt 58-1 Kt 50 Shares purchased for cash
Dt 58-2 Kt 50 Debt securities were purchased for cash
Dt 60 Kt 50 The debt to the supplier (contractor) was repaid in cash or an advance was issued in cash
Dt 62 Kt 50 Cash paid in excess by the buyer (customer) was returned or the advance was returned
Dt 69-1 Kt 50-2 Vouchers were issued to employees, paid for from social insurance funds
Dt 70 Kt 50 Wages paid to employees from the cash register
Dt 71 Kt 50 Cash issued on account
Dt 73-1 50 Loan issued to employee
Dt 75-2 Kt 50 Dividends (income) were paid from the cash register to the founder (participant) of the organization
Dt 76-4 Kt 50 Deposited wages paid from the cash register
Dt 94 Kt 50 The shortage of cash in the organization’s cash desk is reflected (during an inventory or audit of the cash register)
Dt 99 Kt 50 Lost cash and monetary documents were written off as losses due to emergency circumstances