Inventories: what to include, how to take into account
All company assets that have a useful life of less than 12 months should be classified as inventories.
For example, raw materials, materials, semi-finished products, components, packaging, fuel, inventory and other similar assets. To systematize and generalize information about the cost and quantitative indicators of inventories, account 10 “Materials” is used (Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n). These requirements apply to non-profit organizations, commerce and small businesses. State employees use accounting accounts in accordance with Instruction No. 157n. Material reserves in a budgetary institution are reflected in the accounting account of the same name 0 105 00 000.
It is permissible to take into account values in two ways: at actual cost (clause 62 of Order No. 119n) or at accounting prices using 15 and 16 accounting accounts (clause 80 of Order No. 119n dated December 28, 2001).
The company independently chooses the accounting method suitable for the specifics of its activities. This choice must be justified in the accounting policies of the institution. Also in the accounting policy, indicate the forms of primary and accounting documentation that will be used to reflect operations on the movement of money.
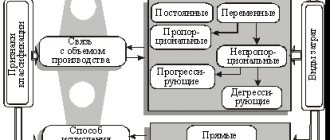
The method for writing off materials from the 10th account should also be written down in the accounting policy. Three methods are allowed:
- Based on the average cost of inventories.
- Based on actual unit cost.
- FIFO method.
The cost of inventories may include not only the actual price paid, but also other costs. For example, consulting services, non-refundable customs and tax duties, non-refundable VAT, delivery costs, and other costs associated with the receipt of goods.
What applies to household equipment and accessories?
What may be included in the list of tools, household equipment and accessories (hereinafter referred to as material assets, MC) has not been determined by anyone. The organization regulates this itself. Typically it includes:
- office furniture and equipment;
- lighting;
- stationery;
- Appliances;
- means related to fire safety;
- hygiene products;
- cleaning equipment and materials;
- tools, etc.
It is possible to purchase such goods both by bank transfer and through accountable persons.
How to account for the purchase of materials through accountable persons, read in Art. “What kind of posting reflects the acquisition of material assets under the report .
To organize accounting, it is necessary to correctly classify MC.
There are 2 options for inventory accounting:
- as part of fixed assets (fixed assets);
- as part of the MPZ.
Important! From 01/01/2021, inventories are accounted for according to new rules established by the new FSBU 5/2019 “Inventories”; the previous PBU 5/01 has become invalid. And fixed assets are accounted for according to the new rules approved by FSBU 6/2020, which are mandatory for use from 01/01/2022.
Some accounting rules have been changed significantly. ConsultantPlus will help you rebuild your inventory accounting. Get trial access to K+ for free and proceed to the material. And in this ready-made solution you will learn in detail about changes in fixed asset accounting.
In any option, objects are taken into account at the actual cost of acquisition, which consists of all costs associated with the purchase. In general, VAT is not included in this amount. It is included in the price only if MCs are used for non-taxable activities (clauses 9-11 FSBU 5/2019 “Inventories”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 15, 2019 No. 180n, clause 12 FSBU 6/2020 “Fixed Assets” , approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 17, 2020 No. 204n).
Opening sub-accounts for account 10
Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n determines that in order to organize complete, reliable and detailed accounting of the company’s material assets, the opening of additional sub-accounts is provided. This approach allows you to group all the organization’s inventory items by type.
| Number | Name | Content |
| 10.1 | Raw materials | Reflect material assets that are used to carry out the main activity |
| 10.2 | Semi-finished products | Components, components, structures and parts that are used in the main and auxiliary production cycles and processes |
| 10.3 | Fuel | Fuel and lubricants, gasoline, diesel fuel, gas, motor oils, etc. |
| 10.4 | Tara | Materials used as containers and (or) packaging |
| 10.5 | Spare parts | Spare parts used for repair and maintenance |
| 10.6 | Other inventories | Values not included in other groups |
| 10.7 | Materials for external processing | MPZ intended for external processing |
| 10.8 | Construction materials | To reflect information about the availability and movement of building materials from developers |
| 10.9 | Household equipment | Materials and equipment, accessories and equipment used to perform general economic work |
Please note that opening all accounts is not necessary. The organization independently decides which subaccounts will be used in accounting. So, for example, account 10.10 - what applies to a particular institution must be defined in the accounting policy. Typically, special equipment (special equipment) is included in this subaccount.
Basic postings with 10 counts
In the table we have collected the main accounting entries, where the 10th account appears.
| Debit | Credit | The essence of the operation |
| 10 | 15 | Materials were capitalized (using account 15) |
| 10 | 20 | Produced materials at the main production facility |
| 10 | 23 | Produced materials in auxiliary production |
| 10 | 29 | Produced materials in service production |
| 10 | 60 | Purchased materials from the supplier |
| 10 | 66/67 | Received materials as a short-term/long-term trade loan |
| 10 | 71 | Purchased materials through an accountable person |
| 10 | 75 | Materials were contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital |
| 10 | 91 | Excess materials found during inventory were capitalized |
| 08 | 10 | Written off materials for commissioning of fixed assets |
| 20 | 10 | Sent materials to main production |
| 25 | 10 | Used materials for general production needs |
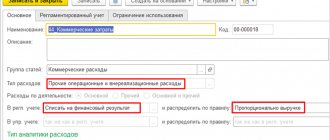
| 26 | 10 | Written off materials as general business expenses |
| 28 | 10 | Written off materials to eliminate defects |
| 29 | 10 | Delivered materials for the needs of service production |
| 44 | 10 | Written off materials as expenses for sale |
| 91 | 10 | Write off the cost of materials sold |
| 94 | 10 | Found a shortage of materials during inventory |
We recommend you the cloud service Kontur.Accounting. In our program you can keep records of raw materials and supplies by warehouses, workshops, types and series. We give all newbies a free trial period of 14 days.
Features of inventory accounting
Account 10 belongs to the active group of accounts. Consequently, debit 10 of the accounting account (for dummies) reflects the receipt (increase) of material assets, and credit turnover reflects the disposal of assets from the corresponding accounting accounts. The ending balance can only be in debit. A credit balance indicates that there is an error in recording accounting transactions.
Inventory accounting needs to be detailed. To do this, provide for maintaining detailed analytical records in the context of items, batches, storage locations, materially responsible persons and departments.
The actual presence of MC must be periodically monitored. Accountants are required to conduct inventory checks to identify deviations from accounting indicators and actual availability. The reconciliation procedure and frequency should be established in the accounting policy.
Revolving balance sheet: accounting 10
When maintaining automated accounting, it is recommended to systematically generate interim reporting in order to control the movement of material assets. One of such reports is the balance sheet for account 10. The accounting document contains information on the availability of MH balances at the beginning and end of the reporting period, as well as on the movement (receipt and disposal) of materials during the reporting period.
SALT is a separate accounting register that reflects information on the availability of material assets at the beginning of the reporting period, information on the movement of inventories (receipts and disposals), and also indicates the amount of raw materials remaining at the disposal of the company at the end of the reporting period.
Principles for drawing up a balance sheet:
- The negotiable SV must necessarily disclose accounting information:
- balance at the beginning of the reporting period - quantity and value;
- cost and quantitative expression of Ministry of Health revenues;
- value and quantity of disposed assets (write-off);
- final balance on account 10.
- If the company has structural divisions, it is necessary to organize additional analytics. For example, create turnover sheets separately for each warehouse space. Indicators of the consolidated balance sheet reflect data for the organization as a whole and are used for reporting.
- Automation of accounting and compilation of WWS does not exempt the entity from the mandatory maintenance of warehouse cards for materials accounting. The card must be issued for one calendar year. Moreover, the document is drawn up for only one item number. It is not allowed to combine MH accounting in cards.
- Primary documents confirming the movement of raw materials must be drawn up on paper. Facts of changes in the indicators of inventories must be certified by the “live” signatures of responsible employees. Keeping records electronically requires certification of documentation with electronic signatures of the chief accountant or head of the company.
IMPORTANT!
The statement reflects not only the value expression (rub.), but also quantitative accounting indicators (kg, m, pcs., units, etc.).
The concept of materials and raw materials in accounting
These nomenclature groups include assets that can be used as semi-finished products, raw materials, components and other types of inventory assets for the production of products and services, or used for the own needs of an organization or enterprise.
Purposes of materials accounting
- Control of their safety
- Reflection in accounting of all business transactions involving the movement of inventory items (for cost planning and management and financial accounting)
- Formation of cost (materials, services, products).
- Control of standard stocks (to ensure a continuous cycle of work)
- Identification of shortages, losses, damage to materials
- Analysis of the effectiveness of the use of mineral reserves.
Example of filling out the OCB
Data from NPO "DOBRO" for March 2022. For inventories used by the organization to conduct its main activity:
- purchased MH for the amount of 200,000 rubles;
- released into production in the amount of 220,000 rubles;
- spoiled in the amount of 3000 rubles.
Balance sheet for accounting account 10 for March 2022:
Accounting and control
A company can organize accounting in two ways.
Option #1.
First, write out a paper document. For example, a request for an invoice for the movement of goods and materials. Then the responsible persons carry out the transfer and complete the execution of the primary document. And only then are they transferred to the accounting department. The responsible accountant enters the data into the program.
Option number 2.
An accountant or warehouse worker enters information about the movement of inventories into a specialized accounting program. Then it prints out the document and submits it to the responsible persons for signature.
Regardless of the chosen accounting option, do not forget about errors. However, accounting indicators must always correspond to actual data. Therefore, it is necessary to organize systematic checks. It is recommended to carry out monthly reconciliations of SALT data with actual warehouse accounting indicators.
Instruct the responsible accountant to carry out counter reconciliations with financially responsible persons. These can be not only MOLs for warehouses, but also for all departments where inventories are stored. Correct any errors found in accounting in accordance with current standards. It is advisable to carry out control activities before the closing of the reporting period.
Accounting for inventory items in accounting: postings and documents
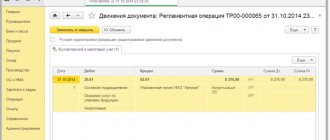
Accounting for inventory items in accounting is reflected on the basis of primary documentation and can be as follows:
- The purchase of materials is made in cash or by bank transfer, confirmed by a purchase agreement, payment and settlement documents or the transfer of a power of attorney to receive goods and materials with subsequent settlement with the supplier. It is received at the warehouse on the basis of a bill of lading or a receipt order. When purchasing materials, additional transportation and procurement costs (for example, delivery) may be reflected.
- Sale of materials - transfer of raw materials to third parties.
- Transfer - from the founders, contractors or sponsors, is accounted for at the estimated value or on the basis of available documents: contracts, payment documents, appraisal reports, etc.
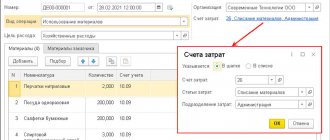
- Write-off of materials - reflects the expenditure of inventory and materials into production. It may imply both the write-off of materials for actual production and the write-off for general business needs. Depends on corr. accounts (20, 23, 25, 26). Disposal may be reflected due to damage or loss of inventory items.
- Shortage of materials or surplus of materials are recorded as a result of inventory. They may be reflected within the normal limits or as a result of loss/damage.
- Operations with customer-supplied raw materials - features of accounting for materials received from another organization.
For production and for own needs, materials are released from the warehouse upon request - invoice or other documents (based on accounting policies); are written off to the production site, which then includes them in the cost of products or services.
Carrying out inventories
Every year, according to PBU, owners are required to conduct scheduled inventories on the basis of an issued order with designated responsible persons. In addition to them, there may be unscheduled (sudden) audits and inventories. Their goal: control over the safety and correct use and write-off of inventory items .