Is it possible to issue a receipt from the PKO to the client along with the cash receipt? Is it even legal to issue such a document? The questions posed are quite interesting.
The reason for this is simple: there are real examples when an individual entrepreneur, selling a product to a client, does not give him a check punched by cash register, but only provides a receipt from the receipt (cash receipt order) and, for example, an invoice. Can an entrepreneur do this? In what cases can a check be replaced with another document? Let's start to figure it out in order.
The concepts of “cash register” and “cash register”: essence and differences
First, a little theory. Let’s start our discussion with the concepts of “cash register” and “cash register”. Most mistakes and misconceptions are due precisely to the fact that their meaning is often confused.
So, the cash desk is all transactions of an individual entrepreneur (or organization) carried out in cash. These can be either income transactions (receipt of income) or expenditure transactions (spending funds for various purposes). All cash transactions must be recorded on cash register. In fact, all individual entrepreneurs and organizations have a cash register; exceptions are very rare: even if all transactions are carried out by bank transfer, you can withdraw money for some business expenses, for example, for the purchase of office supplies.
“Cashier” is a kind of imaginary “wallet” where money comes in and where it comes from for expenses. For organizations, the concept of “cash” looks easier to understand, since in accounting according to the chart of accounts there is a special account 50 “Cash”, which records all cash transactions.
Cash register is a cash register equipment necessary for making cash payments for goods (or services) sold to a client, that is, the machine itself, which issues a check.
The definition from the law generally goes like this:
Cash register equipment - electronic computers, other computer devices and their complexes that provide recording and storage of fiscal data in fiscal drives, generate fiscal documents, ensure the transfer of fiscal data and print fiscal documents on paper in accordance with the rules established by the legislation of the Russian Federation on application of CCT.
Let's immediately note the important differences:
- According to the cash register, only cash received from customers for goods or services purchased from you is recorded; at the cash register, all cash receipts are considered receipts - revenue from the cash register for the day, withdrawals of money from the current account, and so on.
- You cannot spend money from the cash register - there is no expense part, money for expenses can be issued exclusively from the cash register.
Conclusion: cash register is not equivalent to cash register - these are different concepts that mean different things. Cash desk is all cash transactions of an entrepreneur or organization (a kind of “big wallet”), cash register is the actual machine for accepting money from a client and issuing a check. The connection between the two concepts can be easily shown: at the end of the day, the store’s revenue from the cash register is handed over to the cash register of the individual entrepreneur (organization), the transaction is formalized by the receipt.
Which form to use
PKOs are one of the few forms that are approved by law. The used form of cash receipt order in 2020 was approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation No. 88 of 08/18/1998. As you know, the current law on accounting (402-FZ dated December 6, 2011) allows companies to develop primary documents themselves, providing for the presence of mandatory details in them. But it is the documents in question that must be drawn up according to standardized forms. This is due to the fact that their form is established by the authorized body. Such clarifications are given by the Ministry of Finance in information No. PZ-10/2012.
Regulatory regulation of the issue
So, we divided the “cash register” and “cash register” among ourselves. Now we will divide the legislative acts regulating these issues. Let us especially highlight two of them:
- Law No. dated May 22, 2003 “On the use of cash register systems when making cash payments...” No. 54-FZ - regulates the use of cash register systems.
- Directive of the Central Bank dated March 11, 2014 “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions...” No. 3210-U regulates the management of the cash register.
Having studied the documents, we conclude that all individual entrepreneurs and organizations have a cash register, that is, cash transactions (exceptions may occur, but very, very rarely), and therefore everyone must conduct them. Only individual entrepreneurs who take into account income/expenses and physical indicators in accordance with the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (for example, in KUDIR) have the right not to draw up documents for the cash register (receipt, consumables, cash book).
Conclusion: we repeat once again, “cash register” is not equal to “cash register”. The obligation to fill out a cash book has absolutely nothing to do with the mandatory use of cash registers when accepting payments from clients in cash. It is quite possible that you have a cash register, as required by law, but you, as an individual entrepreneur, enjoy the right not to process cash transactions. Or, conversely, you, as an individual entrepreneur, fall under one of the exceptions of Law No. 54-FZ and do not use cash registers, for example, when issuing BSO to individuals, but register cash transactions for receipts, filling out receipts and a cash book for control purposes.
The supplier provided a cash receipt order instead of a cash receipt.
1. The form of a cash receipt order is not equivalent to a cash receipt when conducting cash settlements with a buyer (customer, client), and therefore cannot be the basis for receiving cash without the use of cash register equipment.
<Letter> Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 03/19/2012 N 17-26/23527 <On the obligation of an organization to issue a cash receipt to an individual to confirm receipt of cash> {ConsultantPlus}
- Documents confirming cash payments
Article 861 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes two forms of payment: cash and non-cash. In accordance with paragraph 2 of this article, settlements between legal entities, as well as settlements with the participation of citizens in connection with their business activities, are made by bank transfer. However, these persons have the right to use cash for payments, subject to compliance with the requirements for cash transactions.
In judicial practice, questions arise regarding the assessment of a particular document as acceptable evidence of settlements using cash.
1.1. Conclusion from judicial practice: On the issue of the possibility of confirming cash payments with a receipt for a cash receipt order, there are two positions of the courts.
Position 1. Payments in cash can be confirmed by a receipt for the cash receipt order.
Arbitrage practice:
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North-Western District dated August 16, 2018 N F07-8051/2018 in case N A66-16353/2017
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Ural District dated January 26, 2018 N F09-7959/17 in case N A60-32834/2016
Position 2. Cash settlements cannot be confirmed by a receipt for a cash receipt order if the settlements were carried out in violation of the law.
Arbitrage practice:
Resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated 06/07/2018 N F05-5842/2018 in case N A40-115527/2017
Is it possible to take into account an advance report with a sales receipt, but without a cash receipt?
The advance report must be accepted for accounting, and the amount indicated in it must be taken into account in settlements with the accountable person (reimbursement of expenses) if the report is approved by the manager. As a rule, the manager approves the expense report if he has no doubt that the order has been completed by the accountable person, the costs have actually been incurred, and the valuables have been paid for. A cash receipt is not the only proof of an employee’s integrity. A sales receipt and valuables deposited at the warehouse confirm the fact that the accountable person spent money on their purchase, including in the absence of a cash receipt.
Ready-made solution: Is it possible to accept for accounting an advance report with a sales receipt, but without a cash receipt (ConsultantPlus, 2019) {ConsultantPlus}
2. Is it possible to recognize expenses on an advance report and deduct VAT if there is no cash receipt?
It is possible that a cash receipt is not attached to the advance report on the expenditure of the accountable amount. The absence of a cash receipt in many cases is not an obstacle to accepting an advance report for accounting
Ready-made solution: Is it possible to recognize expenses on an advance report and deduct VAT if there is no cash receipt (ConsultantPlus, 2019) {ConsultantPlus}
3. Article 25 of Law N 2300-1 directly states that the consumer’s lack of a sales receipt or cash receipt or other document confirming payment for the goods does not deprive him of the opportunity to refer to witness testimony.
“Cash Accounts” (4th edition, revised and expanded) (Semenikhin V.V.) (“GrossMedia”, “ROSBUKH”, 2018) {ConsultantPlus}
4.About the absence of cash register receipts when approving the advance report
Description of the situation: In connection with the amendments made to the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment...” from July 1, 2022, sales receipts without a cash register receipt will not be accepted from employees who received money on account. Unfortunately, our employees do not always listen to changes in the law and bring sales receipts without a cash register receipt.
Question 1: Can expenses on these sales receipts be attributed to losses, to account 91?
Answer: An advance report is the primary document for accounting for funds issued to accountable persons for administrative and business expenses. The accountable person attaches documents confirming the expenditure of the issued money.
The advance report is accepted for accounting, and the amount indicated in it is taken into account in settlements with the accountable person (expenses are reimbursed to him) if the report is approved by the manager. As a rule, the manager approves the expense report if he has no doubt that the order has been completed by the accountable person, the costs have actually been incurred, and the valuables have been paid for.
If an accountable person purchases goods at retail from an organization that is obliged to use a cash register, in the absence of a cash register receipt (if there is only a sales receipt), the organization has the right to attribute these amounts to expenses that are not accepted for profit tax purposes (91st account), provided approval of the advance report by the manager or his authorized person.
Question 2: What risks may there be in violating the CCP Law for employees who received funds on account and for the organization?
Answer: In case of violation of the Law on CCP, the main risks are borne by the seller organization in the form of the imposition of an administrative fine for non-use of CCP.
The purchasing organization, whose accountable person did not confirm in the advance report the fact of payment for goods purchased at retail, does not have the right to accept these expenses for profit tax purposes.
Also, in the absence of a cash register receipt and invoice, the purchasing organization will not be able to deduct the amount of VAT on purchased goods.
As for the question of whether it is necessary to withhold personal income tax from accountable amounts, if there is no cash register receipt among the supporting documents, then there is no official position on this issue.
However, there are judicial acts from which it follows that the absence of a cash receipt in the presence of other supporting documents does not provide grounds for including the accountable amount in the personal income tax base.
Thus, in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated December 13, 2010 N KA-A40/15065-10 in case N A40-98411/09-107-657, the court indicated that the absence of cash register receipts in the presence of other documents confirming the fact of spending the disputed amount does not indicate receipt of income by accountable persons.
In the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated February 24, 2010 N KA-A40/669-10 in case N A40-46422/09-112-282, the court rejected the tax authority’s argument that in the absence of a cash receipt, the amount of the advance issued to the employee on account of business expenses are subject to personal income tax. In addition, the employee presented sales receipts, which were recognized by the courts of first and appellate instances as reliable documents confirming the expenses incurred by the employee.
Similar conclusions are contained in the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated April 13, 2009 N F04-1948/2009(4045-A75-49), F04-1948/2009(4043-A75-49) in case N A75-5350/2008 (Definition The Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated August 17, 2009 No. VAS-9991/09 refused to transfer this case to the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation).
Thus, we believe that the absence of a cash receipt in the presence of other supporting documents does not provide grounds for including the accountable amount in the personal income tax base.
Thematic issue: Value added tax: current issues from the practice of tax consulting (edited by A.V. Bryzgalin) (“Taxes and financial law”, 2022, N {ConsultantPlus}
5. The absence of cash receipts for the purpose of purchasing inventory items in the presence of an advance report, sales receipts, acts of writing off inventory items into production cannot indicate that the funds transferred to the account are the employee’s income. This decision was reached by the servants of Themis of the Arbitration Court of the Saratov Region on January 29, 2018 in case No. A57-18148/2017.
Article: Disputed accountables (Krikunova O.) (“Calculation”, 2019, N 1) {ConsultantPlus}
Cash receipt and PKO
The differences described above allow us to conclude that there is a difference between two documents - the PKO and the cash receipt.
A cash receipt is a document issued by a cash register. What is its meaning? For the client, the check is confirmation that the individual entrepreneur has received money from him. Accordingly, in the future, the buyer will be able to file a claim with a receipt if the product turns out to be of poor quality. For individual entrepreneurs, knocking out a check is confirmation of the acceptance of cash, that is, in fact, confirmation of the formation of the amount of total sales revenue.
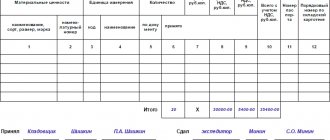
PKO is a primary accounting document used to record cash transactions. The meaning of a receipt order is completely different: it is used directly to record cash flow within your business (or within an organization).
This form looks like this:
Conclusion: PKO is not equivalent to a cash receipt and cannot replace it. With the help of PKO, they register the receipt of funds from various sources, rather than receiving money from customers at the cash register for purchased goods.
Now let's move on to the question itself: is it possible to issue the buyer only a receipt from the PKO? We will try to give a detailed answer. We will rely directly on Law No. 54-FZ.
Details of cash and sales receipts
A sales receipt is a primary document confirming the fact of economic life - the conclusion of a purchase and sale agreement (FZ-402 dated 6/12/11 “On Accounting”, Article 9; Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 493).
In what cases, when selling goods, can a sales receipt be issued instead of a cash receipt ?
A sales receipt does not have a unified form; its details are subject to the same design rules as other primary accounting documents:
- name “Sales receipt” (in the vast majority of cases, the document is numbered for ease of processing);
- date when issued;
- seller's data: TIN, address (legal and physical, if they differ), contact details;
- list of goods (works, services) that were sold and their quantity;
- unit price, cost;
- surname, position, signature of the person responsible for drawing up the document.
The details of a cash receipt, while generally consistent with the requirements of the specified Federal Law and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, differ significantly from those of a commodity receipt. They are dictated by the norms of Federal Law-54 dated May 22, 2003 (Article 4.7-1).
Question: Is there an obligation for individual entrepreneurs to submit documents confirming the legality of non-use of cash register systems for calculations? Is it possible to take into account for income tax purposes sales receipts presented by an accountable person for the provision of services in the absence of cash receipts? View answer
Additionally, a range of information is included:
- form of payment (cash or electronically);
- reg. number of the cash register, serial number of the fiscal drive;
- a website where you can check the authenticity of a check;
- email of the seller and buyer, to which you can send the document in electronic form;
- address of installation of cash register equipment;
- QR code for automatic reading of check data, etc.
On a note! The list of cash receipt details is constantly adjusted and supplemented by the fiscal authorities. Thus, from March 1, the next amendments to the document details come into force, according to Order No. ММВ-7-20 / [email protected] dated 08/29/19 of the Federal Tax Service.
At first glance, the answer to the question about using a sales receipt without a cash receipt appears to be negative, since a cash receipt contains more detailed information confirming the transaction. It meets the requirements of the Federal Tax Service, which makes it possible to unquestionably include a business transaction in the calculation of the tax base. However, you need to understand why and how each document is used in accounting.
What do we have in the source data?
- Cash register systems should be used by organizations and individual entrepreneurs if they make payments in cash, bank cards, or electronic means of payment;
- if all your sales go through a current account (non-cash payment), cash register is not used, as it is simply not needed;
- There are exceptions to the general rule when cash registers may still not be used: provision of services to the public (they may not use cash registers until 07/01/2021);
- specifics of activity or location;
- payment of tax on imputation or patent.
- We have already talked about all the exceptions in the previous article.
- Each of the exceptions to the CCP Law is accompanied by some condition, the fulfillment of which is mandatory (what must be issued instead of a check and how this document must be drawn up).
Conclusion: the main document that serves as confirmation of payment by the client for goods and services is a cash receipt. If the Cash Register Law obliges you to use a cash register, you are required to issue a check; if you may not use a cash register, but you have one (you fall under an exception, but do not use it) – you are required to issue a check.
It turns out that the presence of a cash register obliges the individual entrepreneur to issue the buyer a check, and not some other document. Let's talk about a few more situations:
- you must use a cash register, you have it, but you don’t knock out a check;
- you have the right not to use cash register, but you have it (you don’t use this right) and you don’t knock out a check;
- you must have a cash register, but you don’t have it, and therefore you cannot issue a check.
All these cases are classified as violations of the law. Failure to use cash registers and failure to punch a check are considered violations and will ensure that you are held accountable even when you do issue some document to the buyer (a certain form, a receipt from the PKO, and so on).
Everything is pretty clear here. Now let's get back to exceptions. Each of the exceptions to the CCP Law is accompanied by special requirements. These requirements are as follows:
- in a situation with the provision of services to the public (that is, individuals), cash register systems may not be used, but only on the condition that each client receives a completed BSO from the entrepreneur;
- when using UTII or a patent, you can do without a cash register, but issue a sales receipt or other document at the client’s request. These documents must contain all the details established by law;
- if the activity or location is specific, it is allowed not to issue anything at all.
Conclusion: what can be given to the buyer instead of a cash register receipt if there is no obligation to use a cash register? There are only three options:
- BSO;
- sales receipt or other document, but with a mandatory set of details;
- don't give anything away.
PKO instead of BSO
Is PKO suitable for the listed options? Let's consider the first two points: BSO and “other document”.
I’ll say right away that the BSO has its own requirements for mandatory details (clause 2 of the Russian Government Decree No. 359 of 05/06/2008), in addition, it must be approved by the individual entrepreneur (or LLC) and printed in a printing house. There are similar requirements for “other documents” (the list of details is given in paragraph 1 of Article 4.7 of Law No. 54-FZ as amended on July 3, 2016).
Now let's talk further. If the transaction of accepting cash for goods is processed by the PKO, the client will then receive a receipt for the PKO. Can it replace the BSO or “other document”? No, it cannot, because the lists of mandatory details of these documents differ from the details of the receipt form.
Is it possible to modify the form of the receipt for the PKO so that it meets at least the requirements that apply to the “other document”? This is only possible in theory; in practice there are several significant snags:
- The type of PKO has been approved, it is drawn up according to form No. KO-1 - who will finalize the unified form? There are few people willing.
- In order for a receipt for a PKO to pass as a BSO, it needs not only to be finalized, but also to have the forms printed in a printing house - especially since no one will do this.
- There is one more important point, even more theoretical than the previous ones. Provided that the first two points are fulfilled (let’s imagine this), we will essentially receive a new document. The original purpose of PKO is to record cash transactions at the cash register. Will our new document still be considered suitable for processing cash transactions, since it will be different from KO-1? Will the modified PKO remain legitimate for its original purpose? The issue is very controversial.
Conclusion: there can be a lot of theoretical reasoning on this issue, we have absolutely no need for it. In practice, there is only one conclusion: a receipt from the recipient cannot replace the BSO or “other document” that must be issued to the client if the individual entrepreneur has the right not to use the cash register.
Now let's turn to the last option, when the individual entrepreneur may not give anything to the buyer. In fact, if an individual entrepreneur is not obliged to issue anything to a client, but issues a receipt for a receipt, this does not directly contradict Law No. 54-FZ.
But let's pay attention to this. A receipt from a PKO can only be issued when the cash goes directly to the “cash desk” of the individual entrepreneur (or organization). Let us remind you that it is possible not to issue anything to the buyer only in case of exceptions related to the specific nature of the activity and location.
It turns out that “cash office” practically does not fit in with this exception. For example, an individual entrepreneur cannot receive money at the “cash desk” in any way if he is engaged in retail trade or from tanks, or selling products at a fair. It turns out that issuing a receipt to the client to the receipt in this case indirectly contradicts clause 3 of Law No. 54-FZ.
Conclusion: in this case, theoretically, it is still possible to issue a receipt to the PKO without violating anything. But this possibility is so small, and the justification is so confusing, that it is difficult to draw a conclusion about the legality of such actions.
Is the receipt for the PKO a strict reporting form?
Despite the fact that the implementation of online cash registers is very active, some business entities still have the right not to use them. For example, individual entrepreneurs providing services to the public. Instead of a cash register check, these persons, when receiving money from a buyer or customer, are required to issue a strict reporting form (SRF).
The question often arises: is it possible to use a receipt for a cash receipt order as a BSO? The answer to this question is negative. This is due to the fact that the unified form of the cash receipt document does not meet the requirements for BSO. BSOs, as a rule, are produced using the printing method, although their design using automated systems is allowed. But the PKO does not contain some of the required details for BSO, listed in paragraph 3 of the regulation on cash payments (Government Decree No. 359 dated 05/06/2008). For example, in the unified form under consideration there is no six-digit number and series.
The sum of it all
When paying in cash, issuing to the client a receipt from the merchant as confirmation of payment instead of a check issued by cash register or other documents provided for in case of exceptions is illegal. In any case, the main document is considered to be only a cash receipt. It can be replaced by a BSO, sales receipt or “other document” only in situations provided for by law. PKO is a primary accounting document that has its own meaning - registration of cash transactions within the activity.