What is a shopping book and what is it for?
A purchase ledger is a summary tax document.
It includes information about invoices on the basis of which VAT deductions are applied for the corresponding tax period (quarter). The purchase book is kept in the form of Appendix 4 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 (hereinafter referred to as Decree No. 1137).
From 01.07.2021, the form as amended by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 02.04.2021 No. 534 is used.
The changes according to Government Decree No. 534 dated 04/02/2021 are due to the fact that from 07/01/2021 all taxpayers need to reflect information on the traceability of goods in VAT documents. VAT defaulters will be required to report transactions involving traceable goods.
You can download the updated purchase book form on our website by clicking on the picture below:
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to correctly fill out an invoice and what reporting to submit when performing transactions with goods subject to traceability. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
Based on information from the purchase book, the amount of VAT deduction is reflected in the tax return. And the book’s indicators are included line by line directly in the VAT return. For this purpose, section 8 is provided in its form. There are as many such sections that need to be compiled as there are entries registered in the purchase book for the corresponding quarter.
ATTENTION! The Federal Tax Service has approved further changes to the VAT return form (order dated March 26, 2021 No. ED-7-3/ [email protected] ). The first time you will need to submit a report using this form is for the 3rd quarter of 2022.
You can download the current declaration form by clicking on the image below:
The declaration was also adjusted to the traceability system for imported goods, mandatory from 07/01/2021.
Maintaining a purchase book is the responsibility of VAT payers (clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). After all, only they have the right to deduction.
See also the materials “ Who is the VAT payer? " and " What are VAT tax deductions? " .
Based on the entries in the purchase book, accounting entries reflect the acceptance of VAT for deduction - through the entry Dt 68 Kt 19.
For details, see the material “ Posting “VAT accepted for deduction”: how to reflect it in accounting? " .
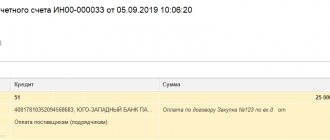
The invoice is issued in a single copy “for yourself”
In this case, it is advisable to use special processing Registration of invoices for advance payments (Bank and cash desk - Registration of invoices - Invoices for advance payments)
, which will automatically create invoices for all outstanding advances according to the established statement rules*.
*The procedure for issuing invoices for advances received is established in the accounting policies of organizations (), as well as in the agreement with the counterparty. By the way, we strongly advise you not to neglect the latest provision of the law and issue invoices for all advances that are not paid by the end of the day. One of our acquaintances, an accountant, has been reprinting books of purchases and sales since 2011, due to the fact that he wrote out advances that were not accounted for within 5 days.
The most important limitation of this method is that before registering advance invoices, we must be sure that:
- The sequence of settlements with customers is relevant
- Duplicate counterparties and contracts were reconciled
- All debt balances are as of 62.01
- All balances of advances are at 62.02
- At 62.02 there are no balances for which the advance should have already been closed
- the registration of advance invoices
has already been processed , it is necessary to restart
Let's briefly consider each of the above restrictions separately:
Restoring the sequence of settlements with customers
In enterprise accounting
There are two ways to transfer documents:
- re-posting of documents in Closing the month
(
Operations - Closing of the month - Re-posting of documents
)
- using the VAT Accounting Assistant
(
Reports - VAT - VAT Reporting
).
Its main task is to correctly perform all regulatory operations for calculating VAT.
Before generating a declaration, you must complete Regulatory Operations
.
These operations allow you to avoid errors. They allow you to restore the sequence of documents, make entries in the purchase book, and also a tool such as Express Accounting Check
allows you not only to see errors, but also to receive recommendations on how to eliminate them.
Each organization should develop regulations for the re-processing of documents and setting a date for prohibiting editing, but this is the topic of a separate independent article.
Checking for duplicate counterparties and contracts
This topic is also quite extensive and, of course, it is better to reconcile doubled counterparties not during reporting, but constantly, in accordance with the developed regulations. Some points can be gleaned from the article Effective work with the directory of counterparties, and to search for duplicate elements of directories, use special universal processing.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the service for checking the details of counterparties and the service for establishing counterparties by TIN.
Checking the correctness of mutual settlement balances on accounts 62.01 and 62.02
To check account balances 62, you can use the Turnover Balance Sheet
with the settings
Expanded balance
and
By subaccounts
.
Let me draw your attention to the fact that many accountants, when analyzing account balances 62, do not enable the Expanded balance
and disable grouping by
Documents of settlements with counterparties
and see approximately the following picture (Figure 1)
Figure 1 - Checking account 62 without an expanded balance and settlement documents
Looking at this table, the accountant makes the following conclusions: at the beginning of the year there are “minuses” in the balance sheet, but during the period they leveled out, and at the end of the quarter the balances are correct - all balances 62.01 are debit, 62.02 are credit.
Let's look at the same report with the expanded balance setting enabled (Figure 2)
Figure 2 – Checking account 62 with setting up the expanded balance
We see that in fact the program considers the amount of 207606.73 for the counterparty “Buyer 6” on account 62.01 as an unclosed advance. On the contrary, the program considers account 62.02 for counterparty “Buyer 6” to be an outstanding debt. Let's consider this situation in more detail, expanding the turnover for the counterparty “Buyer 6” according to the settlement documents (Figure 3).
Figure 3 – Turnover 62.02 for counterparty “Buyer 8” according to settlement documents
We see that the debit turnover according to the document Receipt to current account 16 dated 02/27/2019
is incorrect, since there was no advance balance on this document (there was no loan). To correct this error, it is enough to decipher the turnover with the account card, find the document that made the incorrect turnover and re-post it.
The procedure for correcting identified erroneous movements and balances in mutual settlements is worthy of a separate full-fledged article. For the purposes of this article, we will limit ourselves to the fact that the closure of advances and debts must necessarily take into account settlement documents. Disabling the grouping Documents for settlements with the counterparty
when analyzing mutual settlements - a common and significant mistake.
As a result, after all the corrections, the following picture should be obtained: balances 62.01 - only in the debit of 62 accounts, balances 62.02 - only in credit (Figure 4).
Figure 4 – SALT for account 62 with expanded balance for subaccounts
Checking unclosed (unaccounted) advances
The general essence of checking unclosed advances is that, subject to the previous point, we just need to remove the “By subaccounts” setting and check whether there are simultaneous debit and credit balances for one counterparty/agreement as a whole on account 62. Grouping by settlement documents can be disabled (Figure 5).
Figure 5 – SALT for account 62 with expanded balance
Analyzing this report, we see that “Buyer 2” under contract “No. 2” simultaneously has a debt of 3,399,275.50 and an advance of 3,559,642.50. This situation suggests that advances under this agreement were offset incorrectly. If this error is not corrected, then when automatic registration of invoices for advance payments is made, an advance invoice will be issued for the credit balance of 3,559,642.50 and VAT will be charged.
Let us separately consider the counterparty “Buyer 8”. In general, for the counterparty we see that there is both a credit and a debit balance on account 62, but when detailing the agreements, it is clear that the debit balance is on “agreement 8”, and the credit balance is on “agreement 8.2”. This situation really can happen. We must pay attention to it, but we will not correct anything in this case.
After correcting all unaccounted advances, the picture in the report will change as follows (Figure 6).
Figure 6 – SALT for account 62 with expanded balance after corrections
Registration of invoices for advance payments
Finally, when we are sure that:
- The sequence of settlements with customers is relevant
- Duplicate counterparties and contracts were reconciled
- All debt balances are as of 62.01
- All balances of advances are at 62.02
- At 62.02 there are no balances for which the advance should have already been closed
Only now we can use the automatic issuance of invoices for advances ( Sales - Maintaining a sales book - Registration of invoices for advances
).
Document Invoice
issued with the sign
For advance
registration registers the following movements in the system:
- Accounting entry Dt 76.AV Kt 68.02 for the amount of VAT on the advance
- Entry into the sales VAT
- it is on the basis of the data in this register that
the Sales Book
I repeat, in case of changes in mutual settlements in the period for which processing has already been performed Registration of invoices for advance payment
, it is necessary to re-perform processing, and the program implements the ability not to renumber previously generated documents (this is important if we have already printed previously issued invoices).
Deduction of VAT on advances received
Previously accrued amounts of VAT on advances are subject to deduction in the period in which the advance was offset (debit turnover on account 62.02). To register VAT deductions from advances received, you must create a document Creating purchase ledger entries
(
Operations – Regular operations for VAT – Creation of purchase ledger entries
) and fill out the tab
Deduction of VAT from advances received
.
Document Formation of purchase ledger entries
registers the following VAT movements from received advances in the system:
- Accounting entry Dt 68.02 Kt 76.AV - for the amount of VAT credited in advances during this period
- Entry into the VAT Purchases
– it is on the basis of the data in this register that
the Purchase Book
Comparison of balances 62.02 and 76.AB
If VAT on advances received was calculated correctly, and was also correctly accepted for deduction of VAT on offset advances, then the credit balance of 62.02 * VAT rate should be equal to the debit balance of 76.AB.
To compare balances 62.02 and 76.AB, you can use the Turnover balance sheet
for each of the accounts and compare the amounts of balances 76.AB with those obtained by manually calculating VAT based on account 62.02. For more detailed information on how to check the correctness of VAT calculation on advances, our article Checking VAT on advances on accounts 62.02 and 76.AB for sales for VAT 18% using Excel will help.
Do not hesitate, contact us for help and we will help you set up VAT accounting on advances, correct all errors, resubmit VAT for previous periods, we really have extensive experience in correcting VAT errors.
What goes into the shopping book
The purchase book records:
- Invoices, including:
- received from sellers (clause 2 of the rules for maintaining a purchase book, approved by Resolution 1137; hereinafter referred to as the Rules for maintaining a purchase book);
- advance invoices for the shipment of goods, works, services (GWS) (clause 22 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase ledger), see the material “ Acceptance for deduction of VAT on advances received ” ;
- adjustment invoices to reduce the cost of shipment from the seller and increase it from the buyer (clauses 9 and 12 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase ledger), see the material “ What is an adjustment invoice and when is it needed? " ;
- for construction and installation works for own consumption, when deducting VAT on them (clause 20 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger).
- Other documents that, along with invoices, serve as the basis for deducting VAT, for example:
- strict reporting forms or copies thereof - when deducting travel expenses (clause 18 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger);
- customs declaration and payment documents confirming payment of import VAT - upon import (clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase book);
- statements on the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes - when importing goods from the EAEU (clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase book), etc.
Entries in the purchase book are made as the right to tax deductions arises.
See the material “ What are VAT tax deductions? " .
In this case, invoices are registered in a unified manner (clause 2 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger):
- regular, corrective and corrected;
- received on paper and electronically;
- filled out partly using a computer, partly by hand.
Adjustment of goods receipt
Based on a previously created goods receipt, you can create an adjustment document. To do this, open the previously created document No. 789 dated June 15, 2016
Purchases -> Purchases -> Receipt (act, invoice)
and using the “Create based on” button
Let's create an adjustment document:
The nomenclature now has two lines:
- before change - price and quantity of the original document
- after a change, a new price or quantity is set
Also the supplier costs us 100 rubles. increased the cost of transport):
Register entries are created for the changed amount:
After posting the adjustment document, we will register the adjustment invoice:
See also our video on adjusting sales and issuing an adjustment sales invoice:
What doesn't make it into the shopping book?
Invoices that do not comply (clause 3 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger) should not be included in the purchase ledger:
- requirements of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ( see the material “ What errors in filling out an invoice are not critical for deducting VAT?” );
- established forms (Appendices 1 and 2 to Resolution No. 1137).
In addition, the book does not record invoices received (clause 19 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase ledger):
- upon gratuitous transfer of industrial and technical materials, including fixed assets and intangible assets;
- commission agent (agent) from the principal (principal) for goods and services transferred for sale, property rights, as well as advances received for this sale;
- commission agent (agent) from the seller of goods and services or property rights acquired for the principal (principal), including for advances issued;
- for the amount of prepayment for goods and materials purchased for VAT-free transactions;
- advance invoices issued or received after the seller has received (issued) shipping invoices.
Please note that from clause 19 of the Rules for maintaining a purchase book in its latest edition, subparagraph “e” was excluded, which read as follows: “e) for the amount of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer property rights in non-monetary forms of payment."
Thus, now a “non-cash” advance is not an obstacle to reflecting an advance invoice in the purchase book and, as a result, does not interfere with VAT deduction.
What is reflected in the purchase book
The purchase book reflects the following information:
- in the header - information about the taxpayer-buyer (its full or abbreviated name in accordance with the constituent documents (or full name of the individual entrepreneur), INN and KPP), as well as information about the tax period (its start and end dates);
- in the tabular part - information about the documents serving as the basis for deducting VAT and its amount.
NOTE! If goods and services are purchased for transactions taxed at rates of 20, 10 and 0%, the invoice must be registered in the purchase book in parts - on the dates when the right to deduction arises (clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book, letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 17. 2015 No. 03-07-11/14238 and 03/02/2015 No. 03-07-09/10695).
See the material “ How to apply VAT deduction on export transactions ” .
If the purchase is intended for taxable and non-taxable transactions, an invoice is registered for the amount accepted for deduction based on the proportion of separate accounting (clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase ledger).
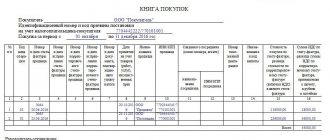
Purchase book according to resolution 1137
According to Resolution 1137, the purchase book is filled out in the following order (clause 6 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book):
- Column 1 indicates the serial number of the record of information about the invoice (including adjustment);
- in column 2 the code of the type of operation is entered (see order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] );
- Column 3 generally reflects the serial number and date of the seller’s invoice; if the deduction is confirmed by other documents, then their details are provided (for example, a customs declaration, an application for import, etc.);
| Data to fill out column 3 | Under what conditions |
| No. and date of the application for the import of goods and payment of indirect taxes with marks from the tax authorities regarding the payment of VAT | When importing goods into the Russian Federation from EAEU countries |
| Registration number of the customs declaration issued upon release of goods in accordance with the customs procedure for release for domestic consumption upon completion of the customs procedure of the free customs zone on the territory of the SEZ in the Kaliningrad region | When reflecting VAT in the purchase book, which is accepted for deduction on the basis of clause 14 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| No. and date of the payment and settlement document or other document containing summary (summary) data registered by the seller in the sales book | When reflecting VAT on an advance (prepayment) received on account of upcoming supplies of goods and materials and subject to deduction from the date of shipment of goods and materials |
- in columns 4–6 - serial numbers and dates of corrected, corrective or amended adjustment invoices;
- in column 7 - the number and date of the document confirming payment of the tax (you must reflect the details of the payment document in column 7 of the purchase book if VAT is deducted only after it is paid: for example, when importing goods into the Russian Federation (see letter from the Ministry of Finance Russia dated November 26, 2014 No. 03-07-11/60221) or return of the advance payment to the buyer in case of termination/change of the contract, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 24, 2015 No. 03-07-11/16044 and March 23, 2015 No. 03-07-11 /15889);
- in column 8 - the date of registration of goods (performance of work, provision of services), property rights;
- in columns 9 and 10 - the name and INN/KPP of the seller, respectively;
- columns 11 and 12 are filled in by the buyer-committee (principal) - they indicate the name, tax identification number and checkpoint of the intermediary commission agent (agent) purchasing the goods and services on his own behalf;
- in column 13 - the name and code of the currency (only in the case of purchasing goods and services, property rights for foreign currency);
- in column 14 - the cost of goods and services, property rights or the amount of the advance payment including VAT;
- in column 15 - the amount of VAT accepted for deduction;
- in column 16 - the registration number of the goods declaration or the registration number of the batch of goods subject to traceability;
- in column 17 - code of the quantitative unit of measurement of the product used for traceability purposes;
- in column 18 - the quantity of goods subject to traceability, in the quantitative unit of measurement of the goods used for traceability purposes;
- in column 19 - the cost of the goods subject to traceability, excluding VAT, in rubles.
A sample of filling out the purchase book using the new form from 07/01/2021 can be downloaded from ConsultantPlus by receiving a free trial access:
Formation of a sales book in 1C 8.3 step-by-step instructions
The sales book in 1C is formed according to entries in the sales VAT . If you need some entry to be included in the sales book, you need to enter it in this register.
Let's take a closer look at what documents make entries in it.
Entry into the sales book in 1C 8.3
In 1C there are two main ways to make an entry in the sales book:
- when registering the primary document for implementation (Implementation (deed, invoice), etc.);
- through the document Formation of sales ledger entries.
Registration of the primary document
Accrued VAT on sales is reflected in the sales book when posting the sales document:
- Sales (deed, invoice);
- Retail sales report;
- OS transfer , etc.
In this case, the document Generating sales book entries for them is not created.
Movements in the VAT Sales :
- Sales of goods in wholesale trade
- Retail sales of goods through an automated point of sale
- Sales of fixed assets
- Reflection of VAT on advance payment in the sales book
- VAT accrual for construction and installation works in a self-employed manner
- Reducing the amount of costs (services). VAT (in the Buyer's accounting)
- Acceptance of VAT for deduction on a credited advance payment using an updated declaration
- VAT deduction on forgotten returns from the buyer
- Reinstatement of VAT when offsetting advances issued to suppliers
Generating sales ledger entries
The document Formation of sales book entries in 1C is used only when reflecting the recovery of VAT from advances in the sales book.
You can create it in the Operations section - Period closure - VAT routine operations.
Movements in the VAT Sales :
Learn more Recovering VAT when offsetting advances issued to suppliers
Manual filling
There are times when you need to manually make an entry in the sales book (for example, there are no primary documents). For such situations in 1C there is a document Reflection of VAT accrual in the section Operations - VAT - Reflection of VAT accrual.
How to create a sales book in 1C 8.3
Where is the sales book in 1C 8.3? Sales Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Sales Book section.
BukhExpert8 recommends checking once again whether all operations have been completed before creating a sales book. To check, go to the link Income Tax Accounting Assistant . If all operations are highlighted in green, then you can create a sales book. PDF
Additional settings for the Sales Book in 1C can be done by clicking the Show settings .
Here you can set selection by counterparty to check records in the Counterparty for selection , and also set up printing of data.
You can print the sales book from 1C by clicking the Print . PDF
Recording in an additional sheet of the sales book in 1C 8.3
On October 31, the accountant discovered that the VAT on the advance payment had not been restored when the advance was offset in the third quarter. It must be reflected in the supplement. sales book sheet.
Create the document Generating sales book entries in the Operations - Period Closing - VAT Regular Operations section.
To make the entry appear in an additional sheet of the sales book, set:
- from - 10.31.2018: error correction date;
- Record extra checkbox sheet ;
- The adjusted period is 09/30/2018 : the last day on which VAT on the advance payment must be restored.
- Adjusting the sales VAT register in the Sales document (act, invoice)
- Recovering VAT from offset advances through an updated declaration
Formation of additional sheets of the sales book in 1C 8.3
An additional sheet of the sales book in 1C 8.3 is also printed from the Sales book in the Reports - VAT - Sales book section.
To generate additional sheets of the sales book in 1C, you need to click on the Show settings Generate additional sheets checkbox .
- for the current period - if the Period in which changes were made is specified, for example, the 3rd quarter;
- for the adjusted period - if the Period in which changes were made is specified, for example, the 4th quarter.
If the Display only additional checkbox is selected. sheets , then only additional sheets will be generated. If the checkbox is not selected, then additional sheets will be displayed after the main sales ledger entries.
You can print additional sheets of the sales book in 1C 8.3 by clicking the Print . PDF
We have successfully discussed how to create a book of purchases and sales in 1C, how to create an additional sheet of the book of purchases and sales in 1C 8.3 and make an entry in them.
Procedure for filling out the purchase book
Basic rules for working with a purchase book:
- fill out the purchase book in a way convenient for you - on paper or electronically;
- indicate cost indicators in rubles and kopecks (with the exception of column 14, filled in when purchasing goods and services or property rights for foreign currency);
- to correct incorrect entries in the purchase ledger, register or cancel the corrected invoice in the additional list of the purchase ledger in the same quarter when the first invoice was received;
- at the end of each quarter (no later than the 25th day of the month following the end of the quarter), sign the paper version of the purchase book from the manager (or an authorized person), lace and number the pages, seal them (if any);
- Keep sales books for at least 4 years from the date of last entry.
Find out what to consider when filling out an invoice from the materials in this section of our website.
Results
So, we found out that:
- the purchase book is maintained by VAT payers in order to determine the amount of tax deduction;
- the form and rules for maintaining a purchase book are strictly regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137;
- information from the purchase book forms the VAT return indicators and is directly included in it;
- Based on entries in the purchase book, VAT deduction is reflected in accounting.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
When to keep a sales book
This book calculates VAT payable. It is filled out in all cases when the obligation to calculate tax arises (clause 3 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137).
Maintaining a sales book is mandatory:
- for VAT payers, including those exempt from payer duties (the latter need a book to confirm the right to exemption (clauses 3 and 6 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation));
- tax agents for VAT, including those who are not taxpayers (“simplified”, “imputed”).
Find out the nuances of working with VAT for taxpayers using the simplified tax system from the material “VAT under the simplified tax system: in what cases to pay and how to take the tax into account .