Conducting any kind of business activity involves the active use of material resources .
During operation, equipment, parts, as well as machines and mechanisms (which are also classified as fixed assets) wear out naturally.
Fixed assets (FPE), the further use of which is not possible or is impractical, are subject to removal from the balance sheet of the enterprise and subsequent capitalization as scrap.
Without these procedures, the transfer of fixed assets for disposal will be illegal and will entail penalties from the fiscal authorities.
If used correctly, scrap ferrous metals can become additional income for an organization.
To do this, it must be written off accordingly, placed in the receipt and sold on favorable terms (including through an auction) to a company engaged in processing scrap ferrous metals. How to capitalize scrap metal from the write-off of fixed assets, and all the intricacies of this process will be discussed below.
Decommissioning of OS
According to clause 33 of the Accounting Regulations of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as PBU), the withdrawal of fixed assets from the company’s assets for their sale as recyclable materials occurs only after they are recognized as unsuitable for further use.
To carry out this procedure, the management of the enterprise creates a specialized commission , which consists of qualified employees of the company.
Responsibilities of the commission:
- Studying the object . Includes a visual inspection of the item, a survey of personnel related to its operation, and testing.
- Establishing the reasons why the element became unusable and the persons potentially involved in this.
- Search for opportunities to partially use an object or its individual parts (assemblies, mechanisms and parts).
- Also, members of the commission must check whether the asset can be sold as a used product, and what its value will be in this case (will it exceed the price of scrap?).
Based on the results of the inspection, an act of the established form is drawn up. The document serves as the basis for disposal of fixed assets.
Today there are three main forms of this paper:
- OS-4 - used for all single objects, except vehicles;
- OS-4a - used to remove motor transport from the balance sheet of an organization;
- OS-4b - relevant when disposing of several objects.
information is entered in the form :
- The nominal value of the asset. It can be restorative or obtained initially.
- Amount of wear . Indicated for the entire service life.
- Expenses that occurred during the dismantling process.
A suitable document is drawn up in two copies. One form is sent to the company’s accounting department, and the second remains with the employee who is financially responsible. This paper, certified by the signatures of the commission and management, serves as the basis for the transfer of property to the warehouse.
If we are talking about transport, it, among other things, must be deregistered with the traffic police , for which a corresponding certificate must be obtained from the inspectorate.
The write-off act is displayed in accounting (hereinafter referred to as BU), in accordance with clause 43 of Methodological Recommendations No. 561, after it is certified by the signature of management.
The corresponding registers of analytical accounting of fixed assets withdrawn from the company's balance sheet are attached to the documents that confirm the facts of their disposal.
Where and how to dispose of fixed assets after write-off?
Writing off fixed assets at an enterprise is a rather complicated procedure. Every time questions arise related to the stage of implementation and the correctness of accounting in the financial statements. Any accountant knows that disposal of fixed assets is the main part of the write-off procedure. The accountant draws up the documents, the commission establishes the validity of the write-off, and after that the OS is dismantled and then transferred for disposal.
Capitalization of scrap metal from write-off of fixed assets
To put scrap on the balance sheet of a company, it is necessary to draw up an act of capitalization of material assets.
Sample act for the receipt of scrap metal :
The document must contain the nominal value of the metal that is included in the balance sheet. Ideally, it is determined based on current LME (London Metal Exchange) quotes, but prices from other official sources are also suitable.
The document specifies the weight of the scrap (at least approximate), its characteristics and indicates the date of its acceptance on the balance sheet.
How to take into account income and expenses when disposing of a fixed asset
Starting from accounting records for 2022, the company must use FAS 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” and FAS 26/2020 “Capital Investments”. The organization independently decides that it applies these standards before the official deadline for their use.
Detailed comments on these standards are available in the information of the Ministry of Finance dated November 3, 2020 No. IS-accounting-28, No. IS-accounting-29.
For example, standard 6/2020 clarifies the rules for displaying transactions for the disposal of fixed assets in accounting:
- when writing off fixed assets, the amount of accumulated depreciation and impairment on it is transferred to reduce its original cost;
- expenses for dismantling, disposal of fixed assets and restoration of the environment are expenses for the period in which they were (if an estimated liability was not previously recognized for them);
- the difference between the book value of the asset being written off and the costs of its disposal, on the one hand, and the proceeds from its disposal, on the other hand, is income or expense in the profit (loss) of the period in which the asset is written off. Accordingly, the financial result upon disposal of an object is indicated in a collapsed manner in the statement of financial results.
As for tax accounting, the residual value of fixed assets upon liquidation and using the linear method of calculating depreciation deductions is taken into account at a time as non-operating expenses (Article 265 of the Tax Code). Loss from the sale of fixed assets is taken into account according to the special rules specified in clause 3 of Art. 268 NK.
Differences in the accounting procedures for losses in accounting and tax accounting lead to temporary differences and the need to recognize deferred tax under PBU 18/02.
Scrap metal accounting and posting examples
The procedure for liquidating fixed assets and accounting for scrap metal in the accounting department is carried out based on paragraphs 29 and 31 of the PBU.
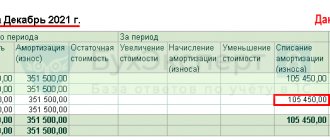
According to this regulatory act, a separate sub-account is opened for account 01. Depreciation accrued during the operating period of the operating system is transferred to its credit their initial cost at which they were taken onto the balance sheet is transferred to debit
After liquidation, the residual value of the object is carried out as operating or other expenses , distributed from an open subaccount to losses and profits (as appropriate). The same applies to liquidation expenses.
If the useful life has expired
Liquidation is carried out upon physical deterioration of the object. This is the most common reason for attrition.
Accounting entries
As an example , we can take a situation where, as a result of the removal from the balance sheet of an enterprise of equipment that was completely depreciated, scrap ferrous metal was formed.
The initial cost of the equipment was forty-five thousand rubles, and the price of the scrap metal obtained was three thousand. During the dismantling process, expenses in the amount of ten thousand rubles were incurred. Of these, seven thousand were staff salaries and three thousand were unified social tax.
In this case, the withdrawal from the balance is displayed like this:
If the useful life has not expired
In this case, the moral obsolescence of the OS or other reasons that make their use impractical can push the enterprise to write it off from the budget. In this case, the initial cost of the property will be higher than depreciation, which entails the formation of a positive balance in the debit of account 01 . It would be correct to write it off to account ninety-one.
In this case, the receipt of scrap metal from the write-off of fixed assets is recorded with the following transactions:
For example , we can take a situation where a company liquidates equipment that initially cost twenty thousand rubles. During operation, its wear and tear amounted to fifteen thousand rubles. Three thousand rubles were spent during the dismantling work, and the materials received were valued at the same amount (three thousand).
The display of such an operation would look like this:
Accounting for the liquidation of fixed assets and the receipt of scrap metal in 1C
This is done as follows:
- From the “Documents” , you need to go to “Asset Accounting” and then to “Asset Write-off”.
- Create a new document and indicate the reason for the write-off (the most common is a breakdown).
- Indicate the name of the organization and the write-off account - 91.02.
- Print the location of the object and the division in which it is registered (relevant for large enterprises).
That's all, the document can be processed. During the posting process, the following account movements are generated:
- Depreciation - Dt 20.01 Kt 02.01.
- Write-off of accrued depreciation - Dt 02.01 Kt 01.09.
- Write-off of the initial cost of the object - Dt 01.09 Kt 01.01.
- Write-off of residual value as expenses - Dt 91.02 Kt 01.09.
The posting of scrap is carried out using the accounting certificate Dt 10 and the subaccount Kt. 91.1, and tax accounting is formed by postings N02.01 and N08. You can clearly see how the write-off occurs in this video:
When using a simplified system, disposal of fixed assets is carried out in the following order:
- An act on disposal of the simplified tax system is drawn up . If one object is written off, form No. OS-4 is used, for several - No. OS-4b is used.
- The base that is subject to taxation for all previous periods upon disposal of fixed assets is recalculated. If the withdrawal occurs before the expiration of a three-year period from the date of placement on the balance sheet, then a penalty in the established amount and the tax base is recalculated for the entire service life of the object.
- In case of disposal due to wear and tear, a commission is created. Complete liquidation is absolutely not reflected in the tax background of the enterprise.
- The amount of the loss is written off, and the profit is classified as non-operating income.
How to write off the OS in 1C-simplified, see this video:
Tax accounting during liquidation of fixed assets, use and sale of scrap metal
According to the norms of paragraph 13 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating income tax, non-operating income should include the cost of materials generated during liquidation. Only those indicated in paragraph 18 of Art. should be excluded from this list. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The moment of income recognition is strictly tied to the method used to calculate income and expenses.
Thus, under the accrual method, the moment of recognition of income will occur on the day when the act of liquidation of the depreciable object is drawn up. And with the cash method - on the day when this object is capitalized.
If the company decides to use the scrap metal generated during liquidation in its production or sell it, the cost of this material is included in material or sales expenses.
NOTE! According to Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the appropriateness of expenses must be justified and documented. If such efforts are not made, tax inspectors will have grounds to exclude these costs from the income tax base and, accordingly, charge an additional amount of this tax.
For information on what changes have appeared in the tax accounting of fixed assets, read the material “Procedure for tax accounting of fixed assets.”
Sales of scrap ferrous metals
Is VAT subject?
Current tax legislation exempts enterprises from paying value added tax when delivering scrap metal only if it was generated during the company's activities.
Written-off fixed assets can be sold to specialized companies without charging VAT by the state.
This type of transaction does not require the seller to have a license for scrap ferrous metals or other permits.
Below is a sample acceptance certificate that can be filled out when selling (purchasing) scrap ferrous metals:
All acts of scrap metal write-off are then entered into the Book of Acceptance and Delivery Acts.
Tenders
Auctions are an effective means of obtaining the maximum possible profit from the sale of scrap ferrous metals obtained as a result of the liquidation of fixed assets. A tender is justified if the object of sale is of significant material value and arouses interest among a potential buyer. For the sake of two tons of scrap metal, this procedure is not worth undertaking.
The auction begins with the preparation of tender documentation . For this purpose, design organizations may be involved. The composition of the document package may vary, but usually it contains the following elements:
- invitation to bidders;
- information about the auction item: in the context of scrap - this is its weight, class, chemical composition, dimensions;
- application forms and instructions to offerors;
- rules and procedure for holding a tender;
- draft agreement with the winner.
Read about the types of ferrous scrap metal here. Do you want to sell scrap at a good price? Find out everything about ferrous metal collection points. You can read about searching and digging for ferrous metal with a metal detector at this link -
Export of ferrous metal scrap
Selling scrap for export is a rather complicated procedure from the point of view of customs legislation. implement it you will need:
- Calculate customs duties.
- Obtain radiation control and explosion safety .
- Create conditions for inspection in the form of a temporary customs control zone.
- Provide the opportunity for inspectors to conduct customs inspections.
- Select samples for testing in the laboratory for chemical composition.
- Prepare an evidence base to confirm the declared value of the goods.
In addition, the following documents will be needed to present to inspectors:
- contract with the buyer; if the amount of the supply agreement is more than fifty thousand dollars, a transaction passport will also be needed;
- constituent documents;
- invoice or invoice;
- waybills - you will need a TTN, CMR or bill of lading depending on the selected type of transportation;
- confirmation of the classification code according to the Commodity Nomenclature of Foreign Economic Activity;
- packing list;
- payment documents confirming payment for goods;
- checks confirming payment of customs duties;
- If there are benefits , their confirmation will also be required.
Contacting a specialized organization that provides customs brokerage services will significantly simplify the registration procedure, but will also require additional costs.
Scrap metal in the hazardous waste classifier
Sales of scrap ferrous and non-ferrous metals
Based on the order of the Ministry of Natural Resources, scrap ferrous and non-ferrous metals belongs to hazard class V. Wastes of this group are considered practically non-hazardous, their impact on the environment is minimal or absent.
At the same time, ferrous metal dust is defined as waste of IV (higher) hazard degree. The degree of impact of waste of this group on the environment is minimal (the recovery period after pollution is up to 3 years).
Receipt of scrap metal in a budget organization
The procedure for removing fixed assets from the balance sheet of a budgetary institution is similar to that in a commercial organization. is also formed , which makes the appropriate decision. But unlike a private enterprise, here the fact of disposal must be thoroughly argued and documented . For this the following can be used:
- expert opinions on the unsuitability of further use of the object;
- certificates from the relevant authorities about the fact of an accident, natural disaster and other precedents that served as the basis for the failure of the OS;
- reports on the nominal value of the asset;
- other papers and forms confirming the unsuitability of the object for further use for its intended purpose.
Unlike private firms, the decision to remove fixed assets from the balance sheet is made by the competent authorities , whose jurisdiction is the enterprise, and not the director (unless the asset was acquired at his expense).
General provisions
A permanent commission for the receipt and disposal of assets created in the institution makes a decision on the write-off of an item of fixed assets due to physical or moral wear and tear and draws up an act on the write-off of an item of fixed assets (except for motor vehicles) (f. 0306003), an act on the write-off of motor vehicles ( f. 0306004).
The write-off of movable and immovable property in federal ownership is regulated by the Regulations approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 14, 2010 No. 834 (hereinafter referred to as Regulation No. 834).
According to paragraphs. “d” , “e” clause 4 of Regulation No. 834 , federal government institutions must coordinate the write-off of real and movable property with the federal government bodies (federal government bodies) under whose jurisdiction they are.
Federal budgetary and autonomous institutions are given independence in making decisions regarding the write-off of movable property (with the exception of especially valuable movable property (hereinafter referred to as VTsDI), assigned to them by the right of operational management or acquired by them at the expense of funds allocated by the founder for the acquisition of such property) ( clause "g" clause 4 of Regulation No. 834 ).
In addition, federal budgetary and autonomous institutions have the right to make an independent decision on the write-off of OCDI, which is under their right of operational management and acquired from funds received from income-generating activities (clause “k”, clause 4 of Regulation No. 834 ).
However, the write-off of real estate (including objects of unfinished construction) and OCDI assigned by the founder to federal budgetary and autonomous institutions with the right of operational management or acquired by them at the expense of funds allocated by the founder for the acquisition of such property, these institutions are required to be coordinated with federal government bodies (federal state bodies) exercising the functions and powers of the founder ( clauses “h” , “and” clause 4 of Regulation No. 834 ).
Within the framework of Regulation No. 834, the Ministry of Culture issued Order No. 957 , which approved the Procedure for approving the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation of a decision on the write-off of especially valuable movable property, as well as federal real estate (including objects of unfinished construction) assigned to organizations subordinate to the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation on the basis of economic rights conducting or operational management .
The list of documents required to make a decision on the write-off of federal property, including real estate (including objects of unfinished construction) and especially valuable movable property assigned to organizations subordinate to the Ministry of Culture with the right of economic management or operational management, was approved by Order of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation dated October 3, 2011 No. 956 .
As a result, the write-off act drawn up by the commission is approved by the head of the institution either independently or after agreement with the federal government body (federal state body) under whose jurisdiction it is located.
Upon completion of the procedure for approving the write-off of the property and approval of the act, it is subject to dismantling.