Regulatory framework and definition of leasing
Let's look at how to make transactions when leasing , but first let's determine what laws govern this operation. Leasing is a financial lease and is described in paragraph 6 of Chapter. 34 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, and is also regulated by the Law “On Financial Leases” dated October 29, 1998 No. 164-FZ. Accounting for leasing transactions is carried out in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia “On the reflection in accounting of transactions under a leasing agreement” dated February 17, 1997 No. 15.
ATTENTION! Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 02/17/1997 No. 15 loses force as of 01/01/2022. Starting from this period, leasing accounting transactions must be taken into account in accordance with FAS 25/2018 “Lease Accounting”, approved. by order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 16, 2018. The standard can be applied earlier by registering this fact in the enterprise’s accounting policies.
To briefly describe the essence of leasing, one party to the transaction (the lessor) buys property from an agreed seller for the second party to the transaction (the lessee) and receives money for this service, transferring the property into the possession of the lessee for a certain period. After this period, the property can be purchased by the lessee.
The specified property is in the possession of the lessor and is recorded on its balance sheet. However, the terms of the leasing agreement may provide for accounting of the leased property on the balance sheet of the other party to the transaction, that is, the lessee.
An example of calculating a leasing agreement
The total amount of the leasing agreement is RUB 751,500.00, including VAT 20% - RUB 125,250.00. Initial payment (advance payment) - 150,000.00 rubles, including VAT 20% - 25,000.00 rubles. Leasing term - 2 years (24 months + the last month the redemption price is paid), redemption price - 1,500.00 rubles, including VAT 20% - 250 rubles. The monthly payment is (751,500.00 - 1,500 − 150,000.00) / 24 = 25,000.00 rubles, including 20% VAT - 4,166.67 rubles.
Read about what the redemption value of a leased asset is here..
It is worth noting that there is no single standard for a leasing agreement, so the advance payment can also be counted as the first monthly lease payment or towards several monthly lease payments. These conditions must be clearly stated in the leasing agreement.
See also “Car leasing agreement for legal entities”.
In the future, we will use the conditions from this example to describe accounting entries.
Features of the purchase of leased cars
If you want to buy a leased car, first of all you should pay attention to the following important points:
A leased car cannot always be purchased by the founder of a company or another individual
The deal will not take place if, for example, the leasing agreement with purchase was drawn up by the company. In this case, she is the lessee, which means she alone has the right to buy the car. If the leasing agreement, which provides for the possibility of repurchase, states that an individual can buy a leased car directly from the leasing company, such restrictions on the transaction are removed.
The leased vehicle may be subject to return to the leasing company
This is a form of leasing (operational leasing), in which the lessor's client simply uses the property without the right to repurchase in the future. If the leasing agreement does not specify the right of redemption at the end of the leasing term and its conditions, the leased car is returned to the leasing company.
The lessee may assign its rights to the sublessee
Moreover, the subtenant can be either a legal entity or an individual. This means that the lessee, who has rented a car, can, with the consent of the leasing company, assign his rights, both the use of the property and the payment for use.
We also note that the tax authorities very closely monitor the purchase of leased cars by individuals. Often the redemption price of a car is lowered - this is beneficial for the buyer who wants to purchase property, but is fraught with tax consequences. In this, supervisory authorities may see the likelihood that the car was specifically purchased for subsequent purchase by an individual (the founder of the company).
In this case:
- the original client (lessee) may not be reimbursed for VAT and monthly payments under the leasing agreement may not be taken into account as expenses;
- the real cost of the leased car, which will be determined during the trial, will be classified as income and monthly lease payments will be taken into account - this will fall on the individual who buys such a car
These are features that you need to carefully consider before purchasing a car after leasing. If such a transaction is carried out correctly and carefully, it will be feasible and very beneficial to the buyer.
Accounting entries for the lessee, property on the lessee’s balance sheet
Let's consider an example of leasing accounting if the property is on the balance sheet of the lessee and its redemption value is paid separately in the last month of the lease.
In this case, the leasing transactions for the lessee will be as follows:
1. The leased item arrived to the lessee:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Note |
| 08 | 76 “Rental obligations” | 626 250 | Leased property accepted for accounting |
| 19 | 76 “Rental obligations” | 125 250 | Input VAT reflected |
| 01 “Property on lease” | 08 | 626 250 | The leased asset is reflected in the fixed assets |
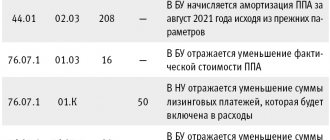
2. From the 1st day following the month of receipt of the leased asset, depreciation is calculated by posting
Dt 20 (23,25,26, etc.) Kt 02 “depreciation of leased property”
Let us assume that the useful life of the leased asset is 60 months. Then the amount of monthly depreciation will be 10,437.50 (626,250 / 60 months).
Transactions for depreciation of fixed assets and options for calculating depreciation can be found here.
3. Since, according to the terms of the example under the leasing agreement, the buyer pays the down payment, the postings will be as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Contents of operation |
| 76 “Rental obligations” | 51 | 150 000 | Payment of the down payment |
| 68 "VAT" | 76.VA | 25 000 | VAT amount on advance |
The VAT amount can be deducted on the received advance invoice, or you can not. In this case, if it is more profitable to defer the VAT deduction, the entries in bold italics do not need to be made.
4. Monthly accounting entries for leasing on the lessee’s balance sheet are as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 76 “Rental obligations” | 76 “Debt on leasing payments” | 25 000 | monthly payment taken into account |
| 76 “Debt on leasing payments” | 51 | 25 000 | monthly payment paid to the lessor |
| 68 "VAT" | 19 | 4 166,67 | accepted for deduction of VAT regarding the leasing payment |
| 76 VA | 68 "VAT" | 1 041,67 | VAT has been restored from the advance payment (25,000 VAT accepted for deduction on the advance invoice / 24 months) |
If VAT on the advance invoice was not accepted for deduction, then the posting in bold italics does not need to be made.
Buying a car after leasing to a legal entity
Purchasing a car by a legal entity after leasing is standard practice. Often, enterprises lease cars for entertainment purposes or with the goal of replenishing/updating their vehicle fleet. After leasing, the cars continue to be in working and usable condition, and businesses buy them back into ownership.
A legal entity can buy the car into ownership either at the end of the leasing agreement, or earlier, if this is provided for in the agreement. The same rules apply here as in the purchase of a car after leasing by an individual: the leasing agreement (or an additional agreement to it) indicates this possibility, and specifies the terms and procedure of the transaction.
To buy the car after leasing, the company makes the final redemption payment. As a rule, it is minimal - the car is depreciated, so this amount is often symbolic. This is the residual value, which can amount to a conventional thousand rubles. After the transaction is completed, the car is transferred from the balance sheet of the leasing company to the balance sheet of the legal entity - the lessee.
Redemption by the lessee of property on its balance sheet
Let's consider the transactions for the redemption of the leased asset.
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 76 “Lease obligations” | 51 “Current accounts” | 1 500 | the redemption value of the leased object is listed |
| 68 "VAT" | 19 | 250 | VAT on the redemption price is deductible |
| 02 “Depreciation of leased property” | 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” | 250 500 | amount of accumulated depreciation (10,437.50 × 24 months) |
| 01 "OS" | 01 “Leased property” | 626 250 | fixed assets transferred from leased to owned |
As already mentioned in the example, there may also be contracts where the redemption amount is not allocated separately, but is included in the monthly lease payments. In this case, a controversial question arises about the date of acceptance of VAT for deduction from the purchase price: is it possible to accept VAT for deduction in full on a monthly basis from leasing payments or is it necessary to accept part of the VAT for deduction only after the purchase of the leased property. Letters from the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 15, 2004 No. 03–04–11/203 and dated November 9, 2005 No. 03–03–04/1/348 indicate that VAT can be deducted in those tax periods in which lease payments are paid . Thus, if the agreement does not highlight the redemption value of the leased asset, the accounting entries for the lease redemption on the lessee’s balance sheet will be similar to the example considered, where the redemption value is highlighted.
Read about the features of tax accounting for leasing agreements in our other article.
About the redemption value in the form of a separate payment
The redemption value can be established in the form of an independent payment transferred by the lessee to the lessor after making all obligatory lease payments, in which it was not included.
When setting a symbolic redemption price in the contract (many lessors set it in an amount not exceeding several thousand rubles), it is worth remembering the position of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, which in its resolution dated July 12, 2011 No. 17389/10 indicated that a low redemption price can be established only if the actual period during which the property is subject to operation coincides with the duration of the leasing agreement. Otherwise, in the opinion of YOU, the transfer of ownership of the property at a very low price (close to zero) is evidence that its real value was included in the monthly lease payments.
In the course of interaction between participants in a leasing transaction, such a situation may have negative consequences for both parties. Thus, the lessor runs the risk of receiving from the lessee a demand for the return of funds allegedly overpaid by him to pay for the redemption price in the event of early termination of the leasing agreement. Lessees will not be able to take into account the depreciation of leased property as expenses incurred, which will entail an increase in the income tax base and, as a consequence, an overall increase in the organization’s costs.
Postings of the lessee, if the property is on the balance sheet of the lessor
Let's consider the same example, but now the leased item is on the lessor's balance sheet.
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 001 "Leased OS" | 751 500 | leased property is registered off balance sheet | |
| 76 “Debt on leasing payments” | 51 | 150 000 | down payment paid |
| 68 | 76.VA | 25 000 | VAT allocated from advance payment |
| 20 (23,25…) | 76 “Debt on leasing payments” | 20 833,33 | monthly payment included in expenses |
| 19 | 76 “Debt on leasing payments) | 4 166,67 | VAT is taken into account regarding the leasing payment |
| 76 “Debt on leasing payments | 51 | 25 000 | advance payment transferred to the lessor |
| 76 VA | 68 "VAT" | 1 041,66 | VAT has been restored from the advance payment |
If the advance invoice issued for prepayment under a leasing agreement does not include VAT for deduction, then the entries in bold italics do not need to be made.
In this case, depreciation is not accrued.
Next is the repurchase of the leased asset (in our case, the initial cost is such that the leased asset can be taken into account as inventory).
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 001 "Leased OS" | 751 500 | leased property was written off off-balance sheet due to the expiration of the leasing agreement | |
| 76 “Rental obligations” | 51 | 1 500 | the purchase price of the leased property is listed |
| 10 "Materials" | 76 “Rental obligations” | 1 250 | leased property was accepted for accounting at redemption value as part of inventory |
| 19 | 76 “Rental obligations” | 250 | VAT included |
| 68 "VAT" | 19 | 250 | VAT on the redemption price is deductible |
Accounting for a leasing agreement with the lessor
Let's look at an example of leasing transactions on the lessor's balance sheet . Let the property purchased for leasing be on the balance sheet of the lessor. Let's take the numbers again from the example above.
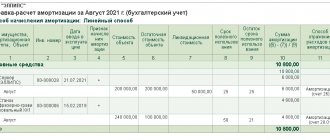
Let's assume that the leased object was purchased by the lessor for 450,000 thousand rubles. (including VAT 75,000). useful life 60 months. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method and amounts to RUB 6,250. ((450,000 - 75,000) / 60 months)
The purchase and commissioning operations are as follows:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | VAT |
| 08 | 60 | 375 000 | OS object received from the supplier |
| 19 | 60 | 75 000 | input VAT reflected |
| 60 | 51 | 450 000 | the object has been paid to the supplier |
| 68 "VAT" | 19 | 75 000 | input VAT is accepted for deduction |
| 03 “Material assets (MT) in the organization” | 08 | 375 000 | OS object is accepted for accounting |
| 03 “MCs transferred for temporary possession” | 03 “MC in the organization” | 375 000 | the equipment is transferred to the lessee |
| 20 (23,25,26…) | 02 | 6 250 | depreciation accrued |
Accounting for leasing payments:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 51 | 62 | 150 000 | an initial payment has been received from the lessee |
| 76 AB | 68 "VAT" | 25 000 | VAT allocated from advance payment |
| 51 | 62 | 25 000 | received monthly payment from the lessee |
| 62 | 90 | 25 000 | revenue is reflected in the amount of the monthly payment |
| 90 "VAT" | 68 "VAT" | 4 166,67 | VAT charged |
| 68 "VAT" | 76 AB | 1 041,67 | VAT refunded on prepayment |
Now let’s consider the process of buying out leased property from the lessor, if he is also the balance holder of this property.
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 51 | 62 | 1 500 | the redemption value of the property was credited to the account |
| 02 | 03 | 150 000 | the amount of accrued depreciation is written off |
| 91 | 03 | 225 000 | the residual value of the leased object was written off (375,000 - 150,000) |
| 62 | 91 | 1 500 | income from the redemption price is taken into account |
| 91 | 68 "VAT" | 250 | VAT is charged on the redemption price |
Let's consider accounting with the lessor if the property is included on the lessee's balance sheet.
Acquisition, payment and commissioning are no different from the case when the lessor is the balance holder.
There is no need to accrue depreciation on the leased asset - based on the terms of the leasing agreement, it must be accrued by the lessee (clause 50 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets). The transfer of the leased object to the lessee is usually reflected in the following order:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Contents of operation |
| 97 | 03 | 375 000 | the leased object is transferred to the balance sheet of the lessee |
| 011 “Assets leased” | 375 000 | the cost of the leased asset is reflected in the off-balance sheet account |
In this case, the costs recorded on account 97 can be recognized as expenses for ordinary activities as income in the form of leasing payments is recognized through a reasonable distribution between reporting periods (for example, in proportion to leasing payments recognized in income) (clause 5, 19 PBU 10/99 “Expenses of the organization”).
The posting in the income generation period will be as follows: Dt 20 (23.25...) Kt 97.
Let's consider accounting for monthly lease payments:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 51 | 62 | 150 000 | an advance has been received |
| 62 | 90 | 150 000 | the advance is recognized in the amount of income |
| 90 "VAT" | 68 "VAT" | 25 000 | VAT charged |
| 20 | 97 | 75 000 | part of the cost of the leased object is recognized as expenses in proportion to recognized income (150,000 × 100 / 750,000 = 20% × 375,000) |
| 51 | 62 | 25 000 | monthly payment has been received into your account |
| 62 | 90 | 25 000 | income is recognized in the amount of the lease payment |
| 90 "VAT" | 68 "VAT" | 4 166,67 | VAT charged |
| 20 | 97 | 12 500 | part of the cost of the leased object is recognized as expenses in proportion to recognized income (25,000 × 100 / 750,000= 3.33% × 375,000) |
The redemption of leased property is registered with the following entries:
| Debit | Credit | Sum | Content |
| 62 | 90 | 1 500 | income is recognized in the amount of the redemption price |
| 90 "VAT" | 68 "VAT" | 250 | VAT charged |
| 20 | 97 | 75 000 | the initial cost of the leased asset not written off at the time of redemption is reflected (12,500 × 24 - 375,000) |
| 51 | 62 | 1 500 | the redemption price of the lease was credited to the account |
| 011 | 375 000 | the leased object is written off balance sheet |
If the redemption value is not separately allocated in the leasing agreement, then the redemption of the leased asset, subject to payment of all payments, is formalized by a single write-off from off-balance sheet account 011 “Fixed assets leased” in the amount of the lessor’s costs excluding VAT.
Leasing: features of tax and accounting for the redemption of leased property
In the Russian Federation, leasing activities are carried out in accordance with Federal Law dated October 29, 1998 N 164-FZ “On financial lease (leasing)”. And in accordance with Article 2 of the mentioned law, leasing means a type of investment activity for the acquisition of property and its transfer on the basis of a leasing agreement to individuals or legal entities for a certain fee, for a certain period and under certain conditions stipulated by the agreement, with the right to purchase the property by the lessee.
The subject of a financial lease agreement can be any non-consumable things used for business activities, except for land plots and other natural objects.
Leasing payments mean the total amount paid by the lessee to the lessor for the right to use the property granted to him - the subject of the agreement. Through leasing payments, the lessor reimburses its financial costs for the purchase of property and makes a profit.
Leasing payments include: depreciation of the leased property for the entire term of the leasing agreement, compensation of the lessor's payment for the borrowed funds used by him, commission to the lessor, payment for additional services of the lessor provided for by the leasing agreement, the cost of the property being redeemed, if the agreement provides for repurchase and the procedure for payment of the specified cost in the form of shares in the leasing payments, the amount of tax on leased property.
On a note
Rental (leasing) payments for rented (leasing) property are considered other expenses associated with production and sales, based on paragraph 10 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, leasing payments are determined by the leasing agreement and are expenses associated with the production and sale of the period in which the obligation to pay them under the terms of the agreement arises, regardless of the date of transfer of the leased asset to the lessee.
In accordance with paragraphs. 10 p. 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, rental (leasing) payments for rented (leasing) property are taken into account when determining the tax base for corporate income tax. If the property received under a leasing agreement is accounted for by the lessee, the lessee's expenses are considered to be rental (leasing) payments minus the amount of depreciation on this property accrued in accordance with Art. Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When classifying leasing payments, depending on the accrual method used, a distinction is made between payments with an advance (deposit), when the lessee first provides the lessor with an advance, before or at the time of signing the leasing agreement, in the established amount, and then, after signing the acceptance certificate of the leased asset into operation, pays, through periodic contributions to the lessor, the total amount of the lease payment minus the amount of the advance (deposit). In practice, leasing companies do not include the advance payment in the income tax base on the basis of paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The leased asset transferred for temporary possession and use to the lessee is the property of the lessor.
When a condition for the purchase of the leased asset is included in the leasing agreement, the parties to the agreement have the right to determine any redemption price of the leased asset. If the leasing agreement provides for the transfer of ownership of the leased asset to the lessee, then the total amount of the lease payment may also include the redemption price of the leased asset. Such an agreement includes elements of a lease agreement and a purchase and sale agreement, which makes it mixed.
Full payment of the redemption price (at the end of the leasing agreement or before this point) serves as the basis for the transfer of ownership of the leased asset to the lessee.
Documentary evidence of the transfer of ownership of the leased asset to the lessee is a leasing agreement, documents confirming payment of the redemption price, and an act of transfer of ownership of the leased asset.
The purchase of property by the lessee can be carried out in the following forms:
Situation one: the redemption price of the property is specified in the leasing agreement and upon expiration of the leasing agreement or before that moment, the lessee pays the redemption price, and, accordingly, the leased asset becomes his property.
The second situation when purchasing property: when the redemption price is not specified in the leasing agreement, but is formalized in a separate agreement, as the Ministry of Finance recommends.
The third situation is the most controversial: when the redemption price is not specified either in the leasing agreement or in a separate agreement on the redemption of property, but it is included in the cost of lease payments paid by the lessee for temporary possession and use of the property.
The Ministry of Finance believes that in this case the entire amount of leasing payments should be considered as an expense aimed at acquiring ownership of the leased asset, which is depreciable property, included in the initial cost of depreciable property after the transfer of ownership of it to the lessee. But he still insists on drawing up an additional agreement to prevent disputes with the tax authorities. But you can still reasonably argue with them on this issue.
The Tax Code states that leasing payments are taken into account as part of other expenses associated with production and sales, in accordance with Art. 264. But regulatory authorities insist that the redemption value and leasing payments are different things, and therefore they must be taken into account separately. Therefore, according to the Ministry of Finance, the lease payment can be classified as other expenses only to the extent that it is paid for receiving the leased asset for temporary possession and use.
In order to satisfy the requirements of the tax authorities, taxpayers often set the minimum redemption price of leasing equipment equal to 1 ruble. The tax authorities' demand is satisfied, but in this action the tax authorities observe a scheme to obtain an unjustified tax benefit.
The validity of the use of certain prices within the framework of a leasing agreement for tax purposes should be established in accordance with the provisions of Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which regulates the principles for determining the price of goods, work or services. At the same time, Article 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain any restrictions regarding the procedure for determining the market price for the repurchase of the leased asset, as well as payments in the form of leasing payments.
However, each taxpayer, when setting the size of the redemption price, must assess the likelihood of recognizing this transaction as controlled in accordance with the provisions of Art. 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, since for controlled transactions there is a risk of additional taxes based on the level of market prices. There is also a risk that the transaction will be considered void. The issue of the legal qualification of a transaction, including a leasing agreement, will be considered in each specific case, taking into account the essence of the transaction and the actual relations arising between its parties.
The Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation indicated that the transfer of the title of owner of the leased asset to the lessee is carried out at a residual price close to zero if the term of the leasing agreement is almost equal to the useful life of the leased property. However, if such a period significantly exceeds the term of the leasing itself, then the expiration of the financial lease period specified in the agreement does not entail complete natural wear and tear of the leased asset and a drop in its current market value to a value close to zero.
Therefore, the establishment in the contract of a symbolic redemption price close to zero means that the actual redemption price was included in the periodic lease payments.
It should be noted that the Federal Tax Service of Russia fully supports the approach of the Ministry of Finance.
At the same time, the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia states the following: if the leasing agreement stipulates that the leased asset becomes the property of the lessee after payment of all leasing payments without indicating the redemption price in the leasing agreement, then the entire amount of leasing payments should be considered as an expense aimed at acquiring ownership of the a leased item, which is depreciable property, included in the initial cost of depreciable property after the transfer of ownership of it to the lessee.
However, the Arbitration Courts categorically do not support the approach of the tax authorities.
On a note
The arbitrators believe that leasing payments are determined by the contract and are an expense of the period in which they are incurred, regardless of the date of transfer of ownership of the leased asset.
Subclause 10, clause 1, art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not make the taxpayer’s right to include the lease payment in expenses dependent on its components. The allocation of the redemption price and its exclusion from expenses made by the tax authority was declared unlawful by the courts.
For example, the Arbitration Court of the Volga-Vyatka District noted that Ch. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish the specifics of attributing to the cost of costs under a leasing agreement, depending on whether it provides for the transfer of ownership of the leased asset to the lessee or not. In both cases, the expenses must include the entire amount of the lease payment. The requirement of the tax authorities to separate the purchase price from the lease payment is not based on the norms of the legislation on income tax.
Similar decisions in favor of taxpayers are made by the courts of other districts: Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated December 20, 2007 N F04-110/2007 (127-A67-14), F04-110/2007 (268-A67-14), FAS Moscow district dated November 26, 2010 N KA-A40/15260-10, FAS Volga District dated February 11, 2010 N A55-3438/2009, FAS Northwestern District dated January 14, 2008 N A56-48233/2006, FAS Ural District dated March 21. 2007 N Ф09-1885/07-С3.
Having analyzed the positions of the Ministry of Finance and the practice of arbitration courts in individual districts, we come to the following conclusion: the lease payment under a leasing agreement is a single payment, regardless of what components it consists of, including the presence of a redemption price in its composition. For the purpose of calculating income tax, leasing payments are expenses associated with production and sales and are subject to accounting in the tax period to which they relate, depending on the method chosen by the taxpayer for recognizing income and expenses.
Thus, there is a need to determine the powers of letters from the Russian Ministry of Finance. Written explanations from the Ministry of Finance are solely for informational and explanatory purposes; they are not officially published, so there is no reason to consider them binding. And the Tax Code, as well as Federal laws and other regulations are official documents that are binding. Therefore, taxpayers should comply only with official documents and should not be afraid to defend their rights in court in disputes arising over different interpretations of laws.
Volvakova Maria Alexandrovna
, 4th year student at Khabarovsk University of Economics and Law, for the website “Bukhgalteriya.ru”
Features of car accounting in leasing
Let's say an organization has leased a car and it is on the balance sheet of the lessee - the transactions in this case are similar to those given above. Also, if the lessor is the balance holder of the leased car, there will be no changes in the postings. That is, a leased car is taken into account for accounting purposes in the same way as other property. The only issue that is added is the payment of transport tax, as well as compulsory MTPL and CASCO insurance.
As a general rule, payment of transport tax is carried out by the person in whose name the car is registered. In the case of a car transferred under a leasing agreement, the condition for paying transport tax is specified in the leasing agreement. The postings are made by the transport tax payer, according to the leasing agreement, regardless of whose balance sheet the leased property is on.
As for the payment of mandatory insurance payments, everything here also depends on the terms of the contract. Most often, payments for compulsory motor liability insurance and comprehensive insurance are included in leasing payments evenly for the entire term of the leasing agreement. But there may be a situation where the lessee pays these payments separately annually or quarterly, independently or through the lessor.
Inclusion of the redemption value in leasing payments
The cost of the acquired property may initially be included in the amount of lease payments transferred to the lessor and distributed evenly between them. According to paragraph 1 of Art. 28 Federal Law No. 164, the leasing payments transferred by the lessor to the lessee include:
- remuneration paid to the lessor;
- costs of acquisition, delivery, installation, maintenance of the purchased leased asset, as well as other additional expenses.
Obviously, the fewer payments the lessee has to make before the lease agreement expires, the lower the redemption price becomes. If he fully repays his existing debt, the redemption value will be reduced to zero. If an additional agreement is concluded before the debt is paid, it must indicate the cost of the leased item, which has already been paid by the lessee by making advance payments throughout the entire term of the agreement, as well as the remaining amount to be paid.
Commission fee under a leasing agreement
Typically, the lessor charges the lessee a fee under the leasing agreement. This includes the preparation and execution of transaction documents. In accounting, this fee should be included in the initial cost of the leased property if the leased asset is on the balance sheet of the lessee. The accounting entries for the commission fee under the leasing agreement from the lessee will be as follows:
If the leased item is on the balance sheet of the lessor, then the lessee makes a commission fee as usual services from the counterparty.
For the lessor, the commission fee is income from ordinary activities or other income and is reflected in the appropriate accounting accounts, regardless of whose balance sheet the leased property will be accounted for.
The procedure for purchasing the leased asset under an additional agreement
To purchase the leased property, the lessee must perform the following actions:
- Notify the lessor of your intention. To do this, a written statement or notification must be sent to him, which must contain:
- Title of the document;
- Full name and position of the person representing the interests of the lessee company;
- name of the lessee company and its legal address;
- details of the main agreement concluded between the parties;
- description of the leased item;
- a request for early repayment of the leasing agreement, as well as justification of the reasons why the applicant made such a decision;
- date of document preparation;
- signature of a person authorized to represent the interests of the company and seal (if any).
- If the lessor does not object to the early repayment of obligations by the lessee, he gives written consent to the conclusion of an additional agreement. agreements.
- The parties form additional an agreement whose provisions govern the procedure for purchasing property.
- A purchase and sale agreement is formed, which allows you to officially register the transfer of ownership of the leased property from one party to the other.
- The lessee is issued an invoice to be paid, or the one for which payments were made is used.
- An act of acceptance and transfer of the subject of the transaction is drawn up.
- All accompanying documentation is transferred to the buyer (provided that it has not been transferred earlier).
***
Leasing accounting is one of the most complex operations in accounting due to the abundance of possible situations and nuances in financial lease agreements. For example, in addition to the cases described, property transferred under a leasing agreement may be non-redeemable, that is, returnable, and can also be purchased ahead of schedule. The article examines the main cases of leasing: accounting of property both on the balance sheet of the lessor and on the balance sheet of the lessee. Possible options for paying the redemption price are described - separately at the end of the leasing agreement or as part of monthly lease payments. An analysis of the transactions for both sides of the transaction is given.
Even more information can be found in the “Accounting” section.
Buying a car after leasing to an individual
A leasing agreement, which provides for the right to buy a car after leasing, is mixed because it contains the terms of both the purchase and sale agreement and the lease agreement. For this reason, it always indicates the amount and procedure for paying the ransom payment.
According to judicial practice, this payment is considered on an individual basis - separately, and not as leasing payments / payments for operating a car. Its size depends on the degree of wear of the machine.
It must be taken into account that the redemption price must be determined separately when the transfer of ownership of the car has already been agreed upon. Otherwise, the company may be suspected and held accountable for fraud, and the transaction itself may be declared void (terminated). Payments under a leasing agreement will be considered expenses for the purchase of a car, which means they will form the initial cost of a depreciable car.
The leasing agreement must also indicate the procedure and sequence for transferring ownership of the car. This is explained by the fact that the agreement, which involves the subsequent purchase of the car, contains elements of a purchase and sale agreement. At the end of the leasing agreement, the client buys the car at a price that he determined together with the leasing company. The procedure and terms of purchase are specified either in the leasing agreement or in the additional agreement.
Still have questions?
Get advice and a personal quote for purchasing a car on lease