Who can provide financial assistance free of charge?
Any of its founders, that is, both individuals and legal entities, can provide financial assistance to the organization. But at the same time, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clearly establishes a list of cases when property received free of charge may not be included in the tax base:
- The individual who contributes the funds has a share in the authorized capital of more than half.
- The legal entity that contributes the funds has a share in the authorized capital of more than half.
- A legal entity that receives funds free of charge has a share exceeding 50% in the authorized capital of the organization that contributes the funds.
This list can be found in paragraphs. 11 clause 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In all other cases, assistance that is expressed in monetary units must be included in the tax calculation.
AGREEMENT ON FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE ON A REFUNDABLE BASIS
Almaty city “___” ______________ 2016
_________________________, hereinafter referred to as the “Lender”, on the one hand, and
Limited Liability Partnership "_________________" , represented by ______________________, acting on the basis of the Charter, hereinafter referred to as the "Borrower", on the other hand,
hereinafter referred to as the “Parties”, and each individually “Party”, have entered into this agreement on financial assistance on a repayable basis (hereinafter referred to as the “Agreement”) as follows:
How to apply for financial assistance from the founder
The Federal Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ requires that all receipts to the organization’s current account and cash desk, including gratuitous assistance, be documented.
The most common method of gratuitous assistance is the conclusion of a gift agreement or gratuitous financial assistance between the one who contributes money and the one who receives it.
Also, the founder can use funds to increase the authorized capital, but in this case, his share must be increased (naturally, except in the case when the company has one founder), and the assistance can no longer be considered gratuitous. In this case, registration occurs in the following way:
- An application is drawn up indicating the amount and conditions for its contribution to the authorized capital.
- Other owners express their consent and decide to make amendments to the company's charter.
- All changes (re-registration of shares) must be made within 6 months after the decision is made.
In any case, before providing assistance, the founder must agree on this at a general meeting (or make a decision individually, if there is only one founder).
Free assistance from the founders: accounting and taxation
Company GARANT
LLC applies PBU 18/02. The shares of the two founders in the authorized capital of the LLC are 99% and 1%. How should gratuitous financial assistance from founders be reflected in accounting and tax accounting?
The right of the founders of the company to provide financial assistance to the company is not limited by law.
Thus, the founder has the right to provide such assistance by making a contribution to the property of the company.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 27 of Federal Law No. 14-FZ of 02/08/1998 “On Limited Liability Companies” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 14-FZ), company participants are obliged, if provided for by the charter of the LLC, by decision of the general meeting of participants to make contributions to the company’s property. Such an obligation may be provided for by the charter of the company upon its establishment or by amending the charter by decision of the general meeting adopted unanimously by all participants of the company.
Contributions to the property of the company are made in money, unless otherwise provided by the charter or decision of the general meeting of participants of the company (clause 3 of article 27 of Law No. 14-FZ).
According to paragraph 4 of Art. 27 of Law No. 14-FZ, contributions to the company’s property do not change the size and nominal value of the shares of its participants in the authorized capital of the company.
Consequently, contributions to the company’s property may be a way for its participants to provide free financial assistance to the company. This is formalized by recording in the minutes of the general meeting of company participants the decision to make contributions to the property of the LLC.
VAT
In accordance with paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, transactions involving the sale of goods (work, services) on the territory of the Russian Federation are recognized as subject to VAT.
According to paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 162 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the VAT tax base is increased by amounts received for goods (work, services) sold in the form of financial assistance, to replenish special-purpose funds, to increase income, or otherwise related to payment for goods (work, services) sold.
Consequently, if the funds received free of charge by the organization from the founders are not related to payment for goods (works, services) sold by the organization, then such funds are not included in the VAT tax base (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/09/2009 N 03-03- 06/1/380).
Income tax
In accordance with paragraph 8 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income in the form of property received free of charge, regardless of whether it was transferred by a legal entity or an individual, with the exception of the property listed in Art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for tax purposes, profits refer to non-operating income that forms the tax base of the reporting (tax) period for calculating tax.
According to paragraphs. 11 clause 1 art. 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the tax base for corporate income tax, income in the form of property received by the organization free of charge from the organization (individual) is not taken into account if the authorized (share) capital (fund) of the receiving party consists of more than 50% of the contribution (share ) transferring organization (individual).
In the situation under consideration, the shares of the founders in the authorized capital of the company are 99% and 1%, respectively. Consequently, funds received free of charge by an organization from a founder with a 99% share in the authorized capital are not taken into account when determining the tax base for income tax. A similar conclusion is presented in letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 20, 2010 N 03-08-05, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated October 10, 2007 N 20-12/096580, dated April 16, 2007 N 20-12/035982, dated October 6, 2006 N 19-11/87982, dated 03/22/2006 N 20-12/22187.
Funds contributed as a contribution to the property of the company by a participant with a 1% share in the authorized capital are taken into account for tax purposes as part of non-operating income on the basis of clause 8 of Art. 250 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Accounting
The procedure for reflecting in accounting and reporting transactions on contributions to the property of the company is not regulated by regulatory legal acts on accounting.
At the same time, accounting for the financial assistance of the founders in the form of contributions of participants to the property of the company as other income contradicts the requirements of PBU 9/99, since according to clause 2 of PBU 9/99, the organization’s income is recognized as an increase in economic benefits as a result of the receipt of assets (cash, other property ) and (or) repayment of obligations, leading to an increase in the capital of this organization, with the exception of contributions from participants (owners of property).
For accounting purposes, contributions to property are not recognized as gratuitously received property, because contributions to property affect the size of net assets, on the basis of which the actual value of the participants' share is determined. According to the Recommendations to audit organizations (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 29, 2008 N 07-05-06/18), in the accounting records of the recipient company, the participant’s contribution to the property is reflected in the debit of the property accounting accounts in correspondence with the credit of account 83 “Additional capital” (see also letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 13, 2005 N 07-05-06/107).
In our opinion, to reflect this transaction in the accounting accounts, it is necessary to make the following entries:
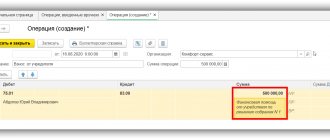
Debit 75 Credit 83 - reflects the amount of debt of participants on contributions to the property of the company based on the decision of the general meeting of participants of the company;
Debit 51 (50) Credit 75 - funds received as a contribution to the property of the company.
Thus, the financial assistance of the founders in the form of a contribution to the property of the company is reflected in the liability of the Balance Sheet (Form 1) in Section III “Capital and Reserves” in the line “Additional Capital” (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2003 N 67n “On Forms financial statements of organizations).
This information is also subject to disclosure in the explanatory note to the annual financial statements.
Considering that there is no income in accounting, and in tax accounting the assistance of a participant with a share in the authorized capital of 1% is recognized as part of non-operating income, in connection with this a permanent difference arises, leading to the formation of a permanent tax liability (clauses 4, 7 PBU 18/02 “Accounting for income tax calculations”).
In this case, the following entry should be made in the accounting:
Debit 99, subaccount “Permanent tax liabilities” Credit 68, subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - a permanent tax liability has been accrued.
For your information:
If the organization plans to return the funds received from the founders, then these funds can be considered as a loan (Article 810 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 807 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, under a loan agreement, one party (the lender) transfers money into the ownership of the other party (borrower), and the borrower undertakes to return the same amount of money (loan amount) to the lender. The loan agreement is considered concluded from the moment the money or other things are transferred.
According to paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 161 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, transactions of legal entities between themselves and with citizens must be concluded in writing.
According to Art. 809 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the loan agreement is compensated, which is expressed in the payment by the borrower of interest on the loan amount. The condition that the contract is free of charge must be specified in the text of the contract itself. Since the purpose of providing funds is to provide financial assistance to the organization, the agreement should indicate that the founder is providing an interest-free loan. At the same time, on the basis of Art. 814 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a loan agreement can be concluded with the condition that the funds received are used for certain purposes.
The chart of accounts reflects loans received depending on their repayment period. To summarize information on the status of short-term (for a period of no more than 12 months) loans and borrowings received by an organization, Account 66 “Settlements for short-term credits and borrowings” is intended in the Chart of Accounts; for long-term loans (for a period of more than 12 months) an account is provided 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings.” The amounts of loans received by the organization are reflected in the credit of account 66 (67) and the debit of accounts 50 “Cash”, 51 “Settlement accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts” and others.
When receiving and returning an interest-free loan from the founder, the accountant must make the following entries:
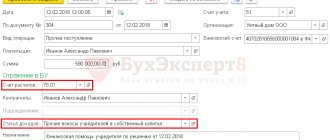
Debit 51 (50) Credit 66 (67) - received an interest-free loan from the founder;
Credit 66 (67) Debit 51 (50) - return of an interest-free loan.
Answer prepared by: Expert of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT Kalashnikov Alexander
Response quality control: Reviewer of the Legal Consulting Service GARANT Monaco Olga
Question from Clerk.Ru reader Evgenia (Vladivostok)
Our organization is based on the simplified tax system, the founder has a 100% share.
According to Article 251, paragraph 11, income for us is not income: 11) in the form of property received by a Russian organization free of charge: from an individual, if the authorized (joint) capital (fund) of the receiving party consists of more than 50 percent of the contribution (share ) of this individual.
Does this item include cash? Tax authorities seem not to mind not counting in income funds received from the founder on a free basis (with a share in the management company of more than 50%), but at the same time they insist on formalizing these contributions in the form of a loan agreement.
In our opinion, a loan agreement is not appropriate here, because no money is returned to the founder, no interest is accrued and no material benefits are accrued.
Are the actions of the tax authorities legal? If not, what documents are required to formalize the founder’s contribution on a gratuitous and irrevocable basis to the organization’s account?
Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes a list of income that is not taken into account when determining the tax base for an organization’s profit tax. In particular, property received by a Russian organization free of charge from an individual is not taken into account as income if the authorized capital of the receiving party consists of more than 50 percent of the contribution (share) of this individual.
From Art. 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation it follows that money is recognized as movable property. In the situation under consideration, the share of the founder is 100 percent, therefore, funds received free of charge from the founder are not included in income when calculating the taxable base for income tax on the basis of paragraphs. 11 clause 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This norm is also applicable to “simplified” people (clause 1, clause 1.1, article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Under a loan agreement, one party (the lender) transfers into the ownership of the other party (borrower) money or other things determined by generic characteristics, and the borrower undertakes to return to the lender the same amount of money (loan amount) or an equal number of other things received by him of the same kind and quality (Article 807 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Since in this case there is no obligation to return the money to the founder, the tax authorities have no right to demand the conclusion of a loan agreement.
Such a transaction is formalized by a gift agreement, and its oral form is possible, since the donor is an individual (Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In a payment order for the transfer of money (or in a cash order), you can use, for example, the following wording: “Free financial assistance from the founder for the development of activities.”
Let me remind you that under a gift agreement, one party (the donor) gratuitously transfers or undertakes to transfer to the other party (the donee) an item of ownership or a property right (claim) to himself or to a third party, or releases or undertakes to release it from a property obligation to himself or to a third person (Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). According to Art. 128 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, objects of civil rights include things, including money.
It is very easy to get a personal consultation with Svetlana Skobeleva online - you need to fill out a special form. Several of the most interesting questions will be selected daily, the answers to which you can read on our website.
Agreement on gratuitous financial assistance from the founder: sample
The agreement is drawn up in writing, in two copies - one for each party.
In order for a document to be drawn up to qualify as a contract of gift or gratuitous assistance, it must contain the following features:
- The subject of the contract must be specified as precisely as possible. The monetary amount is indicated in numbers and words.
- The fact of gratuitousness. That is, it must be indicated that assistance is provided only unilaterally; the receiving party should not have any obligations.
The agreement on gratuitous assistance of the founder, a sample of filling, can be viewed below.
Responsibility for misuse of funds.
If during the proceedings between the parties to the targeted financing agreement it is proven that the recipient of the funds did not plan to use them for their intended purpose, but only received and appropriated these funds, or did not account for them within the established time frame, this act may be qualified under the article “Misuse budget funds"
Also, such an offense can be classified under the article “Fraud,” which already entails criminal liability.
In judicial practice, there are often situations when targeted financing is declared invalid.
The first and main reason is gratuitousness (that is, essentially Donation). It turns out that you can’t just take and transfer money. Judicial practice has taken a clear position that does not allow the conclusion of gratuitous agreements between legal entities.
Financial assistance agreement between legal entities: sample
It is worth mentioning separately about the agreement when assistance is provided by one legal entity to another. In this case, a gift agreement cannot be made - it may be considered void.
This follows from the provisions of Article 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which prohibits gift agreements between legal entities if the subject of the agreement (including funds) is valued at more than 3,000 rubles.
In this case, you can use the following methods:
- Conclude a free financing agreement.
- Conclude an agreement on an interest-free loan, and then not claim it and write off overdue payments (Article 415 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Borrowed funds are not taxed, as are interest savings, but the forgiven loan amount, which forms non-operating income for the borrower, is subject to taxation. A tax base is not formed when funds are received from a founder who owns at least 50% of the borrower's authorized capital.
- Contribute funds to increase the authorized capital. In this case, the organization that contributed the money must increase its share in the authorized capital.
The founder has the right to provide financial assistance to his company.
The law does not establish a list of purposes for which this money can be spent. In accordance with the law, funds received must be documented. If the founder who contributed the assistance is an individual, then a gift agreement can be concluded with him. In cases where assistance is provided by another organization, it cannot be formalized by donation. In some cases, the amount of money contributed free of charge by the founder is not taxed. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
The difference between a targeted financing agreement and a gift agreement.
The possibility of concluding a targeted financing agreement is a controversial issue, since it contains signs of a gift agreement. According to Art. 575 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, donations between legal entities in an amount exceeding 3 thousand rubles are prohibited.
You need to approach the conclusion of such agreements carefully.
Targeted financing is the transfer of funds for a specific project. Whereas donation simply involves the gratuitous transfer of funds. Their further fate depends entirely on the recipient.
Postings for repayable financial assistance
Special attention should be paid to the issue of reflecting the transfer of funds in accounting. Let's look at how repayable financial assistance postings are organized:
- For loans issued for a short period (up to a year), account 66 is used.
- If money is issued for a longer period (from a year), account 67 is used.
Depending on the method of receipt of funds, the mentioned accounts correspond with the accounts on which the receipt of finance is taken into account, namely from 50 to 52. Thus, the entries when receiving temporary financial assistance from the founder have the following form:
- Obtaining a loan for up to a year - D/C 51 (50, 52), 66.
- Obtaining a loan for a year or more - D/C 51 (50, 52), 67.
After the money is returned, the following entries are used: D/C 66 (67), 51 (50.52).