Production accounting, along with financial accounting, is an integral part of management accounting.
Production accounting concerns operations related to the production of self-made products, the performance of various types of work, and the provision of services within the enterprise and to third parties.
It includes:
- quantitative accounting of production volumes, interesting to management and employees of production departments;
- accounting for operations to calculate cost per unit of production, which is necessary mainly for financial departments and company managers.
The main goal of production accounting is to control production costs to identify opportunities to improve the efficiency of the company as a whole.
How are production costs recorded?
Modern production accounting, as a rule, includes accounting for costs and income according to the following analytics:
- by their types;
- by department;
- by type of product (product groups).
In various industries and industries, the object of cost accounting can be products, their parts, a group of homogeneous products, a separate order, the volume of production as a whole for the enterprise or in its individual sections. The choice and features of accounting objects are often determined by the specifics of the business.
All accounts that take into account production costs in transactions are active. Expenses of the main production are maintained on account 20, auxiliary - on account 23, general production and general business expenses - on accounts 25, 26.
At the end of the month, accumulated expenses on the debit of accounts 25 and 26 are transferred to the debit of accounts and/or, while the accounts are closed and have a zero balance. Account 28 takes into account defects in production, account 29 – servicing production.
Learn more about postings to production costs.
Basic accounting operations for production
The most important accounting transactions for production include:
Main production costs
They are taken into account in the corresponding calculation account 20, the debit of which reflects the costs of materials (account 10), wages (70) and taxes accrued on it (69), depreciation of fixed assets (02) and intangible assets (05), losses from defects (account 28 ), services of third-party organizations (60, 76), shortages and losses from damage to valuables (94), deferred expenses (97), and other basic expenses included in the cost directly. One of the ways to distribute costs is direct costing.
Part of the expenses of auxiliary production (account 23), general shop and general business expenses (accounts 25, 26), attributed to the production cost of finished products (details about cost), are also written off here. The credit of this account takes into account the return of materials (10), as well as the completion of production cycles for the production of finished products (40, 43) and semi-finished products sold externally (21).
More details - Postings of the main production.
Expenses of auxiliary production
Expenses of auxiliary production (account 23) include the costs of energy, repair, instrumental facilities, costs of technical control, etc., which are reflected in the same way as on account 20.
More details - Postings for expenses of auxiliary production.
Unfinished production
WIP - materials, parts, products, semi-finished products and other labor products that have entered production, but have not yet gone through all the processing stages provided for in the technological cycle and cannot be used for consumption for their intended purpose. The cost of work in progress at the end of the month is determined by the balance of accounts 20, 23 and 29.
Read more - Postings for work in progress.
Overhead costs
General production expenses (account 25) take into account the costs of maintaining, servicing and/or repairing main and auxiliary workshops and departments that are not related to specific types of products: maintenance and operation of in-shop equipment and transport, wages for workers servicing the workshop, tool wear, electricity costs for workshop work, etc.
Read more - postings to overhead costs
General running costs
General expenses (account 26) reflect the costs of managing the enterprise as a whole, which cannot be attributed to any specific divisions and types of products: maintenance of buildings and property of the plant management, plant laboratories, expenses for administrative and economic needs, remuneration of administrative personnel, and etc.
General production and general business expenses at the end of each month are distributed among the divisions of the enterprise and types of products based on the selected base for distribution.
Marriage
Defects (account 28) – losses in production due to the release of products that do not meet the requirements of standards (specifications), which cannot be used for their intended purpose or are possible, but with restrictions and loss in price and quality.
Marriage can be internal or external, reparable or irredeemable, compensated or unredeemed.
In more detail - marriage postings
Tutorial 1C: Accounting 8
You and I already know how to move inventory items around warehouses and transfer fixed assets into operation. It's time to produce something using the equipment. In this lesson we will consider such issues as product release and write-off of raw materials and inventories for production.
Let's consider such capabilities of the 1C Accounting 8 program as an item specification. When producing certain products, the range of raw materials used is known in advance and certain standards for these raw materials are known. This can be specified in the specifications. There may be several specifications for each item in the nomenclature, for example, depending on the raw materials used and the technologies used. Let's learn how to create such specifications and use them.
Next, let's look at how material and production costs are written off to the cost of manufactured products.
At the next step, we will release the products over the weekend and receive them into the warehouse. In conclusion, we will have a practical task in which you can practice this material.
Let's start looking at the "Production" module. In the “Production” section we have access to such documents as a demand invoice. We have already looked at it in the “Warehouse” section. Using this document, you can assign the cost of inventory items in the warehouse to 20 expense accounts.
The main document that we will use in this lesson is the “Shift Production Report”.
The document “Production Report for a Shift” is intended to reflect operations for the production of finished products, semi-finished products and the provision of services. The document can be entered based on the document Sales of processing services.
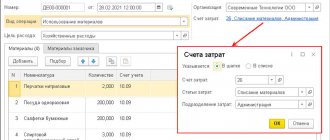
When entering a document, you must indicate the following details in the header:
- Cost account - an account for recording production costs and work-in-process balances from previous periods attributable to the cost of production.
- Cost division is a production division of an organization that produces products and provides services.
To reflect the output of products and semi-finished products, you need to fill out the Products tab. This tab indicates:
- Products - the name of manufactured products, semi-finished products, materials or goods. Can be filled in automatically for products made from materials from a third-party customer, based on the document Sales of processing services .
- Nomenclature group - type of manufactured products, semi-finished products, materials or goods. Can be filled in automatically for products made from materials from a third-party customer, based on the document Sales of processing services .
- The planned amount is the planned cost of manufactured products, semi-finished products, materials or goods. Can be filled in automatically for products made from materials from a third-party customer, based on the document Sales of processing services . Based on the data in this field, the direct costs of the production unit are distributed according to the types and names of products produced by it when performing the routine operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26.
- Specification is a list of cost standards required for the production of products, semi-finished products, materials or goods. Can be filled in automatically for products made from materials from a third-party customer, based on the document Sales of processing services . Specification field will be used when filling out the Requirement-invoice document, Materials .
For organizations paying income tax, the total estimate of direct costs attributable to production is reflected in the same way as in accounting - in planned prices. When closing the month when performing the routine operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26, its value is adjusted to the actual amount of expenses.
To reflect the transaction in the tax accounting of an individual entrepreneur applying the general tax regime, you should fill out the tabular section Materials .
To reflect the provision of services to your own production units, you need to fill out the Services tab. This tab indicates:
- Nomenclature - the name of the services provided.
- Nomenclature group - type of services provided.
- Quantity, Planned price, Planned amount - the volume of service provided, expressed in quantitative and/or cost terms. Based on the data in these fields, the direct costs of the production unit are distributed by type of services provided when performing the routine operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26. If the quantity is filled in, then the price and amount do not need to be filled in. If the amount is filled in, the quantity can be left blank.
- The planned amount is used to distribute direct costs, regardless of whether the quantity is filled.
- Cost division is the division to which the services are provided.
For organizations paying income tax, the total estimate of direct costs attributable to the provision of services is reflected in the same way as in accounting - in planned prices. When closing the month when performing the routine operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26, its value is adjusted to the actual amount of expenses.
To reflect the transaction in the tax accounting of an individual entrepreneur applying the general taxation regime, you should fill out the tabular section Materials .
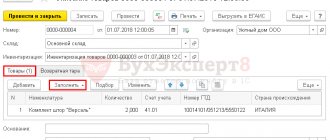
To reflect the release of returnable waste, you need to fill out the Returnable waste tab. This tab indicates:
- Nomenclature - the name of the released returnable waste.
- Cost account - an account for recording the costs of producing products, semi-finished products, materials or goods for which the amount of production costs is reduced by the amount of returnable waste.
- Nomenclature group is a type of manufactured product, semi-finished products, materials or goods for which the amount of production costs is reduced by the amount of returnable waste.
- Cost item is an item of accounting for the costs of producing products, semi-finished products, materials or goods for which the amount of production costs is reduced by the amount of returnable waste.
For organizations paying income tax, the Amount indicates the estimate of the cost of returnable waste, formed in accordance with the requirements of paragraph 1 or paragraph 2 of paragraph 6 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
With a simplified taxation system, in the Expenses (EC) , you need to indicate whether material expenses were included in those accepted at the time of transfer to production.
To reflect the transaction in the tax accounting of an individual entrepreneur applying the general taxation regime, you should fill out the tabular section Materials .
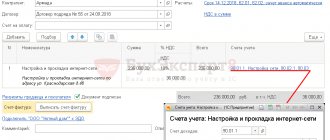
To reflect the write-off of materials as production costs, you need to fill out the Materials tab. This tab indicates:
- Nomenclature - name of materials.
- Cost account is an account for recording the costs of producing products, semi-finished products, materials or goods to which the cost of materials is attributed.
- Product group - the type of manufactured products, semi-finished products, materials or goods to which the cost of materials is assigned.
- Cost item is an item of accounting for the costs of producing products, semi-finished products, materials or goods, which takes into account the costs of writing off materials.
, the Expenses (EC) field indicates the procedure for reflecting expenses in tax accounting.
To reflect the transaction in the tax accounting of an individual entrepreneur applying the general taxation regime, you should fill out the tabular section Materials .
The following printed forms are available for the Shift Production Report
- MX - 18
- M - 11
- The act of providing services
Based on the Shift Production Report , you can enter the following objects:
- Request-invoice
- Sales of processing services
Also in the 1C Accounting 8 program there are two documents:
- provision of production services;
- WIP inventory.
The document “Provision of production services” is intended to reflect operations for the provision of production services. The document can be entered based on the document Invoice for payment to the buyer .
You need to fill out the bookmarks in the document:
- Services
- Cost account
- Settlement of advances
- Settlement accounts
- Additionally
Services tab indicates the content of the service provided, quantity, price, VAT rate, as well as accounts for income, expenses and VAT.
- If the provision of services is of a permanent nature, then it is recommended to enter the name of the service in the Nomenclature directory. If the service is one-time in nature, then you can enter the content of the service in the Service content, additional information .
- Item accounting accounts can be filled out automatically for each item (item group) based on the Item Accounting register.
- The income, expense and VAT account analytics must be specified in the Subconto .
On the Cost Account , the account for accounting production costs for the provision of services and its analytics are indicated.
- Cost account - an account for recording the expenses of the main or auxiliary production, which records the costs associated with the provision of this service.
- Division is the production division of an organization.
- Nomenclature group - type of services provided.
The data in the Settlement of Advances tab must be filled out if the method of Settlement of Advances By Document is selected in the document header.
for the document Provision of production services :
- The act of providing services
- Help-calculation “Ruble amount of document in currency”
Based on the document Provision of production services, you can enter the following documents:
- Cash receipt
- Receipt to the current account
- Invoice for payment to the buyer
- Invoice issued
- Reflection of VAT accrual
- Request-invoice
The document “Inventory of work in progress” is intended to reflect the results of the inventory of work in progress by production divisions and types of output (item groups).
A document must be created in the following cases:
- During the month, the release is reflected; at the end of the month, the total estimate of WIP balances is not equal to zero.
- During the month there is no issue, the beginning balances of work in progress and direct expenses of the current month are recognized as the final balances of work in progress, and the accounting policy on the work in progress establishes the method of accounting for work in progress “Using the document “Inventory of work in progress.”
A document does not need to be created in the following cases:
- During the month, the release is reflected; at the end of the month, the total estimate of WIP balances is zero.
- During the month there is no issue, the initial balances of work in progress and direct expenses of the current month are recognized as the final balances of work in progress, and in the accounting policy on the work in progress , the method of accounting for work in progress is established “In the absence of release, direct expenses are considered as expenses of work in progress.”
When entering a document, you must indicate the following details in the header:
- Cost account - an account for recording WIP balances and direct expenses of the current month.
- Division is the production unit of the organization, which includes the remainder of the work in progress.
In the table section you need to fill in the following details:
- Product group - the type of products manufactured (semi-finished products) or services provided, work performed, the cost of which will include the balances of work in progress in the following periods.
- Remaining amount is the total estimate of WIP balances according to accounting data, calculated based on inventory results.
For organizations paying income tax, the Remaining Amount (RA) indicates the total estimate of work in progress balances according to tax accounting data, calculated based on inventory results.
For organizations using PBU 18 “Accounting for income tax calculations”, permanent and temporary differences in the assessment of work in progress balances are calculated automatically when performing the routine operation Closing accounts 20,23,25,26 in the case of accounting for an issue without using account 40 (accounting policy of organizations , tab Release of products, services ).
, the Expenses (EC) field indicates the procedure for reflecting expenses in tax accounting. This field is available only if the accounting policy for expenses of the simplified tax system states that material expenses are subject to reduction by the amount of work in progress balances.
Finished products
Finished products (account 43) - a type of inventory that was obtained as a result of production activities. In accounting, such inventories are reflected at actual cost, which is the sum of all costs incurred by the enterprise in the process of their production.
In more detail - postings for finished products, sales of finished products.
Expenses of service industries
Expenses of service industries and farms (account 29) are not related to the main production (housing and communal services, preschool institutions, healthcare institutions, culture, catering, sanatoriums, rest homes, etc.), however, they are designed to solve social issues and are necessary to maintain and, if necessary, , restoring the ability to work of employees.
Provided raw materials
Operations with customer-supplied raw materials (tolling) represent the transfer of raw materials by the supplier for processing, processing and production of finished products based on them at the production facilities of the enterprise with the subsequent transfer to the owner of the raw materials of the finished products produced from them in full or in part according to the contract.
During the entire period of its presence at the enterprise, customer-supplied raw materials are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 003, since they do not become the property of the enterprise. Finished products produced from customer-supplied raw materials are reflected in off-balance sheet account 002.
For more details, see the article about customer-supplied raw materials.
Waste
Waste – materials, substances or items generated as a result of production activities that are not suitable for further use or external sale and require processing or disposal. Reflected on account 10.
More details - waste postings
Cost accounting
Product cost is the sum of all enterprise costs for the production of one unit of product. In addition, the cost of semi-finished products of the main production, products of auxiliary, service, ancillary and by-products, as well as the entire volume of commercial products of the enterprise can be calculated.
The process of calculating the cost per unit of production is called costing. Account 20 is used to determine production costs.
Short video on the topic:
Application of count 40
The accounting policy may provide for 2 methods of accounting for the output of finished products:
- using account 40 “Release of finished products” (checkbox Take into account deviations from the planned cost ): the account summarizes information about products produced, work delivered to customers and services provided for the reporting period, and also reveals deviations in the actual production cost of these products, works, services from standard (planned) cost;
Categories of articles on production
- Postings for manufacturing defects
- Postings to work in progress
- Accounting entries for overhead costs
- Accounting entries for production waste
- Cost calculation and calculation methods
- Cost accounting using the direct costing method: postings, examples, nuances
- Accounting entries for sales of finished products
- Accounting for finished products: postings, examples, nuances
- Postings to the cost of production in accounting
- Accounting entries for main production
- Accounting entries for auxiliary production
- Accounting for production costs in transactions