Revenue represents the amount of income from the activities of an enterprise, all financial resources received for the sale of products or the provision of services. For analysis, indicators taken over a certain period of time are used.
The question of how to look at the amount of revenue arises not only when the manager analyzes the work of production. Income may be of interest to financial professionals for a number of reasons.
The amount of income received as a result of commercial activities may be of interest in the following cases:
- when the manager evaluates the company’s performance indicators for a certain period of time;
- to calculate cost recognition standards, incl. for advertising services;
- to determine the amount of income and expenses for the next year;
- to study the demand for goods sold and services provided;
- to adjust the cost of products sold;
- to determine top products;
Accordingly, here the question arises: how to determine the amount of income for a certain period in 1C: Accounting.
The head of the company is most interested in the profit margin, which means that in this article we will discuss this topic in detail.
Revenue indicators in 1C: Accounting 8.3
The amount of income from ordinary activities is determined by the credit of account 90 “Sales” and the debit of accounts depending on the type of activity:
- 20 “Main production”;
- 41 "Products";
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, etc.
The 1st subaccount is used as accounting – 90.01 “Revenue”.
Entries to the account are made cumulatively throughout the year, resulting in a write-off to the 99th account to determine profit and loss from the operation of the enterprise.
Thus, to obtain information in the program, it is necessary to generate a turnover balance sheet (SAS) for account 90.01.
To do this, in the “Reports” menu in the “Standard reports” section, select “Account balance sheet”. In the window that appears, determine the period for which the report is being created, mark the account. 90.01, select a company.
Using the “Show settings” button you can define:
- distribution by certain groups, industries, VAT rates;
- make a general comparative selection;
- select the required necessary indicators;
- customize existing additional fields, such as account;
- sort by specified parameters;
- arrange in the required manner;
All settings are adjusted on specific tabs. Be sure to check the box on the “Grouping” tab next to “By subaccounts”.
The created SALT defines the balance indicators at the beginning and end of the billing period for the debit and credit of the account and subaccounts, as well as all turnover for the period for the debit and credit. This information, among other things, can be viewed by item groups. Determine the products that brought the highest profitability. By clicking on the amount, you can open transactions for all goods included in the amount and view all the data in more detail.
How is income from the sale of goods reflected in accounting?
Revenue is reflected in the receipt of cash and other property. And provided that goods and services (work) are provided on the basis of a commercial loan, in the form of deferred payment, revenue is accounted for according to the amount of receivables. Methods for reflecting it are defined by law:
- cash , when the actual payment is made to the organization’s account;
- accrual method , when a product is shipped, a service is provided, or work is performed upon presentation of payment documents.
In the first case, the generation of revenue is associated with the receipt of funds into the account. In the second, it is determined not by payment, but by the date of shipment. An enterprise, based on the characteristics of its business activities and contractual policy, chooses one method to use, but can change it if desired.
The amount of revenue differs from the cost of goods produced and shipped due to the existence of unsold products; sold with a deferment, the money for which has not yet been received; not paid on time; as well as being in the custody of the buyer.
Products and services sold at selling prices generate revenue, which includes three components:
- Profit. Forms financial assets that ensure the development of the enterprise.
- Cost price. Reimburses production costs.
- Taxes. Provide contributions to the budget.
In accounting, revenue is calculated at selling prices with VAT and excise taxes (gross) or without them (net), as well as at prices determined by the plan.
The organization’s revenue, regardless of the type and type of its activity, is recorded in account 90 “Sales”. It accumulates complete information about the income and expenses of the enterprise.
Postings reflect accounting:
- sold products and goods;
- services provided and work performed;
- leased property, etc.
Revenue is reflected in the entry (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Debit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” – Credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount “Revenue”.
For retail sales, instead of account 62, use account 90 , which corresponds with the cash account:
Debit account 50 “Cash” – Credit account 90.
With the help of accounting, the proceeds from the sale are reflected in the valuation determined by the contract. Based on the invoice, revenue is recognized and the following entries are made :
Debit 62 Credit 90-1 – revenue from the sale of finished products, work performed, services provided, including VAT, is recognized.
An enterprise can reflect net revenue in subaccount 90-1, that is, without VAT . The accrual of value added tax in this case will be reflected by the entry:
Debit 62 – Credit 68 “Calculations for VAT” VAT is charged to the budget.
But still, in practice, revenue is more often reflected taking into account VAT . This is acceptable and legally permitted, although the added value does not relate to income. This method of calculating VAT is reflected in the following entry (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n):
Debit 90-3 – Credit 68 “Calculations for VAT”.
At the same time, based on the invoice, the cost of goods, works, and services sold is written off:
- Debit 90-2 – Credit 20, 26, 43, 41.
- Debit 90-2 – Credit 44 – “Sales expenses”.
The balance sheet does not contain lines to reflect revenue . But at the same time, it is related to revenue, since it reflects the volume of assets and liabilities of the enterprise, as well as their changes, which can be used to judge the fall or growth of revenue.
Read about how to reflect sales revenue in accounting and which line in the balance sheet shows its amount here.
Nuances of accounting for income on accounts 90 and 91
The analysis of profitability indicators for ordinary activities, as already specified, is carried out using account 90.01 “Revenue”. This account has a sub-account:
- nomenclature groups;
- VAT rates;
Other types of income are recorded on the account. 90.01 and are divided by subconto:
- other income and expenses;
- assets being sold;
As a result, if you need to analyze revenue from ordinary activities, then we form SALT according to the account. 90.01. If an analysis of other expenses is required, we create a report on the account. 91.01.
In tax accounting, the amount of revenue is divided into:
- income from sales;
- non-operating income;
Sales income includes income from the sale of goods and services of own production, which goes to account 90.01.1 and is divided by product groups for the sale of goods and services and other product groups.
In addition, the amount of proceeds from the sale of property rights is taken into account. This is the count. 90.01, which is divided into articles:
- realization of property rights without taking into account rights of claim;
- implementation of the right of claim as the provision of financial services;
- exercise of the right of claim after the payment is due;
In tax accounting, existing income from sales is divided into profitability from the sale of other property for a number of items:
- sale of other property;
- implementation of construction projects;
In addition, income from sales for NU purposes includes the amounts of income from the sale of securities and revenue shown on line 340 of sheet 3 of Appendix 3.
Types of revenue items:
- exercise of the right of claim before the payment is due;
- sale of intangible assets;
- sale of fixed assets;
Tax accounting records non-operating income, which is recorded in the account. 90.01.
Thus, to assess the total profitability of the company, SALT 90.01 is created in total with the indicators reflected in the SALT account. 91.01.
For more detailed information containing income and expenses, it is necessary to check the boxes for the corresponding types of items when creating SALT.
All analytics on transactions are recorded in account card 90.01. To view it, you need to click on the amount from the SALT columns.
Factors of change
Revenue from sales of products is the main source of funds and the formation of own financial resources at operating enterprises. The concept of “sales income and methods for determining the moment of sale” are important for calculating financial indicators. In domestic practice, there are two methods for determining the moment of sale: for shipping – accrual; payment – cash method. (Income is determined after receiving money in cash or into the organization's bank account. This method is used for small business tax purposes. All organizations, with the exception of small ones, should use the accrual method, and also take into account income from sales of products after the shipment of products, goods, works and services. Income considered and staged payment for work performed with a long production cycle, as soon as available stages in the sectors of construction, research and development - design work.Small enterprises can be reflected in the accounting of sales revenue in the amount of its payment. These are organizations that have a date determination of income (sales speed), on average for the previous four quarters, the total revenue from the sale of goods (work, services), with the exception of value added tax, did not exceed one million rubles for each quarter.
Analysis of income under the simplified tax system
If a company uses a simplified taxation system, all income is determined on a cash basis. When you deposit funds into the cash register, income is immediately recorded in accounting. In this case, the amount of income for tax purposes is not taken into account in SALT.
This means that in order to evaluate revenue and profit indicators, you need to create a report “Analysis of accounting according to the simplified tax system”. To do this, you need to take the amount from the blocks and check it carefully. Otherwise, there is a possibility that the “Receipts from the Buyer” block will take into account all financial receipts, including fines.
To analyze receipts, you need to click on the block. Additional information about profitability will appear. Let’s say the “Retail Revenue” block contains information about revenues recorded in retail sales reports. By clicking on a report line, you can open the entire document.
The “Income recorded manually” block, containing all the adjustments made, must be analyzed.
Why do you need to know revenue?
Revenue is one of the key performance indicators of an enterprise. Its calculation helps assess the demand for goods and services and determine how interesting your products are to customers.
In addition, by comparing the received revenue with the planned one, you can develop a more effective production and purchasing plan and adjust your marketing strategy. Revenue also helps to develop the right pricing policy and is an indicator of how well prices correspond to the capabilities of the target audience.
The amount of revenue needs to be known, first of all, to the head of the company. Often this data is requested by business partners, creditors and investors.
Let's find out how revenue is calculated.
Estimation of enterprise profit
To analyze and evaluate profits, it is necessary to perform the operation of closing accounts 90 and 91 using the “Closing the month” procedure.
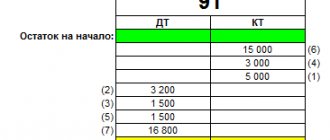
To do this, select the “Month Closing” section in the “Operations” menu. The period is determined and the name of the company is indicated. Upon completion of the transaction on the account. 99 will show the amounts from accounts 90 and 91.
If on account 99 the debit indicator is defined - this is a loss, if the credit indicator is a profit. Thus, you can create a balance sheet for the account. 99 and analyze the “Account Analysis” and “Account Turnover” reports.
Here it will be shown which amounts came from 90 and which from 91 accounts.
By clicking on the amounts, you can open detailed data. Accordingly, the amounts received from the account. 90 are profit or loss from main activities. If from the account 91 – amount of non-operating loss or profit. For industries using the simplified tax system, it is recommended to prepare a report “Analysis of accounting according to the simplified tax system.”
Convenient analytics for enterprise management
It is more convenient for any manager to evaluate revenue using management reports. They are located in the “Manager” menu in the “Sales” column.
This section presents analytics:
- by counterparties, including analysis of payments and sales;
- by nomenclature and nomenclature groups;
- total gross profit;
Thus, you can select any of the reports. Accordingly, it will present information from the accounting reports, but it will be more understandable for the manager.
Firstly, the indicators in the reports are presented in the form of graphs and tables, which allows you to more clearly assess the financial well-being of the company.
Secondly, the reports record the top five leaders by contractor or product range, which makes it possible to draw certain conclusions.
We will look at each report individually.
Revenue analysis by counterparties
By analyzing sales, you can determine cash retail receipts, all financial receipts from payment cards, and the results of payments under agreements. Identify the most profitable counterparties. To do this, in the “Sales by counterparties” section, determine the required time period and select .
In the “Indicators” column, select “quantity” and/or “amount”. On the “Groups” tab, select the required sections:
- contract;
- document;
- counterparty;
- nomenclature;
- nomenclature group;
- organization;
Then click “Generate”.
Using the available graphs, you can identify leading buyers by amount or total quantity, estimate current order volumes and the potential amount of revenue for each production. Please note that all amounts shown include VAT.
Below the graphs is a summary table displaying data for each counterparty by amount and quantity for a certain period of time.
In this way, you can determine the seasonality of sales - periods of maximum and minimum shipment of goods. With its help, sales planning is possible. It should also be taken into account that the report does not present indicators by account. 91.
The “Sales by counterparties (by payments)” form records revenue from customer payments for each month and for 5 leading organizations.
The “Comparison of sales by counterparties” form reflects the amount and number of sales, as well as their growth and decline as a percentage. This will allow managers to conduct additional negotiations with clients and determine more interesting terms of cooperation. And in the future, significantly increase profits by increasing sales volumes.
Revenue amount
Reflect the revenue in accounting in the amount of accounts receivable. And if revenue is recognized at the time (after) repayment of the debt by the buyer - in the amount of receipt of cash (or other property). If the amount of receipts covers only part of the proceeds, the amount of revenue is determined as the sum of received funds and receivables. Such rules are established in paragraph 6 of PBU 9/99.
Determine the amount of receipts and receivables based on the contract price, taking into account all discounts and markups (clauses 6.5 and 6.1 of PBU 9/99).
If the obligation under the contract changes, then the initial amount of revenue is adjusted based on the new conditions (clause 6.4 of PBU 9/99).
An example of determining the amount of revenue from the sale of goods taking into account discounts and changes in liability
On January 20, Torgovaya LLC entered into an agreement for the supply of goods in the amount of 118,000 rubles. (including VAT – 18,000 rubles). According to the contract, the buyer must pay for the goods on February 20. If the goods are paid for ahead of schedule, the buyer is given a 10 percent discount.
The buyer paid for the goods ahead of schedule - February 1.
The initial revenue amounted to 118,000 rubles. (including VAT – 18,000 rubles). After an adjustment was made for the amount of the discount, the revenue amounted to 106,200 rubles. (RUB 118,000 – RUB 118,000 × 10%). The VAT amount is 16,200 rubles. (RUB 106,200 × 18/118).
The organization's accountant made the following entries in the accounting records.
January 20th:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1 – 118,000 rub. – revenue is recognized;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 18,000 rubles. – VAT has been charged.
1st of February:
Debit 51 Credit 62 – 106,200 rub. – payment has been received from the buyer taking into account the discount;
Debit 62 Credit 90-1 – 11,800 rub. – revenue was adjusted by the discount amount;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 1800 rubles. – the amount of VAT on revenue has been adjusted.
Sales analytics by product range and profit assessment
An analysis of the most purchased products can be done using the “Sales by item” report. All necessary report settings are the same as those previously listed.
The graphs compiled will determine which product brought in more revenue and in what period of time, as well as the number of sales. The presented table contains digital indicators by nomenclature and time periods.
The following report form records the amount of revenue received by item groups. “Comparison of sales by product” reflects the change in sales volumes for certain products, expressed as a percentage.
Please note: in all the reports described, revenue is applied only by account. 90 and including VAT. And only the “Gross Profit” report contains graphs for the following sections:
- periods;
- counterparties;
- cash receipt;
- by payment cards;
- contracts;
Consequently, it is possible to determine profitable customers and product range.
Settings are made according to the established scheme.
Below the graph is a table of profitability by customers and by goods.
As a result of the analysis, it is possible to determine what brought the maximum gross profit received over the selected period of time. All information is generated based on account revenue. 90.01 excluding VAT. Account 91 is not displayed.
And one more necessary report “Income and expenses”, which is located in the “Manager” menu in the “General indicators” section.
The report reflects the overall profit for a certain period. The data is shown for core activities excluding VAT for subaccounts of the account. 90 and 91 are not analyzed. The amount of income from subaccounts 90.01 and 90.03 is formed, and the indicator of expenses from 90.02, 90.04, 90.05, 90.07 and 90.08.
Thus, the revenue amount can show different aspects of the business. Taking into account the goals of specialists who determine all indicators, it is possible to evaluate the company’s work by product range, list of contractors, concluded contracts, etc. Accounting evaluates results based on accounting and tax accounting indicators.
You can purchase services that help you work as an accountant here.
Do you want to install, configure, modify or update 1C? Leave a request!
Did you like the article?
Want to receive articles like this every Thursday? Keep abreast of changes in legislation? Subscribe to our newsletter
How is revenue different from profit?
Revenue is just the amount of money a company receives from its operations, excluding expenses. Profit is the difference between revenue and expenses. Expenses are considered to be the costs of maintaining the operation of the enterprise. Also, the following differences exist between revenue and profit.
- Method of calculation . Revenue can be zero or positive, while profit can be negative.
- Compound . It is enough to know all the income of the enterprise to know the revenue. However, to calculate the amount of profit, you need to know the amount of income and expenses.
- Potentiality . Revenue may be potential if the company allows customers to purchase goods in installments. Even if there is actually no money in the account, there is a guarantee that it will be there within the period specified in the agreement. Profit cannot be hypothetical, because it is calculated only on the basis of actual payments.
- Concept complexity . Revenue has a single meaning, while profit has two forms: gross and net. Net profit is the amount of income remaining after paying all taxes.
Let's find out where companies allocate their revenue.