Despite the fact that construction and installation work has been subject to VAT since January 1, 2001, disputes regarding the interpretation of the term “construction and installation works for own consumption” are sometimes resolved only in court.
Carrying out construction and installation work (hereinafter referred to as construction and installation works) for one’s own consumption is subject to VAT taxation (clause 3, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The tax base for these transactions is determined on the last day of each tax period (Clause 10, Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The taxpayer has the right to deduct the accrued amount of VAT from the cost of construction and installation work (paragraph 2, clause 5, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Problematic issues related to the terminology “construction and installation work for own consumption”.
EXAMPLE No. 1
In one of the divisions of JSC “Lutik”, shelving for storing finished products was manufactured.
The following entries will be created in the accounting records of JSC Buttercup:
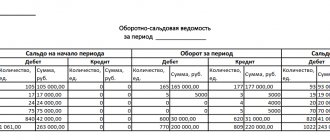
| Contents of a business transaction | Debit | Credit | Amount, in rubles |
| Construction materials purchased for the manufacture of shelving have been accepted for accounting. | 10-8 | 60 | 100 000 |
| VAT is taken into account on the cost of building materials. | 19-4 | 60 | 18 000 |
| VAT is accepted for deduction. | 68 | 19-4 | 18 000 |
| The cost of written-off building materials is taken into account. | 23 | 10-8 | 100 000 |
| The department's costs associated with the manufacture of shelving are taken into account. | 23 | 70,69,02 | 25 000 |
| Reflected as part of capital investments are the costs associated with the manufacture of racks. Calculation: 100,000 rub. + 25,000 rub. = 125,000 rub. | 08-3 | 23 | 125 000 |
Let's look at an example
Initial data.
Romashka LLC is constructing a building using a mixed method: using its own resources with the involvement of third-party contractors.
During the third quarter of 2022, materials worth 500,000 rubles were spent on the work.
Wages for workers involved in construction were accrued in the amount of 600,000 rubles,
her insurance premiums amounted to 181,200 rubles.
The amount of depreciation on fixed assets involved in construction amounted to 100,000 rubles.
In addition, the cost of the contractor’s work on laying the foundation amounted to 450,000 rubles, incl. VAT 75,000 rubles.
Reflection in accounting.
The accountant will reflect these transactions in the third quarter of 2022:
| Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Content | Is CMP for own consumption included in the cost? |
| 08-3 Household method | 10 | 500 000 | Materials written off for construction costs | Yes |
| 08-3 Household method | 70 | 600 000 | Remuneration of workers involved in construction | Yes |
| 08-3 Household method | 69 | 181 200 | Insurance premiums are reflected from wages | Yes |
| 08-3 Household method | 02 | 100 000 | Depreciation was calculated on fixed assets involved in construction | Yes |
| 08-3 Contract method | 60 | 375 000 | Contractor services reflected | No |
| 19 | 60 | 75 000 | Input VAT on contractor services is reflected | — |
The tax base as of September 30, 2021 for the purpose of determining the cost of CMP for own consumption will consist of the following amounts:
500,000 + 600,000 + 181,200 + 100,000 = 1,381,200 rubles.
VAT calculation : 1,381,200 x 20% = 276,240 rub.
Based on the results of the third quarter, the accountant of Romashka LLC will draw up an invoice that will look like this.
In the accounting of Romashka LLC, VAT calculation and deduction will look like this:
| date | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. | Content |
| 30.09.21 | 19 | 68 | 276 240 | VAT charged |
| 30.09.21 | 68 | 19 | 276 240 | VAT is included in deductions |
In the VAT tax return, line 060 will reflect the amounts of 1,381,200 and 276,240, and line 140, respectively, will show the deduction amount of 276,240. Conventionally, we assume that the building under construction at Romashka LLC is intended to be used for core activities subject to VAT.
EXAMPLE No. 2
A gear crushing machine has been installed in one of the divisions of Lyutik JSC. The installation of the machine was carried out by the organization's employees.
The costs of the department that installed the gear crushing machine include the following cost elements:
- workers' wages;
- deductions from payroll;
-electricity;
- other overhead costs of the workshop.
The above expenses in accounting increase the initial cost of the machine.
According to the All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities OK 029-2001, the above works do not relate to construction and installation works (installation of equipment has an OKVED code different from the construction and installation work code). As noted in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated March 28, 2012 No. A40-10464/11-129-46, “... the main feature that allows defining work as construction and installation work is the execution of construction, of which installation work is a part.”
Installation of equipment outside the scope of construction work does not fall under the definition of “construction and installation work for one’s own consumption.”
Thus, as in example No. 1, the organization does not have the obligation to calculate VAT on the cost of installation of the machine.
One of the criteria for classifying completed work as construction and installation work for one’s own consumption is the work being performed by the organization itself, i.e. employees who are in an employment relationship.
Deduction of accrued tax
The amount of VAT accrued on the cost of construction and installation work performed on one’s own can be deducted. But keep in mind that for this to happen three conditions must be met:
– VAT accrued on the cost of construction and installation work has been paid to the budget (and accordingly reflected in the VAT return for this tax period);
– the facility under construction is intended to carry out operations subject to VAT;
– the cost of the constructed facility will be included in expenses when taxing profits (including through depreciation deductions) (clause 6 of Article 171 and clause 5 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In practice, accountants often have the following question: is it necessary to prepare invoices for the completed volume of construction and installation works for their own consumption? And if so, how to correctly register them in the Purchase Book and Sales Book?
Yes, invoices are required. Draw up an invoice for the cost of construction and installation work on the last day of each quarter in which the company carried out this work, in two copies. Register one copy of the document in the Sales Book and store it in the journal of issued invoices (clauses 1, 2 and 25 of the Rules approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 No. 914). Keep the second copy of the invoice in the journal of received invoices.
In the next quarter, the company will have the right to deduct (after the cost of work performed is reflected in the VAT return as part of taxable transactions, and the accrued VAT is paid to the budget). And the same invoice can be registered in the Purchase Book. This procedure is provided for in paragraph 12 of the Rules, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 No. 914.
The following question is often asked: how to correctly fill out lines 4 “Consignee and his address” and 6 “Buyer” of the invoice for the completed volume of construction and installation work for one’s own consumption?
The issue has not been officially clarified. However, in our opinion, based on the requirements of the tax inspectors, the same data must be indicated in these lines of the invoice as in lines 3 “Consignor and his address” and 2 “Seller” of the invoice. That is, it turns out that the company issued an invoice to itself.
EXAMPLE No. 3
The organization carried out construction and installation works with the involvement of individuals on the basis of civil contracts. Work on repairing the premises, installing a cage line, and repairing the vessel was carried out by individuals under civil contracts, who were not engaged in the taxpayer’s main activity, and no employment contracts were concluded with them.
When conducting an on-site inspection, the tax authority assessed these works as construction and installation work for its own consumption with the corresponding VAT charge.
However, as the judges noted (Decision of the Arbitration Court of the Republic of Karelia dated July 31, 2014 No. A26-1492/2014), in order for construction and installation works to be considered carried out on their own - in an economic way, all the requirements of the State Statistics Committee must be collectively met: work performed for the needs of the organization; the work is carried out by non-construction organizations on their own; for work, the organization allocates workers for the construction of the main activity, that is, those who have concluded employment contracts with this organization; the above-mentioned employees of the organization are paid wages according to construction orders.
It is impossible to equate individuals who performed work under concluded civil contracts with their own employees, and the work performed by them with work performed by the organization on its own, which is subject to VAT taxation.
Thus, in this situation, the tax inspectorate had no legal grounds for including these costs in the cost of construction and installation work for its own consumption as an object of VAT taxation.
Composition of construction and installation costs included in the VAT tax base
When performing construction and installation work for one's own consumption, the tax base is determined as the cost of work performed, calculated on the basis of all actual expenses of the taxpayer for their implementation (clause 2 of Article 159 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What is included in the taxpayer's actual expenses? The tax base takes into account only expenses incurred by the taxpayer himself, incl. and costs for the development of design estimates (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 22, 2011 No. 03-07-10/07).
The cost of construction and installation works performed by contractors is not included in the amount of accrued “construction and installation” VAT (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 09.09.2010 No. 03-07-10/12, Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 02.09.2008 No. 4445/08 , Decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 03/06/2007 No. 15182/06, clause 19 of the Order of the Rosstat of the Russian Federation dated 10/28/2013 No. 428) both with a mixed method of performing work, and entirely by the contractor. If an organization transfers customer-supplied materials to the contractor, then the tax base in terms of construction and installation work for its own consumption also does not arise (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 17, 2011 No. 03-07-10/05).
However, in a number of cases, even in the absence of actual costs for construction and installation work, tax authorities try to charge additional VAT using the calculation method for determining the cost of construction and installation work performed.
Construction has begun: we charge VAT
The tax base for construction and installation work performed on a self-employed basis is determined on the last day of each tax period (clause 10 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It turns out that VAT on the amount of construction and installation work performed is calculated on the last day of each quarter in which the work was carried out.
As we have already said, the tax base for self-employed construction is determined based on all expenses for construction and installation work (Clause 2 of Article 159 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This raises the question: should these costs include the cost of work performed by contractors?
The position of official departments on this matter has changed several times. Until January 1, 2006, regulatory agencies believed that the cost of work performed by contractors did not increase the VAT tax base (see, for example, letters of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 24, 2004 No. 03-1-08/819/16 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia in Moscow dated February 25, 2005 No. 19-11/11713).
However, subsequently the Russian Ministry of Finance changed its point of view. Thus, in a letter dated January 16, 2006 No. 03-04-15/01 (it was communicated to the tax inspectorates by letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 25, 2006 No. MM-6-03/63), officials indicated that the cost of construction - installation work performed by the contractor must be subject to VAT. This was explained by the fact that for construction and installation works for own consumption, the tax base is determined based on all actual expenses for their implementation. Consequently, according to financiers, when calculating VAT it was necessary to take into account the full cost of construction work, including work performed by contractors.
Fortunately, relatively recently, letter No. 03-04-15/01 of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated January 16, 2006 was recognized as partially inconsistent with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This conclusion was reached by the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation in decision No. 15182/06 dated March 6, 2007. The tax authorities also had to agree with this (see letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 4, 2007 No. ШТ-6-03/527).
This means that before January 1, 2006, and after this date, when constructing on a self-employed basis with the involvement of contractors, VAT must be charged only on the cost of work performed on one’s own.
Example 2
In 2008, CJSC Progress Construction Corporation began construction of a warehouse for finished products using its own resources. The VAT tax period for Progress Construction Corporation CJSC (like all companies from January 1, 2008) is quarterly. In the first quarter of 2008, construction costs were:
– building materials – 120,000 rubles. (excluding VAT);
– salary of workers who participated in the construction of the facility (including unified social tax and contributions for insurance against accidents and occupational diseases) – 98,000 rubles;
– the cost of foundation installation work performed by the contractor is RUB 330,000. (excluding VAT).
Thus, the tax base for calculating VAT (for construction and installation works for own consumption) in the first quarter of 2008 will be 218,000 rubles. (120,000 + 98,000). And the amount of VAT will accordingly be equal to 39,240 rubles. (RUB 218,000 x 18%).
EXAMPLE No. 4
The taxpayer carried out construction and installation work on its own for its own needs for the construction of a capital construction project - a store building.
The work was carried out by the taxpayer’s family without hiring workers or paying them wages. Based on this, the taxpayer did not have actual expenses for construction and installation work and, accordingly, the tax base for calculating and paying VAT on operations to perform these works did not arise.
However, during the audit, the tax authority assessed additional VAT on the cost of construction and installation work performed using the calculation method, guided by paragraphs. 7 clause 1 art. 31 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, due to the taxpayer’s lack of documents confirming the amount of expenses incurred. The basis for determining the cost of work was information on specific indicators of the cost of a unit of measurement of construction volume, established in the collection No. 26 “UPVS of buildings and structures on state farms, collective farms, intercollective farms and other agricultural enterprises and organizations.”
That is, when calculating the cost of construction and installation work carried out economically, the tax authority calculated the estimated cost of a capital construction project, including both the costs of carrying out the work and the costs of purchasing materials.
At the same time, as noted in the Resolution of the Fifth Arbitration Court of Appeal dated April 3, 2014 No. A51-21000/2013, the cost of a fixed asset is not identical to the concept of the cost of construction and installation work, and therefore the VAT tax base established by the inspection does not correspond to either by size, nor by right of the taxpayer’s obligation to pay VAT.
Formation of the initial cost when creating an OS
Initial cost of fixed assets in accounting
In accounting, assets are recognized as fixed assets (clause 4 of PBU 6/01):
- used for a long time (more than 12 months);
- not intended for resale, i.e. the asset is intended for use in the production of products, performance of work (provision of services), management needs, rental;
- the use of which is aimed at generating income in the future.
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting at their original cost (clause 7 of PBU 6/01).
When creating an OS, the initial cost consists of all the actual costs of constructing, manufacturing, producing the OS and preparing it for working condition (clause 8 of PBU 6/01).
Accounting and formation of costs for the production of fixed assets is determined similarly to the accounting of costs for finished products (clause 26 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 N 91n).
The amount of VAT and other refundable taxes is not taken into account in the initial cost of fixed assets (clause 27 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 N 91n).
All actual costs associated with the creation of fixed assets are taken into account in Dt 08.03 “Construction of fixed assets” (Chart of Accounts 1C).
Initial cost of fixed assets in tax accounting
In tax accounting, assets are divided into depreciable and non-depreciable.
Depreciable property is recognized as having (clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- useful life more than 12 months;
- initial cost more than 100,000 rubles.
Fixed assets include depreciable property, which is a means of labor in the activities of the organization (paragraph 1, paragraph 1, article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The initial cost of the OS is determined based on all the actual costs of constructing, manufacturing and bringing the OS to working condition, and when producing the OS on its own - as the cost of the finished product (clause 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT
If, when creating an operating system, construction and installation work (CEM) was carried out in an economic way for one’s own consumption, it is necessary to charge VAT on the amount of construction and installation work performed (clause 3, clause 1, Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Study the accrual of VAT on construction and installation work performed in-house for your own needs
Accounting in 1C
When creating an OS on your own, the costs that form the initial cost of the OS are reflected in different documents depending on the type of costs, for example:
- document Payroll - to reflect in the initial cost of the fixed assets the costs of wages for employees creating the fixed assets;
- document Requirement invoice - for writing off the necessary materials when creating an operating system;
- other documents, the costs of which will be reflected in Dt 08.03 “Construction of fixed assets”.
If the creation of fixed assets is carried out by contract or mixed method, the costs are also charged to account 08.03 “Construction of fixed assets”.
In this case, the documents may be the following:
- Receipt (act, invoice) - to reflect the services of contractors in the costs of constructing fixed assets;
- Transfer of equipment for installation - to reflect the installation and construction of OS by contract.
In 1C, the distinction between the creation of fixed assets using an economic method or a contract method is carried out by analytics on account 08.03 “Construction of fixed assets” subconto Construction Methods .
Filling out the Construction Methods is required for correct accounting, since VAT must be charged at the end of the quarter on construction and installation work carried out in a self-employed manner.