Capital is the main tool for a business owner, without which the entrepreneurial activity itself cannot even begin. Own capital consists of heterogeneous parts intended for specific purposes. One of the important and mandatory components of the capital of a legal entity is reserve capital. Unlike other shares of capital, there are some contradictory nuances in its formation, use and accounting.
Below we will consider the legal basis for its formation and application, main functions, connection with retained earnings, as well as the intricacies of accounting entries.
What is included in reserve capital ?
What is reserve capital
Any activity cannot be insured against losses. In entrepreneurship, where the financial issue is the main one, the constant presence of some financial “cushion” for unforeseen situations is especially relevant. It happens that it is impossible to obtain the necessary funds in any other way, while there are certain obligations to counterparties or an urgent need for immediate cash investments.
For these purposes, the enterprise must have a certain insurance fund - a reserve. Thus, reserve capital is a certain part of the organization’s property (or its profit), which performs an insurance function that guarantees the operation of the enterprise without interruptions and compliance with responsibility to counterparties. It consists of retained earnings placed in it.
In a broader aspect, the organization’s reserve fund is a financial source for:
- covering the lack of current assets when forming production reserves, unfinished projects, etc.;
- short-term financial investments.
What accounting data is used when filling out line 1360 “Reserve capital” ?
Purpose of reserve capital:
- compensation for losses if this is not possible from other sources;
- redemption of bonds;
- repurchase of shares of LLC or JSC;
- payment of income to investors (if profits do not allow this);
- dividends on preferred shares;
- compliance with urgent obligations to creditors that cannot be repaid in any other way.
Question: Is it possible to indicate in the charter of an LLC that profits are not distributed among the participants, but are directed to the reserve fund or for the statutory purposes of the company? How to reflect this? View answer
Laws of the Russian Federation on reserve capital
The creation of reserve capital is provided for legal entities - joint stock companies and limited liability companies. But the legislative justification for the formation of this part of equity capital for enterprises of different forms of ownership has significant differences.
Question: How to reflect in the accounting of a joint stock company (JSC) the formation of a reserve fund and its use to cover losses of the current reporting year? In accordance with the charter of the joint-stock company, a reserve fund in the amount of 4,000,000 rubles was formed from the net profit of previous years. Based on the results of the current reporting year, according to accounting data, a loss was received in the amount of 500,000 rubles, which, by decision of the board of directors, documented in the minutes, was covered from the reserve fund. View answer
Reserve capital for JSC
The legislative framework for the functioning of joint stock companies is regulated by the Law on JSC - Federal Law No. 208-FZ of December 26, 1995. Clause 1 of Art. is devoted to reserve capital. 35 of this Law. In it, entrepreneurs-shareholders are legally required to create reserve capital in their enterprise. Its size must be determined by the charter documents of the joint-stock company, but in any case not be less than one twentieth of the total authorized capital.
To form it, you need to annually deduct a certain percentage of profit to this fund (the amount of deductions is also specified in the Charter). It can be anything, but not lower than 5% of net profit, until the fund reaches the value defined in the Charter of the joint-stock company.
The purposes of using the reserve fund of a joint-stock company are strictly fixed in the following closed list:
- covering possible losses of the joint-stock company;
- redemption of bonds;
- share repurchase.
IMPORTANT! All these goals can be achieved through the reserve fund if there are no other sources of financing. It is not permitted by law to use money from the reserve fund for purposes not specified in this list.
Reserve capital for LLC
The Law on LLC (Federal Law No. 14-FZ of 02/08/1998) in Article 30 allows, but does not oblige the founders to create a reserve fund, as well as other funds for certain purposes. The dimensions are not strictly regulated, but it is necessary to streamline them in the statutory documents.
Since the LLC Law does not contain an indispensable obligation to create a reserve fund, the purposes of this part of the capital are not regulated. In this case, paragraph 69 of the “Regulations on Accounting and Accounting in the Russian Federation” may serve as a guide to action, which, in addition to the procedure for distributing funds from the reserve fund among various sub-accounts, lists possible ways of spending it. LLCs can use reserve capital for:
- compensation for losses;
- redemption of bonds;
- redemption of founder's shares;
- increase in the authorized capital.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If a JSC or LLC receives foreign investment, its reserve capital must be at least a quarter of the authorized capital, as required by the laws of the Russian Federation.
NWF: working conditions
The National Welfare Fund is formed in rubles. But different options are used to place funds: purchasing foreign currency, investing in bonds, shares, deposits, mutual funds. Money is allowed to be invested only in long-term reliable projects.
In 2022, almost 80% of the total funds were in the accounts of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in euros, US dollars, and British pounds. If necessary, this highly liquid capital will quickly pay off the budget deficit of the state or the Pension Fund.
How is reserve capital reflected in accounting?
As already mentioned, reserve capital is included as an integral part in the equity capital of a legal entity (clause 66 of the Accounting Regulations). Paragraph 69 of the same document stipulates that the reserve fund should be displayed separately in the balance sheet. For this purpose, a special account 82 “Reserve capital” is provided, which is a liability. It displays information about the availability of funds in the reserve fund and their dynamics.
Since funds for the reserve fund are taken from retained earnings, the credit of account 82 will function in correspondence with account 84 “retained earnings, uncovered loss.”
EXAMPLE 1. Supercontract LLC declared in its constituent documents the size of its authorized capital at 50 million rubles. – this figure appeared in the documents after the last meeting of the founders on February 15, 2022. The amount of reserve capital as of this date was 2 million 200 thousand rubles. Net profit according to the final documents of 2016 amounted to 12 million rubles.
The amount of reserve capital, in accordance with the requirements of the law and the Charter of Supercontract LLC, should be 5% of the total equity capital: 50 million rubles. X 5% = 2 million 500 thousand rubles. Annual contributions also amount to the statutory 5%. Thus, the net profit of the previous reporting year will contribute 12 million rubles to the reserve fund. X 5% = 600 thousand rubles.
To achieve the size of the reserve fund provided for by the Charter, 2 million 500 thousand rubles are missing. – 2 million 200 thousand rubles. = 300 thousand rubles. They can be accrued from the net profit of 2016, which was decided by the Board of Founders of Supercontract LLC.
The accounting entry was as follows:
15.02.2017
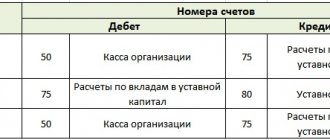
Debit 84, credit 82 – 300,000 rubles. – “Reserve capital has been formed from net profit.”
If the purpose of replenishing the reserve fund is to increase assets, then such an operation must again be reflected under credit 82, but debit 75 must be used - “Settlements with founders”. You can also open additional subaccounts.
EXAMPLE 2. JSC Trayan, represented by its shareholders, decided to increase the value of assets by 6,000,000 rubles, contributing the appropriate funds for this. This decision was reflected in the minutes of the meeting of the joint stock company dated March 13, 2017. Some shareholders transferred the necessary money the next day, March 14, 2017, and the last payment was made on March 21, 2017. This is what the final accounting entry will look like:
14.03. 2022 – 21.03.2017
Debit 51, credit 75 – 6,000,000 rub. – money was received from shareholders for the formation of reserve capital.
21.03.2017
Debit 75, credit 84 – 6,000,000 rub. – reserve capital has been formed through contributions from shareholders.
Target accounting of reserve capital
Since reserve capital (for joint stock companies) can be used exclusively for certain purposes, accounting in each specific case is strictly regulated by the Accounting Rules. The debit of account 82 can be in correspondence with the following accounts provided for in the Account Management Plan:
- 84 “Retained earnings, uncovered loss”;
- 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”;
- 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings.”
Analytical accounting of reserve capital
Unlike accounting, analytical accounting allows you to clarify the areas of use of reserve capital. Reserves formed by enterprises may have different destinations and sources.
- Reserves included in the cost. In accounting, this group of assets is reflected in passive account 96 “Reserves for future expenses.” They are regularly and evenly included in costs, each type of which corresponds to a separate subaccount of this account:
- vacation pay for staff;
- bonuses based on performance results;
- repair of fixed assets;
- warranty repairs and maintenance, etc.
- Reserves included in other income. Initially having different purposes, they are shown in different accounting accounts. When forming them, the amount of the created reserve is subtracted from the cost price, so they will be reflected on the balance sheet at the market value current on the date of entry. These amounts may be written off if they are not used by the beginning of the next accounting period. They are recorded in account 59 “Reserves for depreciation of financial investments.” Such reserves include:
- reserves created by reducing the value of tangible assets - when the market value on the date of entry into the balance sheet is lower than the actual value, the difference forms a reserve;
- depreciation of investment in securities - the same situation as with tangible assets can also arise with securities (purchasing them on the stock exchange at a cost higher or lower than their nominal value, the difference constitutes a reserve).
- Provisions for problematic debt . Problematic (doubtful) debt is a receivable that has not been repaid within the prescribed period and is not secured by guarantee obligations. Such debts can be identified after taking inventory at the end of the year. First you need to assess the debtor's potential ability to repay the debt. The year following the accounting year is allotted for this, during which the amount of debt will be considered a reserve. After this year, the unpaid debt that was the reserve will be listed as debt (5 years are allowed for this) and then will be written off as a loss.
- Additional capital. When an organization is doing well, its capital increases. There is an opportunity to increase assets, including reserve capital. Additional capital may consist of:
- revaluation of enterprise assets (current and non-current);
- the difference between the actual and nominal price of shares used for the authorized capital;
- differences in exchange rates when contributing shares to the authorized capital, if they were made in foreign currency.
ATTENTION! In accounting, when reflecting the balance on account 58 “Financial investments”, it is necessary to subtract the amounts included in the reserve fund for the depreciation of financial investments.
Such a reserve must be taken into account in account 63 “Reserves for doubtful debts” (creation - by debit, writing off and adding reserve balances - by credit).
For accounting of additional capital, account 83 “Additional capital” (credit) and special sub-accounts are intended. A debit can be account 50 “Cash”, 51 “Cash accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts”, etc.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! The amount included in the reserve as additional capital is usually not subject to write-off, except in cases of an increase in the authorized capital, a write-down of fixed assets after revaluation, or a negative exchange rate difference.
EXAMPLE 3. OJSC “Potrebitel” received the opportunity to increase its authorized capital by placing additional shares in it. At par value, the increase would have been 300,000 rubles, but when selling by subscription, 320,000 rubles were paid for the shares.
Entries in the accounting of OJSC "Potrebitel":
- debit 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital”; credit 80 “Authorized capital”, subaccount “Announced capital” – 300,000 rubles. — the increase in the authorized capital is reflected;
- debit 80 “Authorized capital”, subaccount “Announced capital”; credit 80 “Authorized capital”, subaccount “Subscribed capital” – 300,000 rubles. – subscription to shares is reflected;
- debit 51 “Current accounts”; credit 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital” - 320,000 rubles. – the receipt of funds for the purchased shares is reflected;
- debit 75 “Settlements with founders”, subaccount “Settlements for contributions to the authorized capital”; credit 83 “Additional capital” – 20,000 rubles. – the share premium is reflected (the excess of the actual cost of placing shares over their par value).
Features of the reserve fund
The fund's money is managed by the Ministry of Finance, but certain issues are entrusted to the Central Bank. When the Ministry of Finance buys foreign currency, it places it in the accounts of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. Interest is charged on the balance in rubles.
The size of the reserve fund exceeded 7% of the country's GDP? Then the funds are invested in large projects and the purchase of assets. If the figure is less than 7%, capital can only be invested in programs that have already begun. Why exactly 7%? This amount of money is considered to be the optimal safety cushion for the state.
According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, over 10 years the volume of reserve funds has increased by 31% in dollar equivalent. The disadvantages of the National Welfare Fund include the fact that reporting on its work is not transparent. Ordinary citizens do not have access to information about where assets were distributed and what profit the state received from the investment.
Value of reserve capital
Reserve capital or reserve fund (these concepts are used in the same field) has a rather limited scope of application. Its main function is to compensate for certain losses of the organization. The procedure for spending funds from reserve capital does not increase or decrease the assets of a legal entity: it is only reflected in the composition of equity capital.
The reserve fund is an indirect means of saving the finances of an enterprise, because it protects part of the profit from immediate use at the time of its occurrence, and forces it to “save” this part for a “rainy day” of possible losses, thereby insuring the organization from acute negative consequences.