Taxpayers
Transport tax is paid by companies and entrepreneurs with registered vehicles.
Difficulties in determining the taxpayer may arise if a vehicle registered in the name of an individual is transferred to another person on the basis of a power of attorney. In this case, two situations may arise:
- if the power of attorney was issued before July 30, 2002 (the date of official publication of Chapter 28 “Transport Tax”), then the tax will be paid by the person indicated in the power of attorney;
- if the power of attorney was issued after July 30, 2002, then the tax will be paid by the previous owner of the vehicle.
Moreover, in the first case, citizens to whom vehicles are registered must notify the tax office at their place of residence about the transfer of these vehicles by proxy.
On July 1, 2002, the entrepreneur bought a Gazelle minibus and a Volga car.
On July 15, he transferred the Gazelle to the company by proxy. Therefore, the company will pay the transport tax for the Gazelle.
On August 30, the entrepreneur transferred the same by proxy. Since the transfer of the car by proxy occurred after July 30, 2002, the transport tax for the Volga will be paid by the entrepreneur.
Duty to pay tax
Transport tax is required to be paid by the person to whom the vehicle subject to this tax is registered (paragraph 1 of Article 357 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
After the death of the car owner (declaring him dead), the transport tax debt, as well as fines and penalties, must be paid by the heirs. But only within the limits of the value of the inherited property.
Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 19, 2011 No. 03-02-07/1-373.
If the vehicle is registered in the name of a minor child, then the obligation to pay transport tax rests with his legal representatives (parents, adoptive parents, guardians, trustees). Such clarifications are contained in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 23, 2012 No. BS-2-11/666.
Situation: who pays transport tax on a vehicle transferred by proxy?
Transport tax is required to be paid by the person to whom the vehicle subject to this tax is registered (paragraph 1 of Article 357 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
And the fact that the owner issued a power of attorney to another person does not cancel his obligation to pay tax.
Situation: do I need to pay transport tax on a car with transit plates?
No no need.
The obligation to pay transport tax arises only from the moment the car is registered with the State Traffic Safety Inspectorate (Article 357 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Registering a car with the traffic police and issuing Transit signs are different registration actions. When issuing a transit number, a corresponding mark is made in the vehicle passport; a certificate of registration is not issued (clause 33.1 of the Administrative Regulations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia dated November 24, 2008 No. 1001).
In particular, “Transit” signs must be obtained:
– in connection with the removal of a car outside of Russia for permanent stay;
– when transporting the vehicle to the manufacturer for modification (replenishment);
– when driving the car to the place of sale or registration.
In the first case, the issuance of transit numbers occurs after the car is deregistered (clause 43 of the Administrative Regulations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia dated November 24, 2008 No. 1001).
In other cases, “Transit” signs are issued before the vehicle is registered (clauses 4 and 33 of the Administrative Regulations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia dated November 24, 2008 No. 1001).
Thus, the presence of transit plates on a car does not mean that it is registered with the traffic police. This means you don’t need to pay transport tax on it.
Object of taxation
Vehicles that are subject to tax can be divided into three groups:
- motor transport
(cars, motorcycles, scooters, buses and other self-propelled machines and mechanisms on pneumatic and caterpillar tracks); - water
(motor ships, yachts, sailing ships, boats, motor boats, towed vessels, etc.); - air
(planes, helicopters, etc.).
All these vehicles must be registered in accordance with the established procedure.
The following are not subject to taxation:
- rowing boats and motor boats with an engine of no more than 5 horsepower;
- passenger cars specially equipped for use by disabled people;
- •passenger cars with an engine power of up to 100 horsepower, received through social protection authorities;
- fishing sea and river vessels;
- passenger and cargo sea, river and aircraft owned by organizations whose main activity is passenger and cargo transportation;
- •tractors, self-propelled combines, special vehicles registered to agricultural producers;
- vehicles belonging to federal executive authorities, where military and equivalent service is provided;
- wanted vehicles;
- airplanes and helicopters of air ambulance and medical services;
- vessels according to the Russian International Register.
Tax rate
The basic rates for transport tax are established in Article 361 of the Tax Code. Regional authorities can reduce or increase transport tax rates by no more than ten times. In addition, regional authorities can set tax rates taking into account the number of years that have passed since the year of manufacture of vehicles and (or) their environmental class.
Basic tax rates are shown in the table:
| Type of vehicle | Tax rate, rub. in year | |
| Passenger cars with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 100 l inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 100 l s up to 150 l s | 3,5 | |
| over 150 l s up to 200 l s | 5 | |
| over 200 l s up to 250 l s | 7,5 | |
| over 250 l s | 15 | |
| Motorcycles and scooters with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 20 l inclusive | 1 |
| over 20 l s up to 35 l s | 2 | |
| over 35 l s | 5 | |
| Buses with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 200 l inclusive | 5 |
| over 200 l s | 10 | |
| Trucks with engine power (per horsepower) | up to 100 l inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 100 l s up to 150 l s | 4 | |
| over 150 l s up to 200 l s | 5 | |
| over 200 l s up to 250 l s | 6,5 | |
| over 250 l s | 8,5 | |
| Snowmobiles, motor sleighs with engine power (each horsepower) | up to 50 l inclusive | 2,5 |
| over 50 l s | 5 | |
| up to 100 l inclusive | 10 | |
| over 100 l s | 20 | |
| up to 100 l inclusive | 20 | |
| over 100 l s | 40 | |
| up to 100 l inclusive | 25 | |
| over 100 l s | 50 | |
| Other self-propelled vehicles, pneumatic and tracked machines and mechanisms (per horsepower) | 2,5 | |
| Non-self-propelled (towed) ships for which gross tonnage is determined (from each registered ton of gross tonnage) | 20 | |
| Airplanes, helicopters and other aircraft with engines (per horsepower) | 25 | |
| Airplanes with jet engines (per kilogram of thrust) | 20 | |
| Other water and air vehicles without engines (per unit of transport) | 200 | |
Procedure for calculating tax and advance payments
Transport tax is calculated separately for each vehicle. Organizations independently determine the amount of transport tax. Individuals do not need to calculate tax: the inspectorate will send them a request to pay transport tax. To calculate the amount of transport tax that needs to be paid to the budget, multiply the tax base by the tax rate. If you own the vehicle for less than a year (for example, a few months), then the tax is paid only for those months. To calculate transport tax for several months, you need to determine the coefficient:
| Number of full months during which the car is registered to the company | : | 12 months | = | Correction factor |
The tax amount is calculated as follows: the tax base is multiplied by the tax rate and by the correction factor. In this case, the month of registration of the vehicle, as well as the month of deregistration of the vehicle, are taken as a full month. In case of registration and deregistration of a vehicle within one calendar month, this month is taken as one full month.
At the end of each reporting period (Q1, Q2 and Q3), firms pay advance payments for transport tax. They are calculated as follows: the total amount of transport tax (the product of the tax base and the tax rate, taking into account the correction factor) is divided by 4.
And at the end of the tax period (year), the difference between the annual tax amount and the amount of advance payments transferred during the year is transferred to the budget.
Regional authorities may exempt certain categories of firms from paying advance payments for transport tax. In this case, Osvobozhdeniye residents will have to remit tax only at the end of the year.
Transport tax – reporting period and tax
The tax period for transport tax is recognized, for all taxpayers without exception, as a calendar year (clause 1 of Article 360). At the end of this time period, the corresponding fiscal amounts are accrued and paid to the state budget. Regardless of the type of vehicle (vehicle), its capacity, as well as the organizational and legal form of the legal entity, the requirements are the same. Also, the duration of the tax period according to the Tax Code does not affect the place of registration of vehicles, since regions of the Russian Federation can establish reporting periods, but not tax ones.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 360 for the reporting periods for legal entity companies, the first, second and third quarters are recognized. And by decision of local government authorities in individual subjects (regions, territories, republics), payment of advances within the year may not be made (clause 6 of Article 362). In this case, it is considered that there are no reporting periods for labor tax in a particular region of the country - payment of amounts is carried out only at the end of the year. Since the tax period for transport tax is 1 year, and the reporting period is a quarter, the timing of payment under the TN depends on the calculation procedure. Let's consider which dates are regulated at the federal level in, and which ones – at the regional level.
Procedure and deadlines for reporting
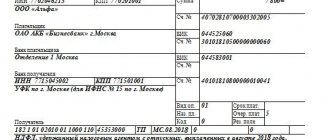
Only companies are required to submit transport tax returns. Individuals do not need to do this - they pay tax based on the notifications that the tax office sends them. The notification form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 5, 2010 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
The transport tax declaration form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 20, 2012 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected] The same order approved the format for submitting the declaration in electronic form.
Since 2011, organizations do not have to submit interim reports on transport tax to the tax office - quarterly calculations for advance payments. However, firms remain obligated to make advance payments throughout the year (if provided for by regional laws).
The deadline for submitting the declaration is no later than February 1 of the year following the expired tax period.
Tax reporting on transport tax
Reporting in the form of a tax return is submitted by companies after the end of the tax period, that is, the calendar year. The filing authority is the territorial division of the Federal Tax Service at the address where the means of transportation are located. The deadline is February 1 of the year following the previous year (clause 3 of Article 363.1). If there are no taxable objects, there is no need to submit empty “zero” reports. If an enterprise owns several vehicles controlled by one region, it is allowed to draw up one declaration with the calculation of the total amount, but subject to agreement with the Federal Tax Service on the procedure for submitting information.
Note! Transport tax in tax accounting is included in other expenses at the time the amounts are calculated (subclause 1, clause 1, Article 264, subclause 1, clause 7, Statute 272).