Fixed assets in budget accounting - 2020-2021: introductory information
In accordance with paragraph 21 of Order No. 157n, the concept of “budget accounting of fixed assets” applies only to certain government organizations.
For example, government institutions, government agencies, extra-budgetary funds. In addition to the unified chart of accounts, a special chart of accounts must be used in budget accounting (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 6, 2010 No. 162n). The remaining government institutions, maintaining accounting and tax accounting of fixed assets in 2020-2021, in addition to the unified chart of accounts, use charts of accounts approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 16, 2010 No. 174n (budgetary institutions) or dated December 23, 2010 No. 183n (autonomous institutions) and other regulations.
For example, FSBU “Fixed assets”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 31, 2016 No. 257. ConsultantPlus experts explained what institutions should take into account when applying this standard. Get trial demo access to the K+ system and study the review material for free.
Read about the regulatory documents governing accounting in budgetary structures here .
In this article we will refer to Order No. 157n as the basis for budget accounting. From the beginning of 2022, public sector organizations must be guided by the new federal standard “Fixed Assets”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 31, 2016 No. 257n (hereinafter referred to as the Standard). These documents reveal the general principles of accounting for fixed assets, as well as the logic for drawing up transactions.
According to clause 8 of the Standard, in order to classify an asset as a fixed asset, the following criteria must be met:
- Property (with the exception of periodicals that make up the library collection of the subject of accounting) is classified as fixed assets, regardless of its useful life.
- The accounting entity predicts the receipt of economic benefits or useful potential from the use of the asset.
- The initial cost of property as an accounting object can be reliably estimated.
If an asset does not meet at least one of the above criteria, it is recorded in off-balance sheet accounts. Information about such material assets is disclosed in the financial statements.
NOTE! Fixed assets do not include objects classified as inventories in accordance with clause 99 of Order No. 157n. For example, fishing gear, gas-powered saws, etc.
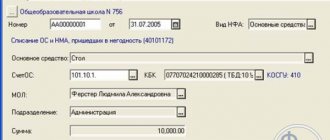
Each inventory item as a unit of accounting for fixed assets must be assigned a number. And an inventory card is created for each object.
To account for fixed assets, a synthetic account 010100000 “Fixed Assets” is provided. The budget accounting account number consists of 26 digits, and only 18–26 digits are used in the accounting of the institution. Depending on the group and type of fixed assets, as well as the essence of their movement, the code in the 22–26 digits changes in the account number.
Below we consider the scheme for generating an accounting account number in a budgetary organization, and also decipher the category codes using an example. A detailed explanation of the categories can also be found in clause 21 of the instructions to the chart of accounts (order No. 157n).
| Account digit number | ||||
| 18 | 19-21 | 22 | 23 | 24-26 |
| Financial support | Accounting object | Accounting object group | Type of accounting object | Type of receipts, disposals of an accounting object |
| Example: account 110118310 “Increase in the value of other fixed assets - real estate of the institution” | ||||
| 1 | 101 | 1 | 8 | 310 |
| 1 - at the expense of the budget | 101—fixed assets | 1—real estate | 8 - other fixed assets | 310 - increase in OS cost |
Read about creating a working chart of accounts in a budget organization here .
Accounting for fixed assets upon admission to budgetary institutions
OS are received by institutions at actual cost, which includes (clause 15 of the Standard):
- cost paid to the supplier;
- the cost of construction work when creating the facility;
- the cost of all costs required to create the OS;
- fare;
- amounts for related services;
- customs duties;
- as well as other costs associated with the purchase/creation of the OS.
NOTE! If the fixed asset will be used in budgetary activities, then the amount of input VAT is included in the initial cost.
- The receipt of fixed assets is reflected in the synthetic account 0010600000 “Investments in non-financial assets”. For example, in a budgetary institution, according to order 174n, it has the following groups of accounts: 010610000 “Investments in real estate”;
- 010620000 “Investments in particularly valuable movable property”;
- 010630000 “Investments in other movable property”;
- 010640000 “Investments in financial lease objects”;
- 010660000 “Investments in the rights to use intangible assets”;
- 010690000 “Investments in the grantor’s property.”
In the accounting of fixed assets, to reflect receipts, separate analytical accounts are allocated, in 24–26 digits of which code 310 is used for each type of fixed assets. This code indicates an increase in the cost of the OS.
Let us consider in the table the main entries for accounting for the receipt of fixed assets using the example of a budgetary institution (order 174n).
| Wiring | Description of posting in fixed asset accounting |
| Dt 010600000 “Investments in non-financial assets” Kt 020800000 “Settlements with accountable persons” (020831660), 030200000 “Settlements for accepted obligations” (030231730) | Purchasing an OS |
| Dt 010600000 “Investments in non-financial assets” Kt 030200000 “Settlements for accepted obligations”, 020800000 “Settlements with accountable persons”, 010400000 “Depreciation”, 030300000 “Settlements for payments to budgets”, 010500000 “Inventories” | Creating an OS object yourself |
| Dt 010110310 “Fixed assets - real estate of the institution” Kt 010611310 “Investments in real estate” | Commissioning of the constructed building |
| Dt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110310, 010120310, 010130310) Dt 010600000 “Investments in non-financial assets” | Commissioning of purchased, manufactured household goods. OS way |
| Dt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110310, 010120310, 010130310) Kt 030404310 “Internal departmental settlements for the acquisition of fixed assets” | The OS object was received from another budget institution that has the same budget resource manager |
| Dt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110310, 010120310, 010130310) Kt 040110190 “Income of the current financial year” | Other gratuitous receipts of fixed assets |
For information on how the accounting policy of a budgetary institution is formed, read the material “An example of an accounting policy in a budgetary institution (nuances)” .
Registration of operational management rights
When transferring real estate, registration of the right of operational management is required.
Any actions to register real estate are carried out on the basis of the provisions of the Federal Law “On State Registration of Real Estate” dated July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ ( Article 1 of the Federal Law dated July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ (as amended on December 30, 2021) “On State real estate registration" {ConsultantPlus}) .
Unique analytical materials of SPS ConsultantPlus will help you when difficult situations arise.
Therefore, a real estate asset can only be transferred if it is registered in the prescribed manner. If this is not done, the transfer is invalid. To register real estate you will need ( Article 15 of the Federal Law dated July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ (as amended on December 30, 2021) “On State Registration of Real Estate" {ConsultantPlus}, Article 18 of the Federal Law dated July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ ( ed. dated December 30, 2021) “On state registration of real estate” {ConsultantPlus} ):
- documents confirming ownership of real estate;
- passport ;
- documents confirming the authority of the representative of the body.
To register the right of operational management itself, you need to collect and submit to the registration authority the following package of documents ( Chapter 3 of the Federal Law of July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ (as amended on December 30, 2021) “On State Registration of Real Estate” {ConsultantPlus}, Art. 18 of the Federal Law of July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ (as amended on December 30, 2021) “On State Registration of Real Estate” {ConsultantPlus} ):
- administrative act on the transfer of property to operational management;
- act of acceptance and transfer of property;
- passport ;
- documents confirming the authority of the representative of the body.
Documents (until January 1, 2023) can be submitted on paper or electronic media by directly contacting the registration authority or sending by mail ( Article 18 of the Federal Law of July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ (as amended on December 30, 2021) “On State real estate registration" {ConsultantPlus}).
The registration period is 7 working days from the date of transfer of documents directly to the registration authority and 9 working days from the date of reception at the multifunctional center for the provision of state and municipal services (Article 16 of the Federal Law of July 13, 2015 No. 218-FZ (as amended on December 30. 2021) “On state registration of real estate” {ConsultantPlus}).
There is no state fee for carrying out these actions (Article 333.35, Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Part Two) dated 08/05/2000 No. 117-FZ (as amended on 11/29/2021) {ConsultantPlus}).
It is worth noting that regarding federal property, which is assigned to federal budgetary institutions, there is an interesting rule, which is that interaction between bodies regarding the coordination of decisions related to the disposal of property should be carried out only in electronic form through the interdepartmental portal for the management of state property on the Internet (hereinafter referred to as the MV portal) by posting electronic documents signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature, including appeals from federal executive authorities. Consideration of appeals on these issues received through paper document flow is not carried out, with the exception of appeals that have restrictions due to the possibility of disclosing official and state secrets, the sending of which is carried out in paper form indicating the type of restriction (<Letter> of the Federal Property Management Agency dated 01/31/2020 No. VYA-08/2882 “On the procedure for disposing of federal property” {ConsultantPlus}).
With the help of SPS ConsultantPlus, you will easily navigate the legislation and track all changes in a timely manner.
Depreciation of fixed assets
Government institutions charge depreciation of fixed assets linearly over their service life. There is also a rule of monthly accruals in the amount of 1/12 of the annual amount. Depreciation charges begin to be reflected in the month following the month the facility is put into operation.
Read about the practical application of the linear method in the article “Linear method of calculating depreciation of fixed assets (example, formula)” .
The useful life is determined based on:
- the expected period of receipt of economic benefits;
- recommendations contained in the manufacturer's documents;
- warranty period for use of the object;
- other methods described in clause 35 of the Standard
When calculating depreciation of fixed assets in budget accounting, the following procedure is applied:
- for an OS object worth over 100,000 rubles. depreciation is accrued in accordance with calculated depreciation rates;
- for an OS object worth up to 10,000 rubles. inclusive, with the exception of library collection objects, depreciation is not accrued, the cost of the object is immediately written off as expenses, then the fixed assets are taken into account in off-balance sheet account 21;
- for a library fund object worth up to 100,000 rubles. inclusive, depreciation is charged in the amount of 100% of the original cost when it is put into operation;
- for another fixed asset costing from 10,000 to 100,000 rubles. inclusive, depreciation is charged in the amount of 100% of the original cost when it is put into operation.”
Depreciation is reflected in the synthetic account 010400000 “Depreciation”.
In a budgetary institution, by order 174n, analytical accounts ending in 410 are used to record entries for depreciation charges, which are used in the following transaction: Dt 040120271 “Costs for depreciation of fixed assets and intangible assets”, 010900000 “Costs for the manufacture of finished products, performance of work, services" (010960271, 010970271, 010980271, 010990271) Kt 010400000 "Depreciation" (010410410, 010420410, 010430410, 010440410, 010460410, 0104 90410).
Operations for calculating depreciation on operating lease accounting objects are reflected in the debit of account 040120224 “Expenses for rent for the use of property”, 040120229 “Expenses for rent for the use of land plots and other isolated natural objects”, the corresponding analytical accounts of account 010900000 “Expenses for production of finished products, performance of work, services" (010960224, 010960229, 010970224, 010970229, 010980224, 010980229) and the credit of the corresponding analytical accounts of account 010440000 "Depreciation of rights to use assets".
How to arrange dismantling
When dismantling a fixed asset, it must be excluded from accounting. The basis for the accountant to reflect such a transaction will be the decision of the Commission on the receipt and disposal of assets, documented in the appropriate act depending on the type of fixed asset (clauses 34, 51 of Instruction No. 157n):
- act on the write-off of non-financial assets (except for vehicles) (f. 0504104);
- act on the write-off of soft and household equipment (f. 0504143);
- act on the write-off of excluded objects of the library collection (f. 0504144).
Accounting for disposal of fixed assets
To account for fixed assets upon their disposal, separate analytical accounts of account 010100000 “Fixed Assets” are also used, ending with 410 and indicating a decrease in the value of the corresponding fixed assets.
For a selection of practical recommendations for writing off certain types of fixed assets in the accounting of public sector employees, see the analytical review from ConsultantPlus experts. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure. And in this publication you will find a sample order for writing off fixed assets in a budget institution.
Let us consider in the table the main entries for accounting for the disposal of fixed assets using the example of a budgetary institution (order 174n).
| Wiring | Description of posting in fixed asset accounting |
| Dt 040120271 “Depreciation costs of fixed assets and intangible assets”, 010900000 “Costs of manufacturing finished products, performing work, services” (010960271, 010970271, 010980271) Kt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110410, 010120410, 010130410)) Dt 21 “Fixed assets worth up to 10,000 rubles inclusive in operation” | Commissioning of an OS costing up to 10,000 rubles. |
| Dt 040120281 “Expenses on gratuitous transfers of a capital nature to state (municipal) institutions”, 040120251 “Expenditures on gratuitous transfers to the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation” Kt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110410, 010120410, 010130410) | Free transfer of an object (at book value) |
| Dt 010400000 “Depreciation” (010410410, 010420410, 010430410) Kt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110410, 010120410, 010130410) Dt 040110172 “Income from operations with assets” Kt 010100000 “Fixed assets” (010110410, 010120410, 010130410) | OS sales |
Results
Budgetary accounting of fixed assets has a complex structure of accounts and their coding.
However, the instructions listed in the article contain detailed explanations and lists of possible entries that can help the accountant. Maintaining budgetary accounting of fixed assets is strictly regulated. All movements of fixed assets must be documented in primary documents and reflected in accounting by accounting entries. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Why is dismantling necessary?
The need to dismantle a fixed asset may arise as a result of the partial liquidation of an object or become an independent business operation, as a result of which several independent objects are formed that need to be formalized and registered.
Signs of dismantling of a fixed asset:
- the fixed asset was previously accepted for accounting (budget) accounting as one inventory item (inventory unit);
- there is a decision of the Commission on the receipt and disposal of assets operating in the institution (clause 34 of Instruction No. 157n);
- the fixed asset is disassembled (divided) into separate parts, which are taken into account as independent objects of fixed assets or are subject to dismantling and destruction.
The dismantling of a fixed asset must be properly documented and reflected in accounting (budget) and tax accounting if your fixed asset is depreciable.
It is not allowed to carry out measures to dismantle a fixed asset without a documentary basis, that is, until the Commission approves the relevant act.