Formation of the initial cost of a fixed asset
The procedure for accounting for fixed assets (FPE) is regulated by PBU 6/01 (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n). This regulatory act (clause stipulates, in particular, what expenses can be included in the cost of the operating system when purchasing it:
- Amounts to be paid under a purchase and sale agreement.
- Customs duties - if the OS is purchased abroad.
- Amounts under the construction contract.
- The cost of consulting services directly related to the acquisition of this asset.
- State duty.
- The cost of the services of an intermediary, if one participated in the purchase and sale.
- Other payments paid when purchasing an OS.
About taking into account transportation costs in this cost, read the article “Are transportation costs included in fixed assets?”
Thus, the process of forming the cost of the OS is quite transparent and clear. Just remember that not all equipment can be classified as an OS:
- In accounting (BU) we will put into account 01 income-generating assets that can participate in the production cycle for more than 12 months and that are not intended for resale. According to clause 5 of PBU 6/01, assets that meet this definition, with a value up to the limit specified in the accounting policy (but not more than 40,000 rubles) can be taken into account as part of the inventory.
- In tax accounting (TA), since 2016, the cost of depreciable property has increased to 100,000 rubles. (Clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, any asset that is valued at this amount or less is written off in tax accounting at a time at the time it is accepted for accounting as an asset.
Read about ways to write off the cost of fixed assets in NU in the materials:
- “What method to choose for calculating depreciation in tax accounting?”;
- "Depreciation bonus in accounting and tax accounting."
Limit size in 2022
The criteria for switching to a simplified regime and the rules for their application are listed in Art. 346.12, 346.13 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Based on the regulations adopted last year, from 2022 new limit values for revenue and number of personnel according to the simplified tax system will be applied. For fixed assets, the limit in 2022 remained the same - 150 million rubles. (Clause 16, Clause 3, Article 346.12 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This amount is used to determine the possibility of the subject transitioning to the simplified tax system and to maintain the right to remain in the special regime.
Accounting for fixed assets in accounting and tax registers
So, until 2016, in both types of accounting, the threshold for the cost of adopting OS was the same: everything that cost 40,000 rubles. and less were taken into account as low-value property. Now the order is a little different. This is clearly seen in the diagram:
Thus, temporary differences appear in tax accounting when purchasing fixed assets costing more than 40,000 rubles, but not more than 100,000 rubles.
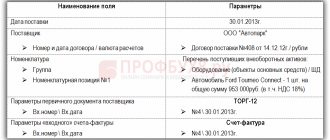
Example
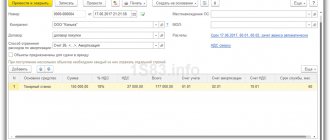
in May 2022, I bought a washing vacuum cleaner worth RUB 80,000. without VAT. The cost of consulting services provided to the company for the purchase of this equipment amounted to 4,000 rubles. without VAT. The facility was put into operation by order of the director from 06/01/2018. When calculating depreciation, the straight-line method is used.
In June 2022, the accountant made the following entries:
- Dt 08 Kt 60 - 80,000 rub. (equipment received from supplier);
- Dt 08 Kt 60 — 4,000 rub. (consulting services are taken into account in the cost of the object);
- Dt 01 Kt 08 — 84,000 rub. (a washing vacuum cleaner is accepted for accounting as an operating system).
In tax accounting, all expenses are written off at once. Let's see how the accountant will reflect the differences that appear.
The useful life is 60 months, the monthly depreciation amount will be 1,400 rubles. (84,000 / 60).
The procedure for calculating depreciation in accounting is described in detail.
After putting the operating system into operation, the accountant will create an accounting entry:
- Dt 68 Kt 77 —16,800 rub. (84,000 × 20%) (deferred tax liability reflected).
Starting in June, during the useful life, depreciation entries will appear monthly in accounting:
- Dt 25 Kt 02 — 1400 rub. (depreciation has been charged).
At the same time, a deductible temporary difference in the amount of 1,400 rubles arises in tax accounting. and monthly postings are generated:
- Dt 77 Kt 68—280 rub. (1400 × 20%) (repaid by IT).
Thus, within 60 months IT will be fully repaid.
Postings for accounting for fixed assets can be found in this material.
IMPORTANT! Temporary tax differences can be avoided. According to sub. 3 p. 1 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer is allowed to independently choose the method of writing off the value of property not related to fixed assets, taking into account its useful life or other economic indicators. Thus, if you add to your tax accounting policy a time-stretched procedure for recognizing expenses for fixed assets worth more than 40,000 rubles, but not more than 100,000 rubles, you will get rid of possible IT and temporary differences in accounting.
Nuances of using bonus depreciation
The depreciation bonus is the next point, which any specialist in asset accounting in an organization should also have a clear understanding of.
IMPORTANT! Bonus depreciation can only be used for tax accounting purposes. Its use does not affect the financial statements in any way.
The essence of the depreciation bonus comes down to the following: at the time of acquiring an operating system, a company can immediately write off up to 30% of the original cost of the operating system as expenses, thus significantly reducing the tax base for income tax.
At the same time, we should not forget that such a premium can be applied not only to new operating systems, but also to existing ones that have undergone modernization.
For more information about modernization, see the article “Modernization of fixed assets - accounting and tax accounting” .
NOTE! For a company that has decided to apply bonus depreciation, it is important to consolidate the corresponding provision in the accounting policy, describing the procedure for its application (to which groups of fixed assets it is applied, what is the amount of the bonus, etc.).
However, the company should be aware that the depreciation bonus can immediately reduce the initial cost of the fixed assets by 30%, which means that depreciation on the object in subsequent tax periods will be accrued in a significantly smaller amount. Despite the tax savings in the 1st tax period (when the asset was accepted for accounting), in subsequent periods the use of such a premium will increase the company’s tax costs.
For information on depreciation methods for fixed assets, see the article “Which method to choose for calculating depreciation in tax accounting?” .
Accounting for a computer worth less than RUB 40,000.
Quite often, accountants have a question about how to account for a computer if its cost is below 40,000 rubles - as part of low-value property, over which many people do not have control, or as an operating system. Indeed, according to most features, a computer fits the definition of a fixed asset.
First, you need to clarify what standards are specified in your accounting policy. If, according to its provisions, the OS, when accepted for accounting, cannot cost less than 40,000 rubles, then any computer with a cost not exceeding this limit must be included in inventory accounts and, at the time of release into operation, taken into account on the balance sheet, for example on a self-opened account 012 “Equipment in operation” (with details by place of storage or use).
If your accounting policy allows you to take into account any asset that meets the requirements of PBU 6/01 as part of the operating system, regardless of its value, then inexpensive computers can be safely attributed to account 01 “Fixed Assets”. At the same time, accounting for fixed assets worth less than 40,000 rubles. will be no different from accounting for objects of higher value.
How to take into account a computer worth less than 20 thousand rubles.
Info
If, according to its provisions, the OS, when accepted for accounting, cannot cost less than 40,000 rubles, then any computer with a cost not exceeding this limit must be included in inventory accounts and, at the time of release into operation, taken into account on the balance sheet, for example on a self-opened account 012 “Equipment in operation” (with details by place of storage or use). If your accounting policy allows you to take into account any asset that meets the requirements of PBU 6/01 as part of the operating system, regardless of its value, then inexpensive computers can be safely attributed to account 01 “Fixed Assets”.
At the same time, accounting for fixed assets worth less than 40,000 rubles. will be no different from accounting for objects of higher value. Results The procedure for reflecting fixed assets worth up to 100,000 rubles.
What needs to be done from March 12 to 16 In order not to forget about important accounting matters, you can keep a diary, install a special program on your smartphone that will remind you of plans, or stick stickers covered with notes on your work monitor. But the easiest way is to read our reminders weekly. < < …
Individual entrepreneurs should not rush to pay 1% contributions for 2022. Firstly, because from this year the deadline for paying such contributions has been postponed from April 1 to July 1. Accordingly, 1% contributions for 2022 must be transferred to the budget no later than 07/02/2018 (July 1 – Sunday). <... The transition from one Federal Tax Service Inspectorate to another will not require mandatory reconciliation. The Tax Service has updated the regulations for organizing work with payers of taxes, fees, insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance, as well as tax agents.
Acceptance for registration of a computer worth less than 40,000
OS upon purchase:
- Amounts to be paid under a purchase and sale agreement.
- Customs duties - if the OS is purchased abroad.
- Amounts under the construction contract.
- The cost of consulting services directly related to the acquisition of this asset.
- State duty.
- The cost of the services of an intermediary, if one participated in the purchase and sale.
- Other payments paid when purchasing an OS.
About taking into account transportation costs in this cost, read the article “Are transportation costs included in fixed assets?” Thus, the process of forming the cost of the OS is quite transparent and clear. In any case, it is important to take into account that fixed assets worth more than 40,000 rubles cannot be reflected in accounting as materials, even if this is provided for in the Accounting Policy. Therefore, fixed assets from 40,000 to 100,000 cannot be accounted for by the organization in account 10 “Materials”. At the same time, when we say “from 40,000,” we mean more than 40,000, since an object with an initial cost of exactly 40,000 rubles can still be taken into account as inventories. Therefore, accounting for expenses of property worth less than 40,000 rubles will be carried out in accordance with the procedure established for synthetic and analytical accounting of inventories. Fixed assets up to 100,000: tax accounting Fixed assets less than 100,000 rubles in tax accounting are not depreciable property (clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Results and conclusions
Accounting for fixed assets, starting in 2022, is subject to updated rules, in particular, the Federal Standard, which significantly brings together the norms of accounting and tax legislation. Property objects up to 100 thousand rubles are not, according to the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, fixed assets on which depreciation must be calculated.
Tax accounting of objects in the cost range of 40-100 thousand rubles allows you to write them off in two ways: entirely at the time of commissioning or over a certain period of time. It is advisable to choose the second option, since temporary differences and the need to record them with additional entries are eliminated if the organization uses OSNO.
Tax accounting of fixed assets of organizations using other taxation systems remains fundamentally the same. In this case, taxpayers take into account the limit on the value of fixed assets contained in the Tax Code.
Acceptance for registration of a computer worth more than 40,000
Add to favoritesSend by email Accounting for fixed assets worth up to 100,000 rubles has a number of nuances. Let's look at what causes them and consider accounting for such objects from the point of view of accounting and tax laws.
Formation of the initial cost of a fixed asset Accounting for fixed assets in accounting and tax registers Accounting for a computer worth less than 40,000 rubles. Results Formation of the initial cost of a fixed asset The procedure for accounting for fixed assets (FPE) is regulated by PBU 6/01 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n).
In this normative act (p.
Quite often, accountants have a question: is it necessary and how to take into account property that meets the characteristics of fixed assets, but is worth less than the established limit, after actually writing off its value in accounting and tax accounting?
In accordance with clause 5 of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Fixed Assets” PBU 6/01, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2001. No. 26n, assets that meet all the characteristics of fixed assets, but whose cost per unit is less than the limit established by the organization’s accounting policy, can be taken into account as part of inventories. Since 2011, the limit has been 40,000 rubles. According to Art. 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, property worth less than 40,000 rubles. is not taken into account as part of depreciable property. For property registered before 01/01/2011, the value limit is 20,000 rubles. both in accounting and for the purposes of calculating income tax.
Thus, the organization has the right to write off as expenses at a time the cost of property included in inventories and put into operation. Write-offs are made in the manner established by the organization’s accounting policy regarding accounting for material expenses.
PBU 6/01 obliges to organize proper control over the movement of these objects in order to ensure their safety in production and during operation.
The need to account for decommissioned but in operation objects arises not only because of the requirements of regulations. If an organization is interested in economical and rational spending of its funds, then correct accounting of decommissioned but operated facilities will allow:
- monitor the safety and serviceability of property, compliance with the rules of operation of property by employees of the organization;
- document and justify the costs of repairing and operating the property, purchasing consumables, purchasing new similar property;
- ensure compliance of the actual availability of property and accounting data when conducting an inventory and correctly take into account the results of the inventory of property;
- if necessary, make claims to persons responsible for damage, destruction or loss of property for compensation for damage caused to the organization (damage in this case may be expressed in the costs of repair and restoration of property, early acquisition of similar property).
If an organization does not keep records of written-off but exploited property, then the consequences may be: the likelihood of proving the validity of expenses for repairs and operation of unaccounted for property; uncontrolled acquisition of new property similar to the one written off, and the likelihood of proving the validity of such expenses; the obligation to register unaccounted property identified as surplus as a result of inventory, and accordingly increase taxable income; the impossibility of bringing to justice those responsible for damage and destruction of the organization’s property.
Methods of monitoring decommissioned but used property worth less than 40,000 rubles. accounting rules are not defined, therefore the organization has the right to independently develop methods for accounting for this property, based on general accounting principles. Unified forms of primary documents for accounting for such property have not been approved. Paragraph 5 of PBU 6/01 determines that these assets can be accounted for as part of inventories. In the rules for accounting for inventories set out in the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for inventories” PBU 5/01, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 07/09/2001 No. 44n, and Methodological guidelines for accounting of inventories, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2001. No. 119n in the current edition, there are also no specific instructions on organizing the accounting of written-off but in use property. Based on the general requirements of these regulations, we can conclude that the organization must approve in its accounting policy an account for accounting for this property, forms of primary documents for property accounting, and document flow rules. Separate orders of the head of the organization approve:
- a list of officials responsible for the safety and operation of property;
- norms of consumption (operation) of property.
Primary documents can be: an object registration card (inventory card); acts on property repairs performed; acts declaring property unsuitable for further use; property disposal acts.
Consumption (operation) rates can be established based on the manufacturer’s data on the service life of the object, operating conditions (load volume, temperature factors, etc.).
Some departmental accounting regulations provide recommendations for accounting for such property and provide samples of primary documents. For example, Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated May 16, 2003 N 750 “On approval of specialized forms of primary accounting documentation” approves the forms of primary documents for recording inventory and household supplies, which can be used as the basis for developing your own primary documents.
Accounting for decommissioned but operating objects worth less than 40,000 rubles. may be maintained in an off-balance sheet account. The Chart of Accounts, in its current version, does not provide for an account for accounting for such property, but in practice it is common to use either an unused account (for example, account 006) or the opening of a new account. In the 1C program, account MTs.04 is used for these purposes. Accounting for the off-balance sheet account is carried out using a simple system, i.e. the account entry is made without correspondence with any other account. The debit of the account reflects the receipt and availability of property, and the credit reflects the disposal of property. Property is accounted for according to nomenclature, and, if necessary, also according to materially responsible persons or in another manner established by the organization. Accounting is carried out by quantity. The cost for accounting purposes may be reflected in the card of this object. Data on this property are not reflected in the financial statements, since in fact their value has already been written off, and further accounting of this property does not affect information about the financial condition of the organization.
For the purpose of calculating income tax, expenses for the maintenance, repair and operation of this property are classified as other expenses, as reported in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 30, 2008 N 03-03-06/1/37: “expenses for repairing property worth less than 20,000 rubles (for example, furniture, computers, office equipment) that meet the criteria provided for in Article 252 of the Code may be taken into account for profit tax purposes as other expenses and recognized in the reporting (tax) period in which they were incurred in the amount of actual expenses "
Is it possible to have inventory worth more than 40,000 rubles? count on the account?
This entry was published in the Asset Accounting section. Bookmark the permalink.
Question
Is it possible in tax accounting to charge depreciation on a fixed asset from 40,000 to 100,000 if the accounting policy states that the cost of property that is not depreciable is repaid monthly in equal installments over the useful life?
Expert's answer
In both accounting and tax accounting, OS recognizes property that is used in the business activities of the company (not consumed as raw materials and not sold as goods). The useful life (SPI) of such property must be more than 12 months, and its initial cost must be (clause 1 of article 256, clause
1 tbsp. 257 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 4, 5 PBU 6/01, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 02/17/2016 N 03-03-07/8700):
- in accounting - above the limit for recognizing assets as fixed assets, established by the accounting policy (this limit cannot exceed 40,000 rubles);
— in tax accounting — more than 100,000 rubles. (Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated May 26, 2016 N 03-03-06/1/30414).
Property that does not meet all these requirements is not taken into account as part of the fixed assets and is not depreciated. The cost of such property in accounting or tax accounting is accordingly taken into account as expenses when it is transferred into operation.
A situation is possible when the useful life of the property is more than 12 months, but its value:
- or in accounting it is 40,000 rubles. and less (less than the limit for recognizing assets as fixed assets, established by the accounting policies);
- or in tax accounting it is 100,000 rubles. and less.
The cost of such property in accounting or tax accounting, respectively, can be taken into account as expenses at a time when transferred into operation or evenly over its useful life, at the choice of the organization. The chosen accounting method must be fixed in the accounting policy (clause 3, clause 1, article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5 of PBU 6/01, Letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 14, 2016 N 03-03-06/1/66456, dated May 20, 2016 N 03-03-06/1/29124).
The explanation was given by Maria Pavlovna Rogozneva, accounting and taxation consultant of LLC NTVP Kedr-Consultant, in March 2022.
When preparing the answer, SPS ConsultantPlus was used.
This clarification is not official and does not entail legal consequences; it is provided in accordance with the Regulations of the CONSULTATION LINE (www.ntvpkedr.ru).
This consultation has passed quality control:
Reviewer - Bushmeleva Galina Vladimirovna, professor of the Department of Accounting and ACD, Izhevsk State Technical University named after. M.T. Kalashnikov
What property is considered depreciable for tax purposes in 2017–2018?
In 2017–2018, property that is used by the company for the purpose of generating income and that belongs to the company by right of ownership should still be considered depreciable. In this case, the useful life of such property must be more than 12 months, and the initial cost must exceed 100,000 rubles. (Clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
NOTE! The cost limit should apply only to those fixed assets that the company put into operation after 01/01/2016 (Clause 7, Article 5 of the Law “On Amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” dated 06/08/2015 No. 150-FZ).
If the company plans to use the property in its core business for more than 12 months, the following options are possible:
- if the company put the property into operation before 01/01/2016, it is recognized as fixed assets if its value is more than 40,000 rubles;
- if the property was put into operation after 01/01/2016, then it can be taken into account as fixed assets only if its value exceeds 100,000 rubles.
On the procedure for accounting for fixed assets worth up to 100,000 rubles. can be read in the article “Accounting for fixed assets worth up to 100,000 rubles” .
What are fixed assets
Fixed assets are property owned by the company or attracted by it from the outside, which is used in its production activities for more than one year and has a value above the limit established by regulations.
There are criteria by which the distinction is made between fixed assets and other property.
How OS can take objects into account:
- Use time over 12 months.
- Such property is used by the company during its activities for production, provision of services, performance of work, or for enterprise management purposes.
- It was purchased for use, not for subsequent sale.
- Its use will allow the organization to generate income.
It follows that buildings, structures, vehicles, equipment, etc. are taken into account as OS.
The leading regulatory act governing the accounting of fixed assets in Russia is PBU No. 6/01. This document defines the indicators for classification as fixed assets, as well as the accounting methodology.
Attention! Among the above-mentioned features of an OS, another important criterion is not indicated - its price. According to PBU, fixed assets must include property whose purchase price is set at 40,000 rubles. For tax accounting, as specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the price of an object that will be used as fixed assets must be from 100,000 rubles.
Useful life of a fixed asset item
This is the period during which its use will bring economic benefits (income) to the organization (clause 8 of FSBU 6/2020).
For individual fixed assets, the useful life is determined based on the amount of production (volume of work in physical terms) that the organization expects to receive from the use of the fixed asset (ibid.).
And, according to clause 9, the useful life is determined from:
- the expected period of operation, taking into account productivity or capacity, regulatory, contractual and other operating restrictions, the intentions of the organization's management regarding the use of the facility;
- expected physical wear and tear, taking into account the operating mode (number of shifts), repair system, natural conditions, the influence of an aggressive environment and other similar factors;
- expected obsolescence, in particular as a result of changes or improvements in the production process or as a result of changes in market demand for products or services produced by fixed assets;
- plans for the replacement of fixed assets, modernization, reconstruction, technical re-equipment.
By and large, I did not find any significant difference between the definition of useful life in FSB 6/2020 and in PBU 6/01 (clause 4 and clause 20). Yes, there are some stylistic differences, but nothing more.
In my opinion, most organizations, as before, will take the Classification of Fixed Assets, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1 dated January 1, 2002, as a guide to action. FAS 6/2020 does not say this directly, but it is not prohibited, which means - allowed.
Although nothing prevents you from using other information - manufacturers’ recommendations, a documented and technically sound conclusion of the commission on fixed assets, etc.
Fixed assets in 2022 – major changes
It was expected that from the beginning of the year there would be significant changes in the accounting of fixed assets. But new regulations were never adopted. Therefore, the old rules continue to apply for a significant number of OS objects.
However, there are some innovations, which, for the most part, affected small businesses that carry out accounting according to a simplified scheme.
Such entities received the right to create the initial cost of the fixed assets based on the amounts of payment to suppliers and contractors installing this facility. If the OS was created in the organization itself, then its price is formed from the amounts paid to contractors and other organizations. All other amounts spent can be transferred to current expenses.
Important! An organization has the right to depreciate fixed assets using a simplified regime once a year on the last day of the year.
Also, business entities with simplified accounting schemes received the right to immediately depreciate at full price fixed assets related to inventory (they have a low price and a short service life). Such measures allow such entities to reduce the burden when calculating property taxes.
In the current period of time, a new classifier of fixed assets has been adopted for use by groups for tax accounting, used to distinguish objects by depreciation groups. Individual objects were transferred from one group to another, and as a result, their depreciation rates will change.
Accounting and tax accounting of fixed assets in 2022
One of the important indicators of accounting for an object as fixed assets is its initial cost. For accounting it is defined as 40,000 rubles, for tax accounting – 100,000 rubles.
Based on these differences, there are some features of accounting for OS objects.
OS costing up to 40 thousand rubles
This kind of OS is usually called low-value, since they have a low cost, but are used in activities for quite a long time.
The company has the opportunity to either immediately write off these fixed assets as inventories or register them as fixed assets and depreciate them. This rule applies to both accounting and tax accounting. However, the company must establish the method used in its accounting policies.
OS costing from 40 to 100 thousand rubles
OS objects with a price ranging from 40,000 rubles to 100,000 rubles are included in the intermediate group.
In accounting they are defined as fixed assets, and in tax accounting as low value.
Therefore, in the first situation, the company needs to register the object (accept for operation) and amortize its price according to the existing methodology.
In tax accounting, a company has the opportunity to transfer the costs of its purchase (production) instantly or take it into account and depreciate it. For tax accounting purposes, the company must also document the adopted method in its accounting policies.
The cost of the OS is more than 100 thousand rubles
The limit of 100 thousand rubles is not used in accounting. There, any property with a price exceeding 40 thousand rubles will be recognized as an asset. However, this has significant implications for tax accounting.
For the purposes of this accounting, fixed assets that were registered later than December 31, 2015, and less than this limit, can be immediately transferred to expenses. If its price is more than 100 thousand rubles, then the object will have to be depreciated using one of the two proposed methods.
Depreciation of fixed assets in 2022
The cost of the operating system must be transferred in small shares to the manufactured products or work performed. This process is called depreciation.
In 2022, the new OS and OKOF classifiers were adopted for use. Although the number of groups remained unchanged, some objects were moved from one to another. As a result, the norms of annual and, accordingly, monthly depreciation calculations change.
There is a group of fixed assets that do not need to be depreciated. These include land plots, natural objects, museum objects and collections, etc. Such a list is indicated in PBU 6/01.
Depreciation is determined from the 1st day of the month following the month in which the asset was taken into account. The process must be stopped from the 1st day of the month following the month in which this OS was deregistered (it was written off, sold, etc.).
In 2022, four methods of determining depreciation can still be used for accounting purposes:
- Linear;
- By reducing balance;
- Write-off based on the amount of the number of years;
- Proportional to the volume of products produced.
For tax accounting purposes, it is also allowed to use two methods:
- Linear;
- Nonlinear.
It is necessary to stop determining depreciation in the following situations:
- A three-month preservation is carried out;
- Reconstruction is in progress;
- OS under repair;
- Modernization lasts more than 1 year.
Attention! The new directories should only be used for objects that began to be used in 2022 and later. There is no need to make corrections to the accounting cards of all previously accepted fixed assets and recalculate their depreciation. This rule is mandatory for both accounting and tax accounting.
Selection of depreciation method
The innovation increases the number of methods for determining depreciation. Previously, only the linear method could be used. Currently, an accountant can use these depreciation methods:
- Linear method. Depreciation is accrued in equal installments every month. Accrual is made throughout the entire life of the facility. To determine the payment amount, you need to divide the original cost of the item by the SPI.
- Reducing balance method. Suitable for assets whose useful life is very short. Also relevant for objects used in aggressive conditions. This method is necessary for accelerated depreciation.
- A method for determining depreciation in proportion to the volume of goods. The method is relevant for items that have a certain potential. That is, the accountant knows how much goods can be produced over a certain period using the asset. To make calculations, you need to multiply the actual volume of production by the depreciation rate.
The depreciation method is chosen by the organization independently. When choosing, you need to take into account the specifics of the subject’s activities. The chosen method must be recorded in the accounting policy.
If the purpose of using an asset has changed, the method for determining depreciation can also be changed. The change is made at the beginning of the reporting period. The new standard requires determining depreciation for the following items:
- Idle.
- Temporarily not in use.
- Items intended for write-off.
The exception is items that have a residual value of zero.
The new standard has changed the initial cost for low-value items. Let's look at all the features:
- Items with an original price of up to 10 thousand rubles are placed in an off-balance account. They do not require depreciation.
- For items worth 10 thousand-100 thousand rubles, depreciation is 100% of the price on the date the object was put into use.
- If the cost of the item is more than 100 thousand rubles, depreciation is determined based on the chosen method.
The standard introduced quite a lot of new principles. All of them must be taken into account in 2022. Otherwise, a violation of the instructions will be recorded.
What documents are used to account for fixed assets
When documenting, a company can use either standard documents offered by Goskomstat or those developed independently. Whatever forms are used, they must be specified in the accounting policy.
Standard forms are divided into several groups:
| Form number | Name | What is it needed for |
| Admission and departure | ||
| OS-1 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (except for buildings, structures) | To record the inflow and outflow of individual fixed assets, it is not filled in for buildings and structures. |
| OS-1a | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of a building (structure) | To record the arrival and disposal of buildings and structures |
| OS-1b | Act on acceptance and transfer of groups of fixed assets (except buildings, structures) | If the recording of the arrival and departure of fixed assets (does not apply to buildings, structures) is performed immediately for the group |
| OS-14 | Certificate of acceptance (receipt) of equipment | Accounting for equipment in storage that will be used in the future |
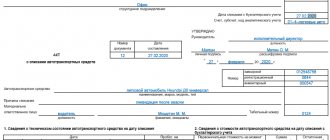
| OS-4 | Act on write-off of fixed assets (except for vehicles) | Write-off of certain OS objects that have become unusable. Not to be filled out for vehicles. |
| OS-4a | Act on write-off of motor vehicles | Write-off of a vehicle that has become unusable |
| OS-4b | Act on the write-off of groups of fixed assets (except for vehicles) | Write off the OS group immediately, not filled in for vehicles |
| Availability and movement | ||
| OS-6 | Inventory card for recording a fixed asset item | Accounting for certain fixed assets and their movement within the company |
| OS-6a | Inventory card for group accounting of fixed assets | Accounting for several similar operating systems |
| OS-6b | Inventory book for accounting of fixed assets | In small enterprises it replaces filling OS-6 and OS-6a |
| OS-15 | Certificate of acceptance and transfer of equipment for installation | Transferring the OS stored in the warehouse for installation |
| OS-16 | Report on identified equipment defects | Recording of defects that were identified during installation, testing, etc. |
| OS-2 | Invoice for internal movement of fixed assets | Recording the movement of assets between departments within the company |
| OS-3 | Certificate of acceptance and delivery of repaired, reconstructed, modernized fixed assets | Registration of OS upon completion of repairs and modernization |
Receipt of fixed assets: accounting procedure
Objects are registered at their original cost. It is important to remember that the initial cost is not only the cost of the object itself, indicated on the receipt or invoice, it is also a number of additional costs.
The initial cost includes (clause 8 of PBU 6/01):
- cost of the object;
- delivery and transportation costs;
- installation costs;
- customs duties (in case of importing an object from abroad);
- state duty (for example, a fee for registering a car);
- wages and contributions, if the fixed asset was built by employees, etc.
All costs are included in the original cost minus VAT.
In accounting, all costs should be accumulated on account 08. Only when a fixed asset is put into operation are the collected costs transferred in full to account 01.
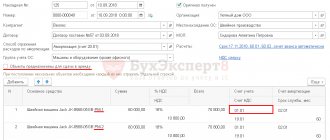
Example. Metr LLC purchased a Renault car from a car dealership for 526,000 rubles, including VAT of 80,237.29 rubles. Registration with the traffic police cost Metr LLC 2,850 rubles.
Accountant Oskina R.L. reflected all transactions as follows:
Debit 08 Credit 60 - 445,762.71 - reflects the cost of Renault;
Debit 19 Credit 60 - 80,237.29 - VAT allocated;
Debit 08 Credit 60 - 2,850 - reflects the fee paid for registering Renault;
Debit 01 Credit 08 - 448,612.71 (445,762.71 +2,850) - the Renault car was put into operation.
Accounting entries
Transactions with fixed assets are reflected in accounting with the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| Receipt of fixed assets | ||
| 08 | 60, 10, 70, 69 | The expenses incurred for the acquisition or creation of OS are recorded in accounting |
| 07 | 60, 10, 70, 69 | The costs of preparing the installation of the OS and its installation are recorded in accounting |
| 08 | 07 | Installation costs transferred |
| 19 | 60 | Input VAT on fixed assets costs is recorded in accounting |
| 68 | 19 | Input VAT is accepted for deduction |
| 01 | 08 | The OS object is accepted for accounting |
| Depreciation | ||
| 20, 23, 25, 26, 29, 44 | 02 | Depreciation of fixed assets was calculated based on the direction of their use |
| Restoration, modernization, repair | ||
| 08 | 60 | The price of a third-party company for repairs and OS upgrades has been fixed |
| 19 | 60 | VAT recorded on contractor's work |
| 08 | 10, 70, 69 | Repairs and modernization of the OS were carried out on our own |
| 01 | 08 | All expenses incurred are written off to increase the cost of the operating system. |
| Sale | ||
| 62 | 91 | Income from the sale of fixed assets is recorded in accounting |
| 91 | 68 | VAT recorded on sales |
| 02 | 01 | Accrued depreciation written off |
| 91 | 01 | The residual value of the asset is written off |
| Liquidation | ||
| 02 | 01 | Depreciation on the liquidated asset has been written off |
| 91 | 01 | Residual value written off |