Receiving an award is always a pleasant event. And if this bonus is based on the results of work for the year, then in fact it turns out that this is the 13th salary. And it’s especially nice to receive the annual final bonus before the new year.
But when calculating and paying the annual bonus, in addition to joyful emotions, the accountant also has some concerns: how to correctly take into account and reflect this bonus in accounting? How then can it be taken into account when calculating vacation and sick leave benefits? And maybe there are some options for accounting and reflecting bonus payments at the end of the year? We will discuss these issues in our article.
The concept of a one-time bonus payment
The procedure and conditions under which bonuses are paid to employees are set out in local regulations (LNA).
Remuneration is paid for successful work, based on the results of work and other production reasons. Typically, such payments are periodic: quarterly, monthly, etc. But if a significant event occurs, for example, an important project is completed ahead of schedule, bonuses are awarded one-time. There are non-productive reasons - anniversaries, holidays. Cash incentives are also paid specifically for the incident that occurred. Thus, a one-time bonus is associated with both production and non-production events and is of a one-time nature. The law does not provide for a clear bonus system; the enterprise itself determines the structure of accrual of incentive payments.
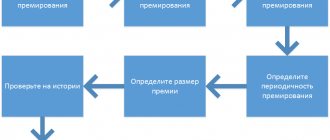
Options for setting up bonuses in 1C 8.3 ZUP
There are 3 main types of bonuses, in terms of the order in which they are reflected in 1C ZUP 3.1:
- Planned are bonuses that are accrued monthly or in certain months. Such bonuses are assigned to employees on a scheduled basis, calculated in the documents Calculation of salaries and contributions or Dismissal and can only be paid together with wages or settlement upon dismissal.
- “Shooting” - this type of bonus is calculated in the documents Calculation of salaries and contributions or Dismissal , only if the value of bonus indicators is entered in a separate document Data for salary calculation (Salary - Data for salary calculation). “Extraordinary” bonuses are not required to be assigned to employees as planned, and their payment is also provided only as part of wages or settlement upon dismissal.
- Bonuses paid under a separate document - these bonuses are calculated in a separate document Bonus (Salary - Bonuses). Payment of such bonuses is possible both as part of wages and according to a separate document Statement... (Payments - All statements for salary payments). This payment option is convenient for bonuses taken into account for personal income tax purposes on the date of payment, in cases where the organization seeks to bring accounting closer to personal income tax and reflects such bonuses in the month of their payment. However, if it is necessary to determine the calculation base for premiums paid under a separate document, it is not possible to take into account accruals of the current month.
In the Accruals (Settings – Accruals), the type of bonus is described by the value of the Accrual in progress .
Planned bonuses correspond to the values Monthly and In the listed months , “shooting” - Only if the value of the indicator is entered , and bonuses paid under a separate document - According to a separate document .
Comparative characteristics of the listed types of bonuses are presented in the table.
| The procedure and stages for reflecting bonuses | Planned bonuses | "Shooting" awards | Premiums paid under a separate document |
| Purpose of the award | Documents of changes in wages or personnel transfer (Personnel – Hiring, Transfers, dismissals) | Not required | Not required |
| Accrual of bonus | Will be carried out automatically monthly / in the months listed by documents Calculation of salaries and contributions or Dismissal without any additional settings | Will be carried out using the documents Calculation of salaries and contributions or Dismissal only if the values of key bonus indicators are entered in the document Data for salary calculation | Produced by a separate document Award |
| Payment of premium | Only together with wages or settlement pay upon dismissal | Only together with wages or settlement pay upon dismissal | Can be paid both as part of wages (calculated upon dismissal) and on a separate statement |
| Base calculation | Flexible setting of the period for determining the calculation base | Flexible setting of the period for determining the calculation base | The calculation base cannot take into account accruals of the current month |
Let's look at examples of setting up each type of bonus in 1C 8.3 ZUP.
In what cases is it prescribed
The purpose of one-time incentive payments is reflected in the local regulations of the enterprise. This is a collective agreement, most often a provision on bonuses. It provides for cases for which employees can be rewarded, including:
- significant employee dates;
- important dates for the organization;
- successful completion of management assignments;
- unplanned initiatives and implementations that led to significant positive results, and so on.
The basis on which a bonus is accrued to an employee is the order of the director. It indicates the reason for the bonus and a link to the clause of the regulation or other LNA.
Example 2. Setting up a “shot” accrual of a quarterly bonus in 1C ZUP
In an organization, employees are awarded a quarterly bonus as a percentage of the salary payment for the previous quarter. However, this bonus is not accrued every quarter, but only when the organization achieves certain profit targets. The bonus percentage can take on a new value each time the bonus is calculated and is set individually for employees. It is necessary to configure the employee Vasilkov I.B. calculation of a quarterly bonus in the amount of 15% of the salary payment for the 3rd quarter of 2022. The bonus will be awarded in December.
According to the conditions of the problem, the quarterly bonus is not awarded every quarter. Setting up a planned premium is not suitable in this case, because Quite often you will have to assign a bonus to employees as planned and then cancel it. It is also quite labor-intensive to charge the quarterly bonus each time using a separate document. The most convenient option in this situation is to set up a “shooting” premium.
First of all, we set up a new Indicator . It will also be assigned to the employee, but its value will be Entered at a time by the data document for payroll calculation .
Next, we’ll set up a new Initial Data Entry Template (Settings – Initial Data Entry Templates). This template will determine the type of document Salary Calculation Data of the Quarterly Bonus Percentage will be entered . On the Salary Indicators , check the indicator we created in the previous step.
In order to be able to specify the Quarterly Bonus Percentage , Payroll Calculation Data, on the Additional tab, select the The document uses several employees .
Let's set up a new Accrual to reflect the quarterly bonus. On the Main , we indicate the purpose of the accrual Quarterly bonus , the method of execution - Only if the value of the indicator is entered . Once the Quarterly Bonus Percentage , it can be specified as an indicator that determines the accrual of the bonus.
On the Base calculation , we indicate the base accrual according to the conditions of the task ( Payment by salary ) and the base calculation period – Previous quarter .
Let us enter for employee Vasilkov I.B. the value of the quarterly bonus percentage in the amount of 15% in the document Data for calculating salaries in December 2022:
Let's calculate the wages of Vasilkov I.B. for December with the document Calculation of salaries and contributions and we will check the calculation of the Bonus with quarterly percentage . the Calculation Base indicator for the 3rd quarter was 105,000 rubles.
The quarterly bonus amount is calculated as:
- 15 (bonus percentage) /100 * 105,000 (salary payment) = 15,750 rubles.
What documents to prepare
The main document defining the grounds for assigning bonus payments is the provision on bonus payments to employees. It states:
- grounds and criteria for bonuses;
- calculation and amount of payment;
- documentary support for bonuses;
- list of employees;
- grounds for deprivation of bonuses;
- sources of financing.
For example, when calculating 13 salaries, the regulations indicate the wording of the grounds for bonuses to employees, for example, the following:
- have worked at the enterprise for more than a year;
- all employees - calculated in proportion to time worked;
- all employees receive 100% of their salary.
It is advisable to develop accrual criteria taking into account the opinion of the team.
One of the conditions is a memo from the employee’s immediate supervisor offering a bonus. The general basis for bonuses is an order from the head of the organization. The document contains a link to the regulations, additional documents (if any), a list of employees receiving bonuses, and the amount of bonuses.
An example of how to calculate a bonus for a year
Programmer R.A. Knopkin a salary of 56 thousand rubles per month is paid. This salary was accrued to him for all 12 months of the past year. The employer instructed an accountant to calculate the annual bonus. The company's collective agreement contains information about the bonus percentage at the end of the year - it is 12%.
Over the past year, the programmer earned: 56,000 rubles. x 12 months = 672,000 rub .
The bonus at the end of the year will be: 672,000 rubles. x 12% = 80,640 rubles .
The accountant is obliged to withhold personal income tax from bonus payments in the amount of: 80,640 rubles. x 13% = 10,483 rub. 20 kop .
The employer will transfer insurance contributions from his own funds in the amount of: RUB 80,640. x 22% = 17,740 rub. 80 kop .
Total, Knopkin R.A. received in hand: 80,640 rubles. — 10,483.2 rub. = 70,156 rubles 80 kopecks .
Taxation of premiums
In accordance with the Tax Code, taxation of holiday bonuses is mandatory. For the purposes of paying personal income tax, it does not matter whether the payment is industrial or not - they are all considered income.
Officials and courts do not agree on the issue of paying insurance premiums. Tax officials refer to the fact that there is no mention of payments not related to labor in the Tax Code, therefore contributions must be paid. The courts take the opposite point of view - the decision of the Supreme Court dated 04/06/2017 No. 306-KG17-2349. The Supreme Court points out that lump sums paid on anniversaries do not relate to the results of work and are not remuneration for work. In this regard, they are excluded from the base for calculating insurance premiums.
Premiums listed in the government list are not subject to income tax (Clause 7, Article 217 of the Tax Code).
How are bonuses accounted for in the tax accounting of an organization? When calculating the taxable base, labor costs include incentive and incentive payments if they:
- indicated in the LNA;
- directly depend on the results of labor, labor function;
- not provided for in Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- comply with the conditions of paragraph 1 of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, documented with supporting documents.
Taking into account the annual bonus when calculating average earnings for vacation pay and business trips
Art. 139 and 167 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as the provision “On the specifics of the procedure for calculating the average salary”, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 24, 2007 No. 922.
However, remuneration for the year will be taken into account in its own special manner in this calculation. The annual remuneration will be included in the calculation of average earnings, regardless of the time of actual calculation. But there are a number of conditions: the premium must relate to the year preceding the year in which the calculation is made. Moreover, if at the time of calculation the bonus for the year has not yet been accrued, then after its calculation you will have to recalculate the average earnings and, accordingly, the amount of payment depending on this earnings (clause 15 of regulation No. 922, letter of Rostrud dated 05/03/2007 No. 1253-6 -1).
Inclusion in the calculation of the full or partial amount of remuneration for the year, as well as for other bonuses, will depend on:
- on the completeness of the employee’s work during the pay period;
- correspondence between the periods for calculating the bonus and the settlement period;
- accounting or non-accounting of the employee’s actual work time when calculating bonuses.
For more information on how year-end remuneration is taken into account when determining average earnings, read the article “Is a bonus taken into account when calculating vacation pay?”
Postings
A cash payment that is not related to incentives for work, for example, an anniversary bonus, is distinguished by its non-work-related basis and irregularity.
Bonuses for labor achievements are reflected in accounting with the following entry: Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44) Kt 70. For tax accounting (when determining the base for paying tax), such bonuses are included in expenses.
One-time remunerations not related to work activities do not reduce the tax base for profits, in accordance with letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 24, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/14283. They must be charged to net profit. Postings can be like this:
- Dt 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44) Kt 70. Expenses refer to expenses that are not taken into account for tax purposes.
- Dt 84 Kt 70. Write off from the profits of previous years.
- Dt 91 Kt 70. If there is no profit for previous years, the costs are included in this year’s expenses, but are not taken into account for tax purposes.
What is a bonus (definition according to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) and how does it relate to salary
The concept of a premium is present in Art.
129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, where it is mentioned among incentive payments that may constitute one of the parts of the salary. That is, a bonus is an incentive payment that is part of the structure of the applied remuneration system. To learn about other forms of employee incentives, read the material “What are the types of bonuses and rewards for employees?”
The employer must develop the structure of the remuneration system and establish the rules for its application, in consultation with representatives of the workforce (Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). When developing this system for the teams of state unitary enterprises and municipal unitary enterprises, it is also necessary to be guided by the uniform recommendations approved for the next year by the Russian tripartite commission for the regulation of social and labor relations.
Thus, the employer must have an internal document containing a description of the system used to remunerate the team (the salary structure of employees). This document may simultaneously contain a description of all the rules established for the calculation of each component of the salary. But it is also possible to develop independent regulations (provisions) for each component of remuneration.
Since 2022, small labor collectives (microenterprises) are allowed not to create internal regulations governing labor law issues (Article 309.2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). However, making such a decision requires detailing all the rules for calculating wages in the employment agreement with each employee. Moreover, to draw up this document, its standard form should be used. This form has already been approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated August 27, 2016 No. 858.
An internal document developed for the team as a whole (or for most of it) allows the employment agreement with each employee not to list in detail all the rules of remuneration established for him, but to limit himself to only referring to a number of internal acts. Therefore, the creation of such acts significantly simplifies the execution of employment contracts. Moreover, regulations can remain in effect without changes for several years. And the labor costs for their development and adoption, even for micro-enterprises, may turn out to be noticeably less than including all the details related to payroll in each employment contract.
simplified tax system
Organizations that pay a single tax on income do not reduce the tax base by the amount of annual premiums (clause 1 of Article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Organizations that pay a single tax on the difference between income and expenses include annual bonuses stipulated by the labor (collective) agreement as expenses. This can be done if bonuses are paid for labor performance. This conclusion follows from subparagraph 6 of paragraph 1, paragraph 2 of Article 346.16 and Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: when is an annual bonus considered stipulated by the employment contract?
An annual bonus is considered stipulated by the employment contract if one of two conditions is met:
- the employment contract specifies the amount and conditions for calculating bonuses (paragraph 5, part 2, article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- the employment contract contains a link to the organization’s local document regulating the procedure for calculating and paying bonuses (for example, the Regulations on Bonuses).
A link to a local document can be formatted as follows: “The employee is paid bonuses provided for in the Regulations on Bonuses (approved by Order No. ___ dated ______).”
This position is adhered to by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated February 5, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/81. It is confirmed by arbitration practice (see, for example, decisions of the FAS of the West Siberian District dated April 17, 2006 No. F04-10064/2005 (20874-A27-37), Far Eastern District dated January 25, 2006 No. F03-A51/05 -2/4903).
Include the amount of bonuses based on the results of work for the year into expenses at the time of their payment (clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of taxation of bonuses based on the results of work for the year. The organization applies a simplification, pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses
Alpha LLC uses simplification. An organization pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses.
The regulations on bonuses for Alpha and employment contracts with employees provide for the payment of an annual production bonus in the amount of 13,000 rubles. to all employees of the organization who have completed their full working period. The bonus is accrued along with the salary in January of the year following the reporting year. The bonus is paid within the deadlines established for the payment of salaries for January.
In January, storekeeper P.A. Bespalov was awarded an annual bonus. It was paid on February 5th.
The bonus amount will be included in the personal income tax base in February. Bespalov has no rights to deductions for personal income tax.
Personal income tax on the premium amount is equal to: 13,000 rubles. × 13% = 1690 rub.
The organization calculates contributions to compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance according to the basic tariff. Contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases - at a rate of 0.2 percent.
The amount of contributions accrued from the premium for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases was: 13,000 rubles. × 0.2% = 26 rub.
The amount of contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance is 3900 rubles, including:
- contributions for compulsory pension insurance – 2860 rubles. (RUB 13,000 × 22%);
- contributions for compulsory social insurance - 377 rubles. (RUB 13,000 × 2.9%);
- contributions for compulsory health insurance credited to the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 663 rubles. (RUB 13,000 × 5.1%).
On February 5, the accountant transferred personal income tax, contributions for compulsory pension (social, medical) insurance and contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases to the budget.
In February, the accountant took into account as expenses:
- bonus amount – 13,000 rubles;
- the amount of insurance premiums is 3926 rubles. (26 rubles + 3900 rubles).
How to calculate a bonus taking into account the regional coefficient and northern bonuses
The regional coefficient and the northern bonus are additional payments of a compensatory nature, taking into account the fact of working in special climatic conditions. They also represent part of the salary that must be paid. The difference between them is that the regional coefficient is paid from the first day of work, and the right to receive the northern bonus and its increase depends on the length of work experience in the relevant area. The size of the coefficient and premium for each region is established by the Government of the Russian Federation, but at the regional level it is possible to increase these values (Articles 316, 317 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 10, 11 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On State Guarantees and Compensations...” dated 02/19/1993 No. 4520- 1).
It is necessary to increase the amount of the accrued bonus at the expense of the regional coefficient when bonuses are calculated from the salary and the corresponding coefficient is in force in the region. In all other cases, the issue of applying the coefficient remains unregulated by law. On the one hand, there is no need to charge a premium taking it into account, because:
- it is already taken into account in the earnings actually accrued for the period;
- the accrual of a bonus in a fixed amount or from the sum of bonus indicators estimated in ruble equivalent is not tied to the salary, which requires an increase by the corresponding coefficient.
On the other hand, the current legislation does not establish the procedure for applying the regional coefficient to bonuses. Therefore, the rules for bonuses can provide for their accrual using this coefficient in all situations for calculating incentive payments included in wages. The justification here is that the bonus is included in the salary.
The procedure for calculating northern bonuses is regulated by an instruction approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of the RSFSR dated November 22, 1990 No. 2. It contains a ban on calculating bonuses for the following bonus payments (clause 19 of the instructions):
- one-time remuneration for length of service;
- remuneration based on the results of work for the year;
- incentives of a one-time nature and not provided for by the remuneration system.
At the same time, the instructions imply the possibility of calculating bonuses based on the results of work for a quarter, season or year, but with the condition that in order to calculate the monthly amount of the bonus, bonuses will be distributed over the months of the corresponding period in proportion to the time worked.
By the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2015 No. AKPI15-1253, the provisions of clause 19 of the instructions prohibiting the accrual of bonuses on remunerations paid for length of service and based on the results of work for the year were declared invalid as contrary to the current Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, the northern bonus should be calculated on all bonus payments provided for in the remuneration system.