The concept of marriage and its types
A detailed description of the defects can be taken from the Methodological Recommendations for the Chart of Accounts for the Agro-Industrial Complex, approved by Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 2001 No. 654. This description applies to all sectors of production. Defects are those products, semi-finished products or works that do not meet the established standards, technical characteristics and norms, while their use for the originally intended purpose is impossible without certain work to correct the deficiencies. Does not apply to marriage:
- products that can be transferred to a lower grade;
- products that do not meet increased quality requirements, but meet the standards for similar products.
There are several types of marriage:
1. At the place of discovery:
- interior;
- external.
2. By the nature of the defects:
- correctable;
- incorrigible (final).
How to reflect in the accounting of a production organization (buyer) the return of defective products (components) to the supplier if the defect is discovered before they are transferred from the warehouse to the main production? The answer to this question is in ConsultantPlus. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
In order to avoid selling low-quality goods, enterprises organize processes to check products before sending them to customers. Such functions are possessed by technical control departments, quality control services, etc. It is these structural units that detect internal defects. External defects are so named because they are discovered outside the boundaries of the enterprise, that is, by the buyer during operation. In addition, both internal and external marriages can be either corrected or irreparable. If the company evaluates the repair or correction of defects as both technically and economically justified, then the defect is correctable. If it is impossible or economically unjustified to correct the shortcomings, then the marriage is final. What is included in the costs attributed to the cost of marriage?
For an internal correctable marriage this is:
- material costs to eliminate deficiencies;
- wages of employees for activities to eliminate shortcomings;
- share of depreciation of production equipment;
- the corresponding share of general production expenses (hereinafter referred to as OPR).
The cost of the defective products themselves with internal correctable defects is not included in losses from defects. If the defect is internal and incorrigible, then its cost includes all the costs that went into producing the defective product, in addition to the costs of preparing and mastering production, organization and management, non-productive and other expenses.
The cost of external defects consists of:
- production cost of the product;
- amount of refund to the buyer for defective products;
- repair costs;
- costs of replacing the product;
- expenses for transporting goods to the buyer.
In addition, the cost of losses from defects also includes the cost of warranty repairs.
Losses from marriage are reduced by:
- in case of possible use of rejected products for other purposes than their intended purpose, its cost is equivalent to the price of possible use;
- deductions from employees guilty of product defects;
- amounts recovered or awarded from suppliers of substandard raw materials, materials, semi-finished products through whose fault the defect occurred.
Accounting for losses from defects
Defects in production are considered to be products, products, semi-finished products, parts, work that, in terms of their quality, do not meet established standards or technical conditions and cannot be used for their intended purpose or can be used after eliminating detected defects.
Depending on the nature of the defects, a distinction is made between correctable and irreparable (final) defects.
Correctable defects are products, semi-finished products (parts and assemblies) and work that can be used for their intended purpose after correction of defects, and their correction is technically possible and economically feasible.
Final (irreparable) defects are considered to be products, semi-finished products, parts and work that cannot be used for their intended purpose and the correction of which is technically impossible or economically impractical, that is, in cases where correcting the defect will require costs exceeding the costs of manufacturing new products instead defective.
In accordance with the Chart of Accounts, accounting for losses from defects is carried out using account 28 “Defects in production”. The debit of account 28 takes into account the cost of irreparable defects, as well as the costs of correcting defects. The credit of account 28 reflects amounts that reduce losses from defects, in particular, the cost of defective products capitalized at the price of possible use, amounts recovered from those responsible for the defects, amounts recovered from suppliers of substandard materials, the use of which was defective.
Non-refundable amounts of losses from defects are included in the cost of those types of products for which defects are detected. If in the period in which a defect was detected, this type of product was not produced, then the amount of losses from defects is distributed by type of product as general production expenses.
Internal marriage
If a defect is detected directly at the enterprise, at certain stages of the technological process, or directly in finished products before they are transferred to customers, the defect is considered internal.
Losses from internal defects are reflected in the costs of the month in which the defect was detected.
The cost of internal irreparable defects, to be reflected on account 28, is determined by the amount of costs for the manufacture of defective products, which includes the cost of raw materials used, labor costs and the corresponding amounts of unified social tax, costs of maintaining and operating equipment, and part of general production expenses.
Accounting for irreparable internal defects is documented by accounting entries:
- Dt 28
“Defects in production”
Kt 20
“Main production”,
21
“Semi-finished products of own production”,
43
“Finished products” - the cost of defective products is written off; - Dt 10
“Materials”,
21
“Semi-finished products of own production”,
41
“Goods”
Kt 28
“Defects in production” - defective products are capitalized at the price of possible use; - Dt 73
“Settlements from personnel for other operations”
Kt 28
“Defects in production” - amounts to be recovered from those responsible for the defect have been accrued; - Dt 76
subaccount “Calculations for claims”
Kt 28
“Defects in production” - amounts to be recovered from suppliers of defective materials have been accrued; - Dt 20, 23 Kt 28
“Defects in production” - losses from defects are included in the cost of production
Example
The company discovered an irreparable defect in a batch of products, the cause of which was the use of low-quality materials.
The costs of manufacturing defective products were: Cost of materials consumed - 25,000 rubles; Salary - 15,000 rubles; The amount of unified social tax is 5,340 rubles; The share of general production expenses is RUB 7,500. The possible sale price of defective products is 20,000 rubles. A claim has been filed against the supplier of low-quality materials; the amount to be recovered is 10,000 rubles.
Contents of operation Dt CT Amount, rub The cost of defective products is reflected (25,000 + 15,000 + 5,340 + 7,500) 28 20 52 840 Defective products are capitalized at the price of possible sale 43 28 20 000 The amount to be collected from the supplier has been accrued 76 28 10 000 Losses from defects are included in the cost of production (52,840 – 20,000 – 10,000) 20 28 22 840
The cost of internal correctable defects includes the cost of raw materials and supplies spent in correcting defects, the wages of employees directly involved in correcting defects, the corresponding amounts of accrued unified social tax, the share of costs for the maintenance and operation of equipment and general production costs attributable to operations to correct defects.
Accounting for correctable internal defects is documented using the following accounting entries:
- Dt 29
“Defects in production”
Kt 10
“Materials” - the cost of raw materials and supplies used to correct the defect has been written off; - Dt 28
“Defects in production”
Kt 70
- calculation of wages for workers involved in correcting defects; - Dt 28
“Defects in production”
Kt 69
- accrual of unified social tax for the wages of workers engaged in correcting defects; - Dt 28
“Defects in production”
Kt 25
- the corresponding share of general production costs is written off; - Dt 73
“Settlements with personnel for other operations”
Kt 28
“Defects in production” - amounts to be recovered from those responsible for the defect have been accrued; - Dt 76
subaccount “Calculations for claims”
Kt 28
“Defects in production” - amounts to be recovered from suppliers of defective materials have been accrued; - Dt 20, 23 Kt 28
“Defects in production” - the costs of correcting defects are included in the cost of production
Example
A defective batch of products was detected at the enterprise.
The costs of manufacturing defective products were: Cost of materials consumed - 25,000 rubles; Salary - 15,000 rubles; The amount of unified social tax is 5,340 rubles; The share of general production expenses is RUB 7,500. Total - 52,840 rubles. The costs for correcting the defect were: Cost of materials used - 8,000 rubles; Salary - 7,000 rubles; The amount of UST is RUB 2,492; The share of general production expenses is 1,500 rubles. Total - 18,992 rubles 5,000 rubles were recovered from those responsible for the marriage.
Contents of operation Dt CT Amount, rub The cost of materials for correcting defects was written off 28 10 8 000 Wages accrued for correcting defects 28 70 7 000 UST accrued 28 69 2 492 General production costs incurred to correct defects have been written off 28 25 1 500 The amount to be recovered from those responsible for the marriage has been accrued 73 28 5 000 The amount collected is withheld from the employees' salaries 70 73 5 000 The amount of losses from defects is included in the cost of production (8,000 + 7,000 + 2,492 - 5,000) 20 28 13 992 The production cost of finished products is reflected (52,840 + 13,992) 43 20 66 832
| New generation berator PRACTICAL ENCYCLOPEDIA OF AN ACCOUNTANT What every accountant needs. The full scope of always up-to-date accounting and taxation rules. Connect berator |
Accounting for defects in production - postings
To account for defects in production, the Chart of Accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, provides account 28. Its debit reflects all costs associated with defective products, their list is given in the previous part of the article. The loan records the amounts that reduce the cost of the marriage (see also the previous part). The amount of losses from defects is included in costs (clause 26 of FSBU 5/2019, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
ATTENTION! From 2021, account for all reserves in accordance with the new FAS 5/2019 “Reserves”. PBU 5/01 has become invalid.
ConsultantPlus experts explained what changes in inventory accounting need to be taken into account from 2022. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
Let us note the moment of documenting the marriage. When withdrawing defective products, it is necessary to draw up a report or notice of the defect. The company develops the form of the document independently; it indicates all the necessary details for the primary documents, as well as the name of the defective product, its number or code, the reasons for the defect, and those responsible for the defect. Such an act (notice) must be attached to the documents for the release of materials that will be used to eliminate defects.
For information on the rules for filling out a demand invoice drawn up when releasing materials, read the article “Procedure for filling out form M-11 demand invoice”.
Let's look at examples of typical transactions that will appear in accounting if an enterprise encounters defects in production. The first example is compiled for an internal correctable marriage.
Example 1
When sewing workwear, defective semi-finished products of our own production were discovered - product parts glued with dublerin. The reason for the marriage was poor-quality dublerin. The costs for correcting the defect were:
- cost of dublerin - 15,000 rubles;
- salary and social contributions - 73,800 rubles;
- share of ODA - 14,200 rubles.
The supplier of low-quality dublerin was presented with a claim in the amount of the cost of the material and labor costs to eliminate the defects, a total of 88,800 rubles. The accounting records reflect the following entries:
| Description | Dt | CT | Amount, rub. |
| The cost of dublerin for eliminating defects is reflected | 28 | 10 | 15 000 |
| Salary and social benefits accrued. fees for eliminating defects | 28 | 70, 69 | 73 800 |
| ODA related to eliminating defects written off | 28 | 25 | 14 200 |
| The amount of the claim has been accrued to the supplier | 76.2 | 28 | 88 800 |
| Received refund from dublerin supplier | 51 | 76.2 | 88 800 |
| Losses from defects are included in costs | 90.2 | 28 | 14 200 |
In the next example, consider the reflection of an internal incorrigible marriage.
Example 2
Due to the inattention of the shift foreman when setting the input data on the equipment, 120 pieces were produced. low-quality metal parts. It is impossible to correct the shortcomings. The costs that were incurred to manufacture these parts were:
- cost of materials - 47,600 rubles;
- salary and social contributions - 39,400 rubles;
- share of ODA - 17,400 rubles.
Parts can be sold for scrap for RUB 200. per piece According to the decision of the head of the enterprise, 47,600 rubles will be withheld from the shift foreman. The average monthly salary of a master is 74,000 rubles. According to the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of monthly deductions from wages should be no more than 20% (74,000 × 20% = 14,800). The accounting records reflect the following entries:
| Description | Dt | CT | Amount, rub. |
| The cost of defective parts is reflected | 28 | 20 | 104 400 (47 600+39 400+17 400) |
| Defective parts are capitalized at the price of possible sale | 10.6 | 28 | 24 000 |
| An amount has been charged that will be recovered from the culprit - the shift foreman. | 73 | 28 | 47 600 |
| The amount in the first month is withheld from the culprit’s salary (posting is done every month until the debt is fully repaid) | 70 | 73 | 14 800 |
| Losses from defects are included in costs | 90.2 | 28 | 32 800 |
Analytical accounting on account 28 is carried out in the context of the product range, structural divisions of the enterprise, causes of defects, cost items and culprits.
What is the essence of innovation?
FSBU 5/2019 (clause 26) says: “The actual cost of ... products does not include costs incurred due to improper organization of the production process.” Among others, losses from marriage are mentioned. In other words, these costs cannot be attributed directly to the cost of production.
To account for defects, the chart of accounts provides account 28. For separate accounting purposes, subaccounts 28/1, 28/2, 28/3, 28/4 can be opened - respectively, “internal irreparable defect”, “internal correctable defect”, “external irreparable defect” marriage", "external correctable marriage". It is no longer possible to use production cost accounts (20, 23, 29) to close it.
Standard postings for internal defects can be as follows:
- Dt 28 Kt 10, 70, 69, 25, etc. - cost of materials, employee salaries with deductions, ODA and other costs for correcting defects;
- Dt 28 Kt 20 – writing off defects from production;
- Dt 10 Kt 28 – returnable materials (waste) from defects are capitalized (maybe Dt 10/5, 10/6);
- Dt 90/2 Kt 28 – losses from defects were recorded.
When accounting for external defects, the following postings are used (all postings are reversed in red):
- Dt 62 Kt 90/1 – revenue if the defect is returned to the manufacturers;
- Dt 90/2 Kt 43 – cost of returned products;
- Dt 90/3 Kt 68 – VAT on returned products.
Further:
- Dt 68 Kt 19 deduction of VAT on returns;
- Dt 90/2 Kt 28 – losses from defects were recorded.
If the person at fault in the company is identified, part of the costs can be attributed to him:
- Dt 73 Kt 28 – accrual;
- Dt 70 Kt 73 – deduction from salary.
If the culprit is determined - the supplier of raw materials, spare parts, which were then put into production, part of the costs can be claimed:
- Dt 76/2 Kt 28 – amount of claim to the counterparty;
- Dt 51, 50 Kt 76/2 – refund of money on a claim in cash or by transfer.
Results
There are several types of marriage. Depending on its classification, the rules for including losses from defects in the cost of production vary. Accounting for defects in an enterprise is important for detecting the causes of defects, analyzing and tracking changes in losses from defects, as well as for improving the quality of manufactured products.
Read about the tax nuances of returning defective products in the material “The buyer returned a defective product.
How to reflect the refund in the seller’s tax accounting? You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Reflection of an external correctable defect
Expenses that increase costs include:
- confirmed costs for correcting defects from the consumer;
- costs of transporting defective products;
- reimbursement of other buyer expenses associated with defective products.
If the defect is corrected by the manufacturer, it is accounted for during the correction time in off-balance sheet account 002.
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | Transaction amount | A document base |
| 60.01 | Transport costs are included in the amount of losses from defects | 200 | Carrier invoice | |
| 10.01, , 69, | Manufacturer's expenses for correcting defects are taken into account | 800 | Help-calculation | |
| 20.01 | Costs for correcting defects by the manufacturer are included in the cost of production | 1000 |
Example of using count 28
At a plant producing various metal parts, the quality control service identified a defective product, which a specialist characterized as an irreparable defect. The acceptance committee conducted an inspection and determined that the defect arose through the fault of the employee. The following calculation was made:
- the cost of creating a part, including costs for casting, wages, experimental work and experimental work, amounted to 50 thousand rubles;
- It is possible to sell a defective part for scrap and receive 12 thousand rubles;
- 10 thousand rubles were collected from an employee of the enterprise;
- Uncompensated damage amounted to 28 thousand rubles.
Basic Concepts
A defect is a product, work process or its component that does not meet established requirements and standards. A defective product cannot be used for its intended purpose without correction.
Identifying and sending the finished product for revision is the concern of the quality control service, which is the most important component of the organizational structure of enterprises.
Based on the specifics of detection, marriage is divided into two large categories:
- external defect identified by the consumer;
- internal defects identified either by quality control department employees or workshop and warehouse workers.
External defects are more expensive for the enterprise, as they contribute to:
- a decrease in customer loyalty to the manufacturer and its products immediately after purchasing the first defective product;
- the formation of losses not only due to the costs of creating products, but also related costs - transportation, sales, compensation, etc.
How will rejected products be reflected in tax accounting?
The write-off of defective goods from the warehouse is not limited to accounting entries alone. This is a complex process in which tax legislation cannot be avoided. The culprit for dragging tax authorities into the algorithm of accounting actions is the returned VAT.
Where should the cost of damaged goods be included?
It is quite risky to take into account the cost of defective goods as expenses in tax accounting, because such a position will have to be defended in court. It is safer for an enterprise to simply not take these expenses into account when calculating income tax. The Tax Code allows you to attribute financial losses from writing off defective products to other expenses in accordance with Art. 264 clause 1 sub. 47 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
But here a controversial question arises: “Can a company that is not a manufacturer of an unsuitable product take advantage of this?” There is no direct prohibition by tax legislation for this, but judicial practice is such that inspectors often oppose accounting for such expenses. And the courts agree with the inspectors on this issue.
On our website you will find other materials about products of poor quality. After reading them, you will learn:
- What can a buyer demand when purchasing a low-quality product and how to file a claim?
- What does it mean to eliminate deficiencies and what is the time frame for its implementation?
- What to do and where to turn when identifying hidden shortcomings?
- What are the significant disadvantages of a technically complex product?
- Where to go when purchasing a low-quality product?
- Who is responsible for the sale of defective goods and is there compensation for damage caused by such goods?
Is it necessary to restore VAT?
No manipulations with VAT restoration are needed in only one case - if the detected defect is recognized as technically inevitable. After all, there is no need to charge VAT to compensate for input tax.
In other cases, VAT restoration is mandatory if the accountant does not want problems with tax inspectors.
Clause 3 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is an exhaustive list of situations in which a legally accepted input tax is subject to restoration. However, in this norm there is no basis in the form of writing off a defect that is unsuitable for subsequent sale. Input VAT must be restored in the period of write-off of goods .
This is due to the fact that these products will not be used to carry out transactions that are recognized as subject to taxation in the Tax Code. In accordance with Article 23 of the Tax Code, established taxes are transferred to the budget by the payer. That is, the payment of a lawfully made decision for the deduction of value added tax is enshrined in legislation and is therefore mandatory.
Writing off defective goods from a warehouse is a long and tedious process. After all, it affects not only accounting, but also the tax office. The amount of losses from marriage in tax accounting as part of accounting expenses reduces the object of taxation with the help of income tax. It is also important to remember the amount of restored VAT - all these are additional costs that fall on the enterprise due to someone’s negligence in the production of products.
Characteristics of 28 accounts in accounting
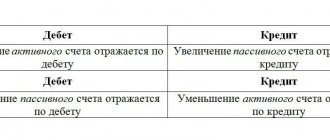
To account for defective production products in the Chart of Accounts, account 28 is used. It is active, as it reflects the cost of defective products and the cost of correcting them at the beginning of the period.
You might be interested in:
Account 20 in accounting “main production”: what is it used for, characteristics, subaccounts, postings
The debit of account 28 reflects the cost of defects identified in production, as well as all costs incurred by the company to bring products to the standards required by regulations.
The credit of the account reflects the cost of the corrected finished product, or the cost of defects written off as costs due to the impossibility of correction, as well as the cost of material assets that can be used, amounts attributed to the guilty parties, etc.
The debit balance of account 28 is determined by adding the initial balance to the debit turnover of the account and subtracting from it the loan amounts for the period under review. Subaccounts 28 accounts
Analytical accounting for account 28 is built in accordance with the characteristics of the activities carried out by the enterprise.
Subaccounts to this account can be opened:
- By structural divisions where product defects occurred.
- In types of defective products.
- According to cost items for correcting defective products.
- Due to the reasons for the occurrence of defects in production.
- For the guilty persons, as a result of whose activities or inaction a defect occurred in production.