Grounds for debt forgiveness by the founder
Debt forgiveness
- this is a firmly and clearly expressed will of the creditor to release the debtor from fulfilling obligations to repay borrowed funds and/or interest and penalties on the loan.
The possibility of debt forgiveness is provided for in Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. However, there is a caveat - writing off the debt should not affect the interests of third parties and the debtor. That is, if a debtor company objects to the forgiveness of its debt obligations, the creditor cannot carry out the write-off procedure on its own - such a transaction is not unilateral.
Moreover, if the creditor company refuses to accept funds to repay the debt, the debtor has the right to transfer the money to the account of a notary or judicial authority.
It is clear that since the founder himself manages his company, acting as a debtor, he will not interfere with debt forgiveness. However, in such a situation it is important to think about the interests of third parties. For example, you should check whether the interests of creditors to whom the founder himself has debt obligations will not be affected.
Creditors may be interested in the possibility of collecting debts from the assets of the business, including from the proceeds of a loan that was supposed to be forgiven. The lender may demand repayment of the debt by:
- destruction of the loan agreement from the founder;
- delivery of a promissory note;
- sending an official mail notification.
Important!
The debt can be forgiven by the founder in whole or in part.
Before executing a debt forgiveness transaction, the creditor must notify the debtor of his offer in writing. If he sends a letter of objection, debt forgiveness cannot be carried out. If the debtor does not take any actions that could be regarded as objections, or agrees to the transaction, the paperwork can begin.
Main features of debt forgiveness between legal entities
From the point of view of lawyers, the operation of debt forgiveness is interpreted differently. Some believe that this action refers to a gift, which is unacceptable between legal entities.
However, Russian legislation (in particular, Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) clearly regulates this action, which differs in the following aspects:
- debt forgiveness is purely a two-way transaction. The decision to terminate obligations under a loan agreement cannot be made only by the lender or the borrower;
- debt forgiveness in the usual form does not imply any compensation. Otherwise, the action is relegated to the category of receiving compensation, which is counted towards payment of existing debt;
- You can forgive debt not only arising as a result of concluding a loan agreement, but also other claims, for example, those arising as a result of the imposition of penalties;
- In order for a loan forgiveness agreement to differ from a gift agreement, it is necessary to economically justify the feasibility of performing this action.
Determining the rate in the loan agreement
Interest-free loans issued to subsidiaries are risky because the lender will be required to pay interest.
In this regard, it is strongly recommended to indicate the interest rate in the loan agreement - this approach is beneficial to the borrowing organization, since interest on the loan is taken into account in order to reduce the tax base for income tax.
Subsequently, the founder signs an agreement to forgive the debt. When the share in the authorized capital owned by the lender turns out to be more than 50%, the amount will not be included in the tax base.
How to register correctly
Since debt forgiveness, as mentioned above, is a bilateral transaction, it must be formalized in one of the following ways:
- an agreement to forgive the entire amount or part of the debt;
- an additional agreement to the current loan agreement on forgiveness of the entire amount or a certain part of the debt.
Before starting the procedure for executing a debt forgiveness agreement, the lender must send a notification to the borrower organization in the following form:
As can be seen from the sample document, the notification should contain the following information:
- about the fundamental document, which in this case is the loan agreement;
- about the amount of existing debt and the time frame when the latter must be fully repaid;
- about the lender’s intention to forgive the debtor his obligations in relation to the entire debt or a certain part thereof.
If the borrower wishes to agree with the lender, then one of the documents listed above should be completed.
Taxation when concluding a loan agreement between legal entities is discussed in detail in the article: taxation of a loan agreement between legal entities. You will find customer reviews about the company E Finance Loan in the comments.
How to apply for debt forgiveness by the founder - legal procedure
The procedure for debt forgiveness by the founder can be formalized in several ways:
| Method for completing a debt forgiveness transaction | The essence of the method |
| Conclusion of an agreement according to which the subject of the transaction will be the release of the debtor from his debt obligations to the founder. | Such a document must be submitted to the lender by the borrower at the time of receipt of borrowed funds from him. The text of the agreement must refer to Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The text of the agreement is formed in any form, but it is necessary to indicate the amount of the debt written off, the name of the organization, details of the parties to the agreement, details of the loan agreement under which the company received a loan from the founder. |
| Conclusion of an additional agreement between the debtor and the founder. | The subject of such an agreement is the founder’s waiver of the right to collect debt from the debtor organization. This document does not cancel the debt, but allows you not to repay borrowed funds without causing legal consequences. |
| Execution of a gift agreement, the parties to which are the founder-lender and the debtor company, and the subject is the amount of debt. | This method is only possible if the founder is an individual. The law prohibits two legal entities from gifting assets to each other. A donation agreement can be concluded:
|
Design methods
As mentioned earlier, if the founder intends to forgive the debt on the loan provided to his company, he must take care of the correct legal documentation of this procedure.
The specifics of the relationship between the founder (creditor) and the organization (borrower) provide for three possible options for forgiveness of existing debt.
Option one - issue a deed of gift
You can draw up a gift agreement, according to which the donor will be the shareholder (creditor), and the donee will be the company (borrower).
The amount of borrowed funds duly transferred to the company by the founder is considered in this case as the subject of a gift.
Accordingly, the donation of this amount, documented and certified by a notary, will be a way to forgive a previously incurred debt.
However, this option is allowed only if the shareholder, acting as a creditor and, accordingly, a donor, is an individual.
If a company participant who provided a loan to it has the status of a legal entity, he does not have the right to enter into a gift agreement with another organization that also has such status.
Option two - draw up an additional agreement
The parties to the loan agreement, that is, the shareholder (lender) and the company (borrower), draw up an additional agreement to this agreement, in
in accordance with which the shareholder (creditor) voluntarily renounces the right to claim funds under the loan provided to the company (borrower).
loan agreement:
- interest;
- interest-free.
An important point is that the above-mentioned right of claim must be clearly provided for in the main agreement, that is, the loan agreement.
The legal relationship established by this additional agreement does not automatically lead to the cancellation of the loan debt.
However, in this situation, it creates legal grounds that allow the organization (borrower) to legally not pay the debt to its founder (creditor).
Option three - enter into a forgiveness agreement
The parties - the participant (creditor) and the business company (borrower) - draw up a new agreement providing for the forgiveness of previously incurred debt.
The subject of this agreement in this situation may be the release of the borrower company from the obligations established by a previously drawn up loan agreement, relevant at the time of concluding a new agreement.
An important nuance - in the text of the agreement providing for the forgiveness of loan debt, it is recommended to include a mention of the provisions of Article 415, prescribed in the Civil Code.
If the parties sign this agreement, the debt of the business company on the loan issued by the founder is actually canceled.
Accounting and postings
In order to correctly reflect the loan forgiveness by the founder in accounting, it is necessary to initially document the very fact that the company received money, accompanied by the occurrence of accounts payable.
If the founder, acting as a creditor, and his company, which is the borrower, enter into a loan agreement, and the funds provided for by this agreement actually come from the founder to the account of the business company, the amount of the loan received is debited to account 51 and reflected on the credit of account 66 (for short-term loan) or 67 accounts (for a long-term loan).
The amount of this transaction is equal to the amount of the loan received.
The primary documents for this operation may be an extract from the servicing bank and the loan agreement itself.
When the parties have formally agreed to forgive the loan debt by signing the proper documents, certain accounting entries are made.
First situation
If the share of the creditor participant in the company that is the borrower does not exceed 50%, the amount of the written off debt is included in the tax base of this business company.
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Posting - written off debt on a short-term (long-term) loan is recorded in other income | 66(67) | 91 |
Second situation
If the share of the creditor participant in the LLC that is the borrower exceeds 50%, the amount of the debt written off is not included in the tax base of this organization.
| Operation | Debit | Credit |
| Posting - written off debt on a short-term (long-term) loan is recorded in other income | 66(67) | 91 |
| A new asset has been formed in the organization, corresponding to the amount of unpaid tax equal to 20% of the amount of the debt written off (under the general tax payment regime) | 68 | 99 |
How to apply for debt forgiveness by the founder - accounting
The company to which the founder has forgiven the debt, after the completion of the transaction, reflects the transactions in the accounting registers:
- DEBIT 66 CREDIT 91, subaccount “Other income”
- if the loan is short-term; - DEBIT 67 CREDIT 91, subaccount “Other income”
- if the loan is long-term; - DEBIT 68, subaccount “Tax Calculations” CREDIT 99
– additional entry in case the amount of the written off debt does not belong to the taxable base (such an entry allows you to update the asset of the enterprise represented by the unpaid tax on the funds written off by the founder).
How to apply for debt forgiveness by the founder - taxation
Let's return to the accounting entries we examined. The amount that will be entered in the first entry is the amount of debt to the founder. The amount indicated in the second entry is the amount of tax deduction that is nominally accrued on the debt. If the taxpayer applies the OSNO regime (general taxation regime), the amount will be 20% of the debt. If the founder owns less than 50% of the authorized capital of the debtor company, the amount of debt is reflected exclusively in the first entry.
In this case, the amount of debt is not subject to tax.
How to apply for debt forgiveness by the founder - tax accounting
How it is necessary to keep tax records will depend on what share in the authorized capital is owned by the founder who issued the loan:
| Share in the authorized capital of the lender | Tax accounting |
| Less than 50% or 50% | The written-off debt must be included in the company's revenue (the amount of debt is included in the taxable base), since the debt becomes property received free of charge - this means that the company has increased its net assets. |
| More than 50% | The forgiven debt will not be recognized as income of the enterprise for tax purposes, and therefore the debt will not be taxed on the basis of Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. |
Important!
Whatever the share of the authorized capital in the ownership of the founder-lender, the interest on the loan must be included in the tax base of the enterprise when the borrower's debt is written off.
Common mistakes
Error:
The borrower did not make demands for payment of the debt from the debtor company. The debtor regarded the lack of demands as a desire to forgive his debt.
A comment:
The lender has the right to demand payment of the debt, but he is not obligated to do so. And the fact that the debtor did not receive demands does not mean that the borrower has expressed his will to forgive debt obligations.
Error:
The founder forgives the organization’s debt, and a gift agreement is concluded, in which the lender sets its own conditions for canceling the debtor’s obligations.
A comment:
The gift transaction assumes the absence of any additional conditions from the person to whom the debt is forgiven. It also assumes gratuitousness and voluntary consent of the debtor to enter into a gift agreement.
How does a founder forgive his company's debt?
Debt forgiveness by the founder under a loan agreement with a business company belonging to him is carried out in accordance with the provisions of Article 415 of the Civil Code of Russia. The rules contained in this article allow the founder of a company to forgive its debt to him, if after this the rights of other persons are not violated. For example, those who are, in turn, creditors of the founder. Despite the fact that possible debt collection can be carried out at the expense of his assets (one of which is a loan to the company, which he is going to forgive).
Legally, debt forgiveness in the legal relationship under consideration can be formalized in several ways:
- By concluding a gift agreement (its parties will thus be the founder of the company and the company itself). The subject of the agreement will be the amount that until that moment was transferred to the business entity in the prescribed manner. The considered option of formalizing the forgiveness of a company’s debt to the founder is possible only if the founder is an individual. If he has the status of a legal entity, then a gift agreement with another legal entity - the borrowing company - cannot be concluded by law.
- By concluding an additional agreement (with the participation of the same parties). The subject of this agreement is the lender’s waiver of the right to claim (which was established by the original agreement) funds from the borrower. From the point of view of the law, this legal relationship does not cancel the debt, but allows the company not to pay it without any legal consequences.
- By concluding an agreement, according to which, in fact, debt forgiveness is carried out. Its subject in this case may be the release of the company from the obligations established by the loan agreement valid at the time of signing the new agreement. At the same time, the text of the agreement may contain a reference to the provisions of Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. After signing this agreement, the legal relationship between the founder of the company and the company itself, the subject of which is the debt of one party to the other, terminates.
It will be useful to study the specifics of tax and accounting of the amount of forgiven debt by a company - an economic entity obligated to pay taxes and implement accounting policies.
Answers to common questions about how to apply for debt forgiveness by the founder
Question #1:
Is it possible to exercise the right to forgive a company's debt to the founder in order to redistribute funds within the enterprise?
Answer:
Yes, issuing a loan and forgiving the debt is beneficial, since the money will be distributed, and the debtor will not have income if the debt is forgiven by the founder with less than 50% of the share capital. If the share of the founder-lender exceeds 50% of the authorized capital, this method is not profitable.
Question #2:
What should you pay attention to when a company’s debt is forgiven by its founder?
Answer:
The Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation insists on including the amount of interest on the loan in the non-operating expenses of the debtor company in the event of debt forgiveness. The founder did not pay interest, and the company itself accrued it and included it in expenses - such an operation cannot be recognized as a gratuitous transfer of property from the point of view of law, and therefore tax benefits do not apply. The amount of debt that has been written off is not included as an expense for tax purposes. These are not justified economic expenses (according to the approval of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation).
Loan repayment to the founder and debt forgiveness in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8
Published 07/21/2018 13:10 In one of the previous articles, we looked at options for helping a founder in an unfavorable financial situation in a company (Receiving a loan from an individual founder and reflecting it in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8.) Today I would like to tell you about the possible options for repaying a loan received from the founder.
In this article, we do not consider in detail the intuitive accounting entries for the standard repayment of a cash loan (Dt 66.03, 66.04 - Kt 50, 51).
Let us dwell on the nuances of the loan repayment procedure:
— cash proceeds cannot be spent on loan repayment; it must be deposited into a current account and then the repayment amount must be transferred by bank transfer;
— the date of return of funds specified in the contract will insure the company against ambiguous interpretation of the validity period of the contract. In other words, after 3 years the company will not have an unjustified tax benefit in the form of written off accounts payable not included in income;
— the amount of the repaid loan from the borrower is not an expense taken into account for profit tax purposes;
- when repaying a loan in cash, the borrower does not have VAT obligations (the transaction is exempt from VAT).
In addition to repaying the loan, there is another option - the founder can forgive the organization’s debt. This can be either the amount of the principal debt or the amount of interest accrued under the loan agreement.
Let's consider how this is reflected in the accounting and tax accounting of an organization on OSNO.
When a debt is forgiven, a corresponding agreement (in writing) is concluded between the organization and the founder.
Debt forgiveness in this case is recognized as a gratuitous transfer of property and is included in non-operating income.
Reflection by the borrower organization of the loan amount forgiven by the founder (the founder’s share in the company’s capital is 50% or less):
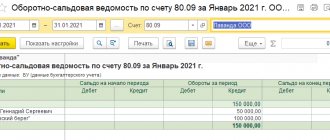
To check, we create Analysis of account 66.03.
But if the founder’s share of participation is over 50%, then such a transaction is not included in the organization’s income. In this case, debt forgiveness can be formalized as an increase in the organization’s net assets. Let us recall that the company's net assets are the company's own funds, which will remain after it pays off its creditors. In other words, the company's equity capital.
Important: If the net assets are less than the authorized capital, the company may face forced liquidation. An increase in the organization's net assets does not affect the amount of the authorized capital.
Let's consider the reflection of the operation of increasing the company's net assets in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8 edition 3.0 (reflection as of the date of the founder's decision).
To check, we will create an Analysis of account 66.03 (loan closed).
And also Analysis of account 75.01 “Calculations for contributions to the authorized (share) capital.”
The “Capital and Reserves” breakdown of the balance sheet reflects the amount of additional capital in account 83.09 “Additional capital. Other sources."
The amount of interest forgiven under the loan agreement is, in any case, regardless of the share of participation of the founder, non-operating income of the organization.
Reason: The amount of forgiven interest on the loan cannot be considered as property received free of charge (clause 11, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Forgiven interest is taken into account in income as accounts payable written off for other reasons.
Important: Postings are made on the date of signing the debt forgiveness agreement.
Reflection by the borrower organization of the amount of accrued interest forgiven by the founder:
We form an analysis of account 66.04.
For an organization that uses the simplified tax system, when a debt under a loan agreement is forgiven, neither the amount of the principal debt (if the founder’s share of participation is more than 50%) nor the interest accrued under the loan agreement is included in taxable income.
Reason: Under the simplified tax system, income includes income from the sale of goods (work, services) and property rights and non-operating income. In addition, under the simplified tax system, income is determined by the cash method (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 31, 2016 No. 03-11-06/2/31354).
Important: Risks under the simplified tax system arise when an agreement on debt forgiveness is not concluded. Upon expiration of the limitation period, such accounts payable must be written off as income (non-operating income of the organization).
Risks under the simplified tax system also arise if it is not a monetary loan, but a property loan, that is forgiven. In this case, the property should not be sold to third parties during the year.
And finally, advice for companies using any of the taxation systems under consideration.
If a company has two founders, it is advisable that the shares are not distributed in the ratio: 50% + 50%. This situation confuses the very possibility of providing financial or property assistance without inclusion in non-operating income. Option: 49%+51% differs slightly, but already allows the company not to take into account the founder’s loan (50% or more) in the tax base.
Author of the article: Irina Kazmirchuk
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
JComments