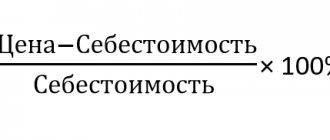In retail commodity organizations where goods are accounted for at sales prices, account 42 “Trade margin” is used. Passive account, loan balance. Formula for calculating the final account balance 42 = Beginning loan balance + loan turnover. Account 42 is not reflected in the balance sheet. And the balance of account 42 is subtracted from account 41 (balance of account 41 - Balance of account 42). We write it down in the RESERVES Assets section of the balance sheet. (since on account 41 the goods are reflected at sales prices and the accounting records of goods should be reflected at the actual cost, subtract the trade margin on account 42 and get the actual cost)
How to calculate trade margins and write them off
The trade margin is accrued by the following posting:
Debit 41 Credit 42 - The trade margin on goods received is reflected.
Debit 90 Credit 42 - (REPOSITION with a minus) - Trade margin on goods sold is written off.
The trade margin includes the company’s income + VAT
Example 1 (easy task):
Condition:
CJSC "Tredax" Bought 10 calculators for 12000 (10*1200) Wh VAT 20%. At a surcharge of 30% excluding VAT. Then I sold 10 of these calculators. The cost of each kettle is 1000 (10,000/10). The total cost is 10,000 rubles.
The accountant will make the following entries:
- Debit 41 Credit 60-10,000 rubles (12000/120*100) -Purchase of calculators.
- Debit 19 Credit 60-2000 rubles (12000/120*20) - VAT on purchase
- Debit 41 Credit 42-5600 rubles (10000*0.3+(10000+10000*0.3)*0.2)(Markup +(cost + markup)*20%) or (10000*1.3*1, 2-10000) - Reflects the markup on purchased goods. (comments on the last formula Cost * 1.3 (30% markup) * 1.2 (120% VAT) - Cost) This formula is difficult to understand, you need to re-read and comprehend.
- Debit 50 Credit 90-15600 rubles (10000+5600) or (1000*1.3*1.2*10)
- Debit 90 Credit 41-15600 rubles - The book value of calculators has been written off.
- Debit 90 Credit 68/VAT-2600 (15600/120*20)-VAT on sales.
- Debit 90 Credit 42-5600-RESTORED trade margin (amount minus)
- Debit 90 Credit 99-3000 (15600-15600-2600—5600) -Profit from sales (Check 10000*30%=3000)
Example 2 (difficult task).
If the organization has an account balance of 42, and goods are purchased at different prices, but the sales prices are the same. Then you need to use another example:
Condition:
The selling price of the product does not change.
At the beginning of the month, 10 units of the calculator were not sold at a price of 120 (incl. VAT 20%)
According to account 42, the balance on these goods is MARKUP in the amount of 100 rubles
During the month, calculators were purchased in two batches of 20 pieces each batch - the first batch cost 1000 rubles. VAT VAT 20% 166 rubles (1000/120*20)
-The second batch costs 1200 rubles. VAT 20% 200 rubles (1200/120*20)
During the reporting period, 30 calculators were sold at a cost of 3,600 rubles (120*30).
Solution:
Inventory of Wh goods is applied to accounting at actual cost, the actual cost of purchased calculators will be 1834 rubles (1000-166+1200-200).
The trade margin on received goods is equal to: (Sales price * number of calculators purchased - Purchase cost) = 120 * 40 (20 + 20) - 1834 = 2966 rubles. (Dt 41 Kt 42)
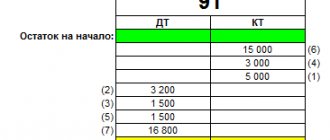
At the beginning of the reporting period, account 41 will have a balance of 1200 rubles (10*120)
Sales price of received calculators = (number of calculators purchased * selling price) = (20+20) * 120 = 4800 rubles.
Sold at sales prices 30pcs*120 rubles=3600 rubles. (dt 62 kt 90)
Balance of goods on account 41 at the end of the month not sold = Balance at the beginning + receipt - Expense = 1200 (120 * 10) + 4800 (40 * 120) - 3600 (120 * 30) = 2400 rubles.
In order to calculate the markup for write-off, you need to know how much markup remains at the end of the reporting period. For this purpose, the instructions for using the chart of accounts provide a formula.
Formula for the amount of the margin balance at the end of the period = (Beginning balance on account 42 + credit turnover on account 42) / (credit turnover on account 41 + end of month balance on account 41) * 100%
Let's calculate %=(100+2966)/(3600+2400)=3066/6000=0.51*100%=51%
=(account balance 41*%)=2400*0.51=1224 rubles is the markup on unsold calculators.
To write off the trade margin on goods sold, we use the formula = At the beginning of the account balance 42 + Extra charge received by calculators - Balance at the end of the period = 100 + 2966-1224 = 1842 rubles (dt 90 kt 42 reversals)
WIRES:
- Debit 41 Credit 60-1834 rubles (1000-166+1200-200) - Goods purchased without VAT
- Debit 19 Credit 60-366 rubles (166+200) - Input VAT reflected
- Debit 41 Credit 42- 2966 rubles (120*40(20+20)-1834) - Trade margin on purchased goods.
- Debit 50 Credit 90-3600 rubles (30*120) - Calculators sold for cash.
- Debit 90-2 Credit 41-3600 rubles - The sales value of calculators has been written off.
- Debit 90-2 Credit 42-1842 rubles (STORNO with a minus) - The trade margin was written off for those arriving on sold calculators.
- Debit 90/VAT Credit 68/VAT-600 rubles (3600/120*20) - Sales VAT is reflected.
- Debit 90 Credit 99-1242 rubles (3600-3600-(-1842)-600) - Profit from sales is calculated and reflected.
The procedure for forming trade margins
According to the law, each enterprise has the right to independently determine the retail price of the goods sold. Consequently, the amount of the trade margin and, as a consequence, the selling price of the goods is determined by the organization in each individual case. At the same time, according to the recommendations of the Ministry of Economy, the selling price of a product must correspond to market conditions, as well as cover possible sales costs and include the amount of income that the organization plans to receive from the sale of the product.
The amount of the trade margin is determined as a percentage of the purchase price of the goods. When deciding on the amount of trade markup on a product, the organization must record this indicator in the register of retail prices. This document is the basis for recording transactions on account 42. The law does not establish a mandatory form in which the register must be compiled. An organization can independently draw up a register form and approve its form in accounting documents.
Subaccounts 42 accounts:
- Account 42.01 - Trading margins at automated retail outlets
- Account 42.02 - Trading margin in NTT
Write-off of markup when marking down goods
If you decide to mark down an item, you need to make a posting for the amount of the markdown REVERSE (with a minus):
Debit 41 Credit 42 REVERSE - Markdown of markup.
If the markdown led to a decrease in the cost of the goods, then the difference must be written off to 91 accounts:
Debit 91-2 Credit 41-For the difference in excess of markdown over actual cost.
Example 3 (easy task)
Condition:
CJSC "Tredax" Bought 10 calculators for 12000 (10*1200) Wh VAT 20%. At a surcharge of 30% excluding VAT. The cost of each teapot is 1000 (10,000/10). The total cost is 10,000 rubles.
Solution:
- Debit 41 Credit 60-10,000 rubles (12000/120*100) -Purchase of calculators.
- Debit 19 Credit 60-2000 rubles (12000/120*20) - VAT on purchase
- Debit 41 Credit 42-5600 rubles (10000*0.3+(10000+10000*0.3)*0.2)(Markup +(cost + markup)*20%) or (10000*1.3*1, 2-10000) - Reflects the markup on purchased goods. (comments on the last formula Cost * 1.3 (30% markup) * 1.2 (120% VAT) - Cost) This formula is difficult to understand, you need to re-read and comprehend.
Calculators were marked down by only 6,000 rubles (including VAT), each by 600 (including VAT)
- Debit 41 Credit 42-5600 rubles REVERSE (minus)
- Debit 91-2 Credit 41-400 rubles (6000-5600) - Write-off markdown exceeding the cost of goods (calculator).
ATTENTION: read VAT when marking down, since VAT was accepted for deduction more than sales VAT, VAT needs to be restored
Examples of transactions and postings on account 42
Example 1. Accrual and write-off of trade margins
Let’s say the Procter store purchased 8 multicookers at a price of 2,360 rubles, incl. VAT – 360 rub. The markup on goods without VAT is 35%.
The accrual of trade margins in the Procter store is reflected in the following transactions:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 41 | 60 | 16 000 | Receipt of goods from the supplier | Packing list |
| 19 | 60 | 2 880 | VAT accepted for accounting | Packing list |
| 68 VAT | 19 | 2 880 | Tax deduction received | Invoice |
| 60 | 51 | 18 880 | Payment has been made to the supplier for the goods | Bank statement/ Payment order |
| 41 | 42 | 9 488 | The trade margin on goods received is reflected | Register of retail prices |
Subsequently, the Procter LLC store sold all 8 multicookers at a price of 3,186 rubles, incl. VAT.
The sale of goods and the write-off of trade margins at Procter LLC are reflected in the following transactions:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 50 | 90.01 | 25 488 | Revenue from the sale of goods is reflected | PKO (KO-1) |
| 90.02 | 41 | 25 488 | The book value of goods has been written off | Implementation report |
| 90.02 | 42 | 9 488 | Realized trade margin reversed | Register of retail prices, Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 90.03 | 68 VAT | 3 888 | VAT accrued for payment to the budget | Implementation report |
| 90.09 | 99 | 5 600 | Financial result from the sale of goods | SALT |
Example 2. Accounting for trade margins when writing off goods for own needs
Let's assume that LunaM LLC sells construction materials at retail. To renovate the store premises, we used our own building materials in the amount of 31,000 rubles. The trade margin is 30%.
Accounting for trade margins when writing off goods for the own needs of LunaM LLC is reflected in the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 44 | 41 | 31 000 | Construction materials were handed over for repairs | Accounting information |
| 44 | 42 | 9 300 | The amount of trade markup on building materials has been written off |
Write-off of markup when using goods for your own needs
For example, if you used the goods for your own needs, then the markup should be written off by posting:
Debit 44 Credit 42-STORNO (with minus) - The trade margin is written off on the cost of goods spent for the trade organization’s own needs.
Example:
Condition:
The cost of goods at sales prices used for the trading organization’s own needs amounted to 30,000 rubles. The markup on these goods is 5,000 rubles.
Solution:
Debit 44 credit 41-30,000 rubles -Write off goods for own needs
Debit 44 Credit 42-5000 rubles - Trade mark-up written off (with minus)
Account 42 in accounting
A trade margin is an added value to the purchase price of a product, used by an organization to cover the costs of selling the product, paying indirect taxes and, ultimately, making a profit.
Account 42 “Trade margin” is passive and is credited when goods are accepted for accounting in the amount of a discount (mark-up) or trade margin.
The main subaccounts 42 accounts are presented in the figure:
The purpose of analytical accounting for account 42 is to ensure separate accounting of the amounts of discounts (markups) and price differences:
- goods for retail trade;
- goods shipped.
The amount of the discount (mark-up) on the balance of unsold goods can be determined by %, based on the ratio of the amount of the discount/mark-up on the balance of goods at the beginning of the month and the turnover on KT 42 accounts without taking into account reversed amounts to the amount of goods sold and their balance at the end of the month:
Main account for inventory accounting
All goods intended for resale, according to the standards of PBU 5/01, should be accounted for in account 41 “Goods”. This account usually has several more sub-accounts, which each company can define and apply independently. It is necessary to take into account inventory items based on several criteria:
- name (nomenclature);
- quantity;
- storage location;
- responsible financially responsible persons.
Cost is the purchase price of goods and materials together with delivery costs, duties, agency fees and similar expenses (clause 6 of PBU 5/01). Plays an important role in accounting.
The meaning of the designated position in the Chart of Accounts
Position 42 of the Chart of Accounts is intended to summarize information about markups on the purchase price of products sold at retail enterprises that record them at their selling price.
For this item, records are also kept of those discounts that were provided by sellers to organizations engaged in retail commercial activities in case of possible product losses or reimbursement of additional transportation costs.
The credit part of the account reflects the amount of added value of goods accepted for accounting.
The amount of markdown or markup for those products that are sold, released or written off as a result of defective goods, their damage, insufficiency in the delivered volume, etc., is reversed, which is recorded in an accounting entry such as:
1) Dt 42
Kt 90.
Analytics for this position should allow for separate accounting of the size of discounts and mark-ups, and the difference in cost related to goods in retail commercial organizations, as well as to shipped goods.