Tax status of an individual
When calculating personal income tax, attention should first be paid to the issue of residence rather than citizenship. Tax residency is determined by the individual’s membership in the state’s tax system. The concepts of currency, migration, any other and tax resident are different.
The Federal Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ “On Currency Regulation and Currency Control” establishes, for example, that currency residents of Russia are every citizen of the Russian Federation and foreigners permanently residing in the territory of the Russian Federation with a residence permit. Citizens of the Russian Federation who continuously reside outside the country for at least 183 days are exempt from restrictions related to the status of currency resident.
The concept of a tax resident is defined in Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This is an individual who is actually in the Russian Federation for at least 183 calendar days over the next 12 consecutive months. At the same time, the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation do not contain requirements for the continuity of the flow of the indicated 183 days (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/15/2017 No. 03-04-05/8334, dated 09/01/2016 No. 03-04-05/51258, dated 04/26/2012 No. 03 -04-06/6-123, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 30, 2012 No. OA-3-13/ [email protected] ).
Tax resident status ensures the use of benefits and deductions when calculating income tax in all countries. An employee may be a tax resident of several states at the same time or, conversely, be a tax non-resident everywhere.
Rules for determining tax status vary from country to country. To avoid double taxation, most countries enter into appropriate agreements providing for tax exemptions, offsets, tax deductions and other tax benefits.
Article 232 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides that the tax agent may not withhold personal income tax if the income is paid to a resident of a foreign state with which the Russian Federation has concluded an international agreement. For example, a resident of a foreign state can receive income on the territory of the Russian Federation. Similarly, a non-resident of the Russian Federation can receive income abroad. In accordance with such agreements, non-residents of the Russian Federation do not pay personal income tax on income from Russian companies received abroad, but include it in the income declaration (in Form 3-NDFL).
Who are residents and non-residents
In relation to personal income tax, the legislator distinguishes 2 types of taxpayers: residents and non-residents.
Residents are individuals who reside on the territory of the Russian Federation for at least 183 days within 12 consecutive months (clause 2 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Exception:
- Russian military personnel serving abroad.
- Employees of government bodies who are on a business trip abroad (clause 3 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
These two categories of persons are considered residents regardless of how much time during the year they are actually in Russia.
Non-residents are considered individuals who live in Russia for less than 183 days over the next 12 consecutive months.
Taxpayer status carries certain tax consequences :
1. The tax rate depends on the status. In general (we will talk about exceptions below) it is:
- 13% – for residents;
- 30% – for non-residents.
Please note that within the framework of currency regulation, non-residents are considered to be all foreigners without a residence permit temporarily staying (residing) in Russia.
We talked in more detail about the procedure for calculating and withholding tax from the income of foreign workers in the article “Foreign workers: what all employers need to know.”
2. The composition of income for each group is different. For non-residents, this is only income that is received from sources in the Russian Federation.
3. Residents, unlike non-residents, have the right to tax deductions for personal income tax.
Personal income tax rates for non-residents
The income of individuals who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation may be taxed at rates of 0, 13, 15, 30%, depending on the source and type of income, as well as the status of a non-resident taxpayer (Articles 207, 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
Individuals - non-residents of the Russian Federation, performing work on the territory of a foreign state and receiving remuneration for performing labor duties from sources in a foreign state are not recognized as taxpayers for personal income tax in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, at a rate of 0% personal income tax is calculated on the income of employees of separate divisions located outside the Russian Federation. According to paragraph 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income from Russian sources received by individuals who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation is taxed at a rate of 30%.
There are exceptions to this rule:
1. Personal income tax in the amount of 13% is withheld from the income of non-residents from labor activities:
- as a highly qualified specialist in accordance with Federal Law No. 115-FZ dated July 25, 2002 “On the legal status of foreign citizens in the Russian Federation”;
- participants in the State program to assist the voluntary resettlement of compatriots living abroad to the Russian Federation, as well as members of their families who jointly moved to permanent residence in the Russian Federation;
- citizens or stateless persons recognized as refugees or granted temporary asylum on the territory of the Russian Federation in accordance with Federal Law No. 4528-1 of February 19, 1993 “On Refugees”;
- foreign citizens of the countries participating in the Treaty on the EAEU (Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan);
- employed on the basis of a patent in accordance with Article 227.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
2. Personal income tax in the amount of 15% is withheld from the income of non-residents in the form of dividends from equity participation in the activities of Russian organizations.
The status of a resident of the Russian Federation ensures the application of personal income tax rates:
- 13% - in relation to income in the form of wages;
- 35% - for income from winnings and prizes.
Only for individuals with the tax status of a resident of the Russian Federation, tax benefits and deductions are available.
An employee who enters into an employment contract or a civil contract with an employer must confirm his tax resident status. The tax agent is responsible for the correct determination of the status of an individual, as well as for the calculation and payment of personal income tax. If an individual does not submit the requested documents about the time of his stay in the Russian Federation, the tax agent has the right to calculate the tax in the manner prescribed for non-residents, that is, at a rate of 30% (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 12, 2013 No. 03-04-06/32676) .
In fact, the personal income tax rate can be 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12, 15 and other percent for some income of individuals (dividends, income on securities, royalties) who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation. The personal income tax rate can be established by an international treaty, and in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 7 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the norms of international treaties of the Russian Federation have priority over the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Step-by-step instruction
On March 28, the general meeting of the founders of the Organization decided to distribute the profit received for 2022 in the amount of 2,000,000 rubles. in favor of the following founders:
- Russian legal entity Karandash LLC, which owns a 50% share of the authorized capital of the company 6 months - 1,000,000 rubles;
- individual (resident of the Russian Federation) Ivanov Alexander Pavlovich, an employee of the organization who owns a 35% share of the authorized capital of the company - 700,000 rubles;
- individual (non-resident of the Russian Federation) Kutuzov Alexander Pavlovich, who owns a 15% share of the authorized capital of the company - 300,000 rubles.
The organization as a tax agent calculates and withholds:
- income tax on income in the form of dividends of a legal entity in the amount of 13%;
- Personal income tax on income in the form of dividends of an individual resident of the Russian Federation in the amount of 13%;
- Personal income tax on income in the form of dividends of an individual non-resident of the Russian Federation in the amount of 15%.
The organization did not receive dividends from other legal entities.
Step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | ||
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Calculation of dividends to an individual resident of the Russian Federation | |||||||
| March 28 | 84.01 | 75.02 | 700 000 | Calculation of dividends | Calculation of dividends | ||
| 75.02 | 68.01 | 91 000 | Personal income tax on dividends | ||||
| Calculation of dividends to an individual non-resident of the Russian Federation | |||||||
| March 28 | 84.01 | 75.02 | 300 000 | Calculation of dividends | Calculation of dividends | ||
| 75.02 | 68.01 | 45 000 | Personal income tax on dividends | ||||
| Calculation of dividends to a Russian legal entity | |||||||
| March 28 | 84.01 | 75.02 | 1 000 000 | Calculation of dividends | Calculation of dividends | ||
| 75.02 | 68.34 | 130 000 | Income tax on dividends | ||||
| Dividend payment | |||||||
| March 28 | 75.02 | 51 | 1 734 000 | Dividend payment | Debiting from the current account - Transfer of dividends | ||
| Payment of personal income tax on dividends | |||||||
| March 28 | 68.01 | 51 | 136 000 | Payment of personal income tax to the budget | Debiting from a current account – Tax payment | ||
| Payment of income tax on dividends | |||||||
| March 28 | 68.34 | 51 | 130 000 | Payment of income tax to the budget | Debiting from a current account – Tax payment | ||
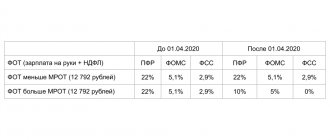
Registration of tax status in “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” (rev. 3)
In order to take into account all possible personal income tax rates, the 1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8 program, edition 3, provides for registration of the taxpayer’s tax status in the employee’s card using the Income Tax link in the Status field (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Taxpayer status
The Established from field indicates the date of the tax period from which the selected status is valid. The history of changes in taxpayer status can be viewed at the link of the same name.
The user can specify one of the following statuses:
- Resident;
- Non-resident;
- Highly qualified foreign specialist;
- Member of the crew of a vessel registered in the Russian International Register of Ships;
- Participant in the program for the resettlement of compatriots;
- A refugee or someone who has received temporary asylum on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- Citizen of a country party to the Treaty on the EAEU;
- Non-resident employed on the basis of a patent.
If the status of a tax resident is not confirmed by the Federal Tax Service in the prescribed form, then it is necessary to determine whether the non-resident has grounds for establishing an exclusive status that ensures the application of a personal income tax rate of 13% to “salary” income. In general, the status of Non-Resident is established, and personal income tax is calculated at a rate of 30%.
Simultaneous application of different personal income tax rates depending on the type of income of an individual
As a general rule, the income of non-resident individuals of the Russian Federation is taxed at a personal income tax rate of 30%. However, for income from labor activities of designated non-residents - highly qualified foreign specialists, citizens of EAEU countries, etc., a rate of 13% is applied.
The labor activity of a foreign citizen is understood as work in Russia on the basis of an employment or civil law contract for the performance of work or provision of services (Article 2 of Federal Law No. 115-FZ of July 25, 2002 “On the legal status of foreign citizens in the Russian Federation”). However, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not specify what exactly is considered income from labor activity. Therefore, it is not always clear to the employer at what rate personal income tax should be withheld from certain payments to this category of employees.
| 1C:ITS For more information about what income of highly qualified foreign non-resident specialists is subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%, see the reference book “Income Tax for Individuals” in the “Taxes and Contributions” section. |
Example 1
| Non-resident employee of the Russian Federation S.S. Gorbunkov, who has the status of “Highly Qualified Foreign Specialist” and works under an employment contract, was accrued in January 2022: a salary of 100,000 rubles, dividends of 100,000 rubles, and a subscription to a fitness club of 100,000 rubles. |
Salary payments, vacation pay, sick leave payments and business trips clearly relate to work activities, and personal income tax is calculated at a rate of 13%.
Dividends do not apply to income from employment, and the personal income tax rate is 15%. The personal income tax rate on in-kind income from paying for a subscription to a fitness club is 30%.
Accordingly, in January personal income tax was calculated in the amount of: 13,000 rubles, 15,000 rubles. and 30,000 rubles (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Certificate 2-NDFL
Consequently, form 2-NDFL contains three Sections 3 “Income taxed at the rate...” (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Printed form of certificate 2-NDFL
Regulatory regulation
Dividends are income received by a participant from an organization during the distribution of profits remaining after taxation, and is determined in proportion to the shares in the authorized capital (clause 1 of Article 43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The decision on the distribution and payment of dividends is made at the annual or extraordinary general meeting of LLC participants (clause 1, article 28, clause 7, clause 2, article 33 of the Federal Law of 02/08/1998 N 14-FZ).
The accrual and payment of dividends is reflected separately for each participant on account 75.02 “Calculations for the payment of income” in correspondence with the accounts (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n):
- 84.01 “Profit subject to distribution”;
- 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”;
- “Current account” or 50 “Cashier”.
When paying dividends to company participants, a Russian organization is recognized as a tax agent:
- for income tax - for payments to legal entities (Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- for personal income tax - for payments to individuals (clause 1 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
As a tax agent, a Russian organization calculates, withholds and transfers the amount of tax to the federal budget (clause 3, clause 6 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Changing the tax status of an individual
If an employee travels outside of Russia, he may lose his status as a tax resident of the Russian Federation. Tax residency in the Russian Federation is not interrupted if an individual travels outside the Russian Federation for no more than six months for treatment or training (clause 2 of Article 207 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is not interrupted in a number of other cases listed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, when traveling outside the territory of the Russian Federation to perform labor or other duties related to the performance of work (provision of services) in offshore hydrocarbon fields.
On the other hand, any non-resident (including a highly qualified foreign specialist; a crew member of a ship registered in the Russian International Register of Ships; a participant in the program for the resettlement of compatriots; a refugee or someone who has received temporary asylum on the territory of the Russian Federation; a citizen of a country party to the Treaty on the EAEU; a non-resident, employed on the basis of a patent), having lived in the Russian Federation for 183 days over the past 12 months, becomes a tax resident.
When determining the tax status of an individual, it is necessary to take into account the 12-month period determined on the date of receipt of income, including those that began in one tax period (calendar year) and continued in another tax period (calendar year) (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 26, 2012 No. 03-04-06/6-123). During the year, tax agents (employers) calculate the taxpayer's status on the date of actual receipt of income in accordance with the provisions of Article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 30, 2012 No. OA-3-13 / [email protected] ).
The status of a resident of the Russian Federation acquired by an individual cannot change in a calendar year, provided that the person has been in Russia for more than 183 days this year. So, July 3 in a non-leap year is the 184th day of the year.
Thus, if as of July 3, 2018, an employee has not left Russia during the year, then his tax status for the current year—a resident of the Russian Federation—is already guaranteed. If an employee acquires the status of a resident of the Russian Federation, which cannot change in the current year, then the tax agent can independently recalculate the tax at a rate of 13% instead of 30%, guided by paragraph 3 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Starting from the month in which the taxpayer’s status changed, previously withheld personal income tax at a rate of 30% is counted towards payment of tax at a rate of 13%.
If at the end of the year (tax period) there is uncredited tax, then its refund is carried out by the tax authority at the place of residence (registration) of the individual (clause 1.1 of Article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To do this, the taxpayer must submit a tax return, as well as documents confirming his status as a tax resident of the Russian Federation (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 27, 2018 No. 03-04-06/12086, dated September 26, 2017 No. 03-04-06/62127, No. 03 -04-06/62126, dated 02/15/2016 No. 03-04-06/7958, dated 04/15/2014 No. 03-04-06/17166, dated 10/03/2013 No. 03-04-05/41061, dated 11/15/2012 No. 03-04-05/6-1301, dated 04/16/2012 No. 03-04-06/6-113, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 06/09/2011 No. ED-4-3/9150, dated 09/05/2011 No. ED-2- 3/ [email protected] ).
This approach is also valid when during the tax period an employee was transferred from the parent organization to a separate division (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 23, 2014 No. 03-04-06/66648).
If the tax status of an individual who is the recipient of income can be determined only at the end of the calendar year, then the recalculation of personal income tax in connection with the acquisition of the status of a resident of the Russian Federation and its return are carried out by the tax authority at the place of registration (stay) of the individual in accordance with paragraph 1.1 of Article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
To do this, the taxpayer must submit to the tax authority a declaration in form 3-NDFL, as well as documents confirming the status of a resident of the Russian Federation in this tax period (see letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 16, 2013 No. 03-04-06/4-11, dated 09.08 .2012 No. 03-04-06/6-230, dated 09.21.2011 No. 03-04-06/6-226, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 10.22.2012 No. AS-3-3/ [email protected] , dated 08.14.2012 No. ED-3-3/ [email protected] , dated March 21, 2012 No. ED-3-3/ [email protected] ).
| 1C:ITS For more information on how personal income tax is recalculated if the status of an individual changes from non-resident to resident during a calendar year, see the “Individual Income Tax” reference book. |
Reporting
6-NDFL
The amounts of dividends paid to individuals and personal income tax calculated from them must be reflected in the calculation of 6-personal income tax (clause 2 of article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- in Section I - for the period of payment to individuals (clause 3.3 of the Procedure for filling out the calculation of 6-NDFL, Article 216 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- in Section II - for the quarter in which the deadline for transferring personal income tax from them came (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 08/09/2016 N GD-4-11/14507).
The tax agent is obliged to pay personal income tax no later than the day following the day of payment of income (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Calculation of 6-NDFL is generated from the section:
- Salaries and personnel – personal income tax – reporting on 6-personal income tax – Create button;
- Reports – 1C Reporting – Regulated reports – Create button – 6-NDFL.
Clicking the Fill out the report on Form 6-NDFL will automatically fill in the amounts of accrued dividends, calculated, withheld and transferred personal income tax.
6-NDFL calculation will be filled in:
- Section 1 Generalized indicators (in two blocks): page 010 – 13% (15%);
- line 025 – amount of accrued dividends;
- line 045 – amount of calculated tax on dividends; PDF
- Section 2 Dates and amounts of income actually received and withheld personal income tax:
page 100 – date of actual receipt of income;
- page 110 – tax withholding date;
- page 120 – tax payment deadline;
- p. 130 – the amount of income actually received;
- line 140 – amount of tax withheld. PDF
2-NDFL
Information about dividends paid to individuals and personal income tax withheld from them must be reflected in certificate 2-NDFL in the period when the dividends were actually transferred to the recipient of the income (clause 2 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A certificate in form 2-NDFL can be generated:
- for the recipient of income from the section Salaries and personnel - personal income tax - 2-personal income tax for employees;
- based on the results of the year as a report, Salaries and personnel - personal income tax - 2-personal income tax for transfer to the Federal Tax Service.
In 2-NDFL, Fill button automatically fills in the following amounts:
- accrued dividends;
- calculated personal income tax;
- withheld personal income tax;
- transferred to the personal income tax budget.
Dividends taxed at a rate of 13% are reflected in the Certificate as part of income taxed at a rate of 13% on the tab 13%.
Dividends, taxed at a rate of 15%, are reflected separately from other income on the tab 15%.
In the certificate of income of an individual in form 2-NDFL the following will be filled in:
For a resident individual:
- Section 2 Information about the individual – recipient of the income: Taxpayer status – 1.
- Section 3 Income taxed at the rate of 13%: Income code – 1010;
- The amount of income is the amount of accrued dividends. PDF
For a non-resident individual:
- Section 2 Information about the individual – recipient of the income: Taxpayer status – 2;
- Section 3 Income taxed at the rate of 15%: Income code – 1010;
- The amount of income is the amount of accrued dividends. PDF
Income tax return
The amounts of dividends paid to other organizations, as well as the income tax withheld from them, must be reflected in the income tax return for the reporting period in which the payment was made:
- Sheet 03 – filled out for each decision of the owners (clause 11.2.1 of the Procedure for filling out the income tax return);
- Section B of Sheet 03 – is filled out for each organization to which dividends reflected in Sheet 03 of Section A were paid;
- Subsection 1.3 of Section 1 of Sheet 01 is filled in with the amounts of tax on dividends paid in the quarter (month) based on the results of which the declaration is submitted (clause 4.4 of the Procedure for filling out the income tax declaration).
The income tax return is generated in the section Reports – 1C Reporting – Regulated reports.
In the declaration, clicking the Fill automatically fills in:
- page 022 Sheet 03 Section A – dividends to legal entities, taxes on which are calculated at a rate of 13%;
- page 030 of Sheet 03 Section A – on dividends from individuals; PDF
- Sheet 3 Section B – on dividends of Karandash LLC; PDF
- Subsection 1.3 Section 1. PDF
Page 050 – dividends accrued to individual income recipients who are not tax residents of the Russian Federation are not automatically filled in.
Needed manually:
- adjust the amount in line 030 , indicating 700,000 rubles. – dividends from Ivanov A.P.
- fill out page 050, indicating RUB 300,000. – dividends of Kutuzov A.P. PDF
Cash flow statement
Organizations that do not use simplified forms of accounting report information on dividends paid and personal income tax withheld from them in the Cash Flow Report (clause 11 of PBU 23/2011).
As part of the financial statements, a Cash Flow Statement (CFS) is generated from the section Reports - 1C Reporting - Regulated Reports.
In ODDS the following is automatically filled in:
- line 4124 – corporate income tax; PDF
- line 4129 – other payments; PDF
- line 4322 – payments for the payment of dividends and other payments for the distribution of profits in favor of the owners (participants) in the amounts of dividends paid. PDF
To access the section, log in to the site.
See also:
- Payment of personal income tax on dividends
- Payment of income tax on dividends of RO NA
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Loans to founders You do not have access to view To gain access: Complete a commercial…
- Issuance to an accountable person from the cash register and return of unused accountable funds...
- Issuance of funds to an accountable person from the cash register...
- Issuance of monetary documents (air tickets) to an accountable person...
Change of tax status in “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” (rev. 3)
A change in the tax status of an employee upon the occurrence of this fact should be reflected in the employee’s card using the Income Tax link, indicating in the Established from field the date of the tax period from which the status changes. Personal income tax recalculation occurs automatically.
Example 2
| Since 02/01/2018, employee S.S. Gorbunkov, who has the status of “Highly Qualified Foreign Specialist” and works under an employment contract (see Example 1), became a resident. |
In this case, personal income tax is automatically recalculated for other income (Fig. 4). Personal income tax, excessively accrued on income in kind, is displayed in the document Payroll for February 2018 in the amount of 17,364 rubles. Deductions for children have been applied since January 2018.
Rice. 4. Recalculation of personal income tax in the document “Payroll”
Please note that automatic recalculation of personal income tax on dividends is not provided in the program. Users can independently enter the Personal Income Tax Recalculation document in the Taxes and Contributions section. By clicking the Fill button, personal income tax is recalculated automatically (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Document “Recalculation of personal income tax”
Payment of personal income tax on dividends
To reflect the amounts of personal income tax paid on dividends, it is necessary to generate the document Write-off from the current account :
- in the Payment order , follow the link Maintain a document debiting from a current account ;
- Bank and cash desk – Bank – Bank statements – Write-off button. PDF
The document generates transactions:
Dt 68.01 Kt – payment of personal income tax on dividends from individuals.
Find out more about paying personal income tax on dividends to individuals
Expanded capabilities of “1C: Salaries and personnel management 8 KORP” for personal income tax accounting
Accounting for personal income tax rates under international agreements
The CORP version of the 1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8 program, edition 3, provides expanded capabilities for personal income tax accounting. In accordance with international treaties of the Russian Federation, in order to avoid double taxation, the program can register the income of non-residents of the Russian Federation in the form of dividends, income on securities, royalties and calculate personal income tax at the specified rates of 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 12, 15%.
A number of international treaties provide for a fractional tax rate (4.5%, 7.5%, 13.5%). However, the current electronic formats of 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL reports do not provide for the possibility of transmitting such data. Therefore, the program does not support these bets.
You can enable the functionality of using taxation in accordance with international treaties in the Settings menu - Payroll calculation - flag Use personal income tax rates provided for by international treaties of the Russian Federation.
At the same time, in the Dividends document it becomes possible to choose the personal income tax rate under an international agreement: 5, 10 or 12%. In the Author's Order Agreement document, you can similarly select the tax rate from the options 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 15%. Personal income tax is calculated automatically at the specified rate.
New rates can also be specified in the Personal Income Tax Accounting Transaction document. Reports 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL correctly reflect the specified personal income tax rates and are automatically filled in using the data registered in the program.
Calculation order
Income tax is determined on all funds received during the month (not on an accrual basis). The calculation is made separately for each amount.
The sequence of calculating personal income tax for foreign citizens in 2018 is as follows:
| Stage | What does it include |
| 1 | Residence is established in accordance with Art. 207 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| 2 | Determine payer status |
| 3 | Set the rate taking into account the above characteristics |
| 4 | The tax base (NB) is determined in accordance with Art. 211 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and calculate the tax |
| 5 | Fill out forms 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL |
Also see “Confirmation of the status of a tax resident of the Russian Federation” - a new service of the website of the Federal Tax Service of Russia.”