Land tax must be paid by organizations and individuals owning land plots. The amount of obligations to the budget is calculated by multiplying the cadastral valuation of the object at the beginning of the tax period and the tax rate. All tax accruals are accumulated in accounting on account 68. To differentiate fiscal obligations, analytical accounting subaccounts are introduced.
Concept of land tax
Land tax is imposed on all those plots that are registered with the organization in the state order. In this case, the current tax regime under which the company operates does not matter; tax liability is present regardless of this factor.
This type of tax burden is regional, the calculation of which is subject to the rules of the Russian entity to which the territory of the land belongs. The Ministry of Defense sets the rate, preferential system, payment frequency, and transfer deadlines. The region determines all the components of the formula for calculating land tax - cadastral value, rates depending on the category of land, the need to pay advances, the availability of benefits for exemption from the tax burden.
At the federal level, a general rate is established, which becomes relevant if the Moscow Region does not issue legislative acts in its region to change the rate established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the region requires the payment of advances, then they must be calculated for each quarter, and then the difference between the annual tax and the advances paid must be paid for the year. If advances are not provided, then it is enough to transfer the annual tax amount to the budget once a year at the end of the year. The deadlines for transfers should be clarified in the legislative acts of local authorities.
What to do if the cadastral value has changed
The cadastral value of the plot may change during the year. This is possible in the following cases.
Firstly, the category (type of permitted use) of the land plot is changed or the cadastral value of the plot is set equal to the market value. In this case, the change must be taken into account only from the next year. This year, determine the tax base based on the cadastral value established at the beginning of the year. There is no need to adjust the tax base for previous periods. This procedure applies regardless of whether the cadastral value of the land has increased or decreased. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 4 of paragraph 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Important
Organizations using “simplified” and “imputed” taxation are recognized as payers of land tax according to the general rules (clause 4 of article 346.26, clause 2 of article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Secondly, by decision of the court or commission for the consideration of disputes on the results of determining the cadastral value. Then take into account the change starting from the period in which the application for revision of the cadastral value was submitted to the court or commission. To calculate the tax, the changed (confirmed by the court or commission) cadastral value can be used no earlier than the date when the original (disputed) cadastral value of the land plot was entered into the state cadastre.
This procedure follows from the provisions of paragraph 6 of paragraph 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 24.20 of the Law of July 29, 1998 No. 135-FZ, paragraphs 18 and 28 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of June 30, 2015 No. 28. Similar explanations to these norms are given in letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 27, 2015 No. BS-4-11/5013.
Thirdly, as a result of correcting an error made by cadastral registration authorities when assessing land or when maintaining the State Real Estate Cadastre.
In this situation, the change must be taken into account starting from the period in which the corrected error was made. This is stated in paragraph 5 of paragraph 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The considered procedure for calculating land tax does not apply in cases where the legal holder of a land plot changes during the year. If the owner of the title changes, the new owner must calculate the land tax (advance tax payments) in accordance with the information about the land plot specified in the state real estate cadastre on the date of state registration of rights. That is, taking into account the new cadastral value or a different tax rate. The new procedure for calculating tax is applied starting from the date of registration of the rights of the new owner to the land plot. This is stated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07/09/2008 No. 03-05-04-02/40.
Calculation of land tax
Upon each calculation of the tax land burden, you must show the calculated result in the accounting department. To reflect the annual tax amount, an accrual posting is made on the last day of the accounting year. To reflect advance tax amounts, an entry is made on the last day of the quarter for which the calculation is made.
Therefore, the organization must post accruals on the following dates:
- 31.03 – for the 1st quarter;
- 30.06 – for the 2nd quarter;
- 30.09 – for the 3rd quarter;
- 31.12 – for the year.
The posting is made for the amount of the calculated land tax.
The following formula is used for calculation:
Land tax = cadastral value * interest rate
To calculate the advance, the specified product should be divided by four.
Since the beginning of March 2015 The use of the standard value of land for calculating tax has been discontinued.
The cadastral value is determined for each site by Rosreestr, after which it is approved by legislative act. You can clarify the value of this cost at the beginning of the year for which the calculation is being carried out in Rosreestr by submitting a request through its official website, or using the special service “Public Cadastral Map”.
The rate may vary depending on the category to which the taxable object can be classified. Local authorities, who are in charge of the territory where the land is located, prescribe the current rates in the laws, for example, in Moscow, Law No. 74 of November 24, 2004 (as amended on April 13, 2016) is relevant, in St. Petersburg – Law No. 617- 105 dated 11/23/12.
Taxes need to be charged only for full months of land ownership. At the moment, we need to pay attention to those organizations that acquired or deregistered plots during the accounting year.
For the month in which a change in the ownership of a land plot was recorded, the tax should be calculated if:
- The land is registered with the state until the 15th day inclusive;
- The land was removed from state registration after the 15th.
If these statements are not met, then the month is considered incomplete and is not included in the calculation.
If the organization loses ownership of land, it stops paying land tax.
How to determine the tax base
To calculate land tax, you need to know the tax base and tax rate.
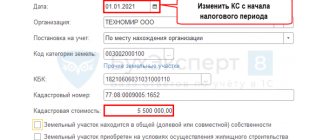
The tax base is the cadastral value of the land plot at the beginning of the tax period. That is, on January 1 of the year for which the company charges tax (clause 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
There are several ways to find out the cadastral value. Firstly, on the Rosreestr website. And there it is better to track changes in this cost. Secondly, the cadastral value of a land plot can be found out at the tax office, where the organization is registered as a land tax payer.
A situation is possible when the land plot is in common shared ownership. Then determine the cadastral value of the part of the site owned by the organization in proportion to its share in the common property. The formula is:
| KSch | = | KSfull | × | D |
Where
– KSch – cadastral value of the part of the land plot that is owned by the organization; – KSpoln – cadastral value of the entire land plot located in common shared ownership; – D – share of the land plot owned by the organization by right of ownership, as a percentage.
Now suppose that the company owns one of the floors (part of it) of a non-residential building. To determine the cadastral value of a land plot, use the formula:
| KSch | = | KSfull | × | Plorg | : | Plosch |
Where
– KSch – cadastral value of the part of the land plot that is owned by the organization; – KSpoln – cadastral value of the entire land plot located in common shared ownership; – Plorg – the area of the premises owned by the organization; – Area – total area of the building.
Postings for calculating land tax
The calculation carried out is shown in the accounting statement, which is used as a documentary justification for the calculated amount of tax; on its basis, the entry for calculating land tax is made.
The calculation is carried out on the last date of each quarter and calendar year; double entries are made in the accounting registers of the enterprise on the same dates.
To reflect information about the tax obligations of legal entities, account 68 is taken, into the subaccounts of which various types of taxes are distributed, the payer of which is the legal entity.
For land tax accounting, a separate subaccount of account 68 is also created, which is called “Calculations for land tax”. The subaccount number does not matter; you can assign it yourself, since the Chart of Accounts does not provide clear instructions. Entries can be made both in debit and credit of this subaccount:
- The debit shows the amount of tax and advances accrued for payment;
- For a loan – amounts paid to the budget.
There is a need to pay land tax if the credit turnover exceeds the debit turnover. Otherwise, the budget becomes due to the organization. This situation may arise due to overpayments or incorrect calculations. Such tax amounts can be returned by the budget to the taxpayer's account or offset against future tax payments.
Land tax may be included in other expenses or expenses for ordinary activities.
When calculating land tax, credit 68 of account interacts with the debit of accounts that take into account the organization's expenses. The account number is determined depending on the company’s activities, the purpose of using the land plot, and the objects located on it:
- D. 20 Cr. 68.Zem.tax – shows the accrual of tax on the site occupied in the main production activity;
- D. 23 Kr. 68.Zem.tax – shows the accrual of tax on the site occupied in auxiliary production activities;
- D. 25 Cr. 68. Land tax - a tax is charged on land used for general production purposes;
- D. 26 Kr. 68. Land tax - a tax is charged on land used for general economic purposes;
- D. 44 Kr. 68. Land tax - land tax is assessed on the site involved in the trading activities of the company;
- D. 91 Kr. 68. Land tax - reflects the accrual of tax on land leased for use for a specific period to another person under a lease agreement. This posting is made if the lease transfer of land is not the main direction of the organization’s business;
- Deb.08 Cr.68.Land tax – shows the accrual of land tax on the site on which construction work is being carried out to construct a future real estate object. This entry is made until the day the constructed object in the form of OS is received on account 01. In this case, expenses in the form of land tax are included in the future initial cost of the property being built on the site.
Postings for payment of land tax
When transferring money to cover the land tax, the organization must be guided by the legal acts adopted by the municipality to which the site belongs. For this purpose, the local legislative framework should be studied. Each region has its own rules and deadlines.
For example, on land located in Moscow, tax must be paid according to Law No. 74:
- For quarters - no later than the end of the next month following the billing quarter;
- One year – until February 1 of the next year inclusive.
In St. Petersburg, payment deadlines in accordance with Law No. 617-105:
- For quarters - no later than the end of the next month following the billing quarter;
- One year – until February 10 of the next year inclusive.
On the day of transfer of non-cash funds to pay off the tax liability for land tax, a posting of the following type is made:
- Deb.68 Land tax Kr.51 – tax (or an advance payment on it) has been paid on a plot of land.
The above transaction is made on the basis of a payment form, for example, an order submitted to the bank to withdraw funds from a client account to the tax account.
What are the tax rates?
Tax rates for land tax are set by local authorities. Rates cannot exceed 0.3 percent in relation to lands provided (acquired) for housing construction, personal subsidiary plots, gardening, vegetable farming, livestock farming, summer cottage farming and occupied by housing stock and housing and communal facilities, as well as agricultural lands. For other land plots, the maximum tax rate is 1.5 percent.
This is provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.