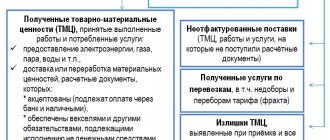
Accounting entries when receiving grant funds
The cost of the land plot based on the purchase and sale agreement amounted to RUB 4,720,000. Funds from the budget were transferred to Alpha's account on January 11. The accountant reflected the transactions for receiving and using state aid funds as follows.
In January: Debit 76 Credit 86– 4,720,000 rub. – reflects the budget debt for the provision of state assistance (based on an agreement). Debit 51 Credit 76– 4,720,000 rubles. – funds received as part of state assistance; Debit 08 Credit 60– 4,720,000 rub.
– reflects the cost of a land plot acquired with state aid funds; Debit 01 Credit 08– 4,720,000 rubles. – the land plot was accepted for accounting; Debit 86 Credit 98-2– 4,720,000 rub. – state aid funds are reflected in deferred income.
Monthly from February to December: Debit 98-2 Credit 91-1– 429,091 rub. (RUB 4,720,000
Receiving, spending and accounting for grants in an organization: postings
Question: Our organization received a grant. We have already provided two quarterly reports to the grantors. What are the transactions used to document the receipt and expenditure of grants? 1. Grantor - Public organization2.
The grant was provided for the implementation of the social project I am a citizen (the essence of the project is to identify active citizens with the help of the media and reward them based on the results)3.
The grant agreement contains an estimate within which we must implement the project.
Attention Funds are issued for the salary of the project manager, accountant, as well as expenses for media, gifts, etc.4. The tax regime of the grantee is USN 6%. Interested in both tax and accounting. Answer Regarding accounting To summarize information on the movement of funds intended for the implementation of targeted activities received from other organizations, account 86 “Targeted financing” is intended.
How to reflect receipt of a grant in accounting
The use of government assistance to finance current expenses (for example, the purchase of materials, payment of wages) should be reflected in the periods of recognition of these costs. When financing current expenses using government assistance funds, make the following entries in your accounting.
When using government assistance for the purchase of materials: Debit 10 Credit 60 – materials have been capitalized; Debit 86 Credit 98-2 – the amount of state aid spent on the purchase of materials is attributed to deferred income; Debit 20 (23, 25, 44...) Credit 10 – materials written off for production; Debit 98-2 Credit 91-1 – the amount of state aid spent on the purchase of materials is taken into account as other income.
The organization received a grant
When calculating the single tax, organizations using the simplified tax system take into account: – income from the sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services) and transfer of property rights, which are determined in accordance with Art.
249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; – non-operating income, which is determined in accordance with Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, the income referred to in Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not included in the tax base.
Important Thus, income provided to a commercial organization within the framework of targeted financing, subject to certain conditions, is exempt from taxation under the special regime of the simplified tax system (clause 14, paragraph 1, article 251, article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Targeted financing for tax purposes are funds, the list of which is contained in paragraphs. 14 clause 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This list is exhaustive (closed).
Grants: reflected in accounting
Situation: how to reflect in accounting the state aid funds spent on the acquisition (creation) of non-depreciable non-current assets? State aid funds should be reflected as deferred expenses and subsequently written off as other expenses. So, if the asset is not depreciated, targeted financing is taken into account as deferred income when the object is put into operation (accepted for accounting).
Accounting for transactions for receiving and spending RFFI grants
Answer: yes, it does. Funds from state extra-budgetary funds are an integral part of the budget system of the Russian Federation (Article 10 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, funds received to finance targeted activities from an extra-budgetary fund (for example, from the Employment Fund) are classified as state aid.
This position is also confirmed by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated January 3, 2002 No. 04-02-05/1/223. Accounting For accounting purposes, government assistance is divided into funds related to the financing of: - capital expenditures for the acquisition (creation) of non-current assets (for example, fixed assets); - current expenses.
Postings on grants
The answer to this question is contained in the Service, which you can find by searching for “free grant receipt” or following the links: https://www.moedelo.org/Pro/View/Questions/111-20545 https://www.moedelo.
org/Pro/View/Questions/111-20452 This answer has been prepared based on the information contained in the question.
If the question referred to a different situation, it is necessary to specify it, outlining it in as much detail as possible.
In this case, the answer can be obtained with a greater degree of accuracy. Current as of January 20, 2021 Question: Our organization received a grant. We have already provided two quarterly reports to the grantors. What are the transactions used to document the receipt and expenditure of grants? 1. Grantor - Public organization2.
- Intellectual property
Organizations can receive funds for purposes such as the development of research activities, culture, sports, education, the preservation of architectural monuments, and support for various technical and creative projects.
They are called grants and are reflected in accounting according to certain rules. In the article we will talk about accounting for grants and provide explanations on reporting.
Grants: what they are, what they are spent on Grants are usually understood as funds in monetary and non-monetary forms that are allocated by individuals, domestic and foreign legal entities in the manner prescribed by law to conduct research or implement specific programs. Grants are usually awarded on a competitive basis. The procedure for their receipt and issuance is established by regulatory and legislative acts.
Funds received in the form of grants can be spent in accordance with the budget items that the applicant draws up when submitting an application. When drawing up this document, the amount of expenses necessary to implement the project is calculated and justified, subject to the conditions and restrictions established by legislative acts in this area.
If several grants are received, estimates are developed for each separately. Estimation and documentation Each application of a potential grant recipient must be justified. This means that all expenses within the framework of a particular project (material, labor, depreciation of equipment, payments to the budget, etc.)
) needs to be calculated.
Legal entities that are recipients of grants must ensure that they maintain separate records of income and expenses for each targeted project. If this requirement is not met, then tax is calculated on the entire amount of the grant from the moment it is received. Calculation of VAT, Unified Tax, Personal Income Tax
- Since grants are not subject to VAT, input tax on these transactions is not claimed for credit. Its amounts are included in targeted financing.
- Unified social tax is calculated on the salaries of employees involved in the implementation of the program for which the grant was received. If such work was carried out under civil contracts, then contributions to the social insurance fund are not charged.
- When an individual receives a grant for the development of science, culture, personal income tax on these amounts is not withheld.
Source: https://yuridicheskaya-praktika.ru/buhgalterskie-provodki-pri-poluchenii-denezhnyh-sredstv-po-grantu/
Accounting with the founder
Select the section you need from the list.
| Subsidies for government tasks | Subsidies for other purposes |
| Grants in the form of subsidies | Subsidies for capital investments |
| Budget reporting |
SUBSIDIES FOR GOVERNMENT ASSIGNMENTS
Transfer the subsidy for government tasks based on the agreement. If the institution has not completed the task or has not completed it in full, it will return the remainder of the subsidy to the budget. The institution will reflect the scope of execution in the report on the state task.
Transfer subsidies to budgetary institutions according to KVR 611, to autonomous ones - according to KVR 621. The KOSGU code will always be 241. In accounting, reflect the LBO for subsidies, obligations assumed to institutions, as well as settlements with them for the transfer of subsidies and return of balances.
If the deadline for the report on the state task falls on the next year, the institution will submit a Notice (f. 0504805) in December of the reporting year. This is necessary to reflect interrelated settlement entries in the accounting of the founder and the institution.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for subsidies for government tasks
- How to form a state task
- KVR and KOSGU for subsidies for government tasks
- Postings for subsidies for government tasks and return of the balance
- How to monitor the implementation of government tasks and accept reports
- When to generate a Notice (f. 0504805) regarding subsidies
- In what cases can a subsidy to an institution be reduced?
SUBSIDIES FOR OTHER PURPOSES
Transfer targeted subsidies to institutions on the basis of a contract or agreement. To authorize expenses, approve information on subsidies for each institution (f. 0501016). After using the grant, the institution will provide an expense report. Unused balance and inappropriate expenses will be returned to the budget.
Transfer subsidies for other purposes to subordinate budgetary institutions according to KVR 612, to autonomous ones - according to KVR 622. Depending on the purpose of the subsidy, use KOSGU codes 241 and 281. In accounting, reflect the LBO for subsidies, obligations assumed to institutions, as well as settlements with them for the transfer of subsidies and return of balances.
If the deadline for the subsidy report falls on the next year, the institution will submit a Notice (f. 0504805) in December of the reporting year. This is necessary to reflect interrelated settlement entries in the accounting of the founder and the institution.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for subsidies for other purposes
- How to provide a targeted subsidy to a budgetary or autonomous institution
- How to check and approve Information on transactions with targeted subsidies (f. 0501016)
- KVR and KOSGU for targeted subsidies to subordinate institutions
- KVR and KOSGU for subsidies to non-subordinate institutions
- Postings for targeted subsidies and return of balances
- When institutions must submit a Notice (f. 0504805)
GRANTS IN THE FORM OF SUBSIDS
Provide grants based on the results of a competition between institutions. The basis is an agreement concluded with the winner.
Transfer grants in the form of subsidies to budgetary institutions according to KVR 613, to autonomous ones - according to KVR 623. Depending on the purpose of the grant, use KOSGU codes 241 and 281. In accounting, reflect the LBO for subsidies, obligations assumed to institutions, as well as settlements with them for the transfer of subsidies. The postings are the same as for targeted subsidies.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for grants
- KVR and KOSGU for grants in the form of subsidies
- Postings for grants and targeted subsidies
- When institutions must submit a Notice (f. 0504805)
CAPITAL INVESTMENT SUBSIDIES
Provide subsidies for capital investments on the basis of an agreement. If, after the purchase or construction of real estate, the institution has an unused balance of the subsidy, the institution will return it to the budget. To authorize capital investment costs, approve information on subsidies for each institution (f. 0501016).
Reflect subsidies according to CVR group 410. Apply KOSGU depending on the economic content of expenses - 222, 224, 226, 296, 310, 330, 340, etc. In accounting, reflect LBO for subsidies, obligations assumed to institutions, settlements with them for subsidies, as well as the OCI indicator in the account 204.33.
If the deadline for the subsidy report falls on the next year, the institution will submit a Notice (f. 0504805) in December of the reporting year. This is necessary to reflect interrelated settlement entries in the accounting of the founder and the institution.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for subsidies for capital investments
- How to conclude a capital investment subsidy agreement with an institution
- KVR and KOSGU for subsidies for capital investments
- Entries for capital investment subsidies
- Is it necessary to certify Information on transactions with targeted subsidies (f. 0501016) for subsidies for capital investments
- How to check and approve Information (f. 0501016)
- When institutions must submit a Notice (f. 0504805)
BUDGET REPORTING
Settlements with subordinate institutions for subsidies and grants should be reflected in the Debt Information (f. 0503169). Reflect obligations for subsidies and grants in the Report (f. 0503128). Reflect the return of subsidies from previous years from institutions in the Cash Flow Report (f. 0503123) and the Budget Execution Report (f. 0503127).
More on the topic
All clarifications on reporting
- How to reflect in the Information (f. 0503169) settlements with institutions for subsidies
- The procedure for filling out the Report on Budget Obligations (f. 0503128)
- How to reflect the return of subsidies from previous years in the Report (f. 0503123)
- How to reflect the return of subsidies from previous years in the Report (f. 0503127)
Grants accounting
One of the sources of replenishment of working capital of enterprises can be grants. National accounting standards use a similar concept - targeted financing. Let's consider the procedure for accounting for types of targeted financing from its recipients.
Grants concept
Grant is a free subsidy to enterprises in cash or in kind for scientific or other research, development work and other purposes, with subsequent reporting on their use.
In national accounting standards, the concept of “grant” corresponds to the concept of “targeted financing”. The basic principles of accounting for the operation to receive it are set out in paragraphs 16–19 of P(S)BU 15 “Income” and Instruction No. 291.
These standards contain the following classification of target financing:
- funds released from taxation due to the provision of income tax benefits;
- targeted financing of capital investments;
- targeted financing to compensate for expenses (losses) incurred by the enterprise;
- financing to provide support to an enterprise without establishing conditions for its expenditure on the implementation of certain activities in the future.
Targeted financing can come as subsidies, allocations from the budget and extra-budgetary funds, targeted contributions from individuals and legal entities, etc.
General accounting rules
Targeted financing is not recognized as income until there is confirmation that it will be received and the company fulfills the conditions of this financing.
Targeted financing is accounted for in account 48 using the appropriate subaccounts depending on the type of financing:
- 481 “Funds released from taxation”;
- 482 “Funds from the budget and state trust funds”;
- 484 “Other means of targeted financing and targeted revenues.”
On the credit side, account 48 reflects funds intended for special purposes intended to finance certain activities, on the debit side - amounts used in certain areas, recognizing them as income, as well as the return of unused amounts.
Let's consider how types of targeted financing are reflected in accounting.
Funds released from taxation due to the provision of income tax benefits
Income tax.
Currently, the list of such benefits is small - these are income tax benefits provided by:
- enterprises founded by public organizations of disabled people from certain types of activities (clause 142.1 of the Tax Code);
- Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant and enterprises participating in the liquidation of the Chernobyl accident (again, subject to the fulfillment of the relevant conditions of clauses 142.2, 142.3 of the Tax Code);
- income tax benefits for enterprises - aircraft manufacturing entities engaged in the development and/or production and final assembly of aircraft and engines for them (under the terms of clause 41, subsection 4, section XX of the Tax Code). The Tax Code provisions provide for liability for the misuse of funds exempt from taxation. The use of such funds must be related to the activities of the taxpayer, the profits from which are exempt from taxation.
As for the benefits for enterprises of disabled people (clause 142.1 of the Tax Code), the directions for using state assistance received in the form of tax benefits (i.e.
intended use of the released funds) are given in the appendix to the Application of a public organization of disabled people for granting an enterprise, organization founded by public organizations of disabled people, permission to use tax benefits (its form is approved by Order No. 545).
The amounts of released funds are recognized in accounting as received target financing in accordance with national accounting standards (clause 41, subsection 4, section XX of the Tax Code).
Accounting . Amounts of target financing received (including funds exempt from taxation in connection with the provision of income tax benefits) are recognized as income during those periods in which expenses were incurred to fulfill the conditions of target financing (clause 17 P(C) BU 15).
These funds are accounted for in a subaccount 481.
EXAMPLE 1 An enterprise founded by a public organization of disabled people, as a result of applying income tax benefits (clause 142.1 of the Tax Code), received funds exempt from taxation in the amount of UAH 5,000. and sent them to charity assistance for disabled workers.
Accounting for these transactions will be as follows:
(UAH)
Printable table available on the page: https://uteka.ua/tables/32620-0
| No. | operations | Source documents | Accounting | ||
| Dt | CT | Sum | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| 1 | Accrued tax liabilities for income tax | Tax return for corporate income tax* | 98 | 641/income tax | 5 000 |
| 2 | The amount of funds exempted from taxation is reflected as part of targeted financing | Not issued | 641/income tax | 481 | 5 000 |
| 3 | Charitable assistance provided to disabled employees (transferred to card accounts) | Order for the issuance of charitable assistance, bank statement | 977 | 311 | 5 000 |
| 4 | Income is recognized in the amount of expenses for providing charitable assistance to disabled employees | Not issued | 481 | 719 | 5 000 |
Targeted financing of capital investments
Accounting . Amounts of targeted financing of capital investments are recognized as income during the period of useful use of the relevant investment objects: fixed assets (hereinafter referred to as fixed assets), intangible assets, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Aohn9pNFlLs
Initially, the entire amount of target financing received is credited to account 69 “Deferred income”. Income from such financing is determined in an amount proportional to the amount of depreciation of non-current assets, simultaneously with its accrual, and is reflected in the accounting entry Dt 69 - Kt 745 “Income from freely received assets.”
At the same time, non-current assets acquired through targeted financing are taken into account in the general manner, since they are not considered received for free. In particular, the fixed asset is credited to the balance sheet at its original cost (it is determined in accordance with clause 7 of P(S)BU 7), as well as an intangible asset acquired at the expense of this source (the initial cost is determined in accordance with clause 10 of P(S)BU 8) .
Depreciation in accounting is calculated in accordance with clauses 22–30 P(S)BU 7, clauses 25–31 P(S)BU 8.
The most common way to obtain targeted financing for capital investments is capital transfers (budget classification code 3210 in accordance with clause 1.5 of Instruction No. 333).
These are gratuitous unilateral payments by governing bodies that do not lead to the emergence or settlement of financial claims.
They are intended to purchase capital assets, compensate for losses associated with damage to fixed assets, or increase the capital of recipients of budget funds.
This category also includes transfer payments to enterprises to cover losses that they have accumulated over a number of years or that arose as a result of extraordinary circumstances.
Capital transfers are considered gratuitous, non-refundable payments that are one-time and irregular in nature for both the supplier (donor) and their recipient (beneficiary).
Funds allocated from the budget as capital transfers have a designated purpose (clause 1.6 of Instruction No. 333).
Income tax.
Section III of the Tax Code does not provide for adjustments to pre-tax financial results for differences in the form of capital transfers received from the budget for the purchase of fixed assets for use in business activities. These transactions are reflected according to the accounting rules when generating financial results (letter of the State Fiscal Service of Ukraine dated December 23, 2016 No. 22319/5/99-99-15-03-02-16, hereinafter referred to as Letter No. 22319).
Source: https://uteka.ua/publication/commerce-12-xozyajstvennye-operacii-9-uchet-grantov
Procedure for document flow when receiving a grant
Grants are issued by the Government, the President of the Russian Federation, private foundations, including organizations of foreign origin. Grant requirements are determined by the funding source. Grants issued by government agencies are aimed at supporting young scientists, developing science, research and institutions.
Grants are issued primarily on a competitive basis. An agreement is drawn up for the subsidy - the main document regulating the implementation of the project. The document states:
- Details and addresses of the parties.
- Subject of the agreement, rights and obligations of the parties.
- Procedure for presenting funds.
- Detailed description of the assignment and scientific tasks.
- Plan of work stages.
- Estimate calculated for each stage.
The appendix to the document contains agreements with persons involved in the practical implementation of the project.
Accounting for subsidies in accounting
Receiving subsidies, i.e. Targeted government assistance is today a popular form of business support for the implementation of government programs or compensation for lost income to companies. Let's learn how to reflect subsidies in accounting.
Reflection of subsidies in accounting
The definition of a subsidy as targeted assistance (PBU 13/2000) is the main condition for the application of account 86 “Targeted financing”. It is on it that amounts are accumulated, united under the single term “subsidies” - revenues are taken into account, the use of funds for their intended purpose is controlled, and unused amounts are returned.
A company can record the receipt of a subsidy in two ways:
- Having recorded the budget debt in the debit of the account at the time of signing the agreement on the provision of subsidies. 76, and upon receiving a subsidy - by crediting it:
D/t 76 K/t 86 – for the amount of the proposed subsidy;
D/t 51 (08, 10) K/t 76 – for the receipt of funds, investments, goods and materials, property, etc. within the framework of a targeted subsidy agreement;
- Upon receipt of funds:
D/t 08, 10, 51 K/t 86 – for the amount of the subsidy.
If subsidized funds are used to finance costs incurred in previous reporting periods, then subsidies are accounted for in accounting in the structure of other income:
D/t 76 K/t 91/1 - for the amount of budget debt;
D/t 51 K/t 76 – for the amount of the received subsidy.
The procedure for accounting for budgetary assistance for capital investments (clause 9 of PBU 13/2000) provides for the reflection of subsidized amounts as part of future income. By posting D/t 86 K/t 98, the subsidy amounts are written off from the account. 86 at the time of putting the OS or intangible equipment into operation.
During the useful life (USI) of depreciable assets or during the period of recognition of expenses associated with fulfilling the conditions for providing a subsidy for the acquisition of non-depreciable property, funds from the account.
98 are written off evenly (or in the amount of depreciation accrued per month) to the financial results of the company as non-operating income.
Return of subsidies
An important feature of the use of subsidy funds is the company’s obligation to spend them strictly for their intended purpose, strictly observing the agreed terms of provision.
The legislation does not provide for any alternative options; if it is impossible to implement projects for which a budget subsidy was received, the funds received will have to be returned.
The return of the subsidy is carried out depending on the method of recording the funds received and the moment the obligation to return the funds arises.
If the subsidy is returned in the year of its receipt, then the company only needs to reverse the entries that accompanied its receipt (except for D/t 51 K/t 76) and use. At the time of actual transfer of the returned subsidy, a reverse accounting entry is made - D/t 76 K/t 51.
Refunds of subsidies received in previous years are processed as follows:
| Operations | D/t | K/t |
| By capital investment | ||
| The debt to repay the subsidy is reflected | 86 | 76 |
| Subsidy funds were restored in the amount of accrued depreciation | 91/2 | 86 |
| The subsidy amount has been restored | 98/2 | 86 |
| At current costs | ||
| Debt to repay previously provided subsidies | 86 | 76 |
| The amount of the subsidy was restored to the amount of actual expenses incurred. | 91/2 | 86 |
Subsidy in accounting: postings in examples
Due to the subsidy allocated by Stroyka LLC, in January 2021 the company acquired a plot of land for development worth RUB 3,500,000. According to the concluded agreement, the construction of the house will continue from February 1, 2022 to July 30, 2022 - 18 months. Accounting for the subsidy in the company’s accounting will be reflected in the following entries:
| Operations | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| Budget funds credited | 51 | 86 | 3 500 000 |
| The cost of the site is reflected in the company’s capital investment structure | 08 | 60 | 3 500 000 |
| The site has been registered | 01 | 08 | 3 500 000 |
| Reflection of subsidies in the accounting of deferred income | 86 | 98/2 | 3 500 000 |
| Monthly write-off of a share of the subsidy amount into non-operating income (3,500,000 / 18 months) for non-depreciable property, such as a land plot | 98/2 | 91/1 | 194 444 |
In May 2022, Radon LLC purchased a set of equipment as part of the state support program in the amount of 560,000 rubles. The monthly depreciation of the complex amounted to 4,666.67 rubles. (560,000 / 10 / 12 months), it was accrued from June 2022 to May 2022 - 12 months.
A year later (in May 2021), an audit revealed a violation of the intended use of the allocated subsidy, and the subsidy was returned to the budget on the basis of a drawn up act. The accountant recorded the transactions with the following entries:
| Operations | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| Subsidy repayment debt | 86 | 76 | 560 000 |
| The amount of depreciation is taken into account as part of deferred income (4666.67 x 12) | 98/2 | 91/1 | 56 000 |
| Subsidy funds were restored in the amount of accrued depreciation (4666.67 x 12) | 91/1 | 86 | 56 000 |
| The subsidy amount has been restored (560,000 – 56,000) | 98/2 | 86 | 504 000 |
| The subsidy is transferred to the budget | 76 | 51 | 560 000 |
Taxation of subsidies
Accounting for state aid when calculating income tax depends on the recognition of the subsidy as targeted financing for profit tax purposes (clause 14, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, for commercial companies, subsidies aimed at financing the overhaul of apartment buildings and common property in them are recognized as targeted.
The company has the right not to include such subsidies in taxable income, but subject to mandatory conditions, such as:
- maintaining separate records of income and expenses for target operations;
- use of subsidized funds for specified purposes.
Payment of budget assistance in other cases is not recognized as a target, and, therefore, commercial companies do not have the right to exclude it from taxable income. Those. subsidies are taken into account when calculating income tax as part of non-operating income. The date of their recognition will be considered the date of receipt of funds into the account (clause 2, clause 4, article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Source: https://spmag.ru/articles/uchet-subsidiy-v-buhgalterskom-uchete
Accounting in institutions
Select the section you need from the list.
| Subsidies for government tasks | Subsidies for other purposes |
| Grants in the form of subsidies | Subsidies for capital investments |
| Financial statements | Borrowing subsidies |
SUBSIDIES FOR GOVERNMENT ASSIGNMENTS
Reflect the subsidy in accounting based on an agreement with the founder. If you do not complete the task or do not complete it in full, return the remainder of the subsidy to the budget. The amount of the return will be determined by the founder based on the state assignment report.
Reflect subsidies using analytics code 130 and KOSGU code 131. Reflect calculations on account 205.31 “Calculations for income from the provision of paid services (work)” according to KFO 4.
If the deadline for the report on the state task falls on the next year, give the founder a Notice (f. 0504805) in December of the reporting year. This is necessary to reflect interrelated settlement entries in the accounting of the founder and the institution.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for subsidies for government tasks
- Analytics and KOSGU codes for subsidies for government tasks
- Accounting for subsidies for government tasks
- Accounting for the return of subsidies for government tasks to the budget
- Typical transactions for subsidies
- How to submit a report on the use of subsidies for government tasks
- In what case should the remaining subsidies for government tasks be returned to the budget?
- For what purposes should savings from government subsidies be used?
- Is it possible to pay off last year’s creditor using a subsidy for the current year’s government task?
- When to generate a Notice (f. 0504805) regarding subsidies
- Example of a Notice (f. 0504805) to the founder about closing settlements for subsidies
- How to reflect the purchase of a fixed asset from two sources: subsidies and paid activities
SUBSIDIES FOR OTHER PURPOSES
Reflect targeted subsidies in accounting based on a contract or agreement. To authorize expenses, provide information about subsidies to TOFK (f. 0501016). After using the subsidy, provide the founder with an expense report. Return unused balances and non-target expenses to the budget.
Reflect subsidies using analytics code 150. Depending on the purpose of the subsidy, use KOSGU codes 152 and 162. Reflect calculations using KFO 5 on accounts 205.52 and 205.62.
If the subsidy report is due in the next year, give the founder a Notice (f. 0504805) in December of the reporting year. This is necessary to reflect interrelated settlement entries in the accounting of the founder and the institution.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for subsidies for other purposes
- Analytics and KOSGU codes for targeted subsidies
- Accounting for targeted subsidies
- Accounting for the return of balances of targeted subsidies to the budget
- How to reflect in accounting the return of a targeted subsidy due to paid activities
- Typical entries for subsidies
- How to submit a report on subsidies for other purposes
- When to return unused balances of targeted subsidies to the budget
- Which BCC should I use to return the remaining subsidy?
- When can subsidy savings be used for other purposes?
- When to generate a Notice (f. 0504805) regarding subsidies
- How to generate Information on transactions with targeted subsidies (f. 0501016)
GRANTS IN THE FORM OF SUBSIDS
Grants will be provided if you win a competition between institutions. The basis is an agreement concluded with the government agency that organizes the competition.
Reflect grants in the form of subsidies using analytics code 150. Depending on the purpose of the grant, use KOSGU codes 152 and 162. Reflect calculations using KFO 5 on accounts 205.52 and 205.62. The postings are the same as for targeted subsidies.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for grants
- Analytics and KOSGU codes for grants in the form of subsidies
- Accounting for grants in the form of subsidies
- Typical entries for subsidies
- Should I take into account bonuses accrued from the grant when calculating vacation pay?
CAPITAL INVESTMENT SUBSIDIES
Subsidies for capital investments should be reflected in accounting based on the agreement. To authorize expenses, provide information about subsidies to TOFK (f. 0501016). After using the subsidy, register the property and provide the founder with a report on expenses. Return unused balances and non-target expenses to the budget.
Grants in the form of subsidies are carried out using analytics code 150 and KOSGU code 162. Calculations are reflected in account 205.62 “Calculations for capital receipts to budgetary and autonomous institutions from the public administration sector” according to KFO 6.
If the subsidy report is due in the next year, give the founder a Notice (f. 0504805) in December of the reporting year. This is necessary to reflect interrelated settlement entries in the accounting of the founder and the institution.
More on the topic
All clarifications on accounting for subsidies for capital investments
- Analytics and KOSGU codes for subsidies for capital investments
- Accounting for capital investment subsidies
- Accounting for capital investment objects
- Accounting for the return to the budget of balances of subsidies for capital investments
- Typical entries for subsidies
- How to submit a capital investment subsidy report
- How to return the balance of the subsidy for capital investments to the budget
- Which BCC should I use to return the remaining subsidy?
- Should I compile Information (f. 0501016) on subsidies for capital investments?
- When to generate a Notice (f. 0504805) regarding subsidies
- How to generate Information on transactions with subsidies (f. 0501016)
- How to transfer capital investments due to subsidies under KFO 6 into property under KFO 4
BORROWING SUBSIDIES
When there is a temporary shortage of money for one type of financial support, institutions borrow their own funds internally from other sources. There are three options for institutions to use money:
1. Within one personal account. For example, when there is not enough subsidy for a government task to pay a creditor under KFO 4, you can use funds at temporary disposal under KFO 3.
2. From another personal account. For example, before the targeted subsidy under KFO 5 is received in a separate personal account, the creditor can be paid through paid activities under KFO 2 from another personal account. Budgetary institutions were granted this right in 2022. More details>>
3. Within the total cash balance in the cash register.
More on the topic
All clarifications on borrowing subsidies
- How to borrow internally before the targeted coronavirus subsidy arrives
- Which entries should reflect the borrowing within the total balance - on the personal account or at the cash desk between KFO 2, 3 and 4
- What transactions should be used to reflect borrowing between different personal accounts - according to KFO 5 and KFO 2, 4
- Is it possible to carry out internal borrowing of government funds under KFO 4
- Is it possible to borrow money from other sources if the founder transfers the subsidy for other purposes late?
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Reflect unused balances of subsidies in the Balance Sheet (f. 0503730) in the lines for accounts 205.00 and 201.11. If you return balances to the budget, reflect the transactions in the Report on the Execution of the FHD Plan (f. 0503737) and in the Cash Flow Report (f. 0503723). Disclose information about activities financed by targeted subsidies in the Information (f. 0503766).
More on the topic
All clarifications on reporting
- How to reflect the balance of the targeted subsidy in the Balance Sheet (f. 0503730)
- How to reflect the return of the balance of last year’s subsidy to the budget in the Report (f. 0503737)
- How to reflect the return of the balance of last year’s subsidy to the budget in the Report (f. 0503723)
- How to compile Information on the implementation of activities within the framework of subsidies for other purposes and for capital investment purposes (f. 0503766)
Accounting entries when receiving a subsidy grant for the creation of socially significant programs
Purpose of subsidies A subsidy is a government subsidy. It is designed to help a legal entity or individual entrepreneur solve one of the financial issues:
- cover part of the business expenses;
- reimburse part of past losses;
- compensate for part of the lost profits.
The state provides subsidies in 2 main ways:
- Pricing regulation - with this money, the authorities help entrepreneurs somewhat compensate for the costs that have increased due to the rise in prices of raw materials, fuel, energy, etc.
- Socio-economic programs - in order to promote economic growth and development, the state subsidizes production and enterprises that are significant from a social point of view.
REFERENCE! State-owned enterprises, as well as commercial and non-profit organizations can count on subsidies from the state.
If at the end of the second tax period not the entire amount of the subsidy has been spent, then the difference between the subsidy received and the subsidy recognized will have to be recognized as income at the end of the second year.
5 tbsp. 346.5, paragraph 1 of Art. 346.17). With the simplified tax system, this procedure applies both to the object “income minus expenses” and to the object “Income”. But at the same time, organizations must keep records of the subsidy amounts spent.
Expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets are taken into account as expenses when determining the tax base from the moment these objects are put into operation during the tax period in equal shares on the last day of the reporting (tax period) in the amount of paid amounts. Expenses to pay the cost of goods purchased for further sale are taken into account for tax purposes (under the simplified tax system) on the date of sale of the goods. The object of UTII taxation is imputed income.
Rules for accounting for grants under the usn, eskhn, examples of postings, taxes
Source: Glavbukh magazine The State Program for the Development of Agriculture and Regulation of Markets for Agricultural Products, Raw Materials and Food for 2013–2021, approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 14, 2012, is aimed at creating the necessary conditions for conducting agricultural activities.
No. 717. It provides for measures designed to help farms ensure the renewal of fixed assets, planting and caring for perennial plantings, increasing soil fertility, etc. At the same time, as practice shows, state support in the form of subsidies can be provided to agricultural organizations to compensate for losses or costs .
Reflection of the cost of the site as part of capital investments RUB 5,670,000. contract for the sale and purchase of a land plot 01 08 Acceptance of a land plot for registration RUB 5,670,000. land purchase and sale agreement 86 98/2 Reflection of the subsidy amount as part of deferred income RUB 5,670,000.
agreement on the provision of subsidies 98/2 91/1 Monthly accounting of state assistance as part of other income (5,670,000 rubles: 11 months) 515,455 rubles.
agreement on the provision of a subsidy Financing of work on the maintenance of property in apartment buildings The management organization "Monolit" received funds to pay for work on the repair and maintenance of property in an apartment building (RUB 4,740,000):
- RUB 2,320,000 — materials;
- RUB 2,420,000 - workers' wages.
What changed
Government agencies received another reason to transfer subsidies. Budgetary institutions can reimburse their expenses for COVID-19 from targeted funds. They were also allowed not to cut expenses if the state task was not fulfilled due to the pandemic. In addition, both budgetary and autonomous institutions keep accounting for subsidies according to the new rules.
New for authorities. Regional government agencies can transfer subsidies to non-subordinate budgetary and autonomous institutions. This applies to targeted subsidies to prevent the deterioration of the economic situation, as well as to prevent and eliminate the consequences of coronavirus. The new rules are in force from April 1, 2022 (Part 9 of Article 2.1 of the Law of November 12, 2019 No. 367-FZ). Read the recommendations on which KVR and KOSGU to transfer subsidies to non-subordinate institutions.
New for Federal Agencies . Institutions that have suffered due to the coronavirus pandemic can spend government funds on priority expenses, regardless of the volume of government services provided. The remaining subsidies do not need to be returned, but rather pay salaries, transfer taxes, contributions, pay for utilities, protective equipment and disinfection. The new rules are effective from May 23, 2022. More details>>
In addition, targeted subsidies can be used to reimburse such expenses, including those paid through paid activities. Budgetary institutions were given the right to borrow money from other sources before receiving the targeted subsidy. The new rules will come into force on July 23, 2022. More details>> Previously, only autonomous institutions could borrow against targeted subsidies. Read the recommendations on how to carry out internal borrowing before the targeted coronavirus subsidy arrives.
New for all budgetary and autonomous institutions. From January 1, 2022, institutions reflect subsidies using new analytics codes, and also use the GHS “Revenue” in accounting. Compare the 2022 and 2022 analysis codes for all subsidies in the table.
| Type of subsidy | 2020 | 2019 |
| Subsidy for other current purposes Subsidy for other capital purposes Subsidies for capital investments | 150 “Gratuitary cash receipts” | 180 “Other income” |
| (Clause 12.1.5 of the Procedure for applying BCC No. 85n) | (Clause 12.1.7 of the Procedure for applying BCC No. 132n) |
Income from subsidies for government tasks of the institution is classified as income from sales. Reflect these incomes in accounting:
- on the day of signing the subsidy agreement - as part of deferred income;
- on the day when the state task was fulfilled - as part of current income.
Grants and targeted subsidies are classified as income from non-exchange transactions. Reflect them:
- in deferred income – on the day the agreement is signed;
- in the income of the current period - as the terms of the agreement are fulfilled.
Read in more detail when to recognize subsidies for government tasks, grants and targeted subsidies according to the GHS “Revenues”. The Ministry of Finance provided recommendations for accounting for subsidies in a letter dated 02/04/2020 No. 02-06-07/6939. Download standard entries for accounting for subsidies for budgetary and autonomous institutions.
Grant income and expenses
– Business Law – Grant Income and Expenses
Government of the Russian Federation.
Currently, interested federal executive authorities are working to compile and approve a list of Russian organizations whose grants (gratuitous assistance) provided to taxpayers to support science, education, culture and art in the Russian Federation are exempt from personal income tax (hereinafter - List). When determining the conditions under which a Russian organization can qualify for inclusion in the List, it should be assumed that the Russian organization must necessarily have the status of a non-profit organization; grants must be provided for the implementation of specific programs in the field of science, education, art, culture, and environmental protection , as well as for conducting specific scientific research.
- Dt 76 Kt 86 = 1,000,000 – for the amount of the grant to be received;
- Dt 51 Kt 76 = 1,000,000 – grant funds received;
- Dt 60 Kt 51 = 499500 – transferred to the supplier for materials included in the estimate;
- Dt 10 Kt 60 = 423305 – materials are capitalized;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 = 76195 – VAT on inventory items;
- Dt 20 Kt 10 = 423305 – materials were used for repairs within the budget of the grant;
- Dt 20 Kt 70, 69 = 500500 – wages, unified social tax, insurance contributions to employees for work included in the estimate have been accrued;
- Dt 86 Kt 19 = 76195 = VAT write-off on grant materials;
- Dt 98 Kt 91/1 = 923805 - the cost of work is included in other income.
In the currency of a foreign state Funds from foreign grantors may come in the currency of other states. Such receipts must be converted into rubles in accordance with PBU 3/200.
Fund selection
To receive a grant, you need to choose a suitable fund: the approval of the project depends on this. When choosing a fund, consider:
- goals and objectives that the foundation sets for itself;
- areas of work - what projects are financed: protection of rights, health care, education, science and research, ecology and others;
- preferred programs - what format of events are supported: educational, expeditionary, publishing activities, organization of conferences, etc.;
- regionality – in which territories the fund provides subsidies and financing.
Select a fund that is similar in nature of work, requirements, goals and objectives of this NPO. Grant-giving foundations finance projects in accordance with priority areas of activity.
How can a commercial organization take into account a received grant?
Issue dated December 17, 2010 At the end of the year, the grantor who transferred funds to an individual submits a report on income tax f.2-NDFL to the tax authorities. article: → “Why do you need a 2-NDFL certificate? How to fill out the form."
Reporting on grants at the enterprise The grantor has the right to demand a report on the expenditure of funds allocated by him and compliance with its estimate. Moreover, he may require such reports not only upon completion of the target program, but also at its various stages. The legislation does not establish any form of reporting as such.
Therefore, it is drawn up in free form, agreed upon between the parties.
What is a grant and in what account is it reflected upon receipt?
Receiving a grant is no exception.
To reflect the receipt and expenditure of funds received as a grant, the grant recipient can use both unified forms of documents and those developed by the enterprise independently, subject to their approval and consolidation in the accounting policy. The procedure for documenting operations for the movement of funds under a grant is established by the local regulations of the grant recipient.
Grants: what they are, what they are spent on
Grants are usually understood as funds in monetary and non-monetary forms that are allocated by individuals, domestic and foreign legal entities in the manner prescribed by law to conduct research or implement specific programs. Grants are usually awarded on a competitive basis. The procedure for their receipt and issuance is established by regulatory and legislative acts.
Funds received in the form of grants can be spent in accordance with the budget items that the applicant draws up when submitting an application. When drawing up this document, the amount of expenses necessary to implement the project is calculated and justified, subject to the conditions and restrictions established by legislative acts in this area.
If several grants are received, estimates are developed for each separately.
General concepts of taxation of grants
Targeted financing in the form of grants is not subject to taxation and is not included in the taxable profit or single tax base (clause 14, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Expenses incurred using the funds of the received grant are not taken into account in expenses that reduce the tax base. The article provides the exact concept of a grant, its purpose and organizations providing targeted funds. The conditions for recognizing targeted income as a grant are indicated in the table.
| Sign | Detailed description |
| Grant characteristics | Transfer of funds is free of charge and without refund |
| Limited list of grantors | Individuals, non-profit organizations and foreign companies according to the Government list |
| Types of research areas | Education, art, culture and others listed in paragraphs. 14 clause 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
It follows from the provisions that funds provided by commercial organizations, foundations or aimed at other items not listed in the list cannot be recognized as grants for tax purposes. Earmarked revenues that do not qualify or are not accounted for separately are included in enterprise income.