In any production process, failures can occur, resulting in instead of finished products. A manufacturing defect is understood as a product that has gone through certain stages of processing, but does not meet the required characteristics and properties. However, this will not include products that are manufactured to increased requirements, since the characteristics of the finished product will not exactly correspond to the standard ones, but will be higher. Also, a downgrading of a product’s grade is not considered a defect, for example, the assignment of flour, initially produced as first-grade, to a second grade, established at the quality control stage.
As a rule, the organizational structure of manufacturing enterprises includes a quality control department, which is responsible for identifying defects and redirecting them for revision if necessary. Depending on the location of detection of defective products, defects are divided into:
- internal (identified by the quality control service, or directly by the workshop/warehouse employees);
- external (identified by the end user).
To minimize reputational risks, it is more profitable for an enterprise to identify defects either at the production or warehousing stage, this will avoid deterioration in the loyalty of product consumers to the brand.
Economically, external defects are more expensive for an enterprise, since in addition to the direct costs of producing the product, it includes sales costs, transportation costs, and also causes indirect damage to the company’s reputation.
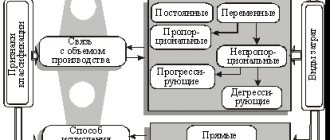
Defects include products, parts or work that do not meet established standards or technical specifications in quality and cannot be used for their intended purpose or can be used only after correction.
| Buy ★ bestselling book “Accounting from scratch” for dummies (understand how to do accounting in 72 hours) > 8000 books purchased |
What to do if a manufacturing defect is identified?
At one of the stages: during the production process, storage of finished products in a warehouse, or after selling the goods to the final buyer, a defect is identified.
Responsible employees determine what type of “rejected products” are: (click to expand)
- correctable defects (products are subject to modification, after which they acquire all the required technical characteristics. It is important that the costs of modification are economically justified);
- irreparable defect (rework of rejected products is impossible, or the costs of rework are too high and not economically justified).
If a decision is made to eliminate product defects and the defect is considered correctable, then the product is sent to the workshop for revision. To the cost of repairable defects, the costs of materials, employee wages with deductions, etc. are added. Subsequently, the product is returned for sale.
If the defect cannot be corrected, the responsible employee determines what in the product can be usefully used in production, and what should be recycled? If the components retain their usefulness (for example, zippers in a tailoring workshop), they will be separated from the rejected product and used for their intended purpose in the production of similar products. The cost of useful scrap parts is determined by the price of possible use.
If an enterprise produces warranty products, then it is obliged to create a reserve for repairs. In this case, losses from defects are written off against the guarantee reserve (account 96).
When identifying rejected products, the person who caused the defect is always identified. The culprit may be a supplier of low-quality materials or an employee of the enterprise. A claim is submitted to the supplier. If it is recognized by the supplier, the amount of compensation paid by him is counted towards the reduction of defective expenses.
If an employee is found to be at fault, then the amount of expenses related to the marriage is established and is subject to deduction from wages. By law, you can deduct no more than 20% from your salary each month.
What is considered marriage
When writing off, it is important for the accountant to understand what is considered a defect and what is not. You can be guided by the Chart of Accounts of Accounting for the Agro-Industrial Complex and methodological recommendations for its application (Prospect of the Ministry of Agriculture dated No. 654 06/13/01), which provides an industry-wide description of production defects. These are products, semi-finished products, parts, units and works:
- not meeting standards, technical specifications, building codes;
- not used for its intended purpose without additional costs for correction.
According to the nature of the defects, marriage is divided into correctable and irreparable, or final. Correctable defective products include those that can be used for their intended purpose after modification (correction), if it is recognized as economically profitable. A defect that cannot be technically corrected or is not economically viable is final.
The classification of defective products as various types of defects must be confirmed by a document. As a rule, this is an act signed by competent employees of the company.
Marriage is also divided into internal and external.
In the first case, low-quality products are detected by the company's control service, and in the second - outside the company, by the buyer.
These types of marriages can also be correctable or irreparable and must be documented.
Products that do not meet the enhanced quality standards, but meet the standards for similar products, as well as those of a lower grade compared to the total mass of the lot, are not considered defective.
In accordance with the classification of marriage, the costs for it also vary. Thus, the cost of a correctable defect may include the salary of workers involved in these operations, with deductions, the cost of energy resources, and the cost of correcting the same external defect may include the amount of transportation costs if it is necessary to correct the defect from the buyer, etc.
Account 28 for recording marriage
To account for defects, account 28 is used. The account is active. During the month, a debit account turnover is formed, including production costs incurred during the creation of defective products, as well as rework costs. Credit turnover - amounts received from the culprits to reimburse expenses for the defect, as well as parts of the defect that have not lost their usefulness and are subject to return to production. The final balance is the amount of losses. It is subject to write-off at the end of each month. It is written off either to the costs of manufacturing similar products or to account 25.
It is advisable for manufacturing enterprises to maintain analytical accounting on account 28. The subaccounts for which analytics will be collected must be specified in the accounting policy. A special feature of analytical accounting of marriage is the ability to collect information in accounting on the reasons for the marriage and the persons through whose fault the marriage occurred. Such analytics allows you to track the sources of defects and improve the production process, increasing its efficiency.
Accounting for manufacturing defects is important for tax purposes. It affects the two most important taxes - income tax (IP) and VAT. You should understand the intricacies of tax accounting in a separate article. Now let's look at the most common cases.
Losses due to marriage are officially expenses that reduce the tax base of an NP. When calculating the costs of losses due to defects, it should be taken into account that only that part that could not be attributed to materials or to the guilty person can be attributed to expenses. Also, all business transactions involving marriage must be documented in the prescribed manner.
When accounting for VAT on internal defects, there are often controversial issues with the tax service. In order to avoid disputes, manufacturing enterprises “restore” VAT. With an external defect in tax accounting, everything is more clear: the company reduces the amount of VAT that it previously accrued and paid by the amount of VAT on the sale of the returned product.
Losses from marriage: accounting and use
If in the manufacture of products that turn out to be defective, the employee is not at fault, then payment for labor for its production is made on an equal basis with suitable products. Complete defects caused by the employee are not subject to payment. If a partial defect is recognized due to the fault of the employee, then the products are paid at reduced prices depending on the degree of suitability of the products (Article 156 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). These prices are usually set by the organization's management.
Example 1 An employee is given a piecework wage. In a month he produced 160 units. products. According to the prices per unit of production, the employee is charged 95 rubles.
Upon acceptance of products, manufacturing defects were detected in 11 products. It happened due to the fault of the employee. At the same time, 3 products were recognized as completely defective, and 8 units were considered partially defective. The suitability of this part of the rejected products was recognized by management as 80 percent. Based on this ratio, a decision was made on the rates of payment.
At the end of the month, the employee was accrued 14,763 rubles. (95 RUR/unit x (160 units – 11 units) + 95 RUR/unit x 80% x 8 units).
________________
End of example 1
Since the release of defective products entails direct losses for the employer, expressed in excess consumption of raw materials, materials, increase in production costs, then for the damage caused to him in connection with the release of defective products by the employee through his fault, the latter can be held financially liable in the prescribed manner (Art. 238 Labor Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, its total value cannot exceed the average monthly earnings of the employee (Article 241 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Every month you can withhold no more than 20% of your earnings (Article 138 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let's look at possible accounting options using examples.
Internal irreparable marriage without culprits
Example 2 A worker made a defect in the manufacture of products.
The marriage is declared final. There are no persons responsible for making the defect. It was considered inappropriate to continue using MPZs obtained from defective products. The cost of rejected products consists of the cost of materials - 6,500 rubles, accrued wages of production workers - 1,600 rubles, unified social tax and insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases - 592 rubles, expenses of auxiliary production, general production and general business expenses - 1808 rubles.
When writing off the cost of rejected products - 10,500 rubles. (6500 + 1600 + 592 + 1808) the following entry is made in accounting:
Debit 28 Credit 20
— 10,500 rub. — the cost of the marriage is written off;
Since there are no values that reduce the cost of scrap, it is fully attributed to expenses for ordinary activities:
Debit 20 Credit 28
— 10,500 rub. – losses from marriage are reflected.
_________________________
End of example 2
Internal irreparable defect due to the fault of the employee
Example 3 We use the data from example 2. The marriage is declared irreparable.
In this case, the employee’s fault was established. A decision was made to compensate him for material damage in the amount of average earnings - 7,500 rubles. The cost of materials obtained from defective products is 2,350 rubles.
When reflecting these transactions in the accounting accounts, the following entries are made:
Debit 28 Credit 20
— 10,500 rub. — the cost of the marriage is written off;
Debit 10 Credit 28
— 2350 rub. – reflects the cost of materials obtained from defective products;
Debit 73 subaccount “Calculations for compensation of material damage” Credit 28
— 7500 rub. – the employee’s debt for compensation for losses from marriage has been accrued;
Debit 20 Credit 28
— 650 rub. (10,500 – 2350 – 7500) – losses from defects are taken into account in expenses for ordinary activities.
Taking into account the existing limitation on the amount of deductions from wages, the following entries are made in accounting for several months until the debt is fully repaid:
Debit 70 Credit 73 subaccount “Calculations for compensation of material damage”
- a deduction has been made from the employee’s salary to pay off the debt.
____________________
End of example 3
Correctable marriage due to the fault of the employee
Example 4 An organization produces furniture.
The technical control department drew up a marriage report. A set of upholstered furniture was rejected. The marriage was recognized as correctable; it arose through the fault of the employee. To correct the marriage, in addition to the culprit, another employee is brought in. The latter was awarded 1,500 rubles for correcting the defect. The total rate of unified social tax and tariffs of insurance premiums for worker accruals is 37%. The cost of materials consumed when correcting defects is 3,500 rubles, the amount of general business expenses associated with correcting defects is 145 rubles. The guilty employee compensates for material damage in the amount of average earnings, which is 4,200 rubles.
The work of the guilty worker to correct the marriage is not paid.
In the event of a correctable defect, losses from the defect are reflected in the organization’s accounting records as follows:
Debit 28 Credit 10
— 3500 rub. — materials for correcting defects were written off;
Debit 73 subaccount “Calculations for compensation of material damage” Credit 28
— 4200 rub. — the worker’s debt for compensation for material damage is reflected;
Debit 28 Credit 70
— 1500 rub. – wages were accrued to the second employee for correcting the defect;
Debit 28 Credit 69
— 555 rub. (RUB 1,500 x 37%) – UST and insurance premiums are charged;
Debit 28 Credit 26
— 145 rub. – reflects the amount of general business expenses associated with correcting the defect;
To determine losses from defects, it is necessary from the total amount of expenses associated with correcting defects - 5,700 rubles. (3500 + 1500 + 555 + 145) subtract the amount reimbursed by the employee - 4200 rubles. Result - 1500 rubles. (5700 – 4200) and is taken into account in production costs:
Debit 20 Credit 28
— 1500 rub. — losses from defects are included in expenses for ordinary activities.
Since the employee compensates for material damage in the amount of average earnings, the amount due is withheld in installments over several months:
Debit 70 Credit 73 subaccount “Calculations for compensation of material damage”
— part of the amount of material damage (no more than 20 percent of earnings) is withheld from the earnings of the guilty employee.
___________________
End of example 4.
Correctable external defect
When reflecting an external correctable defect transaction in accounting, almost the same entries are used as for an internal correctable defect, since in this case there is no replacement of sold products.
Example 5 The buyer of a refrigerator contacted the organization that produces them with a complaint regarding its operation. These shortcomings are recognized as a correctable defect. To bring the refrigerator into working condition, it was necessary to replace a number of parts, the cost of which was 2,460 rubles. For carrying out corrective work, an employee of the organization was awarded 800 rubles. Transportation costs associated with the employee’s departure amounted to 144 rubles.
The organization does not create a reserve for warranty repairs.
Corrected external defects are reflected in accounting as follows:
Debit 28 Credit 10
— 2460 rub. – reflects the cost of parts used to repair the refrigerator
Debit 28 Credit 70
— 800 rub. — wages were accrued to the employee who carried out work to eliminate the defect;
Debit 28 Credit 69
— 296 rub. (800 rub. x (28% + 4% + 0.2% + 3.4% + 1.4%)) – unified social tax and insurance premiums are accrued;
where 1.4% is the tariff for compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases;
Debit 28 Credit 26
— 144 rub. – employee travel expenses are included in losses from marriage;
Debit 20 Credit 28
— 3700 rub. (2460 + 800 + 296 + 144) - losses from defects are included in expenses for ordinary activities.
_________________
End of example 5
Incorrigible external marriage
Example 6 In July 2004, a furniture manufacturing organization sold a set of upholstered furniture.
Its cost is 25,960 rubles, including VAT - 3,960 rubles. The cost of the set is 16,490 rubles. The buyer discovered defects in it. They were presented with a demand for the return of previously paid money, as well as compensation for expenses associated with the purchase of furniture. Their value is 1000 rubles. The organization, recognizing the defect as irreparable, agreed with the buyer’s demands. The furniture was removed by the organization's transport, the costs amounted to 450 rubles. The cost of materials obtained during disassembly of the defective kit, at the price of possible use, amounted to 5,740 rubles. A complete set of documents on the fact of marriage being examined was received by the accounting department in August.
The organization does not create a reserve for warranty repairs and warranty service.
In July, in the accounting records, the sale of a set of upholstered furniture was accompanied by the following entries:
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
— 25,960 rub. — revenue from the sale of a set of upholstered furniture is reflected;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
— 3960 rub. — VAT charged;
Debit 90-2 Credit 43
— 16,490 rub. — the cost of the sold sofa is written off;
Debit 51 Credit 62
— 25,960 rub. - money has been received from the buyer.
When determining the financial result from sales for July 2004, the profit from the sale of a set of upholstered furniture was also taken into account - 5,510 rubles. (25,960 – 3960 – 16,490):
Debit 90-9 Credit 99
— reflects the financial result from sales for July 2004.
Upon receipt in August of a set of documents documenting an external irreparable defect, the following entries are made in accounting:
Debit 90-9 Credit 99
— 5510 rub. – the amount of profit received from the sale of a set of furniture was reversed;
Debit 62 Credit 90-1
— 25,960 rub. — the proceeds from the sale were reversed;
Debit 90-3 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
— 3960 rub. — the amount of accrued VAT is reversed;
Debit 90-2 Credit 43
— 16,490 rub. — the cost of finished products was restored;
Debit 28 Credit 43
— 16,490 rub. – reflects the cost of the rejected set of upholstered furniture;
Debit 62 Credit 76
— 25,960 rub. — the debt to the buyer is reflected;
Debit 28 Credit 76
— 1000 rub. — the buyer’s expenses associated with the purchase of furniture are taken into account;
Debit 28 Credit 23
— 450 rub. – transport costs associated with the return of a set of furniture are reflected;
Debit 76 Credit 51
— 26,960 rub. (25,960 + 1000) – the amount due to the buyer is transferred;
Debit 10 Credit 28
— 5740 rub. – reflects the cost of materials obtained during disassembly of the defective kit;
Debit 20 Credit 28
— 12,200 rub. (16,490 + 1000 + 450 – 5740) - losses from external defects are taken into account in expenses for ordinary activities.
___________________
End of example 6
Use of marriage
The resulting defect can be used in its new capacity for the needs of the organization itself. Thus, in some organizations the technological process provides for the reuse (recycling) of defects as returnable waste for the production of products. Let us recall that returnable production waste refers to the remnants of raw materials, materials or semi-finished products formed during the transformation of the source material into finished products, which have lost completely or partially the consumer qualities of the source material (chemical or physical properties, including fullness, configuration, etc. ) and therefore used at increased costs (reduced product yield) or not used at all for their intended purpose (clause 27 of the Basic Provisions). The same definition was given to returnable waste in paragraph 6 of the Regulation on the composition of costs. At the same time, the Regulations also defined the procedure for their assessment. Returnable waste could be valued by:
Example of using 28 count
In March 2016, an inspector discovered a defect at a plant producing parts for the defense industry. The controller classified it as not correctable. The acceptance committee found that the defect arose due to the fault of the milling machine operator.
The cost of creating the part amounted to 50,000 rubles, including the cost of casting, employee salaries with deductions, depreciation of equipment, maintenance and experimental work.
A rejected part can be scrapped for 12,000 rubles. It was decided to collect 10,000 rubles from the milling machine operator.
| Business transaction | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| Rejected part written off | 28 | 20 | 50 000 |
| The rejected part is accepted for accounting at the price of scrap metal | 10 | 28 | 12 000 |
| The amount of compensation for the marriage is allocated to the guilty person | 73 | 28 | 10 000 |
| Unreimbursed losses on defective parts were included in the costs of production of GP | 20 | 28 | 28 000 |
A fixable marriage. Calculation of the cost of partial defects (account 28)
As we said above, a marriage can be fixable or irreparable. Depending on this, different entries are made in accounting. Let's consider both cases, using examples. Let's start with postings for correctable defects.
Ivanov manufactured a defective part. Petrov corrected him.
Costs for correcting defective products: (click to expand)
- cost of materials 100 rubles,
- Petrov's salary is 500,
- insurance premiums from Petrov’s salary 180.
500 was withheld from Ivanov’s salary at a reduced rate. What transactions need to be reflected?
Postings for accounting for correctable defects
| Sum | Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 100 | 28 | 10 | Material costs for correction are taken into account |
| 500 | 28 | 70 | The cost of salary for an employee correcting a defect is taken into account |
| 180 | 28 | 69 | Accrued insurance premiums from the salary of the employee who corrected the marriage were taken into account |
| 500 | 73 | 28 | Withheld from the salary of the guilty employee |
| 280 | 20 | 28 | Losses from defects are written off to the cost of production |
As we see from this example, if it is possible to correct the defect, then in the debit of the account. 28 collects all costs for correcting defective products.
From a loan account 28 the amount of these costs is written off to the cost of production in the debit of the account. 20 “Main production”, as discussed in the previous article.
If some fine is withheld from the guilty employee (we read about the employee’s financial liability), then the costs of correcting defective products are partially reduced, and the fine is written off from the credit account. 28 to the debit of the account. 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations.”
We will consider account 73 in detail in the near future, do not forget to subscribe to our newsletter to learn about the release of new articles.
Concept and types
The current legislation on accounting and tax accounting does not contain the concept of “marriage”.
It is disclosed in industry recommendations for accounting and calculating products only on the basis of how this term is specified in paragraph 38 of the Basic Provisions for Planning, Accounting and Calculating Costs at Industrial Enterprises, approved by government agencies of the USSR in 1970. According to this document, those production products that do not meet standards or technical specifications and cannot be used for their intended purpose or can, but only after correction, are considered defective. Depending on the possibility of using a product with defects and on why, where and at what moment such a defect occurs, there are the following types:
An irreparable marriage. Calculation of the cost of final marriage (account 28)
Ivanov allowed an irreparable defect in the part.
According to the calculation, the actual cost of the final defect was:
- materials - 100 rub.,
- transportation costs - 20,
- salary - 500,
- insurance premiums - 180,
- general production expenses - 30.
500 were withheld from Ivanov. Returnable waste after writing off the defective part amounted to 80 rubles. What kind of wiring do we do?
First of all, we calculate the cost of the final defect: 100+20+500+180+30=830 rubles.
Postings for accounting for irreparable defects
| Sum | Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 830 | 28 | 20 | The cost of the defective part has been written off |
| 500 | 73 | 28 | Deducted from an employee who allowed the production of a defective part |
| 80 | 10 | 28 | Returnable waste from rejects is entered into the materials warehouse for further use. |
| 250 | 20 | 28 | The remaining losses from defects are written off to the cost of production |
Defects in production can also be grouped according to the location of the defect: internal and external.